Unit 3: Helminthes (Trematodes)
48
Lecture 4 - Pulmonary fluke
Paragonimus westermani
Common name: oriental lung fluke.
Disease: Paragonimiasis.
Biology:
Adult worm lives in (fibrous capsule in the lung & other
tissue of the body.
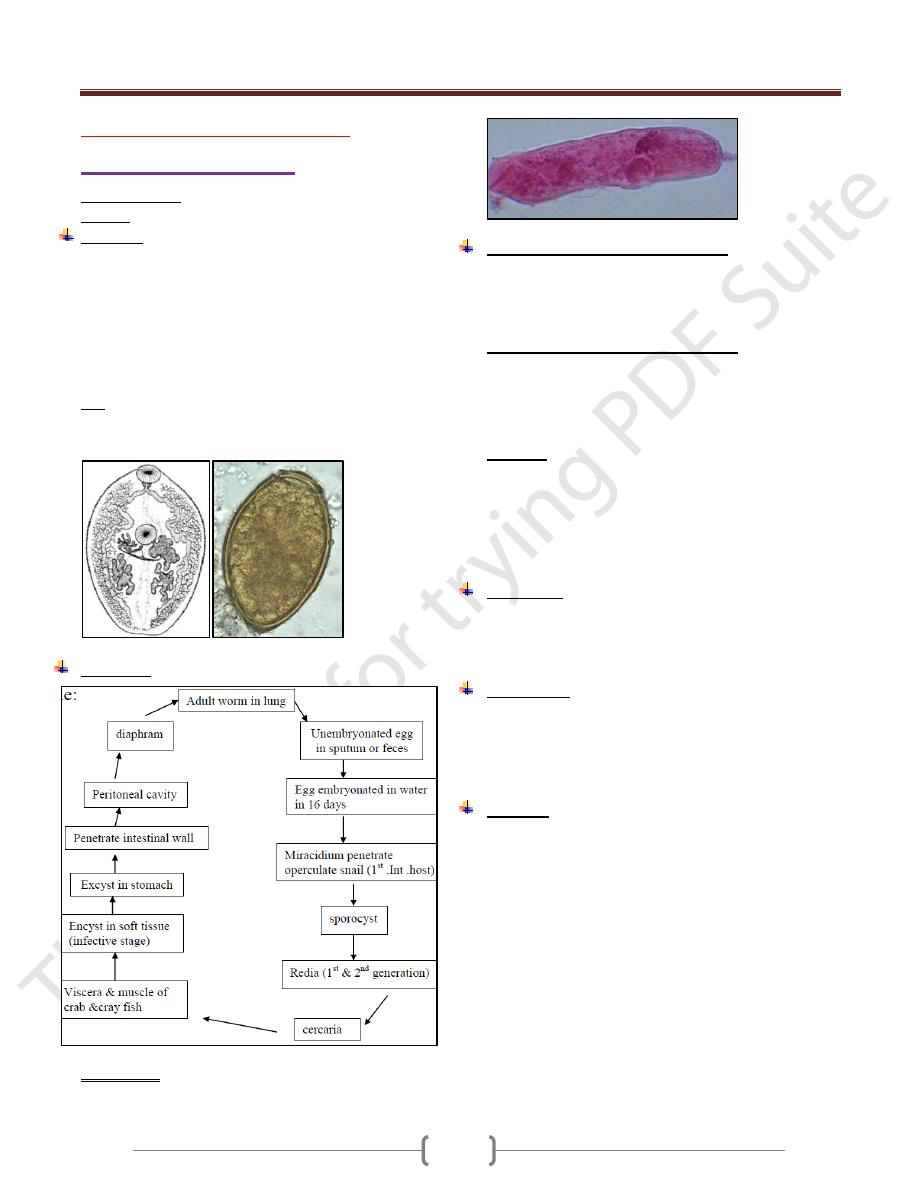
The worm stout & reddish-brown in the living state.
7.5-12 mm in length , 4-6 mm in breadth, 3.5-5 mm in
thickness.
Tegument with scalelike spines
The oral & ventral suckers are subequal.
Egg: Ovoid, thick-shelled, golden-brown in color
&flattened operculum (80-118)-µ--m by (40-60)µ—m.
They are unembryonated when laid
Life cycle
Microcercus: Minute 200-µ-- m in length with large oral
sucker, dorsal stylet & delicate knob like tail.
Pathogenesis & Symptomatology:
In the lung there is host –tissue reaction consist of
eosinophilic &neutrophilic infilteration around the worm ,
followed by development of thick fibrous capsule which
cause cough with blood in sputum .
Ectopic location of the worm including:
Liver, intestinal wall, mesenteric lymph nodes,
peritoneum, muscles, myocardium, testes, pleura, brain &
subcutaneous tissue .In these abnormal sites, there is
tendency for development of abscesses &
pseudotubercules, or the lesion may be ulcerative
Symptom:
Occasional cough with rusty sputum, dyspnea, fever,
malaise, anorexia.
In ectopic location cause leukocytosis with fever,
purulent effusion
In the brain will cause epilepsy
Diagnosis:
recovery of eggs in feces , sputum or pleural aspirate
by intradermal & serodiagnostic test
x –ray to see fibrous capsule
Treatment:
Bithionol in 10 to 15 doses on alternate days.
Niclofolan is effective in a single oral dose but
produce side effect
Praziquantel in 3-day course.
Control:
No eating fresh water crabs & crayfish only when well cooked
