Unit 4: Virology
251
Lecture 4 - Antiviral Drugs
I- Early events inhibitors
1)
Amantidine
:
It inhibits uncoating of the virus by blocking the "ion
channel" activitiy of the matrix protein (M2 protein) in
the virion as shown in the figure below. This drug
specificallyinhibits influenza A but not C and B types. It
has CNS side effects.
Rimantidine is similar to amantidine but with fewer side
effects.
2)
Enfuvirtide ( Fuzeon)
:
It is a synthetic peptide that binds to gb41 on the surface
of HIV, thereby blocking the entry of the virus into the
cell. It is a fusion inhibitor. As shown in the figure below
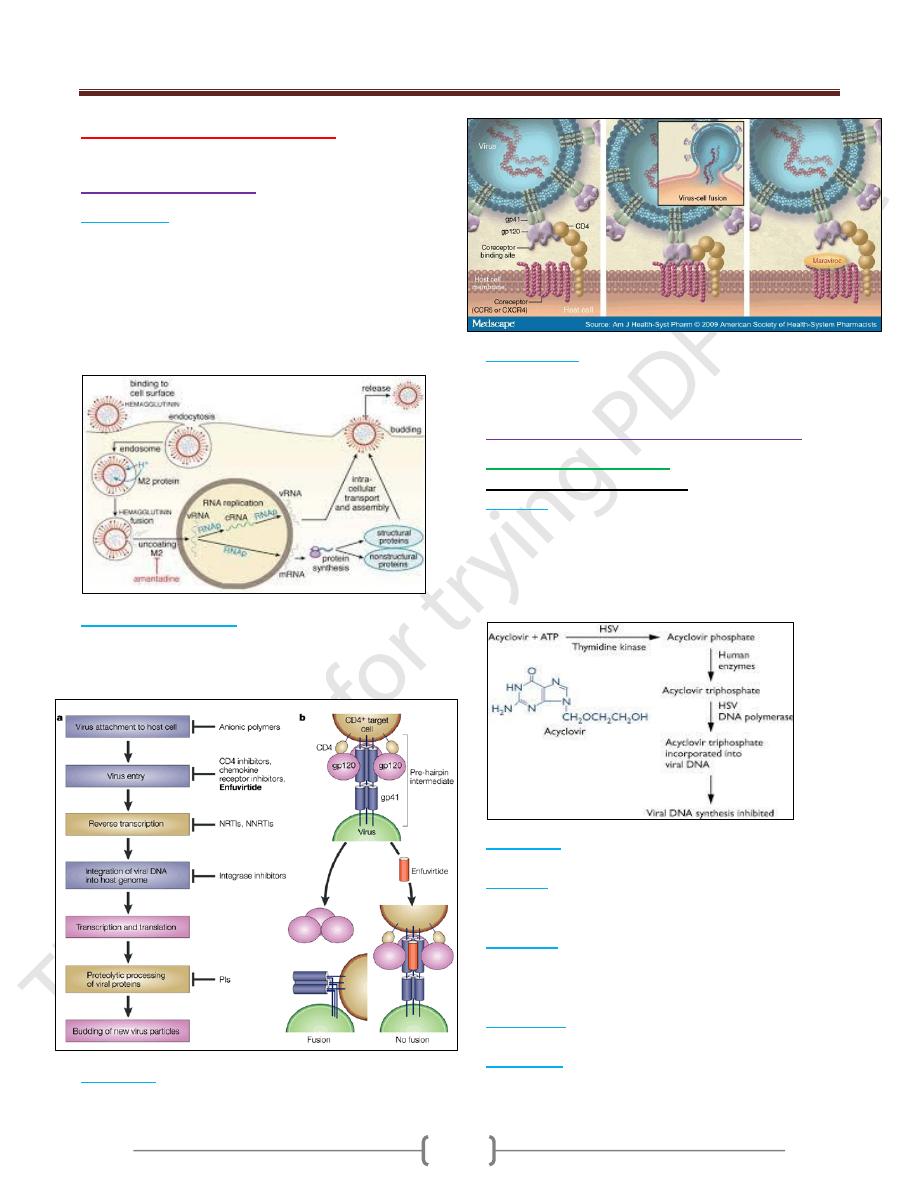
3)
Maraviroc
it blocks the binding of HIV to CCR-5 as
shown in the figure below.
4)
Palivivumab
:
it is monoclonal antibody directed against
the fusion protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
II-
II- Inhibitors of Viral nucleic acid inhibitors
A. Inhibitors of herpes virus.
Nucleoside analogue inhibitors:
1) Acyclovir
: it acts against HSV1 and -2 and Varicella
zoster virus (VZV). It is a guanosine analogue. As shown
in the figure below.
Derivatives of acyclovir are (Valacyclovir, penciclovir,
and Famciclovir).
These drugs have no effects on latency.
2) Ganciclovir
it is more active against Cytomegalovirus.it
is a guanosine analogue.
3) Cidofovir
: used in the treatment of retinitis caused by
CMV. It is a nucleoside analogue of cytosine that lacks a
ribose ring.
4) Vidarabine
: treatment of encephalitis and keratitis
caused by HSV-1 but less effective than acyclovir. It is a
nucleoside analogue with arabinose in place of the normal
sugar, ribose.
5) Idoxurudine
: it is effective in the treatment of
keratocnjuctivitis caused by HSV-1.
6) Trifluridine
: it is used topically for treatment of
keratoconjuctivitis because it is too toxic for systemic use.

Unit 4: Virology
251
Nonnucleoside inhibitors.
1) Foscarnet:
it is a pyrophosphate analogue. It binds to
DNA polymerase at the pyropghosphate cleavage site and
prevents removal of the phosphate from nucleoside
triphosphate(dNTP). This inhibits the addition of next
dNTP . the drug inhibits DNA polymerase of all
herpesviruses especially HSV and CMV.
B. Inhibitors of retroviruses.
Nucleoside inhibitors
1) Zidovudine (AZT,Retrovit, azidothymidine):
It does not require a virus-encoded kinase to be
phosporylated, CK phosphorylate the drug, it is active in
both infected and non-infected cells.it cause chain
termination As shown in the figure below.
2)
Others:
didanosine (ddI), lamivudine
(3TC), stavudine (d4T), abacavir and
Emtricitabine (FTC)
. ) .(لالطالع فقط
Nonnucleoside inhibitors (NNRTI):
It doesn’t cause chain termination but it is binds near the
active site of reverse transcriptase and induce
conformational changes that inhibits synthesis of viral
DNA. As shown in the figure below.
E.g., in drug-naïve patients (nevirapine and efavirenz)
In drug-experienced patient (etravirine).
C. inhibitors of hepatitis B virus:
i. Adefovir
: nucleoside analogue of adenosine
monophosphate. it inhibits DNA polymerase of Hepatitis
B virus. it is useful in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B
infection.
ii. Entecavir
: it is a guanosine analogue.
iii. Lamivudine
iv. Telbivudine
: it is a thymidine analogue. it is useful in the
treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
D. inhibitors of other viruses.
v. Ribavirin
: it is a nucleoside analogue.
It inhibits the synthesis of guanine nucleotides.
It is used in the treatment of pneumonitis caused by
respiratory syncytial virus in infants and to treat severe
influenza B infection.
It is also used in combination with alpha-interferon for the
treatment of hepatitis C.
III. Inhibition of integrase:
Raltegravir
is an integrase inhibitors used in HIV
infection.as shown in figure below.
IV. Inhibition of cleavage of precursor
polypeptides (protease inhibitors).
A. Inhibition of HIV.
e.g.,
saquinavir followed by indinavir, ritonavir,
lopinavir and tipranavir; more recently, atazanavir,
fosamprenavir and darunavir
have become available.
(االسماء لالطالع فقط
)
B. inhibitors of Hepatitis C virus:
Boceprevir and telaprevir
used in HCV.

Unit 4: Virology
251
V- Inhibitors of viral protein synthesis:
1) Interferons
2) Fomivirsen
: it is an antisense DNA that blocks the
replication of CMV ( antisense is a single –stranded DNA
that has a sequence complemantory to that of viral
mRNA. it is the only antisense that is approved to be used
in treatment of human disease.
3) Methisazone
: it inhibits the protein synthesis of
poxviruses, by blocking the translation of late mRNA.
VI- Inhibition of release of virus:
1- Zanamivir (Relenza) and oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
inhibits the neuraminidase of influenza virus. The drug is
effective against both influenza A and B viruses. These
drugs are effective only against strains of influenza virus
resistant to amantidine.
