Unit 3 - Immunological factors in disease
31
Lecture 4 - Autoimmune disease
Is the presence of immune responses against self-targets.
It is identified by the presence of low titer autoantibodies
or autoreactive T cells.
Caused by failure of immunological tolerance:
Physiology & pathology of autoimmunity
Immunological tolerance
Tolerance
Autoimmune diseases
1 clonal deletion in
bone marrow and
thymus
Some autoreactive cells inevitably
evade deletion and escape to
peripheral circulation
2 suppression of
autoreactive cells by
regulatory T cells
generation of hyporesponsevness
(anergy) in lymphocytes which
encounter the antigens in the
absence of costimulatory signals
3 privileged sites (eye)
released Ags from these sites
Factors predisposing to autoimmune diseases
1) Genetic factor:
HLA genes (B27 association with ankylosing spondylitis,
type I diabetes associated with DR3/DR4, Myasthenia
gravis DR3
Genes determining cytokines activity, costimulation &
cell death
2) Environmental factor:
a) Infection with microbs
Eg. Acute rheumatic fever following streptococcal
infection, Reactive arthritis following bacterial infection
This is due to cross reactivity ( molecular mimicry),
Release of sequestered Ags, production of
inflammatory cytokines that leads to tissue damage
b) Drugs (Halothane, methyl dopa)
3) Sex:
Female more affected than males.
Classification of autoimmune diseases
•
It is classified as:
1) Organ specific diseases
2) Non –organ specific (Multisystem) diseases
There is some overlapping between them
The predominant mechanisms in tissue damage is type II,
III and IV hypersensitivity reactions
Mechanisms of tissue damage n autoimmunity:
1) Type II HS: binding of cytotoxic IgG and IgM to cell
surface causes cell killing
2) Type III HS: IgG or IgM bind soluble Ags to form immune
complexes which trigger classical complement pathway
3) Type IV HS: activated T cells, NK, phagocytes
Investigations in autoimmunity
a) Detection of specific autoantibodies in the patient’s
serum. The Ab is quantified either by titer ( minimal
dilution at which the Ab can be detected or by
concentration in standardized unit)
- This includes:
1- Rheumatoid factor 2- anti CCP Ab
3- Anti nuclear antibody 4- Abs to extractable nuclear Ags
5-Anti DNA antibodies 6-Antiphospholipid antibodies
7- Anti neutrophils cytoplasmic antibodies
b) measurement the complement components
Autoantibodies
RF
It’s an autoAb director against FC region of human IgG
It may be any Ig class but IgM is most commonly tested
In general a titer > 1:40 is considered positive
50% of patients with RA are + for RF at the time of
diagnosis. 25% will become seropositive in the first two
years of disease Thus it is insensitive to rule out RA at the
time of diagnosis
It has low specificity for RA because it is associated with
other conditions:
1) SLE
2) TB
3) elderly >65 ys
4) RA with extra –articular manifestation
5) Sjogen’s syndrome
6) mixed essential cryoglobulinaemia
7) primary billiary cirrhosis
The major indication for RF testing is to evaluate
prognosis in RA
When it is positive, it is associated with more sever
erosive disease and extra –articular disease manifestations
such as nodule, vasculitis.
Anti-CCP antibody
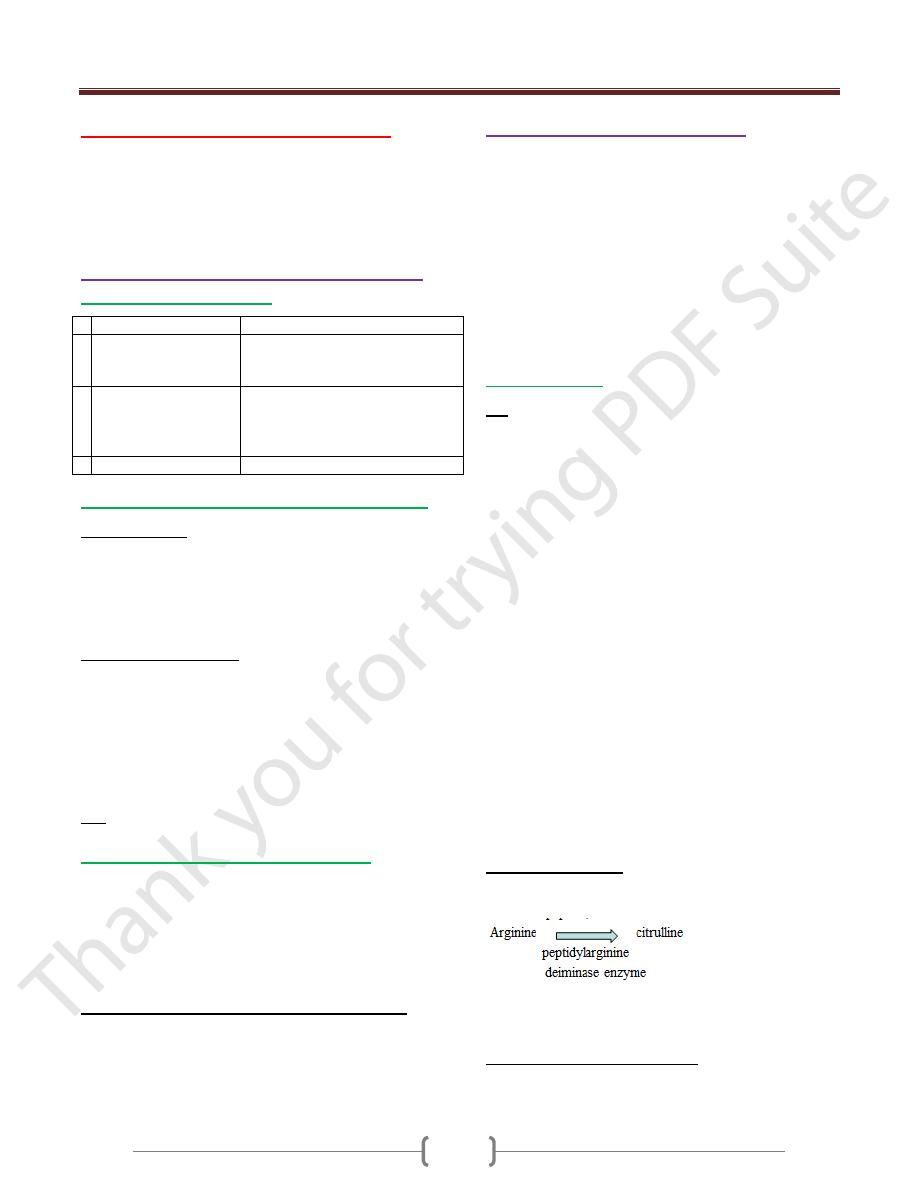
Abs to CCP (cyclic citrullinated peptide)
In this peptide, aa converted to
It is more specific test than RF for RA
It is a better predictor of an aggressive disease course
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
Are group of Abs which bind to components of the nucleus
Titer >1:80 is usually considered positive
Unit 3 - Immunological factors in disease
32
It is positive in (SLE, Scleroderma, dermatomyositis,
mixed connective tissue disease, autoimmune hepatitis,
5% of healthy individuals have an ANA titer >1:80
It is not useful in the diagnosis (RA, autoimmune thyroid
disease, malignancy and infectious disease)
Repeating ANA is not useful, no role for serial monitoring
of ANA titer
No correlation with disease activity
Abs to extractable nuclear Ags(ENA)
When ANA is positive , it is useful to establish which
nuclear component is being recognize
Some nuclear Ags are soluble and can be extracted from
the nucleus
There is little value in testing for ENA if the ANA is negative
It’s include Abs to (histone, centromere, smith, RNA
polymerase I)
Anti DNA Abs
Abs to single strand DNA is not specific
Abs to Double strand DNA is highly specific for SLE (95%)
Very high titers are associated with more sever disease
including renal and CNS involvement in SLE
They are useful in disease monitoring as an increase in Ab
titers is associated with disease activity and may precede
disease relapse
Antiphospholipid Abs (APL)
Are associated with the development of venous and
arterial thrombosis and recurrent fetal lose
It may be either: primary or secondary
It may be associated with SLE , malignant conditions,
infections and rheumatic conditions
There are sevaral kinds of APL Abs (anticardiolipin and
lupus anticoagulant)
Anticardiolipin Abs are Igs directed against phospholipid
particularly β2 glycoprotein-1.
Lupus antigoagulant Abs are Igs directed against
prothrombin and occasionally β2 glycoprotein-1.
They have overlapping specificity, if there is a clinical
suspicions of APLsyndrome, both tests should be performe
Lupus antigoagulant Abs should not be done when the
patients is on anticoagulant therapy.
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)
It is an IgG Abs directed against cytoplasmic constituents
of granulocytes.
It is of two types:
1) Cytoplasmic (c-ANCA): Abs to proteinase -3 associated
with Wegener’s granulomatosis
2) Pernuclear (p-ANCA): Abs to myeloperoxidase,
lactoferrin & elastase, it is associated with microscopic
polyarteritis
Atypical p-ANCA which are not due to myeloperoxidase
are commonly found in patients with ulcerative colitis and
autoimmune liver disease.
Serial measurement of anti-PR3 or anti –MPO antibodies
may be useful for disease monitoring.
Measurement of complement activity
Quantitation of complement components (C3 and C4),
may be useful in the evaluation of immune complex
mediated diseases (SLE)
Cryoglobulinaemia
Cryoglobulins are Ig that form precipitates in the cold
It is classified into 3 types: Type I, Type II & Type III
Testing for this Cryoglobulins requires the transport of a
serum to the laboratory at 37C0
Type I
Monoclonal IgM paraprotein
It is associated with lymphoproliferative disease
Symptoms: Rayanaud’s phenomenon , retinal vessel
occlusion, arterial and venous thrombosis
Protein electrophoresis done for detection IgM
monoclonal Ab
Serum viscosity raised
Type II
Monoclonal IgM paraprotein directed against IgG
Associated with infections (HBV, HCV)
Symptoms: small blood vessels vasculitis, purpuric rash ,
arthralgia ,hepatosplenomegaly, coetaneous ulceration, :
Rayanaud’s phenomenon
RF strongly positive, Decreased C4
Protein electrophoresis done for detection IgM
monoclonal Ab
Type III
Polyclonal IgM or IgG directed towards IgG
Associated with infection (HBV,HCV) SLE, RA
Symptoms: small blood vessels vasculitis, purpuric rash ,
arthralgia ,hepatosplenomegaly, coetaneous ulceration, :
Rayanaud’s phenomenon
RF strongly positive, Decreased C4
No monoclonal paraprotein
Management includes avoidance of cold and treatment of
underlying pathology
Type II and III need immunosuppression and or
plasmapheresis to remove the pathogenic Abs
