Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
2
A
A
n
n
a
a
l
l
o
o
g
g
-
-
T
T
o
o
-
-
D
D
i
i
g
g
i
i
t
t
a
a
l
l
C
C
o
o
n
n
v
v
e
e
r
r
s
s
i
i
o
o
n
n
Most signals of practical such as speech, radar, sonar, and audio signals are
analog. To process analog signals by digital means it is first necessary to convert
them into digital form. That is, to convert them to a sequence of numbers having a
finite precision. This procedure is called analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion, and the
corresponding devices are called A/D convertors (ADCs).
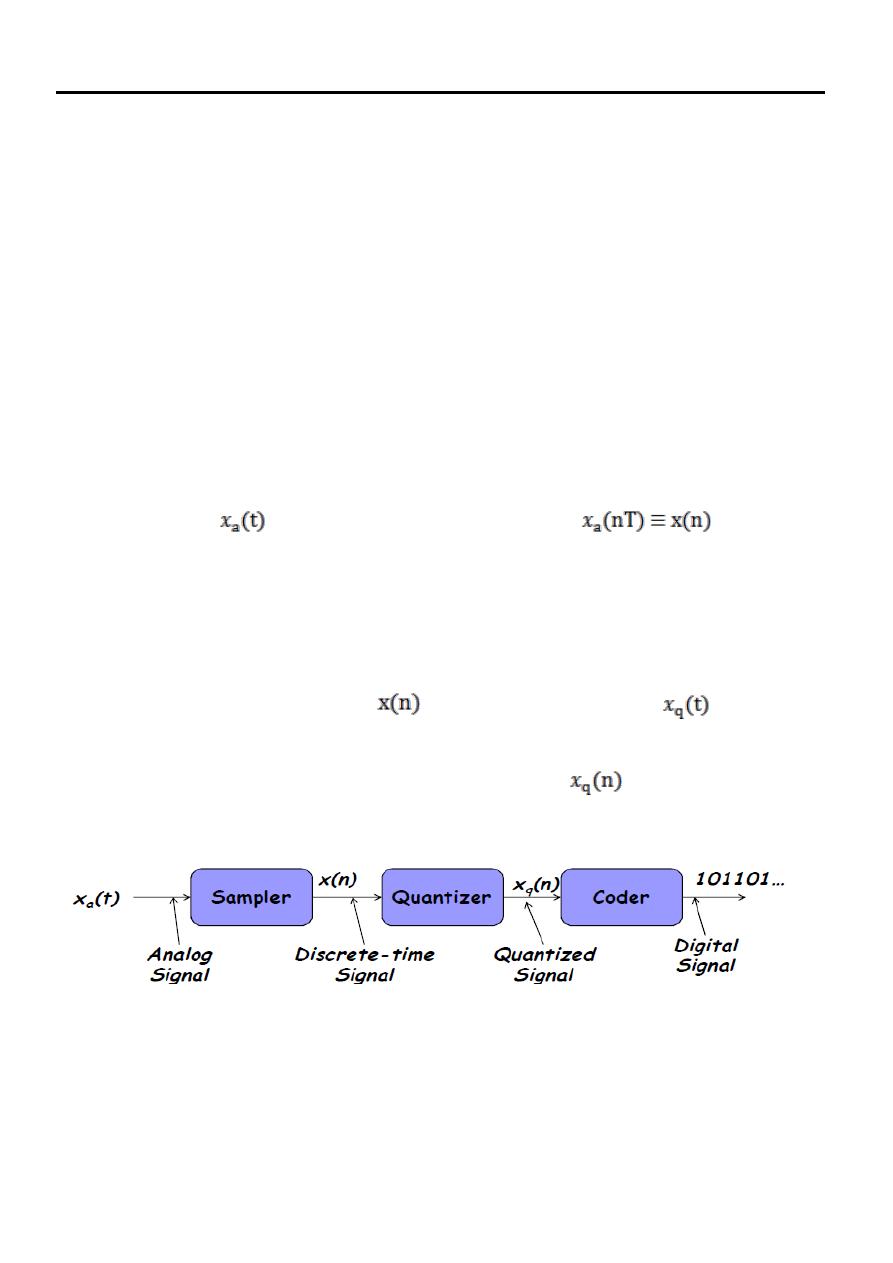
The analog to digital conversion can perform through three steps as shown in Fig.(1)
1. Sampler: - This is the conversion of a continuous-time signal into discrete-time
signal obtained by taking samples of the continuous-time signal at discrete-time
instant. Thus if
is input to the sampler, the output is
where T is
called the sampling interval.
2. Quantization: - This is the conversion of a discrete-time continuous-valued signal
into a discrete-time discrete-valued (digital) signal. The value of each signal sample
is represented by a value selected from a finite set of possible values. The difference
between the unquantized sample
and the quantized output
called the
quantization error.
3. Coding: - In the coding process, each discrete value of
is represented by a b-
bit binary sequence.
Figure (1): The basic parts of A/DC
Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
3
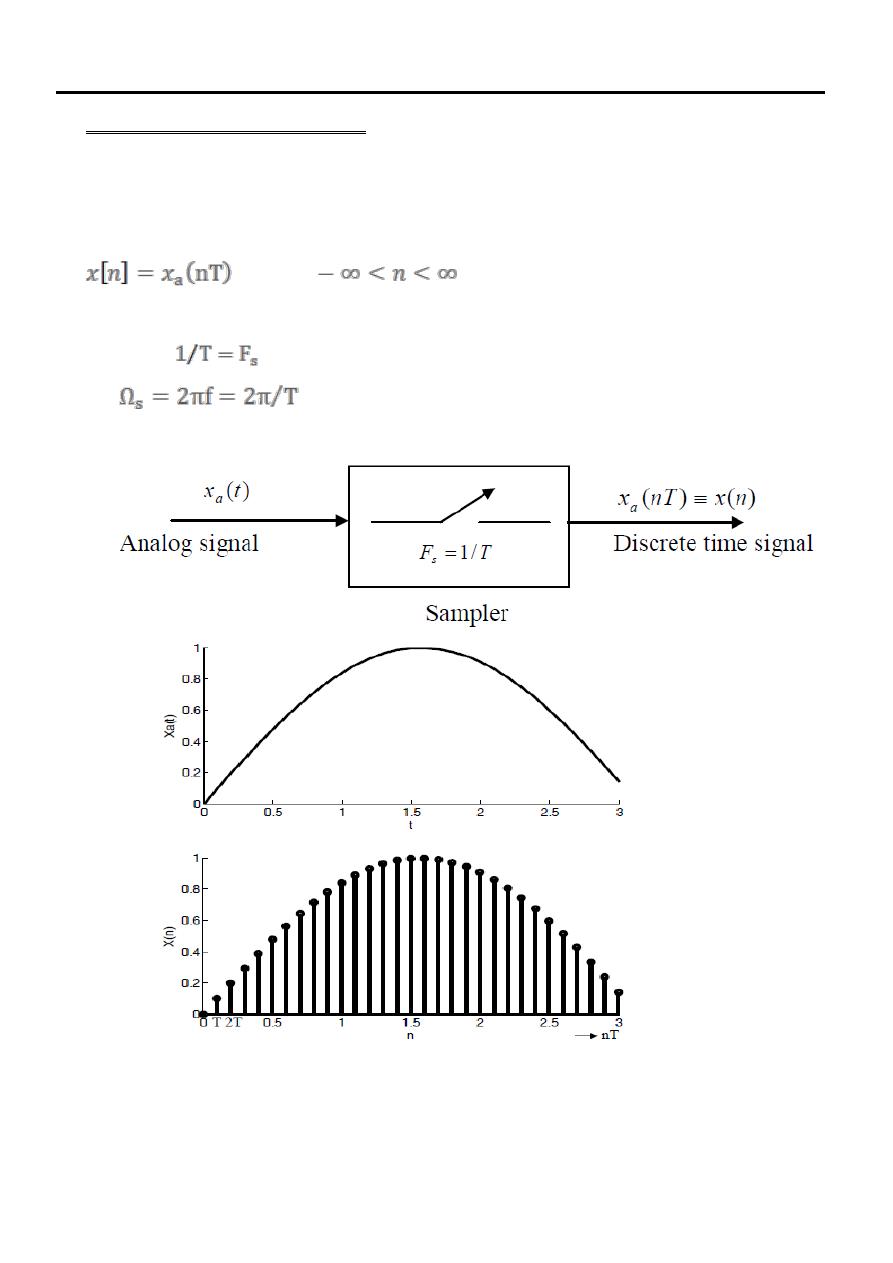
Sampling of analog signal
There are many ways to sample an analog signal. One of them is the periodic or
uniform sampling, which is the type of sampling used must often in practice. This is
described by the relation
Where x[n] is the discrete-time signal obtained, T is called sampling period. Its
reciprocal
is the sampling frequency. We also express sampling frequency
as
when we to use frequencies in radians per second
.
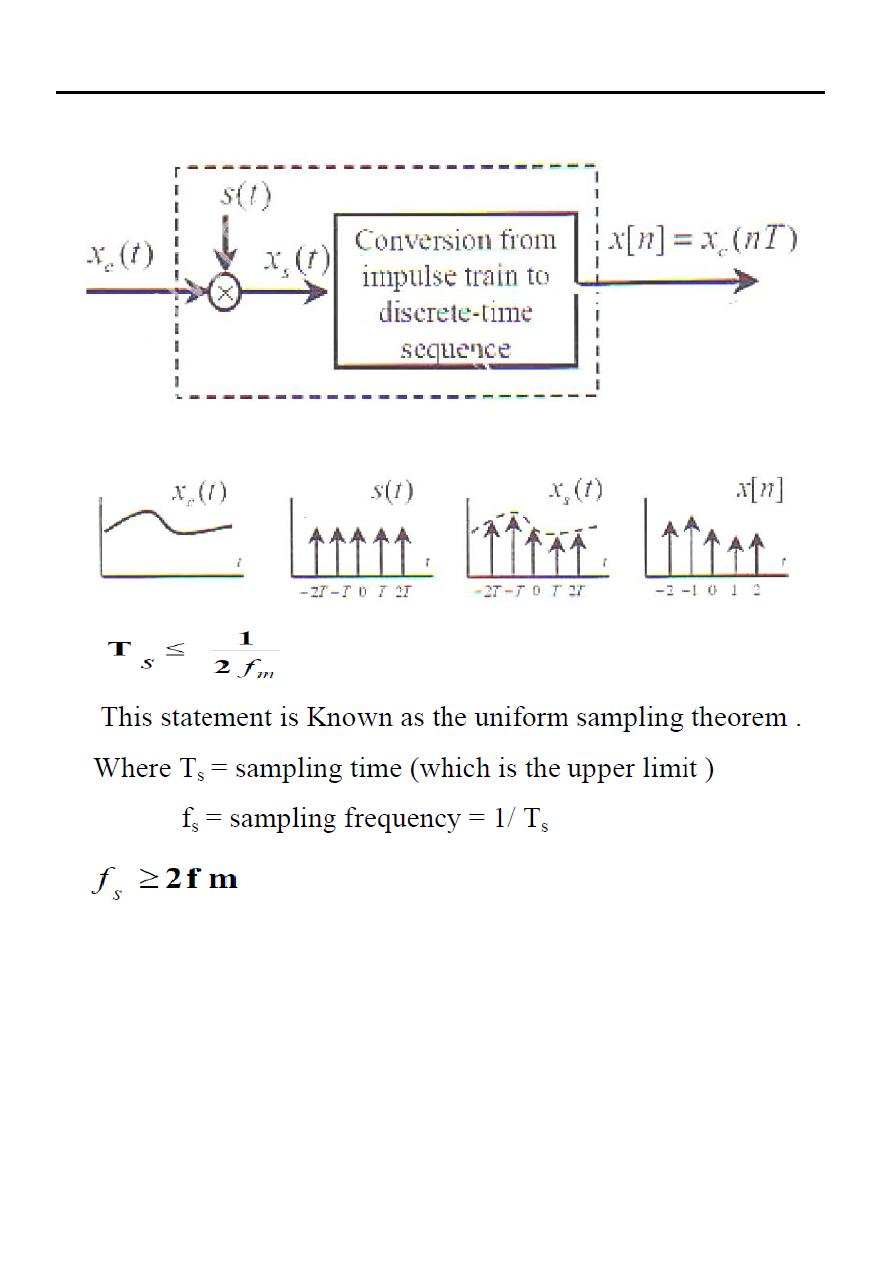
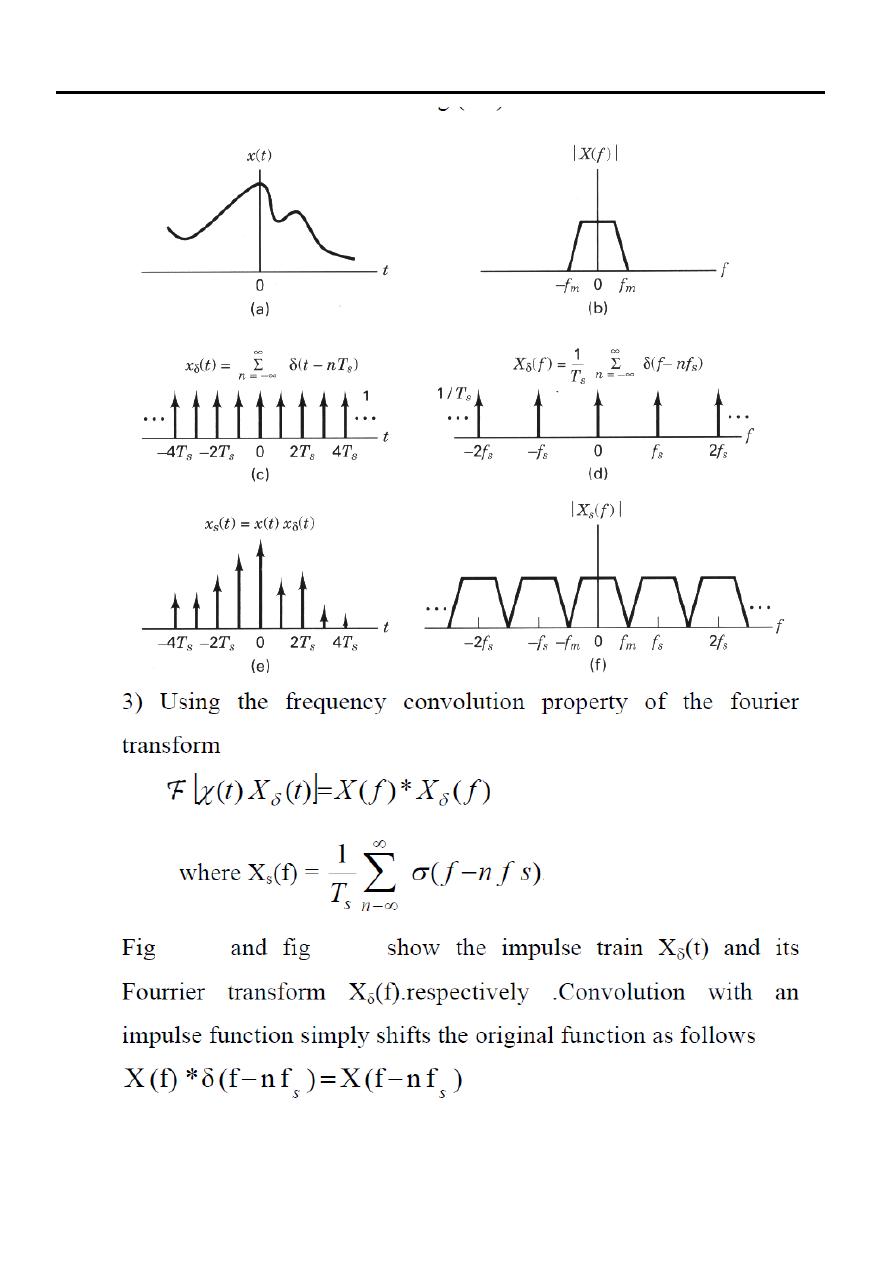
We use the following two stage mathematical representation of the sampling process.
Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
4

Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
5
1
1
1 (a)
1 (b)
1 (c)
Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
6
1 (c)
1 (d)
1

Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
7
1 (f)
1
2 (b)
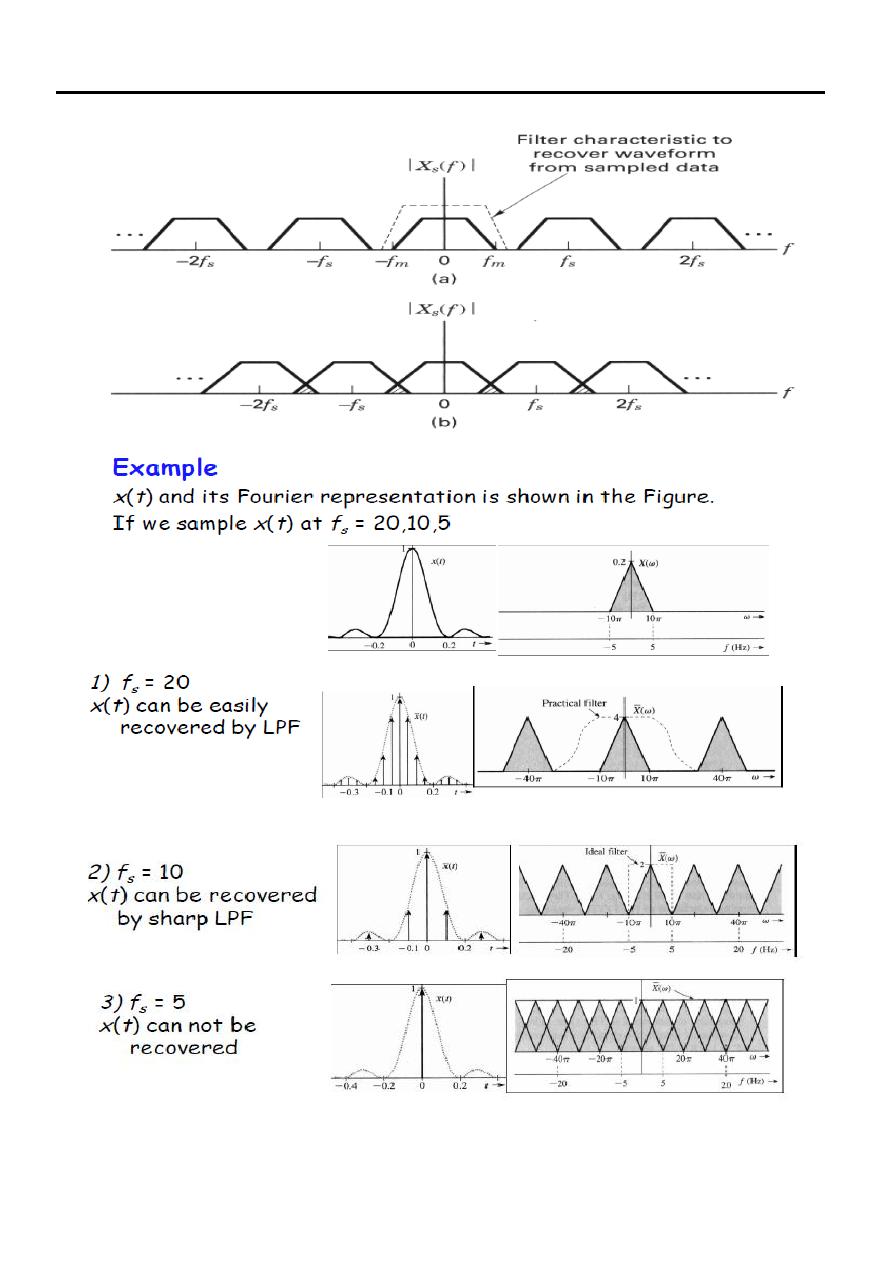
Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
8

Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
9
1

Signals & Systems Lecture Five
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
01
1
