
Lec.3
Pedatrics
6th
2016/9/6
Session notes
د.رياض العبيدي
Neonatal jaundice
Prolonged neonatal jaundice means more the physiological
pathological
Ask about family Hx , TORCH infection
Hemorrhagic disease of newborn indicate Vit.K deficeincy syndrome
DDx of Generalized bleeding tendency ?
1-ITP ( idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura )
2-Haemophilia
3-Factor 7 , 5 deficeincy
Hemprrhagic disease classified as :
1-early type : 24 hours
2-classical : 24 – 7 days
3- late : > 7 days
Late hemorrhagic disease , eg ; liver disease ( cholastasis ) , alpha1-
antitrypsin deficeincy , galactosemia , malabsorption
Invx : PTT , PT , CBC , BT ( Bleeding profile )
In Vit.K PT increase , APTT increase , BT normal
Approach to patient with hemorrhagic disease :
1-Bleeding profile
2-CBC

3-GUE : to search for bile pigment cholestasis
4-Urine reducing substance : to look for galactosemia
5-chromatography : to check for amino-acid
6-ASPG , ASPOT liver enzyme to see if there is hepatitis
7-alkaline phosphatase enzyme
8-Blood group : ABO , Rh to excludenspissated bile syndrome is defined
as partial or complete obstruction of the extrahepatic biliary system by
impaction of thick bile or sludge in the distal common bile duct during
the neonatal period
9-congenital infection : TORCH ( Toxoplasmosis rubella ,
Cytomegallovirus , Herpes virus ) to measure IgM or IgG
10-US : intrahepatic biliary diltation
11-Hida test
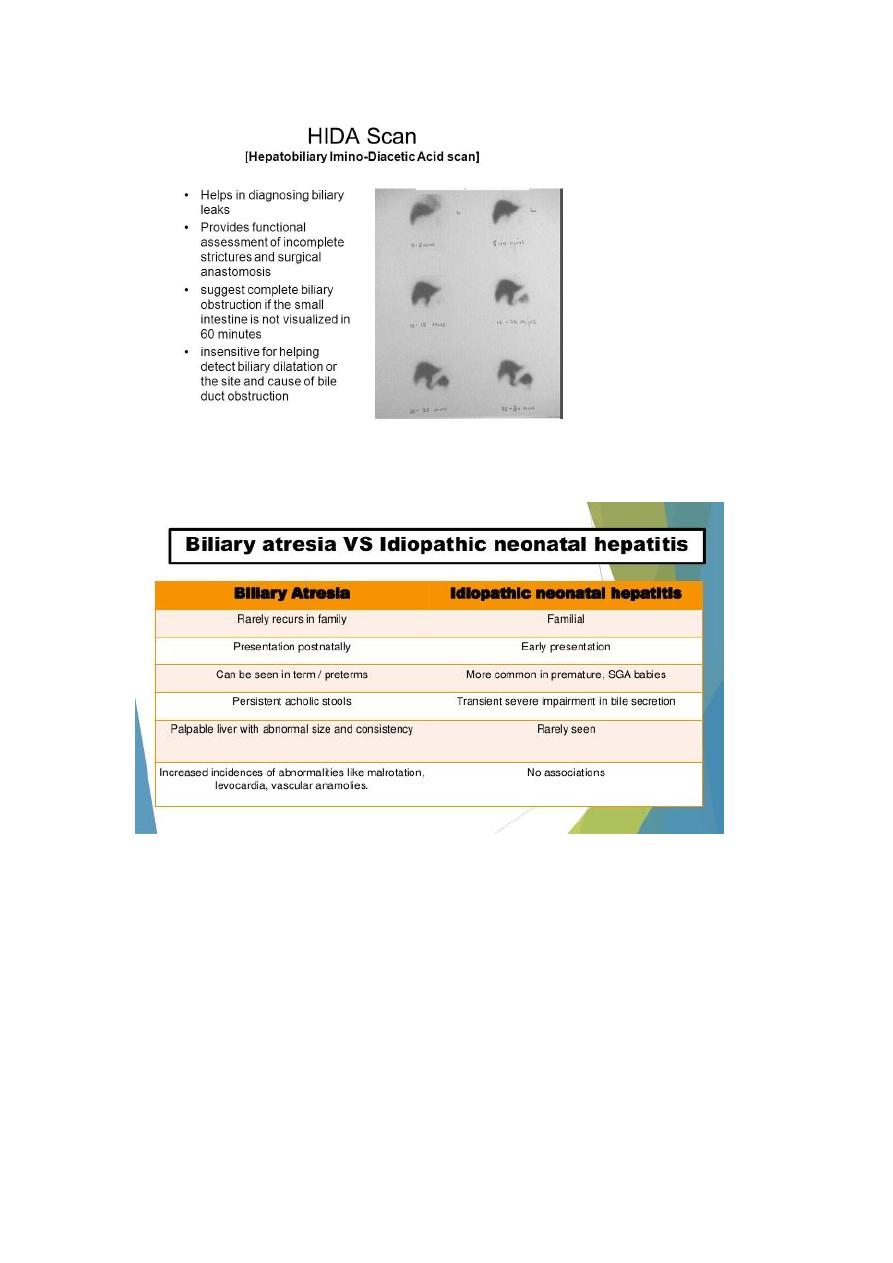
Difference between Biliary atresia and neonatal hepatitis
On Exam :
1-cataract : associated with galactosemia
2-face : if ugly Argyll syndrome
3-Heart : look for coarctation of aorta , VSD
4-convlusion : seek for hypoglycemia
Treatment :

Vit. K replacement mainly fresh frozen plasma
There is 3 types of vitamin K ( 1,2,3)
Is given mainly IM and mointor the patient to avoid anaphylactic shock
Surgical opreation for biliary atrsia Kasai
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Random blood sugar should be :
>11 mmol/l or 200 mg/l
In fasting > 7 mmol/l or 127 mg / l
Look for this sign in DKA :
1-Tachypnea
2-dehydration
3-Abdominal pain
4-vomiting
5- polyuria , polydepsia
Management
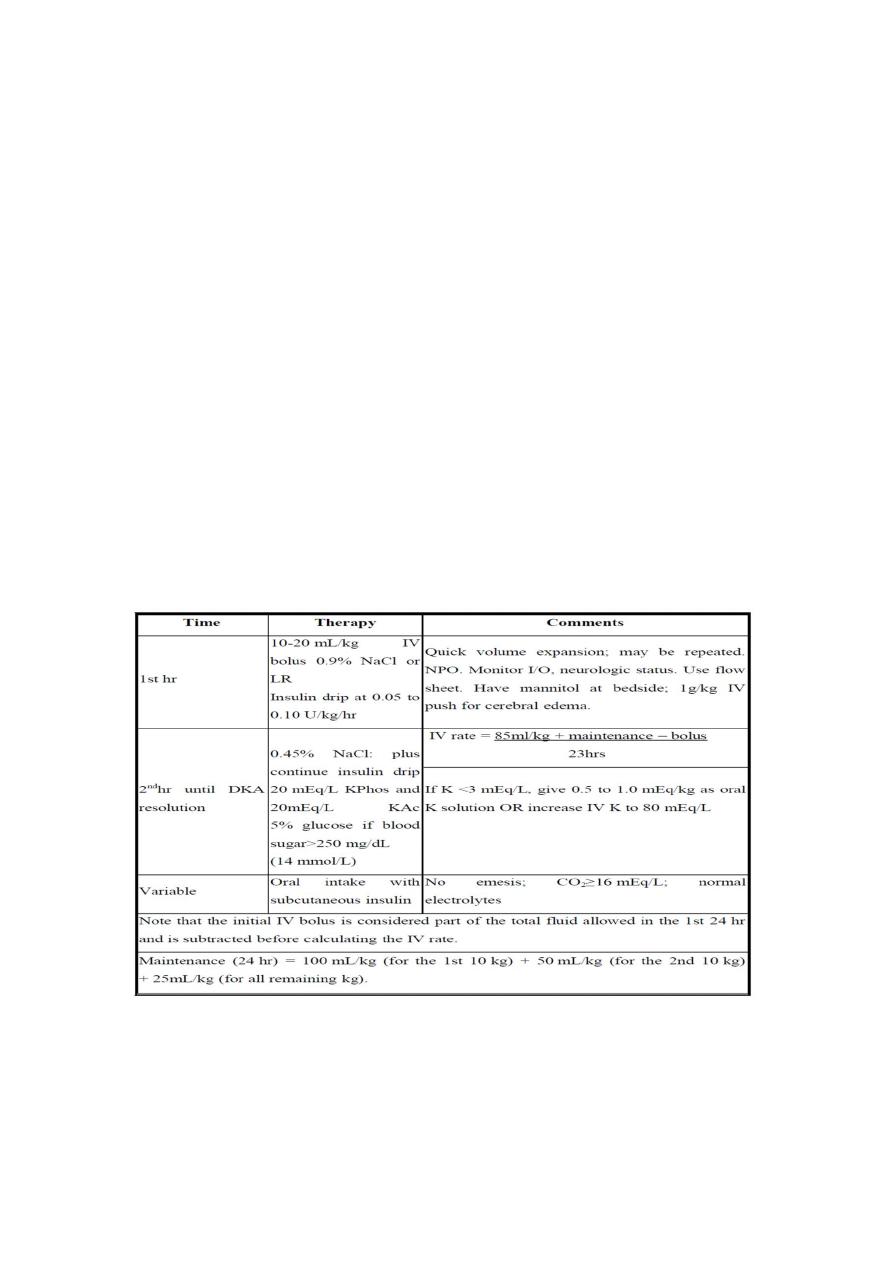
1-hospital admission
2-monitoring
3-IV canula
4-Draw bolld sample for : RBS , seum electrolyte
5-blood gas analysis ( BGA)
6- Serum BUN
Even pateint is severely dehydrated urin still present due to osmotic
diuresis
7-HbA1c ( glycosalted hemoglobin )
For past 3 months if > 6.5 is diagnostic for DKA
There pseudohypernatremia in DKA
Treatment (impt)
