Unit 3: Helminthes (Nematodes)
86
Lecture 1 - Introduction
General characteristics
The word nematode comes from a Greek word Nema that
means thread.
Nematodes are unsegmented, elongate & cylindrical with
bilateral symmetry with a complete digestive tract which
started with mouth, esophagus, intestine & end in sub-
terminal anus. They have no circulatory system & nutrients
are transported through body via fluid in body cavity
(pseudocelom).The nematode has no respiratory system.
Pseudocelom (pseudocoel) Body cavity of nematode
which is filled with fluid in which internal organs float.
Body wall
The body wall is consists of an
Outer cuticle is tough and flexible, so does not allow
volume of the worm to increase and keep the hydrostatic
pressure inside the worm very high; this is why the round
worm appears round. Therefore, as the worm grows, it has
to molt and form new cuticle. This cuticle is periodically
shed during the life of nematode as it grows, usually four
times before reaching adult stage. The first molt and
occasionally the second molt may take place in the egg.
The remaining molts occur in the definitive host.
Inner muscular layer: aligned longitudinally along the
inside of the body, so the nematode can only bend from
side to side.
Intermediate thin syncytial hypodermis that secretes
the cuticula and binds it to the outer surface of the muscle
fiber. Arising from the hypodermis, cords project toward
the body cavity at the dorsal, ventral, and lateral lines,
dividing the muscles into distinct quadrents.
The excretory system
Consists of two tubes running inside the lateral chords. At
anterior end these tubes are interconnected and open in
the midventral region as an excretory sinus.
Nervous system
It is composed from a circumesophageal nerve ring and
short ventral nerve cord and small dorsal nerve cord.
Sensory structures at the anterior end called Amphid and
at the posterior end called phasmids.
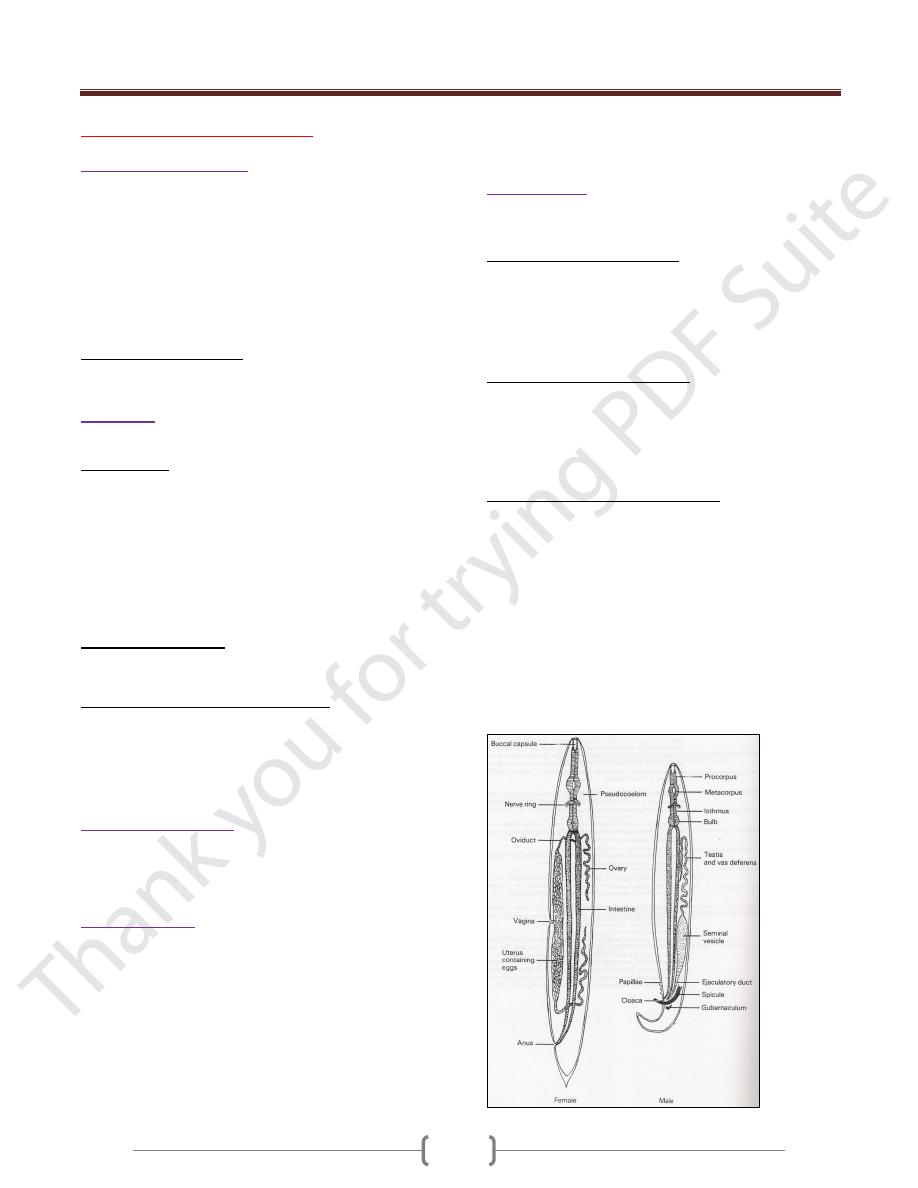
Male is smaller than female and have a characteristic bent
tail for holding the female for copulation. In male, the
intestine narrows and turn ventrally to become the cloaca.
The cloaca opens to the exterior via the anus. There is no
cloaca in the female, so the gut and reproductive system
are independent of each other and they don’t share ducts
or openings, as they do in the male.
Reproduction
Nematodes are bisexual (dioecious) but in few instances
the female may be parthenogenetic
The male reproducti ve system consist of a single tubule
, beginning as a testis , then a seminal vesicle , a vas
deferens and an ejaculatory duct opening into the cloaca.
Accessory copulatory structures consist of 1 or 2 copulatory
spicules which move out of the cloaca & inserted into the
genital pore of the female during copulation.
The female reproductive system may be composed of a
single reproductive set as in Trichinella and Trichuris, but
in most nematodes the inner organs are paired. The
following regions can be recognized: ovary, oviduct,
seminal receptacle, uterus, vagina, ovejector and vulva
which is ventral in position.
The stages in the nematode life cycle are the egg, four
larval stages, and the adult. At the end of each larval stage
a new cuticula is secreted and the old one is molted.
The daily production of eggs per female varies in different
species. The stage of development at the time of
oviposition also varies, in some species the eggs are
unembryonated (Ascaris and Trichuris), in hookworms
are in the early stage of cleavage, and those of
Strongyloides frequently are in the morula or a more
advanced stage, in filariae, Trichinella and Dracunculus,
the eggs develop completely and the larvae hatch in utero
to be discharged as larvae or microfilariae.
