
Unit 2: Bacteriology
102
Lecture 8 - Nocardia & Listeria
monocytogenes
Nocardia
Nocardia is
a genus of weakly staining Gram-positive,
catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria. It forms partially
acid-fast beaded branching filaments (acting as fungi, but
being truly bacteria). It has a total of 85 species. Some
species are non-pathogenic while others are responsible
for nocardiosis. Nocardia are found worldwide in soil that
is rich with organic matter. In addition, Nocardia are oral
microflora found in healthy gingiva as well as periodontal
pockets. Most Nocardia infections are acquired by
inhalation of the bacteria or through traumatic
introduction.
The genus Nocardia includes species with morphology
similar to that of the actinomycetes, differing from them
in that the natural habitat of these obligate aerobes is the
soil and damp biotopes. The pathogens known for
involvement in Nocardiosis, a generally very rare type
of infection caused by N. asteroides and other species
include N. brasiliensis, N. farcinia, N. nova, and N.
otitidiscaviarum.
N. asteroids Direct Partial Acid Fast Stain
Morphology and culture.
Nocardia are Gram-positive, fine, pleomorphic rods that
sometimes show branching. They can be cultured on
standard nutrient mediums and proliferate particularly
well at 30 °C.
Pathogenesis and clinical picture.
Nocardia penetrate from the environment into the
macroorganism via the respiratory tract or dermal
wounds. An infection develops only in patients with
predisposing primary 5diseases directly affecting the
immune defenses. Monoinfections are the rule. There are
no typical clinical symptoms. Most cases of infection
involve pyogenic inflammations with central necroses.
The following types have been described: pulmonary
nocardioses (bronchial pneumonia, pulmonary abscess),
systemic nocardioses (sepsis, cerebral abscess, abscesses
in the kidneys and musculature), and surface nocardioses
(cutaneous and subcutaneous abscesses, lymphocutaneous
syndrome).
Actinomycetomas are tumorlike processes affecting the
extremities, including bone. An example of such an
infection is Madura foot, caused by Nocardia species, the
related species Actinomadura madurae, and
Streptomyces somaliensis. Fungi can also be a causal
factor in this clinical picture.
Diagnosis
Detection of the pathogen by means of microscopy and
culturing techniques is required in materials varying with
the specific disease. Due to the long generation time of
these species, cultures have to be incubated for at least
one week. Precise identification to differentiate
pathogenic and apathogenic species is desirable, but
difficult.
Therapy
The anti-infective agents of choice are sulfonamides and
cotrimoxazole. Surgery may be required.
Epidemiology and prevention
Nocardioses are rare infections. Annual incidence levels
range from about 0.5 to 1 case per 1 000 000 inhabitants.
The pathogens, which are present in the natural
environment, are carried by dust to susceptible patients.
There are no practicable prophylactic measures
Unit 2: Bacteriology
103
Listeria monocytogenes
Morphology and culture.
Microscopically, Listeria species appear as small, Gram-
positive rods, which are sometimes arranged in short
chains, nonsporeforming and catalase-positive. In direct
smears they may be coccoid, so they can be mistaken for
streptococci. Longer cells may resemble corynebacteria.
Flagella are produced at room temperature but not at
37°C. Hemolytic activity on blood agar has been used as a
marker to distinguish Listeria monocytogenes among
other Listeria species, but it is not an absolutely definitive
criterion. Further biochemical characterization may be
necessary to distinguish between the
different Listeria species.
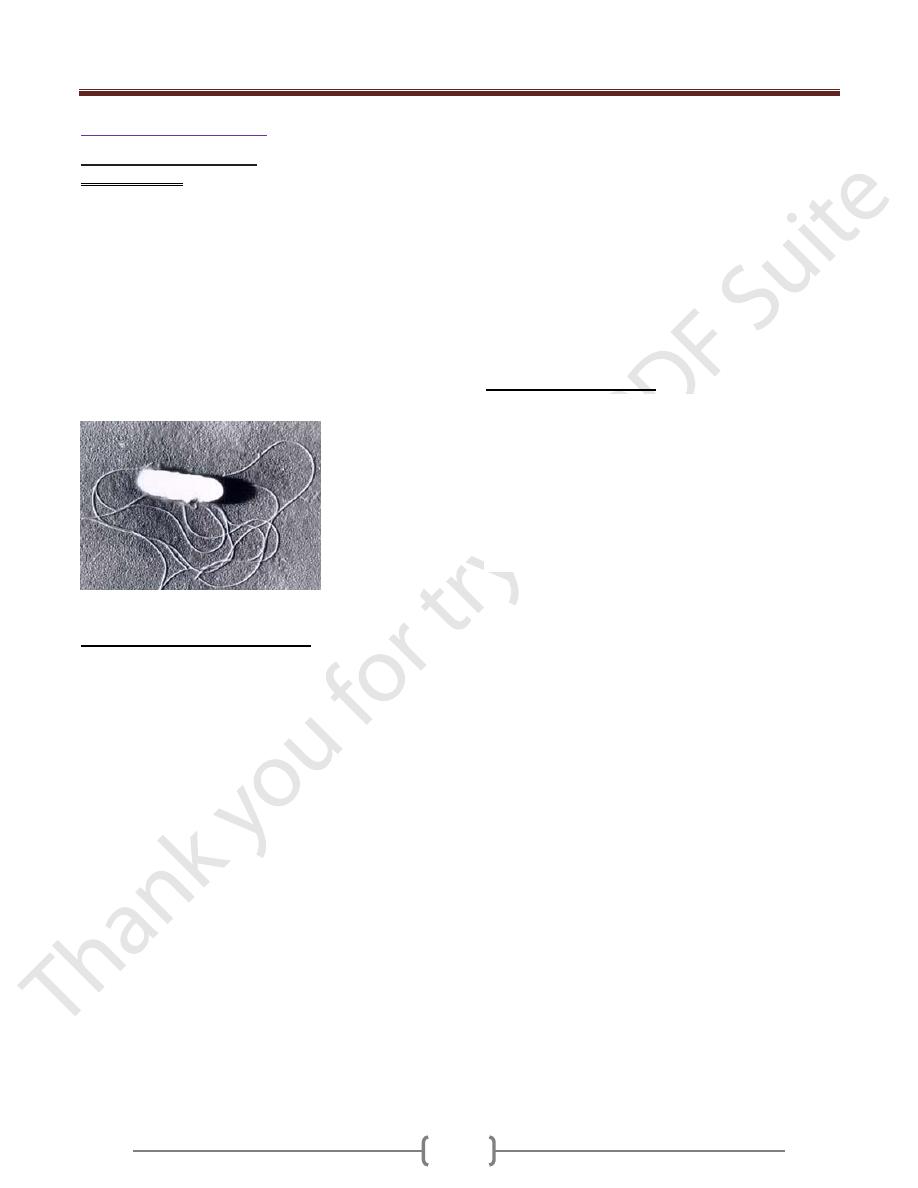
Listeria monocytogenes Scanning Electron Micrograph
Pathogenesis and clinical picture
Listeria monocytogenes is presumably ingested with raw,
contaminated food especialy that food stored in the
refrigerator for a long period of time. An invasin secreted
by the pathogenic bacteria enables the listeriae to
penetrate host cells of the epithelial lining gastrointestinal
system. The term listeriosis encompasses a wide variety
of disease symptoms that are similar in animals and
humans. Listeria monocytogenes causes listeriosis in
animals and humans. The true incidence of listeriosis in
humans is not known, because in the average healthy
adult, infections are usually asymptomatic, or at most
produce a mild influenza-like disease. Clinical features
range from mild influenza-like symptoms to meningitis
and/or meningoencephalitis. Illness is most likely to occur
in pregnant women, neonates, the elderly and
immunocompromised individuals, but apparently healthy
individuals may also be affected. In the serious (overt)
form of the disease, meningitis frequently accompanied
by septicemia, is the most commonly encountered disease
manifestation. In pregnant women, however, even though
the most usual symptom is a mild influenza-like illness
without meningitis, infection of the fetus is extremely
common and can lead to abortion, stillbirth, or delivery of
an acutely ill infant. Overt listeriosis following infection
with L. monocytogenes is usually sporadic, but outbreaks
of epidemic proportions have occurred. After engulfment
by macrophage, the bacterium may escape from the
phagosome before phagolysosome fusion occurs mediated
by a toxin, which also acts as a hemolysin, listeriolysin O
(LLO). This toxin is one of the so-called SH-activated
hemolysins, which are produced by a number of other
Gram-positive bacteria, such as group A streptococci
(streptolysin O), pneumococci (pneumolysin), and
Clostridium perfringens. The hemolysin gene is located
on the chromosome.
Treatment and Prevention
If diagnosed early enough, antibiotic treatment of
pregnant women or immunocompromised individuals
can prevent serious consequences of the disease.
Antibiotics effective against Listeria species include
ampicillin, vancomycin, ciprofloxacin, linezolid and
azithromycin. Because pregnant women, older adults,
and people with weakened immune systems are at higher
risk for listeriosis, CDC recommends specific certain
measures for these persons.
