( ECG ) :
Electrocardiography
Definition :
Recording the electrical activity of the heart
SPEED 25-50 mm/sec according to the activity
Prolonged PR interval BBB normal 3-5 small sequares
Short PR interval WPW
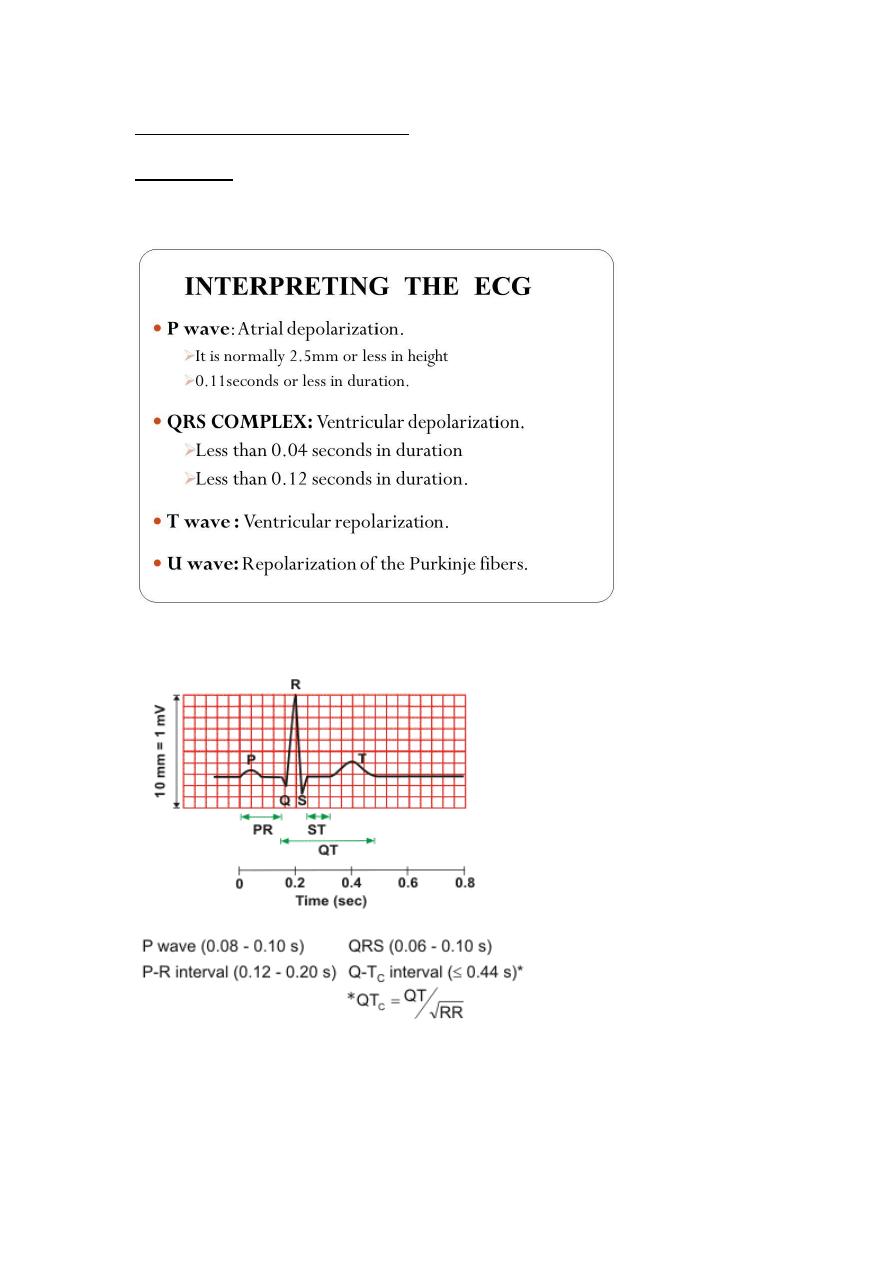
QRS from beginning of Q till to the end of S
Prolonged in QRS BBB
QTc from end of QRS till to end of T-WAVE
QTc interval
QT interval prolonged if > 0.45 sec
ECG reading :
When read ECG should be done in a structured approach

1-rhythm : regular or irregular
Look for the interval between the R-R wave
2-Rate :
3-The axis : it is right or left axis
How you going to assess the axis ?
before birth baby's right ventricle is the predominent and the left
ventricule is not-functioning as baby receive blood from his circulation
and mother and is it is oxygenated blood already by SVC TO RA AND
RIGHT VENTRICLE
right ventricular predomiance
to decide the axis look for the
lead I ,II, III , avF = limb leads
Chest lead V1-V6
Example : 1 day
Shanking of hand lead I shaking hand with lead II right axis deviation
If lead I upward and lead II or III downward it is left axis deviation
If the two leads looks toward the same side it is normal axis

If the two leads looks downward it is undetermind axis
Extreme right or left
Axis
0 90 normal
90 180 right axis
0 - 90 left axis
0 - 180 inderterminated axis or extreme
Right ventricular predominance
In normal Chest lead cover the right ventricle from V1-V5
V6 receives the voltage from left ventricle as it is lies posterior
predominantly
In patient with VSD can be present with right ventricular hypertrophy
and left to rigth shunt
And pulmonary hypertension
If V6 is negative it is RVH

IF V6 is positive it is LVH
AFTER that look for the inerval :
QRS , P-wave , QT interval , ST , PR
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Criteria :
Prominent right axis devation
Prominent R IN V1
Small S in V6
UP ward T-wave in ( V 1 , 2 , 3 )
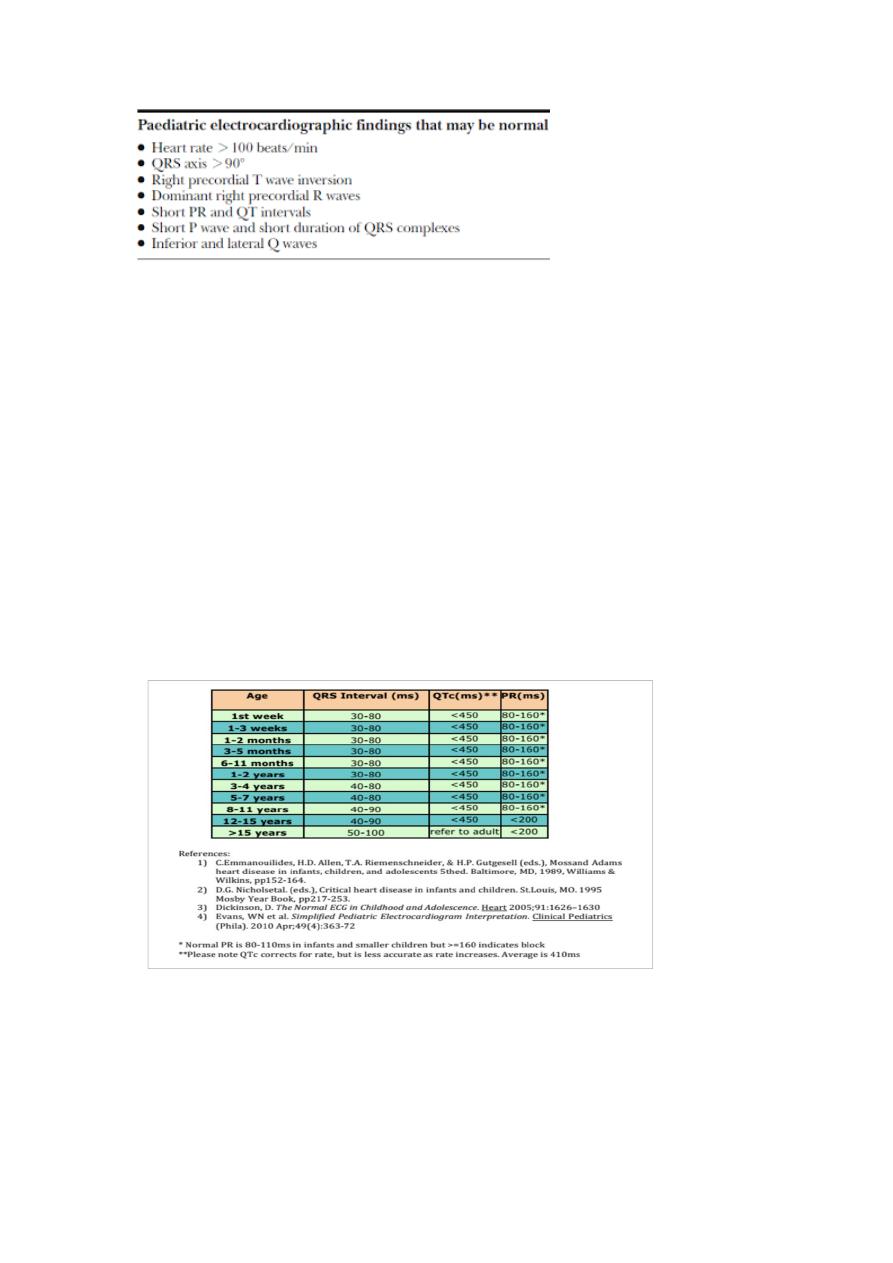
It is must be inverted in first 6 days untill 6 years
And it may be inverted in 6 years 0- 12 years
One of the main differences from Adult ECG
When child grows right axis deviation changed from right toward the
normal site
During the first year of life right axis effects is resolved
Normal RS progression proceed during child growth and changed from
right axis deviation
Toward left axis deviation
Prominenr R in V1 decrease and increase in V6
Prominent S1 increase in V1 and decrease in V6
Can MI presentd in pediatrics ?
1-familial hyperlipidemia
2-anamolus origin from left coronary artery
3-Kawasaki

4- thrombophilia inheretd anti-thrombin
p- pulmonale right atrial hypertrophy
p-mital left atrial hypertrophy
Best reading for ECG from lead II
And take a trace ECG to discover rythem abnormality
Tented T-wave in in lead II indicate hyperkalemia
V4 R mains V4 on the right side and it is similar to V1
Sinus arrythemia Sinus arrythmia : occur during inspiration by increased
heart beats
-Ectopic beat with pause temporary
ساليد
41
QRS distorted
Right ventricular hypertrophy : upward T-wave in V1 , V 4
Strain pattern in V6 IN left ventricular hypertrophy
Complete bundle branch block or RS-R pattern
ساليد
41
Look for V4 QRS M-shape
This condition presented in ostium primeum canal associated with
Down's syndrome
ASD+VSD = AV CANAL
QT prolonged in
1-congenital:
a-autosomal recessive
b-autosomal dominent

2-acquired :
Hpypocalcemia most common and less in hypokalemia ,
hypomagnesimia
The danger when changed to arrythmia and it is bradycardia
EaComplrte heart block
QRS MUST be followed by T
tachycardia + absent p-wave = SVT
Tx :
Short PR , J-wave , wide QRS Wolf parkinsonian white syndrome
SVT + adenosine
اخر ساليد
ECG RBBB IN OSTIUM PRIMEIUM
LBBB IN CARDIAC SURGERY
