Lecture 1 - Introduction to Surgery
3
Surgical diagnosis depends on: Sound knowledge of:
Anatomy
Physiology
Pathology
Specific history & clinical examination
Radiology
Surgical history
History of the chief complaint is the key step in surgical
diagnosis.
There is no standard surgical history of each disease as
the disease may present with certain symptoms and the
other patient present with the other or part of it as their
symptoms may take time to appear or never appear.
There are 2 types of surgical history:
1) Outpatient or emergency room history; Specific complaint
of the patient is pinpointed.
Objective: is to obtain diagnosis on which treatment is
ordered.
2) Clerking history: is the history of the patients who was
admitted for an elective surgery.
Objective: is to assess that the treatment planned is
correctly indicated & to ensure that the patient is suitable
for that operation
Outpatient or emergency room history:
You may ask
When the symptom started.
How it has progressed.
Whether there are any associated symptoms.
Whether the symptoms are improving or getting worse.
What relieve & what aggravate the symptoms.
What were the effects of the drugs which were taken.
History of previous illnesses, concurrent illnesses.
Drug therapy.
Allergies.
Complications related to anesthesia.
Clerking history
The clerking history centers on direct questioning of the
patient about specific points related to the complaint.
Examples:
1) Ask about signs of prostatism in patients with benign
prostatic hypertrophy to compare them with postoperative
state to assess the effect of the surgical procedure.
2) In a patient who was referred by a physician :
Ask about the indications for surgery.
The surgeon's decision whether or not the patient will
benefit from the operation.
These are particularly important in patients with non-
malignant condition where continued medical
treatment is an option.
Clinical Examination
Examine the whole patient particularly before operation.
The examination should be as thorough as in a routine
medical examination.
In examining a specific surgical structure one should
follow an accurate clinical description for example in :
Diagnosis of lump:
1) Site, size, shape, surface, consistency , mobility.
2) Important physical signs these includes:
Thrill, sign of compression, sign of indentation, sign of
aneurysm (pulsatile masses).
Ulcer:
Site, size, shape, floor, base, edge &surrounding tissues.
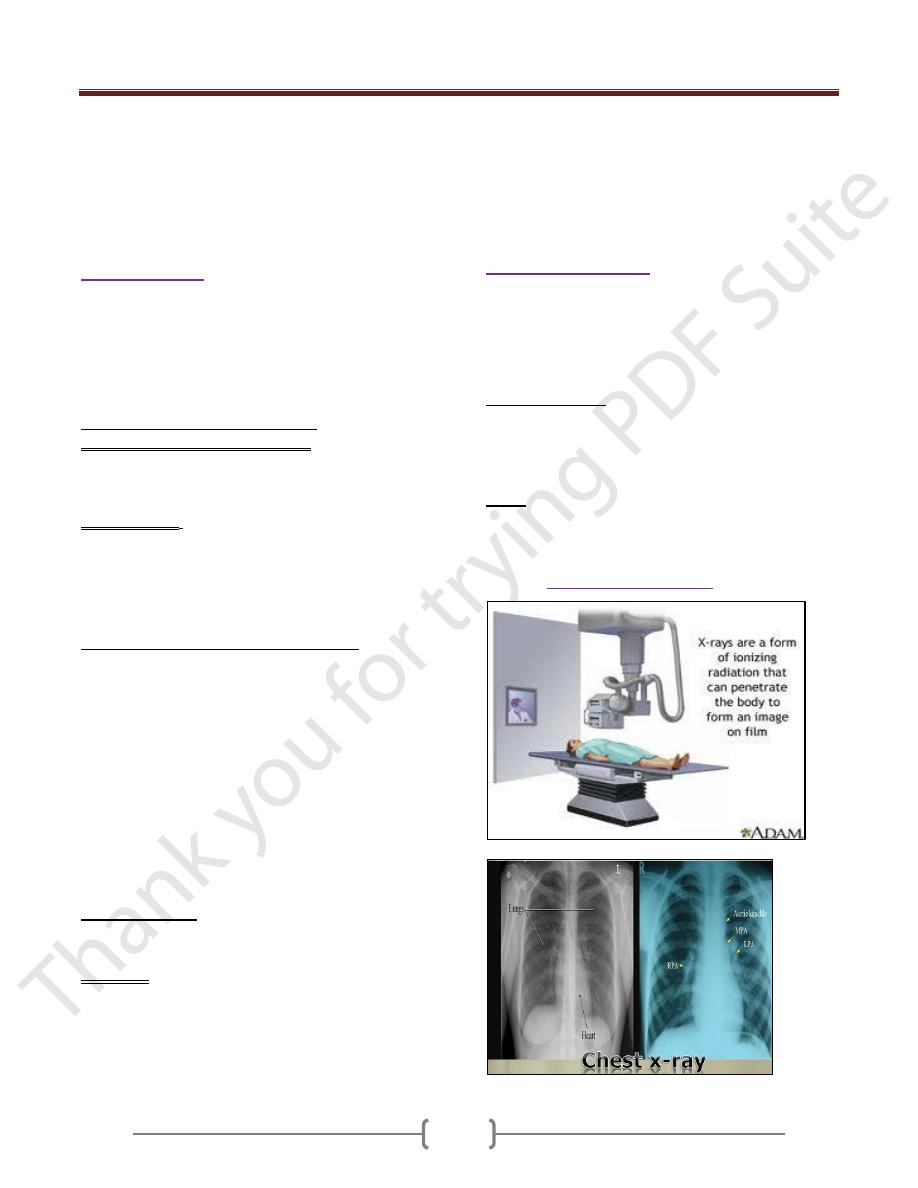
Confirmation of the diagnosis could be done by:
(Diagnostic
Radiology or imaging
)
Lecture 1 - Introduction to Surgery
4
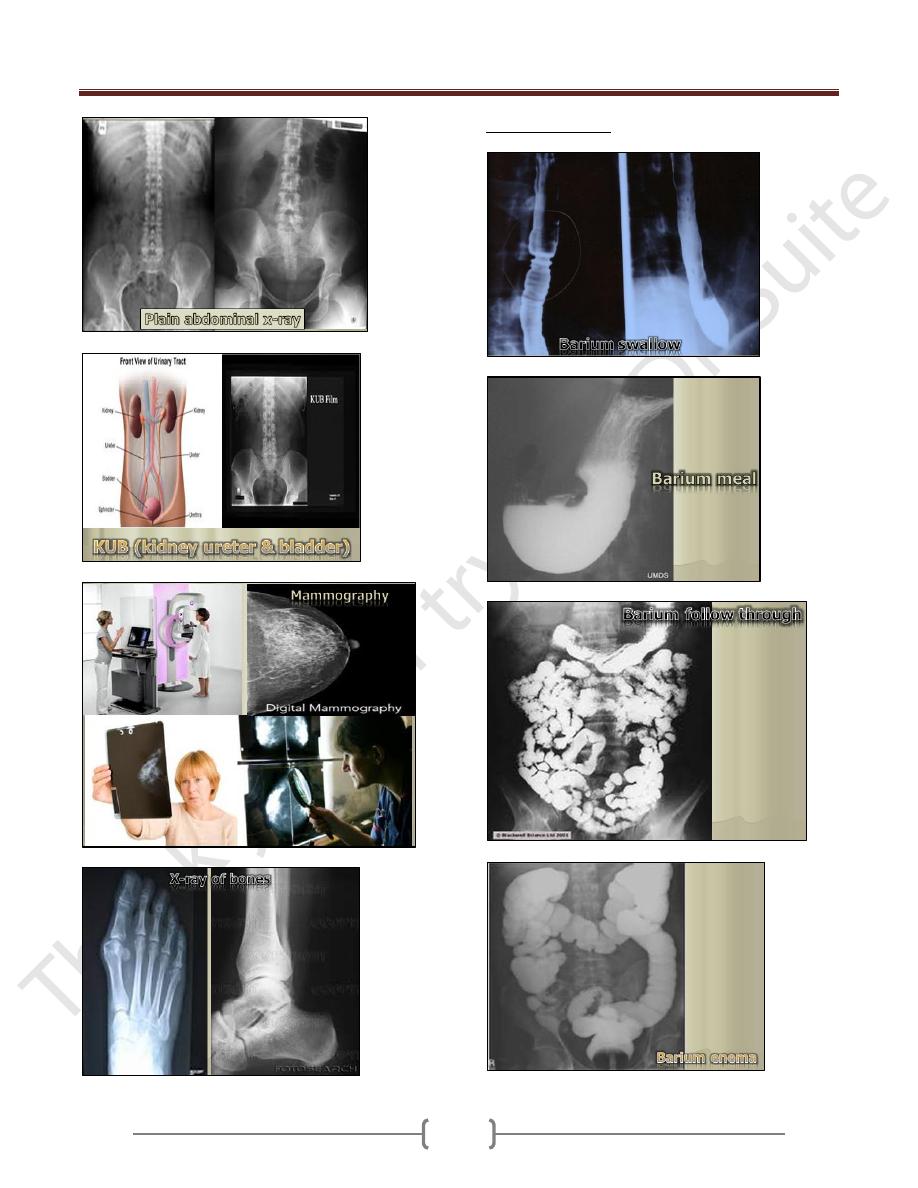
B. Contrast Studies
Lecture 1 - Introduction to Surgery
5
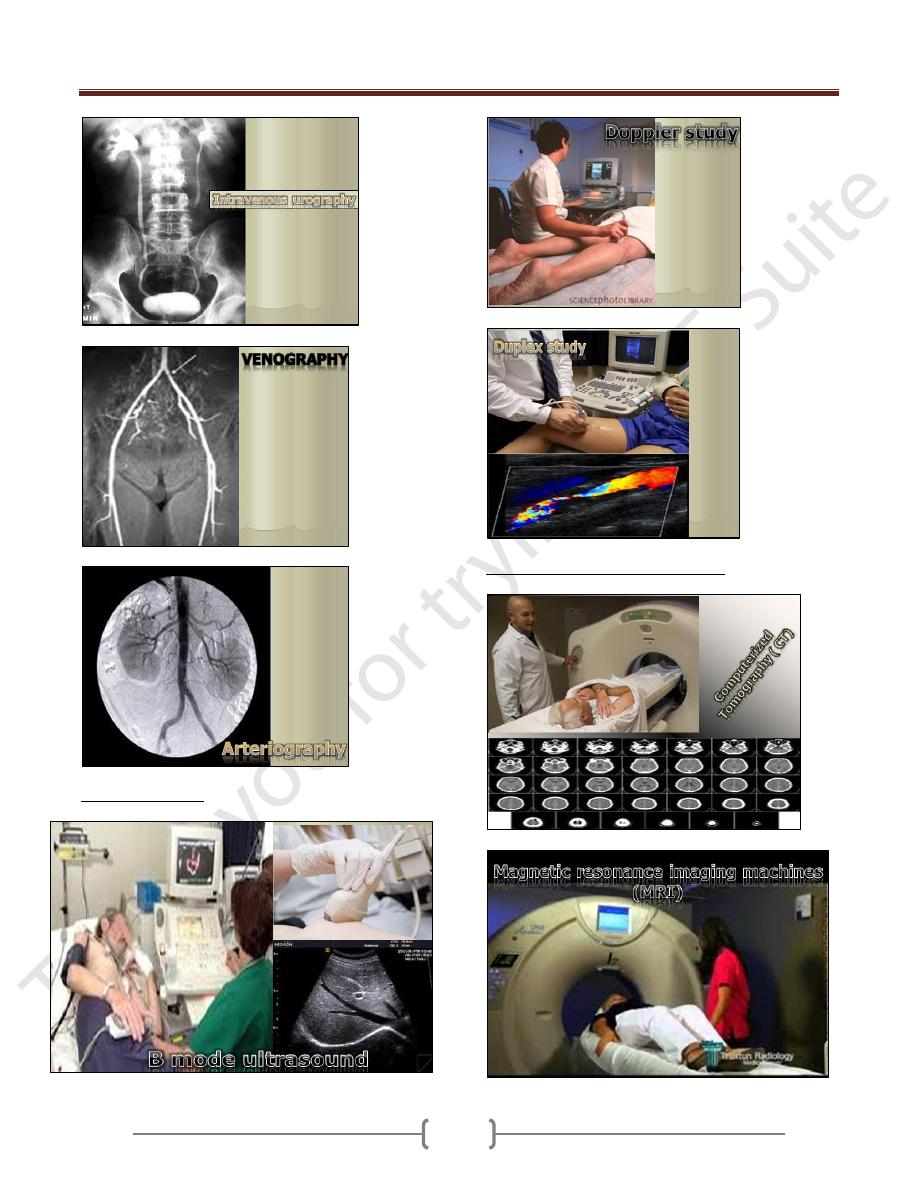
Ultrasound Studies
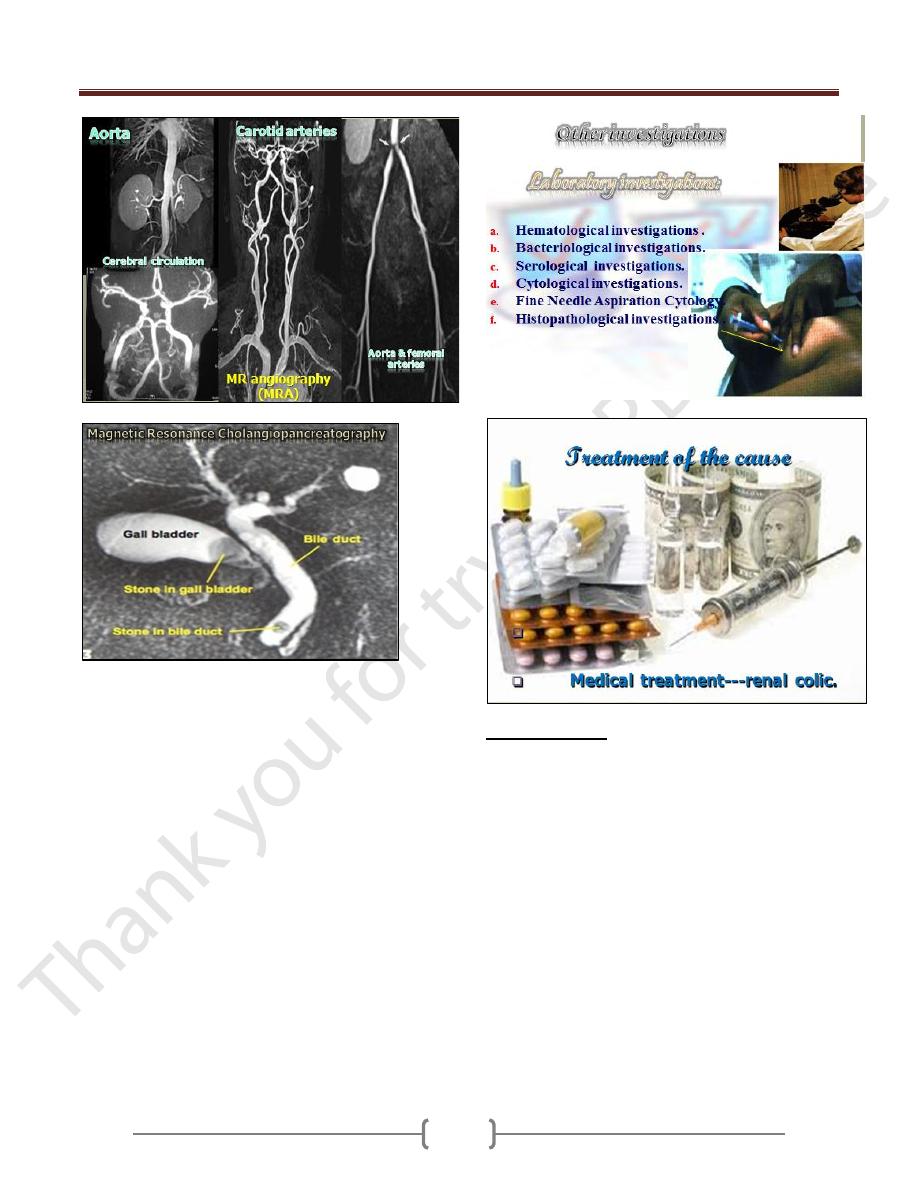
Advanced Radiological investigations
Lecture 1 - Introduction to Surgery
6
Surgical treatment
Appendectomy
Cholecystectomy
Drainag e of an abscess
