
Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
24
Lecture 2 + Half 3 – Cholinergic Agonists

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
25
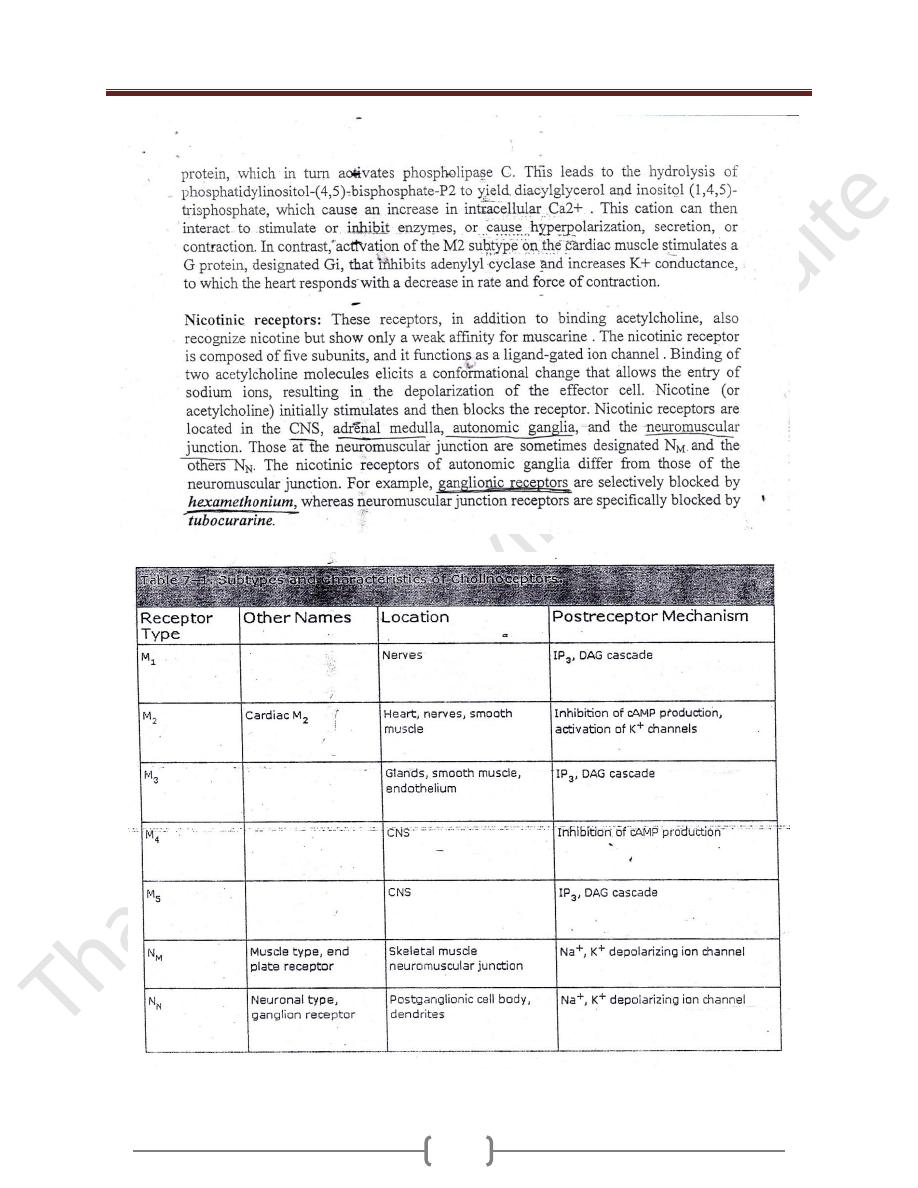
Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
26

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
27

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
28
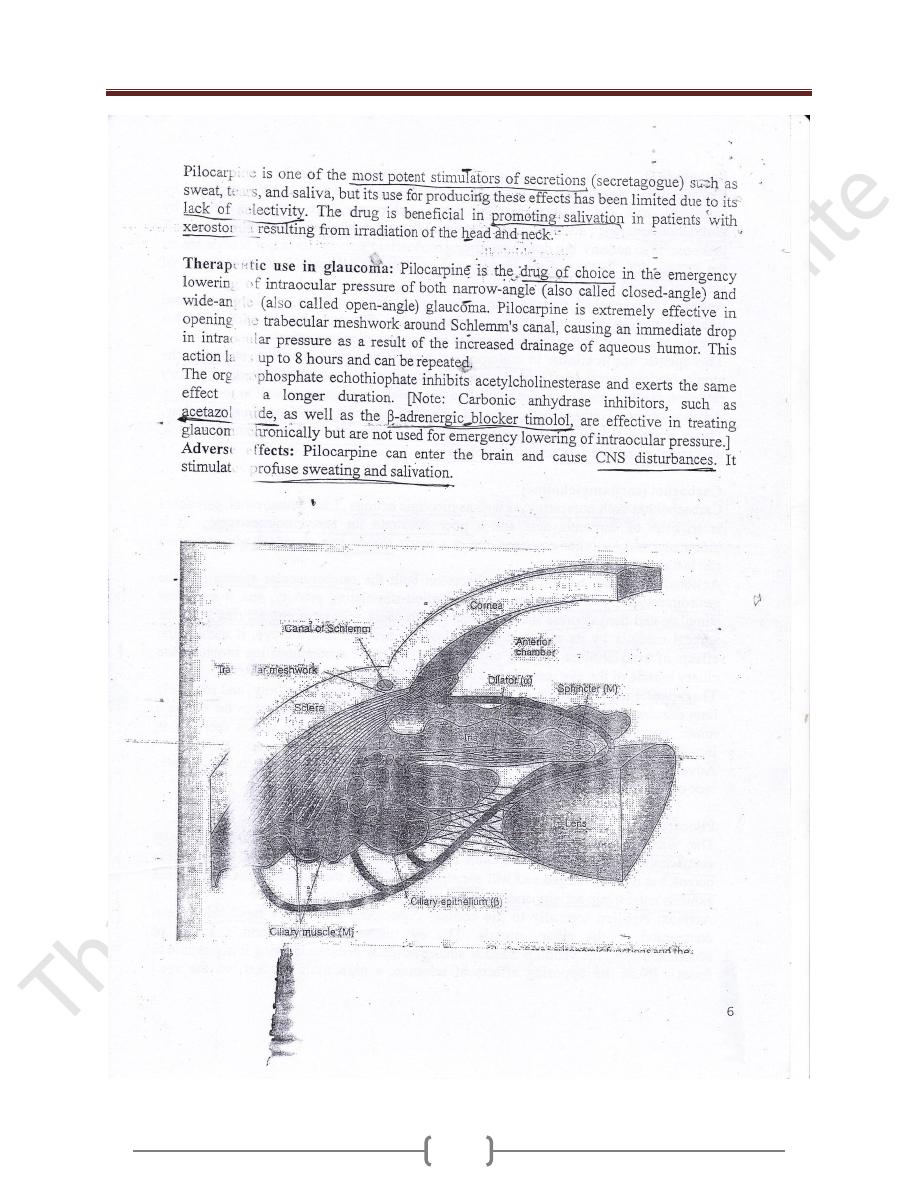
Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
29

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
30

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
31
not enter the CNS. Its effect on skeletal muscle is greater than that of physostigmine,
and it can stimulate contractility beforeit paralyzes. Neostigmine has an intermediate
duration of action, usually 30 minutes to 2 hours. It is used to stimulate the bladder and
GI tract, and it is also used as an antidote for tubocurarine and other competitive
neuromuscular blocking agents. Neostigmine has found use in symptomatic treatment
of myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disease caused by antibodies to the nicotinc
receptor at neuromuscular junction. This causes their degradation and, thus, makes
fewer receptors available for interaction with the neurotransmitter.
Adverse effects of neostigmine include those of generalized cholinergic stimulation,
such as salivation, flushing, decreased blood pressure, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea
and bronchospasm. Neostigmine does not cause CNS side effects and is not used to
overcome toxicity of central-acting antimuscarinic agents such as atropine.
Pyridostigmine and ambenonium
Pyridostigmine and ambenonium are other cholinesterase inhibitors that are used in the
chronic management of myasthenia gravis. Their durations of action are intermediate
(3 to 6 hours and 4 to 8 hours, respectively), but longer than that of neostigmine.
Adverse eff ects of these agents are similar to those of neostigmine.
Demecarium
Demecarium is another cholinesterase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma. Demecarium is
a quaternary amine that is structurally related to neostigmine. Mechanisms of actions
and side effects are similar to thos od neostigmine.
Edrophonium
The actions of edrophonium are similar to those of neostigmine, except that it is more
rapidly absorbed and has a short duration of action of 10 to 20 minutes (short-acting
agent). Edrophonium is a quaternary amine and is used in the diagnosis of myasthenia
gravis. Intravenous injection of edrophonium leads to a rapid increase in muscle
strength. Care must be taken, because excess drug may provoke a cholinergic crisis.
Atropin is sntidote.
Tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine
Patients with Alzheimer disease have a deficiency of cholinergic neurons in the CNS.
This observation led to the development of anticholinesterases as possible remedies for
the loss of cognitive function. Tacrine was the first to become available, but it has been
replaced by others because of its hepatotoxicity. Despite the ability of donepezil ,
rivastigmine, and
galantamine to delay the progression of Alzheimer disease, none can stop its
progression. GI distress is their primary adverse effect.
Anticholinesterases (irreversible)
A number of synthetic organophosphate compounds have the capacity to bind
covalently to acetylcholinestrase. The result is a long-lasting increase in acetylcholine
at all sites where it is released. Many of these drugs are extremely toxic and were
developed by the military as nerve agents. Related compounds, such as parathion, are
used as insecticides.

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
32

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
33

Unit 2: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
34
