Unit 3: Helminthes (Trematodes)
44
Lecture 3 - Intestinal Flukes
Fasciolopsis buski
Common name: Giant intestinal fluke.
Disease: Fasciolopiasis
In several conturies of south east Asia
Biology:
Large ,fleshy worm (20-75)mm long, (8-20)mm in width,
(0.5-3) mm thick
Tegument is spinose, oral sucker is smaller than the
nearby acetabulum. Small branched ovary, uterus is short,
convoluted .highly branched tests .Simple intestinal caeca.
Habitat: the worm lives attached to the wall of the
duodenum &jejunum of the man & pig.
Egg: large ,shaped-like hen ُ s egg (130-140 )--µ-m by
(80-85)
µm—, thin transparent shell , small operculum at
one end & are unembryonated when evacuated in the
host ُ s feces . .yellowish – brown in color
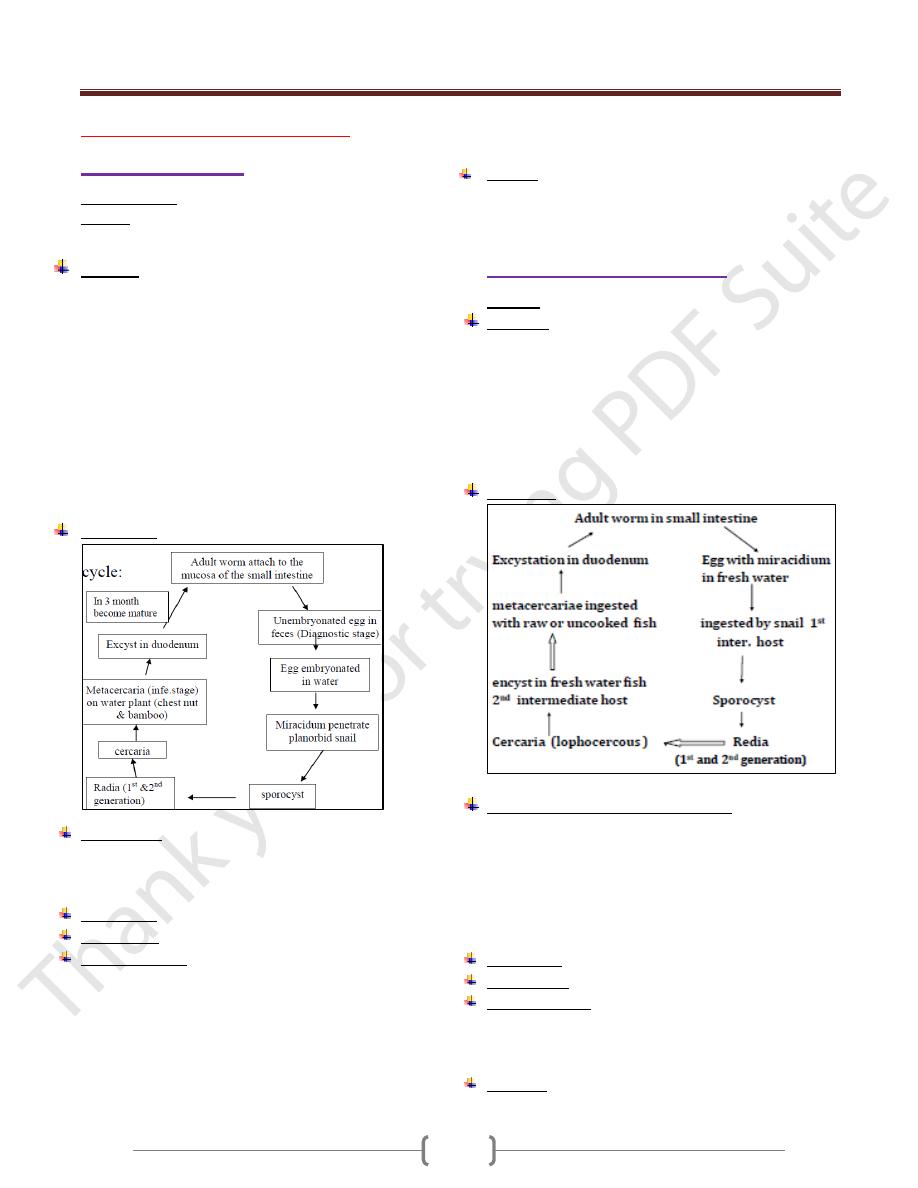
Life cycle:
Symptoms:
Include diarrhea and abdominal pain.
Heavier infection causes edema of legs, face, ascites,
eosinophilia. Some patients die of intestinal obstruction
and malnutrition.
Diagnosis
: by demonstration of eggs in stool.
Treatment
: Praziquantel is the drug of choice
Epidemiology:
Human beings acquire the infection by eating
contaminated raw water plants, especially
When peeling off the outer layers with their teeth. Rate of
infection is more in children.
Using of human excreta containing eggs to fertilize fields
of aquatic plants provide a major source of inoculum for
the molluscan stage of the life cycle.
Several animals including rabbit, pigs and dogs serve as
reservoir hosts.
Control:
Human excreta are treated before use as fertilizer.
Adequate washing of water plants with hot
Heterophyes heterophyes
Disease: Heterophyiasis
Biology:
Minute pyriform worm, rounded posteriorly,
It measures 1.o _ 1.7 mm in length by o.3 _ o.4 mm in
breadth covered by minute spines . Oral sucker very small,
but ventral sucker is large .There is a genital sucker which
lies on the lateral posterior border of the ventral sucker.
Seminal vesicle lacks the cirrus sac & cirrus organ.
Egg:
small 28_ 3o µm by 15 _ 17 µm, with operculum.
Life cycle
Pathogenesis and symptomatology
Superficial irritation of the intestinal mucosa with excess
secretion of mucous.
In heavy infection, colicky pain and mucous diarrhea.
At times the worms encysted in the tissue, Eggs get into
mesenteric venules or lymphatic, carried to heart, brain or
spinal cord where they stimulate granulomatous reaction.
Diagnosis
: Recovery of eggs in faeces .
Treatment
: Praziquantel and Niclosamide are effective
Epidemiology
: Heterophyes is found in variety of wild
and domestic
Mammals especially fish eating mammals which acquired
the infection by eating fish in a raw, salted or dried.
Control
: The easiest possible measure is the avoidance
of consuming under cooked fish.
