Subjec: Signals and Systems
Lecture 9
Lecture: Dr.Manal Kadhim
Electromechanical Eng.Department
Electromechanical Systems Branch
Fourth Year.
1
F
F
a
a
s
s
t
t
F
F
o
o
u
u
r
r
i
i
e
e
r
r
T
T
r
r
a
a
n
n
s
s
f
f
o
o
r
r
m
m
DFT is defined for finite duration sequences. Although it is a computable
transform, the straight forward implementation is very inefficient, especially when
the sequence length N is large.
This led to development of other efficient algorithms. All these algorithms are
collectivity known as Fast Fourier Transform algorithms.
Fast Fourier Transform Representation
The basic strategy that is used in the FFT algorithm is one of "divide and conquer."
which involves decomposing an N-point DFT into successively smaller DFTs. To see
how this works, suppose that the length of x(n) is even (i.e., N is divisible by 2). If
x(n) is decimated into two sequences of length N/2, computing the N/2-point DFT of
each of these sequences requires approximately
multiplications and the
same number of additions. Thus, the two DFTs require
multiplies
and adds. Therefore, if it is possible to find
the N-point DFT of x(n) from these
two N/2-point in fewer than
operations
Decimation-in-Time FFT
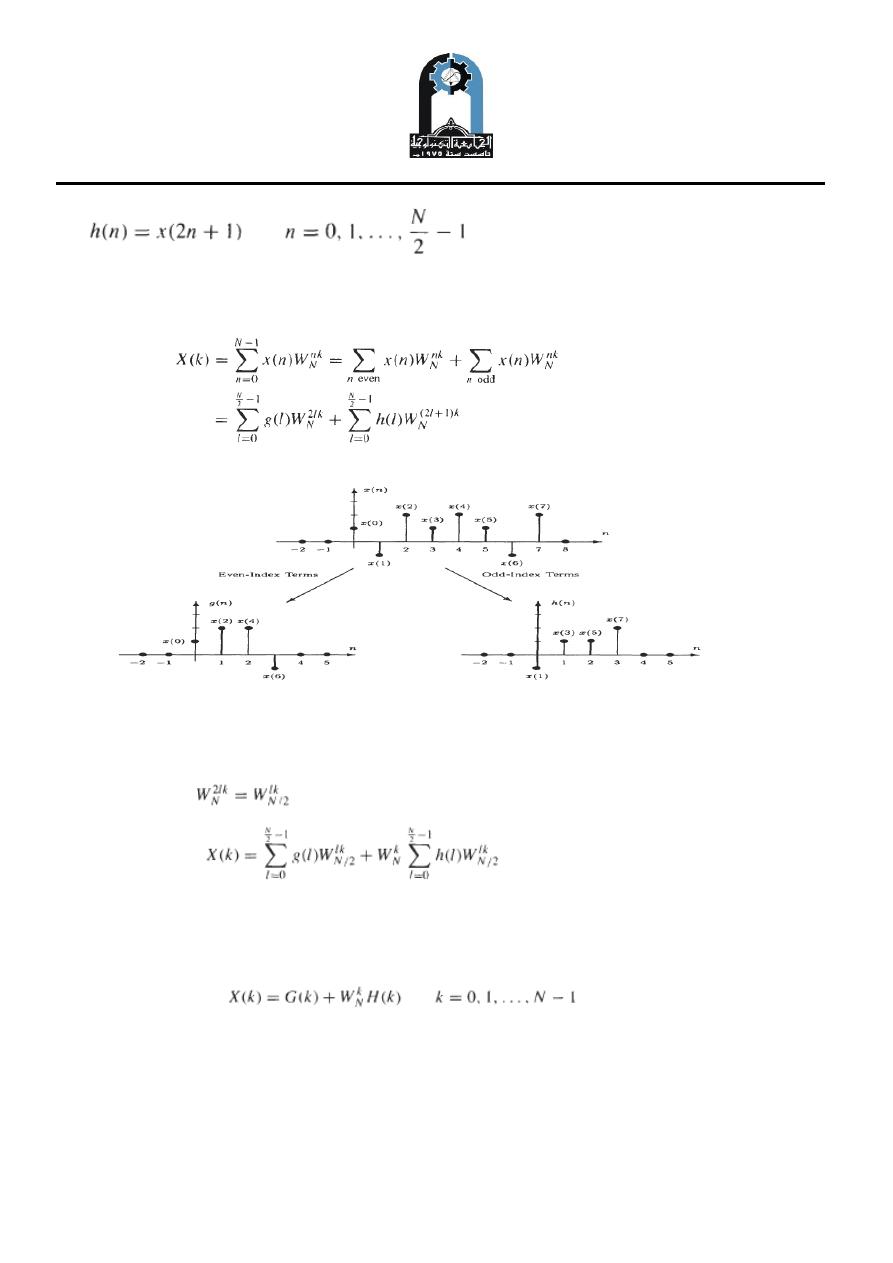
The decimation-in-time FFT algorithm is based on splitting (decimating) x(n) into
smaller sequences and finding X ( k ) of these decimated sequences.
Let x(n) be a sequence of length N =
, and suppose that x(n) is split (decimated)
into two subsequences, each of length N/2. As illustrated in Fig. (1), the first
sequence, g(n), is formed from the even-index terms,
and the second, h(n), is formed from the odd-index terms
Subjec: Signals and Systems
Lecture 9
Lecture: Dr.Manal Kadhim
Electromechanical Eng.Department
Electromechanical Systems Branch
Fourth Year.
2
In terms of these sequences, the N -point DFT of x(n) is
………………… ..
(3)
Figure (1): decimation the sequence of length N=8 by a factor of 2.
Because ,
Eq. ( 3 ) may be written as
(4)
Note that the first term is the N/2-point DFT of g(n), and the second is the N/2-point
DFT of h(n):
(5)
It can be seen that the DFT algorithm of Eq. (4) is composed of 2 DFTs of size N/2.
Figure (2) shows the flow graph for the computation of an elementary 2-point DFT
called a butterfly.
(2)
Subjec: Signals and Systems
Lecture 9
Lecture: Dr.Manal Kadhim
Electromechanical Eng.Department
Electromechanical Systems Branch
Fourth Year.
3
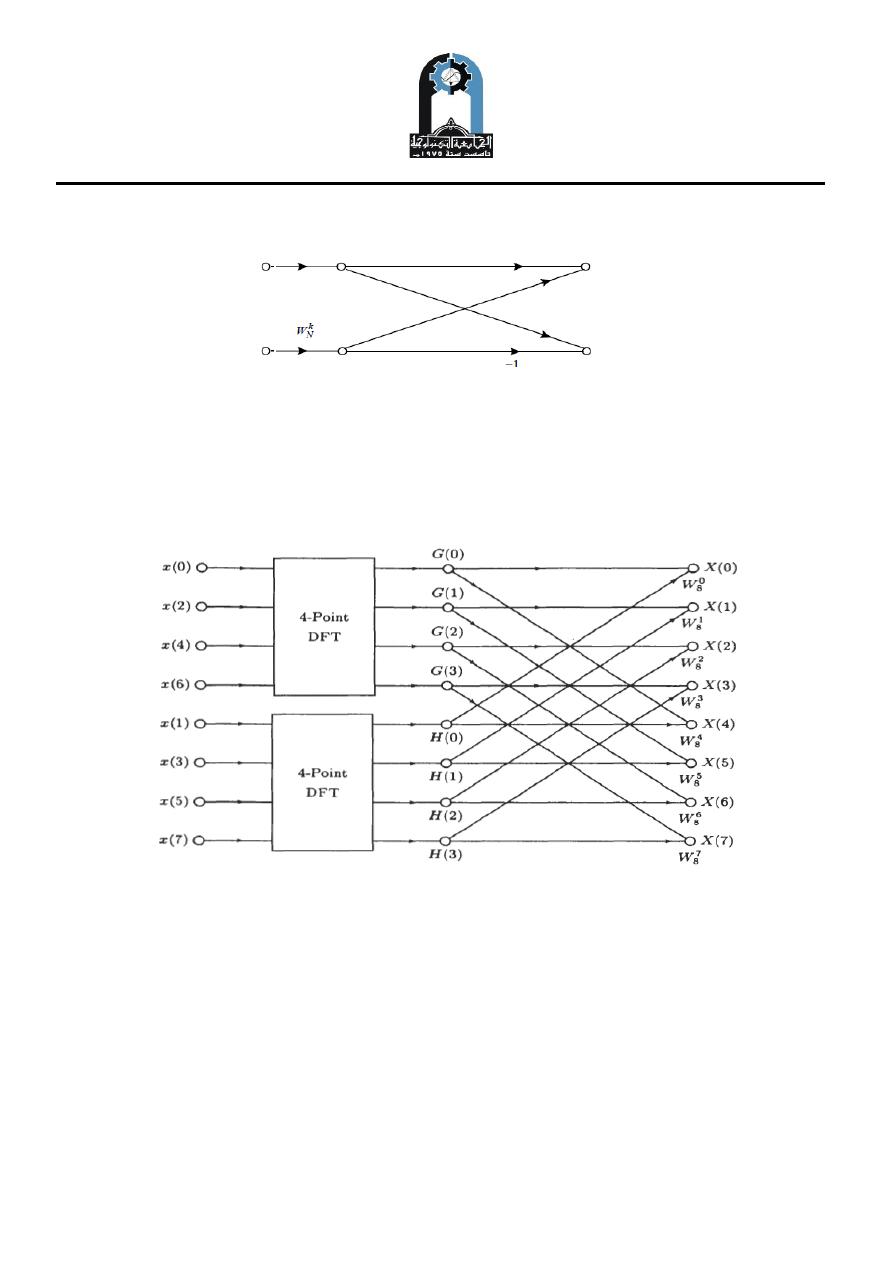
Figure (2):
2
-point DFT
A block diagram showing the computations that are necessary for the first stage of an
eight-point decimation-in-time FFT is shown in Fig. (3).
Fig. (3). An eight-point decimation-in-time FFT algorithm after the first decimation
where the first term is the N /4-point DFT of the even samples of g( n ) and the
second is the N/4-point DFT of the odd samples. A block diagram illustrating this
decomposition is shown in Fig. (4). If N is a power of 2, the decimation may be
continued until there are only two-point DFTs .
Subjec: Signals and Systems
Lecture 9
Lecture: Dr.Manal Kadhim
Electromechanical Eng.Department
Electromechanical Systems Branch
Fourth Year.
4
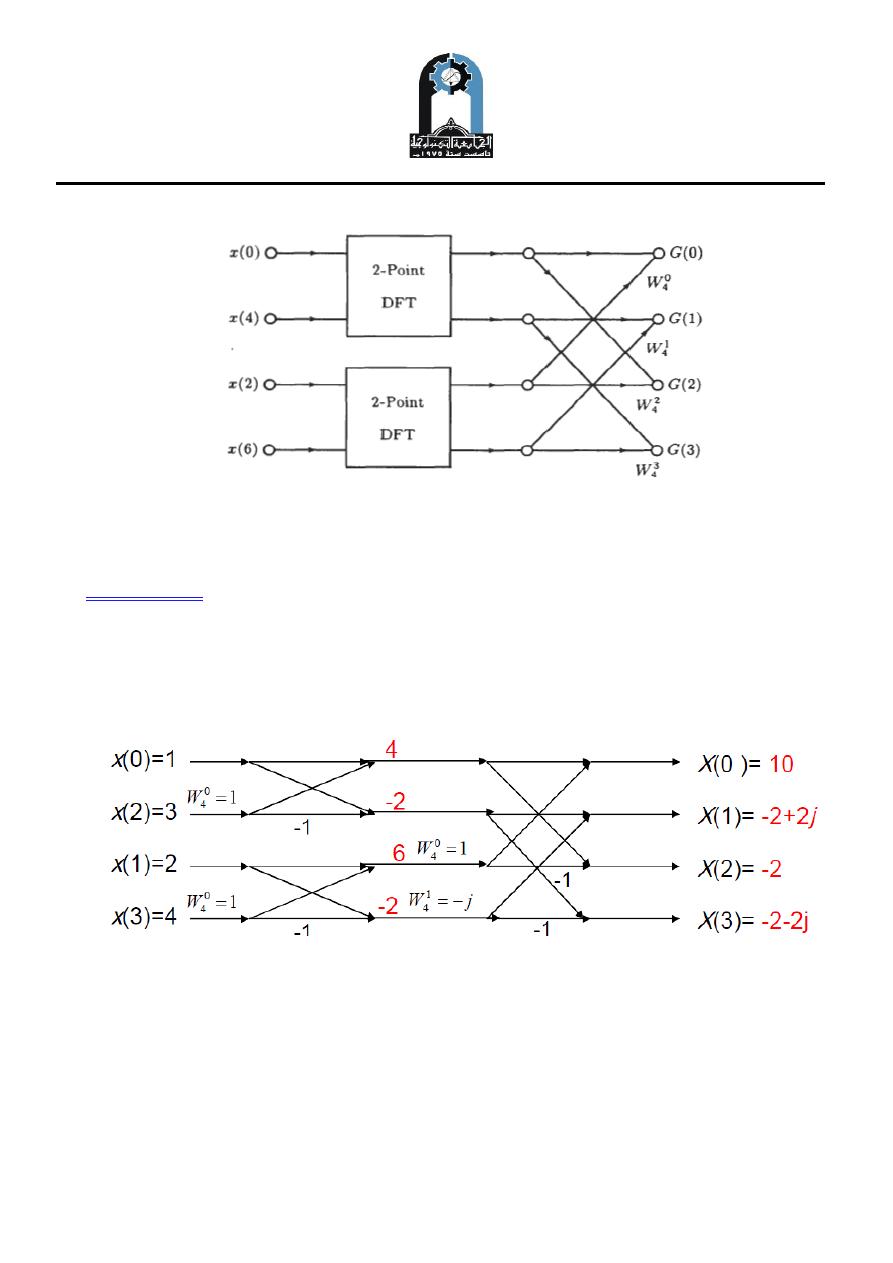
Fig. (4): Decimation of the four-point DFT into two two-point
DFTs in the decimation-in-time FFT.
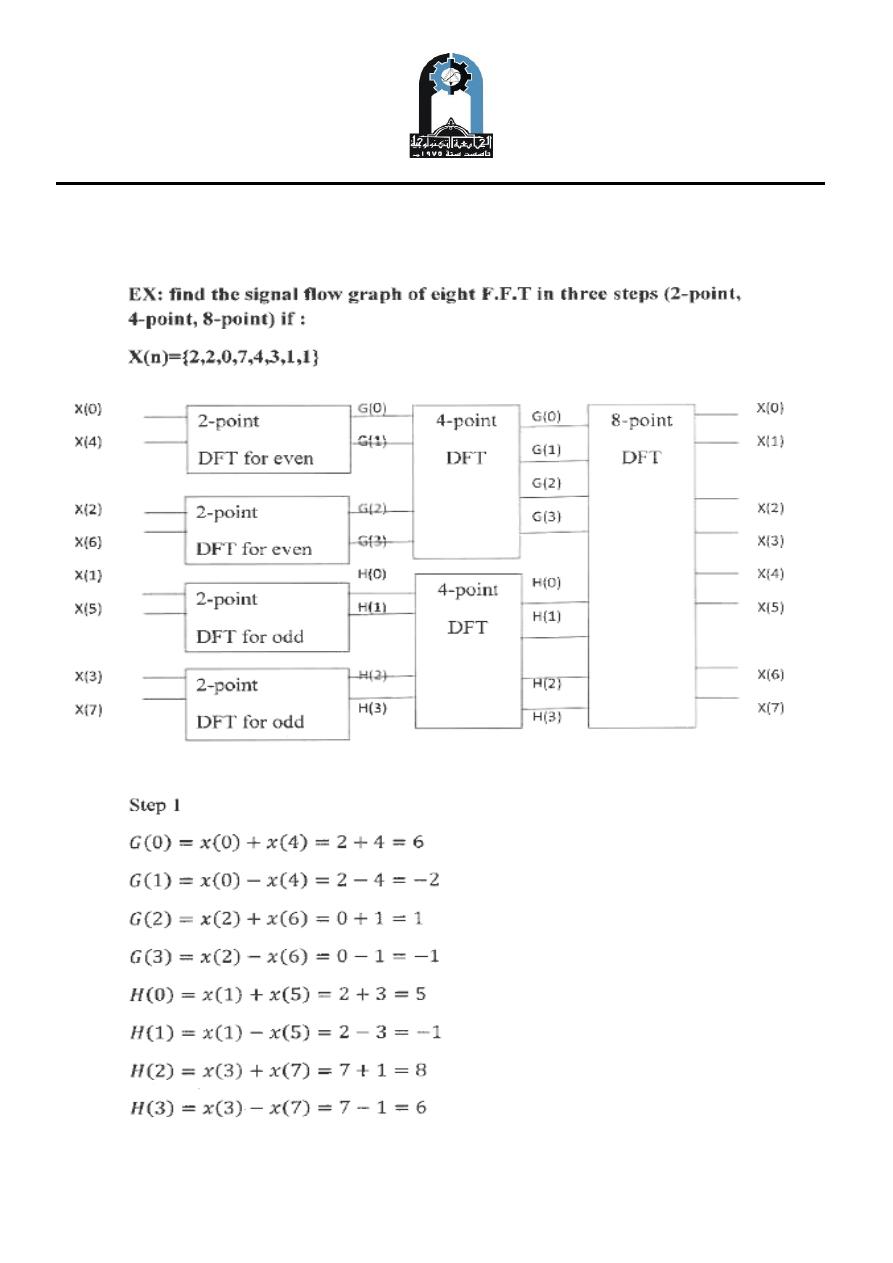
Example (1):
Given a sequence x(n) where x(0) = 1, x(1) = 2, x(2) = 3, x(3) = 4 and x(n) = 0
elsewhere ,find DFT for the first four points
Subjec: Signals and Systems
Lecture 9
Lecture: Dr.Manal Kadhim
Electromechanical Eng.Department
Electromechanical Systems Branch
Fourth Year.
5

Subjec: Signals and Systems
Lecture 9
Lecture: Dr.Manal Kadhim
Electromechanical Eng.Department
Electromechanical Systems Branch
Fourth Year.
6
Subjec: Signals and Systems
Lecture 9
Lecture: Dr.Manal Kadhim
Electromechanical Eng.Department
Electromechanical Systems Branch
Fourth Year.
7
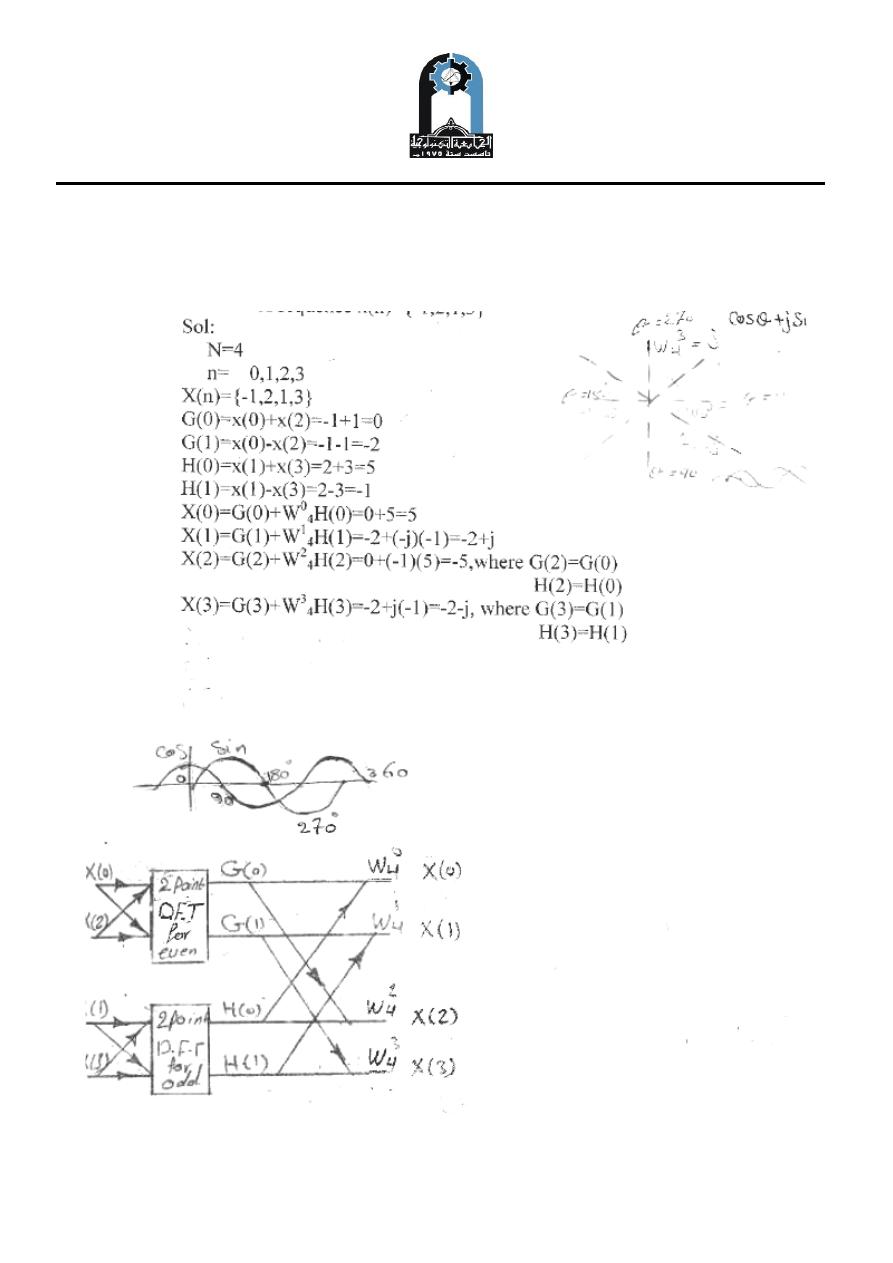
Draw the signal flowgragh of 4- point FFT and used it to find DFT of sequence
x[n]={-1,2,1.3}.
