ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٩
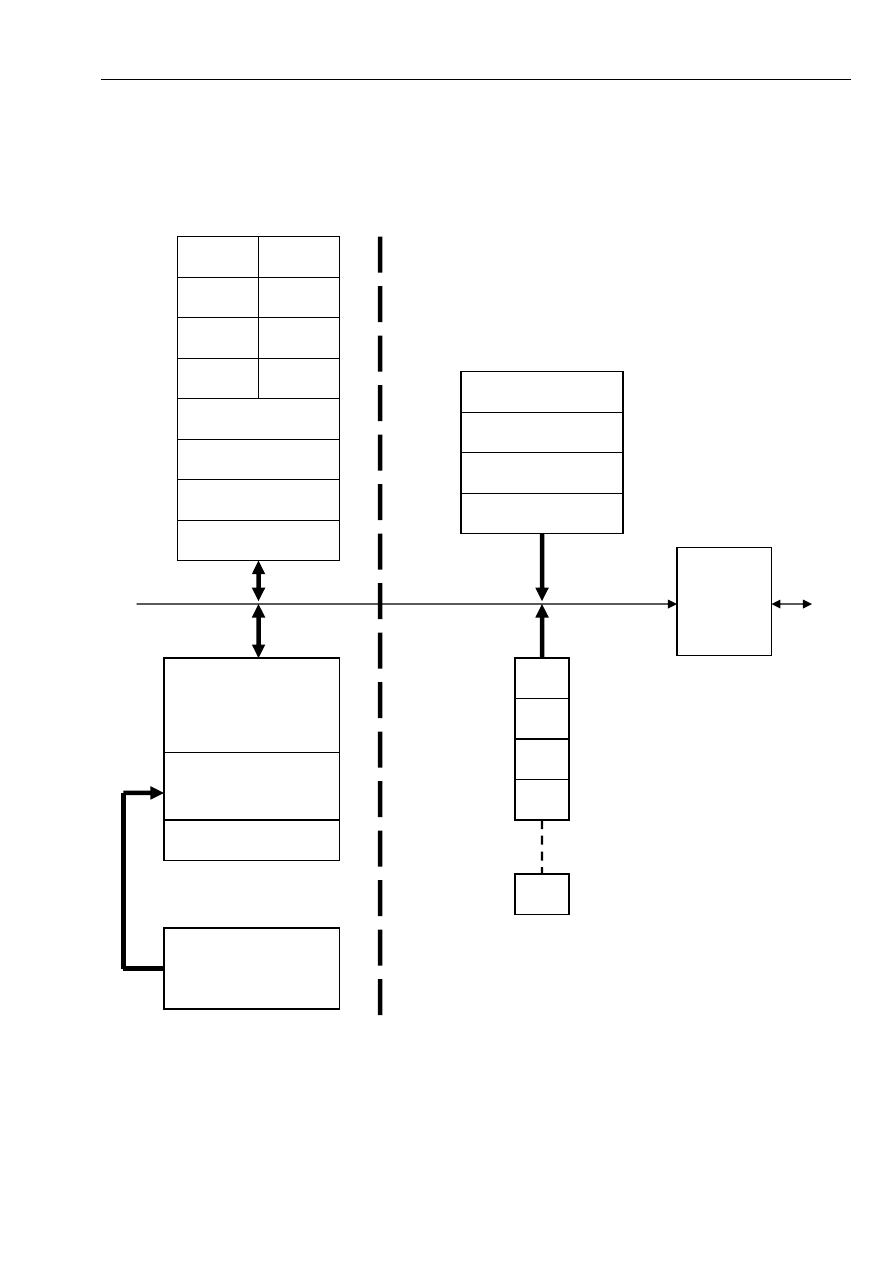
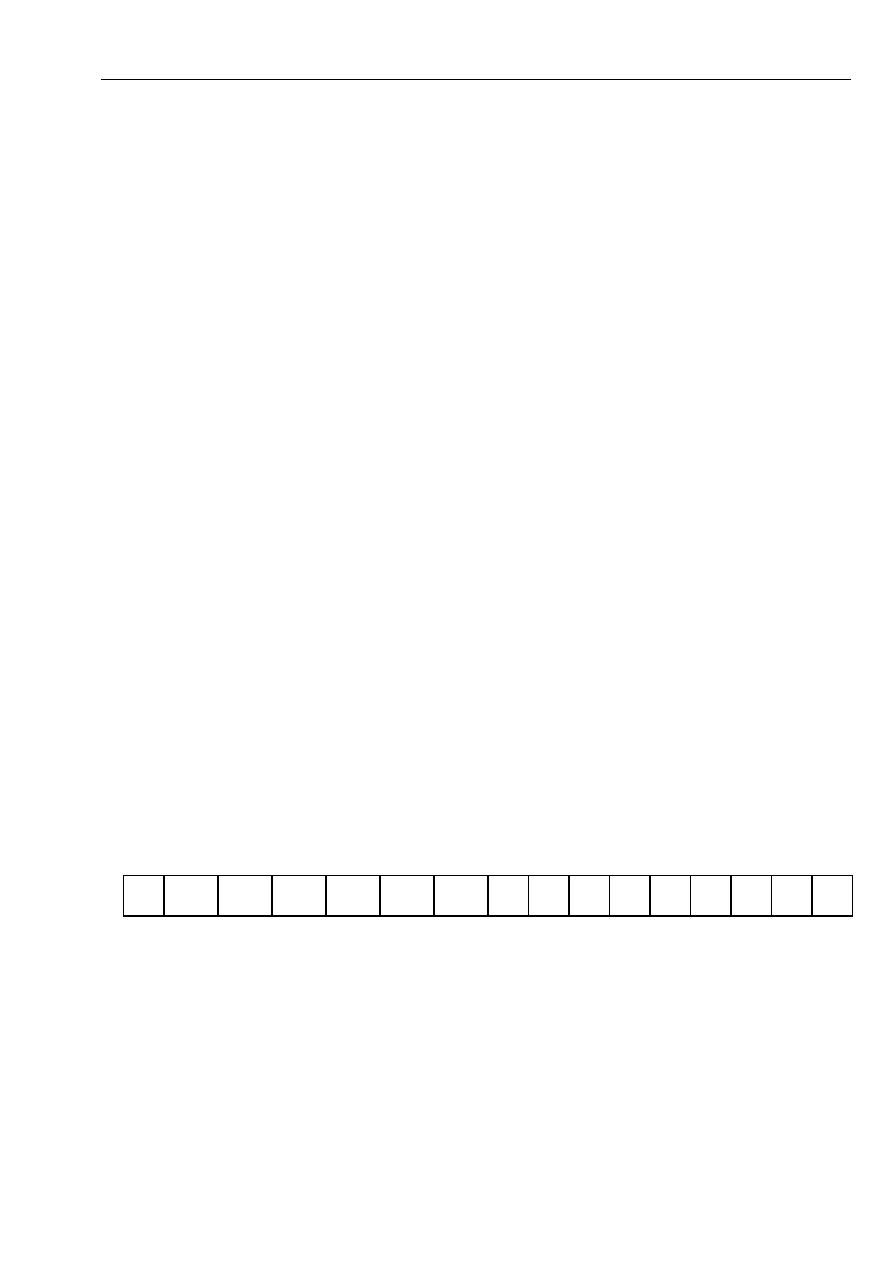
2.1 Processor Organization
We will consider the processor organization of 8086 processor, which can see it diagram in
Figure -1-
ﺴﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﻋﺘﻤﺎﺩ ﻫﻴﻜﻴﻠﺔ ﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
8086
ﻭﻜﻤﺎ ﻤﻭﻀﺢ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺭﺴﻡ
١
Fig -1- Execution Unit and Bus Interface Unit
8086 Processor Organization
AH
AL
BH
BL
CH
CL
DH
DL
SP
BP
SI
DI
CS
ES
SS
DS
ALU :
Arithmetic and
logic unit
CU:
Control unit
Flags Register
Instruction
Pointer
1
2
3
4
n
Bus
Control
Logic
Program control
Segment
Register
Bus
General
purpose
register
Pointer
Register
Index
Register
Instruction
Queue

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٠١
The organization of 8086 Processor is partitioned into two logical units
a. Bus Interface unit (BIU)
b. Execution Unit (EU)
ﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﻘﺴﻴﻡ ﻫﻴﻜﻴﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
8086
ﺍﻟﻰ ﻭﺤﺩﺘﻴﻥ ﻤﻨﻁﻘﺘﻴﻥ
ﻫﻤﺎ
:
ﺃ
.
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ
ﺏ
.
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ
2.1.a. Bus Interface Unit (BIU)
The role of the BIU delivers instructions and data to the EU. The most important function of the
BIU is to manage the Bus control unit which response of making synchronization between the
CPU and the Device is connected to it, by reading it specification. And the other function of the
Bus Control Unit is specify which device is connected when more than one device is request an
service from CPU at the same time with respect to priority specified from the designer or the
user.
ﺃ
.
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﺩﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻲ ﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﻫﻭ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻰ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ
.
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻭﻅﻴﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻴﺔ ﻫﻭ ﺘﻨﻅﻴﻡ
ـﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟ
Bus
ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼل ﻗﺭﺍﺀﺓ،ﻪﻌﻤ ﻁﻭﺒﺭﻤﻟﺍ ﺯﺎﻬﺠﻟﺍﻭ ﺞﻟﺎﻌﻤﻟﺍ ﻥﻴﺒ ﻥﻤﺍﺯﺘ لﻤﻋ ﻥﻋ ﺔﻟﺅﻭﺴﻤ ﻥﻭﻜﺘ ﻲﺘﻟﺍﻭ
ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺍﺼﻔﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺼﺔ ﺒﺎﻟﺠﻬﺎ
ﺯ
.
ـﻭﺍﻟﻭﻅﻴﻔﺔ ﺍﻻﺨﺭﻯ ﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟ
Bus
ﻫﻭ ﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﺍﻱ ﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﻴﺭﺘﺒﻁ ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﻴﻁﻠﺏ
ﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﻤﻥ ﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﺨﺩﻤﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻨﻔﺱ ﺍﻟﻭﻗﺕ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼل ﺍﻓﻀﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺘﺤﺩﺩ ﻤﻥ ﻗﺒل ﺍﻟﻤﺼﻤﻡ ﺍﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ
.
Another function of the BIU is to provide access to instructions. Because the instructions for a
program that is executing are in memory, the BIU must access instructions from memory and
place them in an instruction queue, which varies on size from 5 instructions to 7 instructions
depending on the processor. This feature enables the BIU to look ahead and prefetch
instructions so that there is always a queue of instructions ready to execute.
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻭﻅﻴﻔﺔ ﺍﻻﺨﺭﻯ ﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﻫﻭ ﻋﻤل ﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﻟﻼﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ
.
ﻭﺒﺴﺒﺏ ﺍﻥ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫﻩ ﻴﻜﻭﻥ
ﻭﺒﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﻴﺠﺏ ﺍﻥ ﺘﻘﻭﻡ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﺒﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻭﻭﻀﻌﻬﺎ ﻓﻲ ﻁﺎﺒﻭﺭ، ﺓﺭﻜﺍﺫﻟﺍ ﻲﻓ ﺩﻭﺠﻭﻤ
ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﺘﺭﻭﺍﺡ ﻁﻭﻟﻪ ﺒﻴﻥ
٥
ﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻰ
٧
ﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺒﺎﻻﻋﺘﻤﺎﺩ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
.
ﻭﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺼﻴﺔ ﺘﻤﻜﻥ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
١١
ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻤﻥ ﺘﺤﻀﻴﺭ ﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ
ﺠﺎﻫﺯﺓ ﻟﻠﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ
ﻭﻗﺩ ﺘﻡ ﺠﻠﺒﻬﺎ ﻤﺴﺒﻘﺎ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻭﺒﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﺘﻭﻓﻴﺭ ﻁﺎﺒﻭﺭ ﻤﻥ
ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﺎﻫﺯﺓ ﻟﻠﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ
.
Manage the segment register and controlling the process of addressing the memory is another
function of BIU. The segment register is considering the most important set of registers in 8086
CPU and we have four types of segments:
ﺘﻨﻅﻴﻡ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺯﺌﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﻋﻨﻭﻨﺔ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻫﻭ ﻭﻅﻴﻔﺔ ﺍﺨﺭﻯ ﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ
.
ﺘ
ﻌﺘﺒﺭ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺯﺌﺔ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻫﻡ ﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﻀﻤﻥ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
8086
ﻭﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺍﺭﺒﻌﺔ ﺍﻨﻭﺍﻉ ﻤﻥ
ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺯﺌﺔ
:
1. Code segment register
ﺸﺭﻴﺤﺔ ﻭﻤﺴﺠل ﺘﺠﺯﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ
2. Data segment register
ﺸﺭﻴﺤﺔ ﻭﻤﺴﺠل ﺘﺠﺯﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
3. Stack segment register
ﺸﺭﻴﺤﺔ ﻭﻤﺴﺠل ﺘﺠﺯﺌﺔ ﺍ
ﻟﻤﻜﺩﺱ
4. Extra segment register
ﺸﺭﻴﺤﺔ ﻭﻤﺴﺠل ﺘﺠﺯﺌﺔ
ﺍﻻﻀﺎﻓﻲ
Let us first define the segment as a special area defined in a program that begins on paragraph
boundary, that is, at a location evenly divisible by 16, or hex 10. Although a segment may be
located, almost anywhere in memory and in real mode (executing one program in one time) the
size of segment is 64 KB and the size of the space it takes in memory is equal to the space
required for the program execution. In addition, we note that there is another mode of operating
is called protected mode (executing more than one program in one time) which can process
working in it.
ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﻟﻨﻌﺭﻑ
ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ
ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻫﻭ ﻋﺒﺎﺭﺓ ﻋﻥ
ﻤﻨﻁﻘﺔ ﺨﺎﺼﺔ ﻤﻌﺭﻓﺔ ﻤﻥ ﻓﺒل ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺒﺩﺍ ﺒﻤﺎ ﻴﻌﺭﻑ ﺒﺎل
Paragraph boundary
ﻭﻫﻭﻋﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻴﻘﺒل ﺍﻟﻘﺴﻤﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ
16
ﺍﻭ
10
ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻨﻅﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺴﺎﺩﺱ ﺍﻟﻌﺸﺭﻱ
.
ﻭﻴﻤﻜﻥ

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٢١
ﺍﻴﻥ ﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻱ ﻤﻜﺎﻥ ﺒﺎﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻭﻓﻲ ﻨﻤﻁ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﻐﻴل ﺍﻟ
ﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
)
real mode
) (
ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﻨﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﻓﻲ ﻭﻗﺕ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﻓﺎﻥ
ﺤﺠﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺴﻴﻜﻭﻥ
64KB
ﻭﺴﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﺤﺠﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﺨﻭﺫ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ
Let us exam the four types of segment and begin with
1. Code segment
The code segment contains the machine instructions that are to execute. Typically, the first
execute instruction is at start of this segment, and the operating system links to that location to
begin program execution. As the name implies, the code segment (CS) register addresses the
code segment. If your code area requires more than 64KB, your program may need to define
more than one code segment.
ـﺍﻥ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟ
Code
ﻴﺤﺘﻭﻱ ﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻻﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺴﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫﻫﺎ
.
ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎ ﺍﻥ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫﻱ ﺍﻻﻭل ﺴﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﻓﻲ ﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ
ﻭﺴﻴﺭﺘﺒﻁ
ﻨﻅﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﻐﻴل ﻤﻊ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺯﻭﻥ ﺒﻪ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﺍﻻﻭل ﻟﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ
.
ﻭﺴﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﻫﻨﺎ
ﻙ
ﻤﺴﺠل ﺒﻨﻔﺱ ﺍﻻﺴﻡ
ﻴﺤﺘﻔﻅ ﺒﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ
.
ﻭﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ ﺤ
ﺠﻡ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﺍﻜﺒﺭ ﻤﻥ
64KB
ـﻓﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﻌﺭﻴﻑ ﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﻤﻥ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﻟﻠ
Code
.
2. Data Segment
The data segment contains a program's defined data, constants, and work areas. The data
segment (DS) register addresses the data segment. If your data area requires more than 64KB,
your program need to defines more than one data segment.
ﻤﻨﺎﻁﻕ ﺍﻟﻌﻤل، ﺕﺒﺍﻭﺜﻟﺍ ، ﺞﻤﺎﻨﺭﺒﻟﺍ لﺒﻗ ﻥﻤ ﺔﻓﺭﻌﻤﻟﺍ ﺕﺎﻨﺎﻴﺒﻟﺍ ﻰﻠﻋ ﺕﺎﻨﺎﻴﺒﻟﺍ ﻊﻁﻘﻤ ﻱﻭﺘﺤﻴ
.
ﻭﻴﻌﻨﻭﻥ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺨﺎﺹ ﻟﻬﺫﺍ
ﺍﻟﻐﺭﺽ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
.
ﻭﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﻴﺤﺘﺎﺝ ﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﻤﻥ
64KB
ﻓﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﻭﻟﻴﺩ ﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﻤﻥ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
.
3. Stack segment
In simple terms, the stack contains any data and addresses that you need to save temporarily
during an execute a subroutines related to the main program. The stack segment register
addresses the stack segment.
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺩﺱ،ﺔﻁﻴﺴﺒ ﺕﺎﻤﻠﻜﺒ
)
Stack
(
ﻴﺤﺘﻔﻅ
ﺒﺸﻜل ﻤﺅﻗﺕ ﺒﺎﻱ ﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﺍﻭ ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻨﻴﻥ ﻴﺤﺘﺎﺠﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻲ ﺍﺜﻨﺎﺀ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ
ﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻓﺭﻋﻲ ﻤﺭﺘﺒﻁ ﺒﻪ
.
ـﻭﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺨﺎﺹ ﻴﻌﻨﻭﻥ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟ
Stack
.

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٣١
Segment Boundaries
The segment is begin with an address called paragraph boundary which mean an address begin
with digit 0 from the right side of 5 digits address .Therefore, it will be choose an location with
address starting with zero digit. Because of the length of any segment is 64KB, which equal to
65536 locations and when convert to hexa after subtract one of the number the result, is
FFFFH.
ﻴﺒﺩﺍ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺒﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﻴﺴﻤﻰ
paragraph boundary
ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﻌﻨﻲ ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﻴﺒﺩﺍ ﺒﺭﻗﻡ ﺼﻔﺭ ﻤﻥ ﺠﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻴﻥ ﻟﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﻤﻥ
ﻭﺒﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﻓﺎﻨﻪ ﺴﻴﺨﺘﺎﺭ ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﻴﺒﺩﺍﺀ ﺒﺎﻟﺭﻗﻡ ﺼﻔﺭ، ﻡﺎﻗﺭﺍ ﺔﺴﻤﺨ
.
ﻭﺒﺴﺒﺏ ﺍﻥ ﺤﺠﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﻫﻭ
64KB
ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﺴﺎﻭﻱ
٦٣٥٥٦
ﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﻭﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﺘﺤﻭل ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻨﻅﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺴﺎﺩﺱ ﻋﺸﺭﻱ ﻤﻁﺭﻭ
ﺡ ﻤﻨﻬﺎ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ
ﻓﺎﻥ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺘﺞ ﻤﺴﺎﻭﻱ ﺍﻟﻰ
FFFFH
.
The segment begins with address 0000H to FFFFH as the offset inside the segment. Therefore,
we will use a set of register to locate the staring address of segment and can define as:
A segment register is 16 bits long and provides for addressing an area of memory known as the
current segment, to reduce the complexity of processor register it store 4 digits instead of 5
digits and insert 0 digit from right of the address of segment register.
ﻴﺒﺩﺍ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺒﺎﻟﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ
0000H
ﺍ
ﻟﻰ
FFFFH
ﻭﻜﻤﺎﻓﺔ ﺍﺯﺍﺤﺔ ﺩﺍﺨل ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ
.
ﻭﺒﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﺴﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺤﺘﻔﻅ ﺒﻌﻨﻭﺍﻨﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﻘﺎﻁﻊ ﻭﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺘﻌﺭﻴﻑ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ
:
ﺒﺎﻨﻪ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺒﻁﻭل
16bit
ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩ ﻟﻌﻨﻭﻨﺔ ﻤﺴﺎﺤﺔ
ﻭﻤﻥ ﺍﺠل ﺘﻘﻠﻴل ﺘﻌﻘﻴﺩ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻓﺎﻨﻪ ﻴﺨ، ﻲﻟﺎﺤﻟﺍ ﻊﻁﻘﻤﻟﺍ ﻰﻤﺴﺘ ﺓﺭﻜﺍﺫﻟﺍ ﻥﻤ
ﺯﻥ ﺍﺭﺒﻌﺔ ﺍﺭﻗﺎﻡ ﺒﺩﻻ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻤﺴﺔ ﻤﻊ ﺍﻀﺎﻓﺔ
ﺼﻔﺭ ﻤﻥ ﺠﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻴﻥ ﻋﻨﺩ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺠﻭﺩﺓ ﻀﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل
.
Let ' take an overview about segment registers:
ﻟﻨﻠﻘﻲ ﻨﻅﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻨﻭﺍﻉ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ
1. Code Segment register (CS): contains the starting address of a program's code segment. For
normal programming purpose, you need not reference the CS register.
ﻤﺴﺠل ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻭﻫﻭ ﻴﺤﻭﻱ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ
.
ﻭﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻤﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﺩﻴﺔ ﻻﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻰ ﻫﺫﺍ
ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل
.

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٤١
2. Data Segment register (DS): contains the starting address of a program data segment.
Instructions use this address to locate data.
ﻤﺴﺠل ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﻭﻫﻭ ﻴﺤﻭﻱ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﻟﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﻤﻭﻗﻊ
ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
.
3. Stack Segment register (SS) Permits the implementation of a stack in memory, which a
program uses for temporary storage of address of a program's stack segment in the SS register.
For normal programming purpose, you need not directly reference the SS register.
ﻤﺴﺠل ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺩﺱ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﺴﻤﺢ ﺒﺎﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺩﺱ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ
ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻤﻥ ﻗﺒل ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻟﻠﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺅﻗﺕ ﻭﻫﻭ
ﻴﺤﺘﻔﻅ ﺒﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺩﺱ
.
ﻭﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻤﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﺩﻴﺔ ﻻﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻰ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل
.
4. Extra Segment register (ES): used by some string (character data) operations to handle
memory addressing. The ES (Extra segment) register is associated with DI (index register).
A program that requires the use of the ES may initialize with an appropriate segment address.
ﻤﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻻﻀﺎﻓﻲ ﻭﻫﻭ ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻤﻊ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺴﻼﺴل ﺍﻟﺤﺭﻓﻴﺔ ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻨﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ
.
ﻭﺘﺭﺘﺒﻁ ﻤﺴﺠل
ES
ﻤﻊ ﻤ
ﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﻔﻬﺭﺴﺔ
DI
.
ﻭﻫﻲ ﺘﻭﻟﺩ ﺍﻥ ﺍﺤﺘﺎﺝ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﺴﻼﺴل ﺍﻟﺤﺭﻓﻴﺔ
.
5. FS AND GS registers Additional extra segment registers on the 80386 and later processors.
Management OF Generated Segments
ﺘﻨﻅﻴﻡ ﺘﻭﻟﻴﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﻁﻊ
Example: Find the configuration of segments generated by two programs , first Program A deal
with arithmetic operations and has 800KB in its programming section and 600KB in its data
sections and 900 KB in stack sections while second Program B has 1048 KB code and 660KB
data and 2066 KB as stack memory. And Find the total number of segments generated.
ﺠﺩ ﻜﻴﻑ ﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﻨﻅﻴﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﻟﺩﺓ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼل ﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺠﻴﻥ ﺍﻻﻭل ﻴﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻊ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﻭﻴﻤﺘﻠﻙ
800KB
ﻓﻲ ﺠﺯﺀ
ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻤﺠﺔ ﻭ
600KB
ﻟﺠﺯﺀ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﻭ
900KB
ﻟﺠﺯﺀ
Stack
ﺒﻴﻨﻤﺎ ﻴﻤﺘﻠﻙ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻨﻲ
1048
ـﻜ
Code
ﻭ
660KB
ـﻜ
Data
ﻭ
2066KB
ٍ ـﻜ
Stack
.
ﻭﺠﺩ ﻋﺩﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﻜﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤ
ﺘﻭﻟﺩﺓ ﻤﻥ ﻗﺒل ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺠﻴﻥ
.

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٥١
Sol
The default size of any 64 KB and we have three types of segments
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﺤﺠﻡ ﺍﻻﺼﻠﻲ ﻟﻠﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﻫﻭ
64KB
ﻭﻟﺩﻴﻨﺎ ﺜﻼﺜﺔ ﺍﻨﻭﺍﻉ
Code segment , Data segment , Stack segment
Therefore the Program A has these segments
Number of segments = size of section / size of one segment
No. of code segments = 800KB / 64 KB= 12.5 =13 segments
No. of data segments = 600KB / 64 KB= 9.375 =10 segments
No. of stack segments = 900KB / 64 KB= 14.0625 =15 segments
And for Program B has these segments
No. of code segments = 1048KB / 64 KB= 16.375 =17 segments
No. of data segments = 660KB / 64 KB= 10.3125 =11 segments
No. of stack segments = 2066KB / 64 KB= 32.28125 =33 segments
2.1.b. Execution Unit (EU)
The role of the EU is to execute instructions, whereas the BIU delivers instructions and data to
the EU. The EU contains an arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), a control unit (CU), and a number
of registers. These features provide for execution of instruction and arithmetic and logical
operations.
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻬﺩﻑ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴ
ﻭﺤﻴﺙ ﺍﻥ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺘﻘﻭﻡ ﺒﺠﻠﺏ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ، ﺕﺍﺯﺎﻌﻴﻻﺍ ﺫﻴﻔﻨﺘ ﻭﻫ ﺫﻴﻔﻨﺘﻟﺍ ﺓﺩﺤﻭ ﻥﻤ ﻲﺴ
ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻰ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ
.
، ﻭﺘﺤﺘﻭﻱ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺏ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻨﻁﻕ ﻭﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻭﻋﺩﺩ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
ﻭﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﻭﻨﺎﺕ ﺘﻭﻓﺭ ﺍﻤﻜﺎﻨﻴﺔ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻤ
ﻨﻁﻘﻴﺔ
.
We can classify the components of EU to :
1. Pointers Registers
ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﺸﻴﺭ
The Three pointer registers are the IP, SP, and BP.
ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺜﻼﺜﺔ ﺍﻨﻭﺍﻉ ﻤﻥ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﺸﻴﺭ ﻭﻫﻲ
IP,SP,BP
.

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٦١
Instruction Pointer (IP) register
The 16-bit IP register contains the offset address of the next instruction that is to execute. The
IP is associated with CS register in that The IP indicates the current instruction within the
currently executing code segment. You do not normally reference the IP register in program,
but you can change its value when using the DEBUG program to test a program. The 80386
and later processors have an extended 32-bit IP called the EIP.
ﻴﺤﺘﻭﻱ ﻤﺴﺠل
IP 16-bit
ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺍﻻﺯﺍﺤﺔ ﻟﻼﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ
ﻭﺒﺎﺭﺘﺒﺎﻁ ﻤﺴﺠل،
IP
ﻤﻊ ﻤﺴﺠل
CS
ﺤﻴﺙ ﻴﺘﻭﻟﺩ
ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻲ ﻀﻤﻥ ﻤﻘﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﻨﻔﺫ ﺤﺎﻟﻴﺎ
.
ﻭﻻﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻜﻡ ﺒﻘﻴﻤﺔ ﻤﺴﺠل
IP
ﺒﺸﻜل ﺍﻋﺘﻴﺎﺩﻱ ﻤﻥ ﻗﺒل
،ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ
ﻭﻟﻜﻥ ﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺘﻐﻴﻴﺭ ﻗﻴﻤﺘﻪ ﻓﻲ ﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﺴﺘﺨﺩ
ﺍﻡ ﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ
DEBUG
ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﻘﻭﻡ ﺒﺘﺩﻗﻴﻕ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻻﺨﻁﺎﺀ ﺤﻴﺙ
ﻴﻤﻜﻨﻨﺎ ﻤﻥ ﺠﻌل ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻴﻨﻔﺫ ﺨﻁﻭﺓ ﺨﻁﻭﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺤﻜﻡ ﺒﺎﻟﻤﺴﺠل
IP
.
ﻭﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ
80386
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺒﻌﺩﻫﺎ ﺘﺤﺘﻭﻱ ﻋﻠﻰ
ﻤﺴﺠل ﻤﻭﺴﻊ ﺒﻁﻭل
32-bit
ﻭﻴﺴﻤﻰ
EIP
.
Stack Pointer (SP) register
The 16-bit SP register provides an offset value, which when associated with the SS register,
refers to the current word being processed in the stack. The 80386 and later processors have an
extended 32-bit stack pointer, the ESP register. The system automatically handles these
registers.
ﻴﻘﺩﻡ ﻤﺴﺠل
16 – bit SP
ﺍﻻﺯﺍﺤﺔ
ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺭﺒﻁ ﻤﻊ ﻤﺴﺠل
SS
ﻟﺘﻌﻨﻭﻥ ﺍﻟﻜﻠﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺠﻭﺩﺓ ﻓﻲ
stack
.
ﺘﻤﺘﻠﻙ ﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ
80386
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺒﻌﺩﻫﺎ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺏ
32
ﺒﺕ ﺍﻱ ﻤﺴﺠل ﻤﻭﺴﻊ ﻤﻥ ﻨﻭﻋﻴﺔ
stack pointer
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺭﻭﻑ
ESP
.
ﻭﺍﻟﻨﻅﺎﻡ
ﺍﻟﻴﺎ ﻴﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻊ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
.
Base Pointer (BP) register
The 16 – bit BP facilitates referencing parameters, which are data and addresses that a program
passes via the stack. The processor combines the address in the SS with the offset in the BP.
The 80386 and later processors have an extended 32-bit BP called the EBP register

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٧١
ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻤﺴﺠل
BP
ﺫﻭ
16 bit
ﻭﻫﻲ ﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻨﻭﺍﻨﻴﻥ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺭﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻰ،ﺕﻼﻤﺎﻌﻤﻟﺍ ﺭﺸﺅﻴ
stack
.
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
ﻴﺠﻤﻊ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل
SS
ﻤﻊ ﺍﻻﺯﺍﺤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺠﻭﺩ ﻓﻲ
BP
.
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ
80386
ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺒﻌﺩﻫﺎ ﺘﻤﺘﻠﻙ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺴﻊ
ﻤﻥ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل ﺫﻭ
32
ﺒﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺴﻤﻰ
EBP
.
2.Addressing Using Pointer Registers and Segment Registers
We have rules for determine the final address of information founded in Memory and we have
four different kinds of as:
1. Final address for CODE: value in CS with digit 0 from right + IP
1. Final address for DATA: value in DS with digit 0 from right + Address in the instruction
1. Final address for WORD in Stack: value in SS with digit 0 from right + SP
1. Final address for PARAMETER in Stack: value in SS with digit 0 from right + BP
EX1 Find the final address for these information's:
1. CODE if you know that CS=1FE4 and IP=BB6A
2. DATA if you know that DS=55862
10
and the address in the instruction is 4237
8
3. WORD in Stack if you know that SS=110110111100110
2
and SP=5678
16
and found the Final
address for PARAMETER if BP=36985
10
.
SOL:
1. Final address for CODE: CS0 + IP
1FE40
+ BB6A
2B9AA
2. Final address for Data : DS0+Address in the instruction
The DS is in the decimal system and we must convert it to the hexadecimal as fllow
16 55862
16 3491 6
16 218 3
16 13 A
16 0 D

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٨١
Therefore the value of DS=DA36
And the of the address in the instruction is in Octal and we must converted into Hexadecimal
4 2 3 7
100 010 011 111
8 9 F
Therefore, the value of address in the instruction is 089F
And the final of address of Data is:
DA360
+ 089F
DABFF
3. Final address of WORD in the Stack: SS0 + SP
The value of SS in the binary Form and we must converted into Hexadecimal form
0110110111100110
6 D E 6
Therefore, the value of SS=6DE6
6DE60
+ 5678
734D8
And final address for PARAMETER is SS0+BP
BP= 36985
10
9079
16
6DE60
+ 9079
76ED9
ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٩١
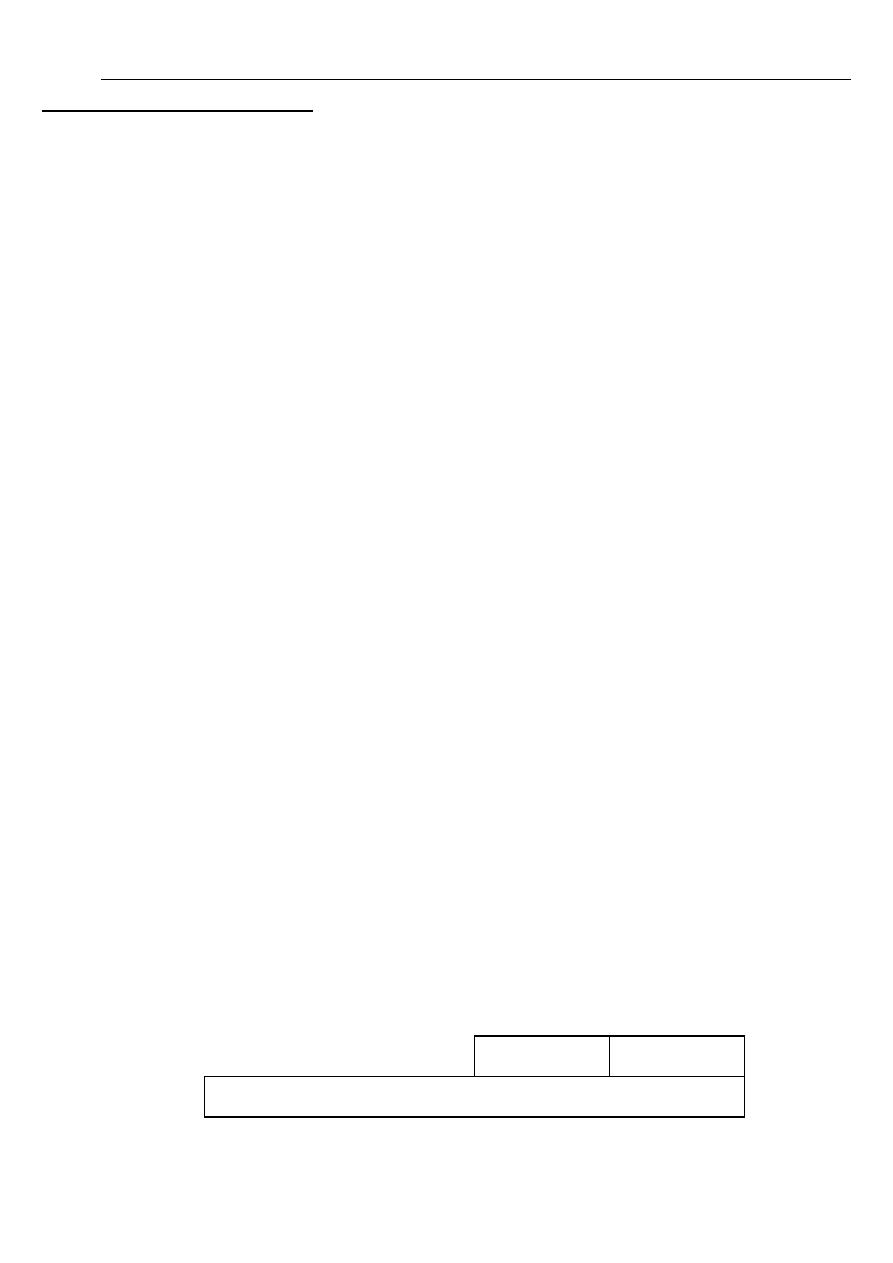
3.General – Purpose Registers
The AX, BX, CX and DX general – purpose registers are the workhorses of the system. They
are unique in that you can address them as one word or as a 1- byte portion. The leftmost byte is
the "high" portion and the rightmost byte is the "low" portion. For example, the AX register
consists of an AH (high) and an AL (low) portion, and you can reference any portion by its
name. The 80386 and later processors support all the general – purpose registers, plus 32-bit
extended versions of them: the EAX, EBX, ECX, and EDX.
ﺘﻌﺘﺒﺭ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
AX, BX, CX and DX
ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻻﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻤﺔ ﻭﻤﻨﺎﻁﻕ ﺍﻟﻌﻤل ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻨﻅﺎﻡ
.
ﻭﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
ﺍﻟﻭﺤﻴﺩﺓ ﻀﻤﻥ ﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
8086
ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺍﻥ ﺘﻘﺴﻡ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺠﺯﺌﻴﻥ ﻜل ﻤﻨﻬﺎ ﺒﺤﺠﻡ ﺒﺎﻴﺕ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﻭﻴﺴﻤﻰ ﺍﻟﺠﺯﺀ
ـﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻴﺴﺎﺭ ﺒﺎﻟ
high
ﻭﺍﻟﺠﺯﺀ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻴﻥ ﺒﺎل
low
.
ﻭﻟﻭ ﺍﺨﺫﻨﺎ ﻤﺴﺠل
AX
ﻜﻤﺜﺎل ﻓﺎﻨﻪ ﻴﺘﻜﻭﻥ ﻤﻥ
AH(high)
ﻭﺠﺯﺀ
ﺍﺨﺭ ﻫﻭ
AL(low)
ﻭﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻱ ﺠﺯﺀ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼل ﺍﺴﻤﻪ
.
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌ
ﺎﻟ
ﺞ
80386
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺒﻌﺩﻫﺎ ﺘﺩﻋﻡ ﻜل ﺍﻨﻭﺍﻉ
ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻻﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻡ ﺍﻀﺎﻓﺔ ﻨﺴﺦ
32-bit
ﺍﻟﻤ
ﻭﺴﻌﺔ ﻤﻥ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﻭﻫﻲ
EAX, EBX, ECX, and EDX
.
The following assembler instructions move zeros to the AX, BH, and ECX registers,
respectively:
ﻭﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻴﺴﻤﺒﻠﻲ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﺘﻨﻘل ﺍﻟﺼﻔﺭ ﺍﻟﻰ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
AX, BH, and ECX
ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻭﺍﻟﻲ
MOV AX,00
MOV BH,00
MOV ECX,00
AX register
The AX register, the primary accumulator, is used for operations involving input / output and
most arithmetic. For example, the multiply, divide, and translate instructions assume the use of
the AX. Also, some instructions generate more efficient code if they reference the AX rather
than another register.
AH
AL
AX
EAX
ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٠٢
ﻴﻌﺘﺒﺭ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل
AX
ﻫﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﻜﻡ ﺍﻻﺴﺎﺴﻲ ﻭﻫﻭ ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ ﻭﻤﻌﻅﻡ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ
.
ﻭﻜﻤﺜﺎل ﻋﻠﻰ
ﻭﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻨﻘل، ﺔﻤﺴﻘﻟﺍ ، ﺏﺭﻀﻟﺍ ﺕﺎﻴﻠﻤﻌﻟﺍ ﻩﺫﻫ
ﺘﻔﺘﺭﺽ ﺍﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ
AX
.
ﺒﻌﺽ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺘﻭﻟﺩ
code
ﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﻜﻔﺎﺀﺓ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ
ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻊ
AX
ﺒﺩﻻ ﻤﻥ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﺨﺭﻯ
.
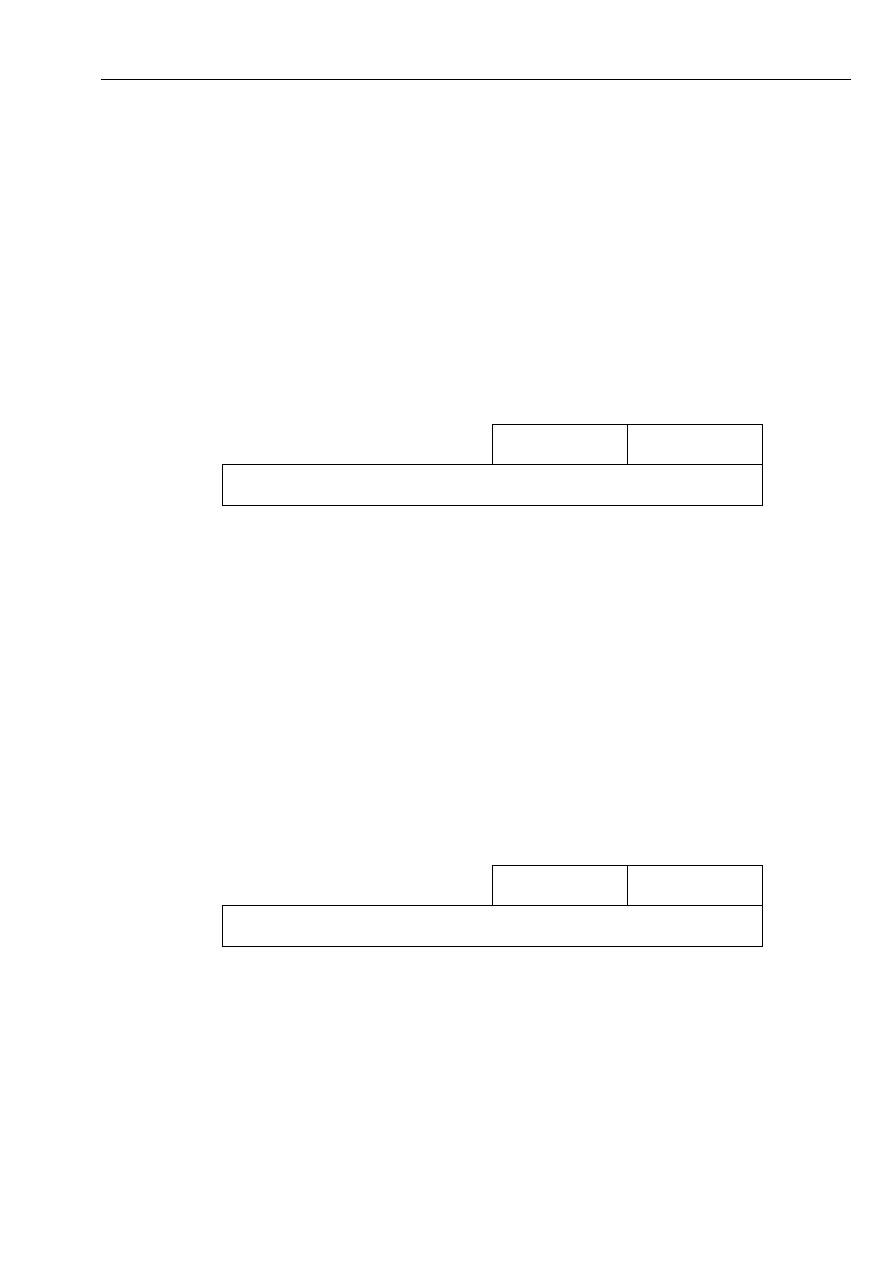
BX register
The BX is known as the base register since it is the only general – purpose register that can be
used as an index to extend addressing. Another common purpose of the BX is for computations.
ﻴﺴﻤﻰ ﻤﺴﺠل
BX
ﺒﻤﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﻘﺎﻋﺩﺓ ﺤﻴﺙ ﺍﻨﻪ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﻭﺤﻴﺩ ﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺍﻥ ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ
ﻜﻤﺅﺸﺭ ﻀﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻭﻨﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺴﻌﺔ
.
ﻭﺍﻟﻭﻅﻴﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﺨﺭﻯ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺒﺎﺕ
.
CX register
The CX is known as the count register. It may contain a value to control the number of times a
loop is repeated or a value to shift bits left or right. The CX may also be used for many
computations.
ﻴﻌﺭﻑ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل
CX
ﺒﺎﻨﻪ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﻌﺩﺍﺩ
.
ﻭﻫﻭ ﻗﺩ ﻴﺤﺘﻭﻱ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﺘﺴﻴﻁﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﺩﺩ ﻤﺭﺍﺕ ﺘﻜﺭﺍﺭ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺤﻠﻘﺔ ﺘﻜﺭﺍﺭﻴﺔ ﺍﻭ
ﻭﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺍﻥ ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺭﻴ، ﺭﺎﺴﻴﻟﺍ ﻭﺍ ﻥﻴﻤﻴﻟﺍ ﻰﻟﺍ ﺕﺎﺘﺘﺒ ﻑﻴﺤﺯﺘ ﺔﻤﻴﻗ
ﺎﻀﻴﺔ
.
BH
BL
BX
EBX
CH
CL
CX
ECX
ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
١٢
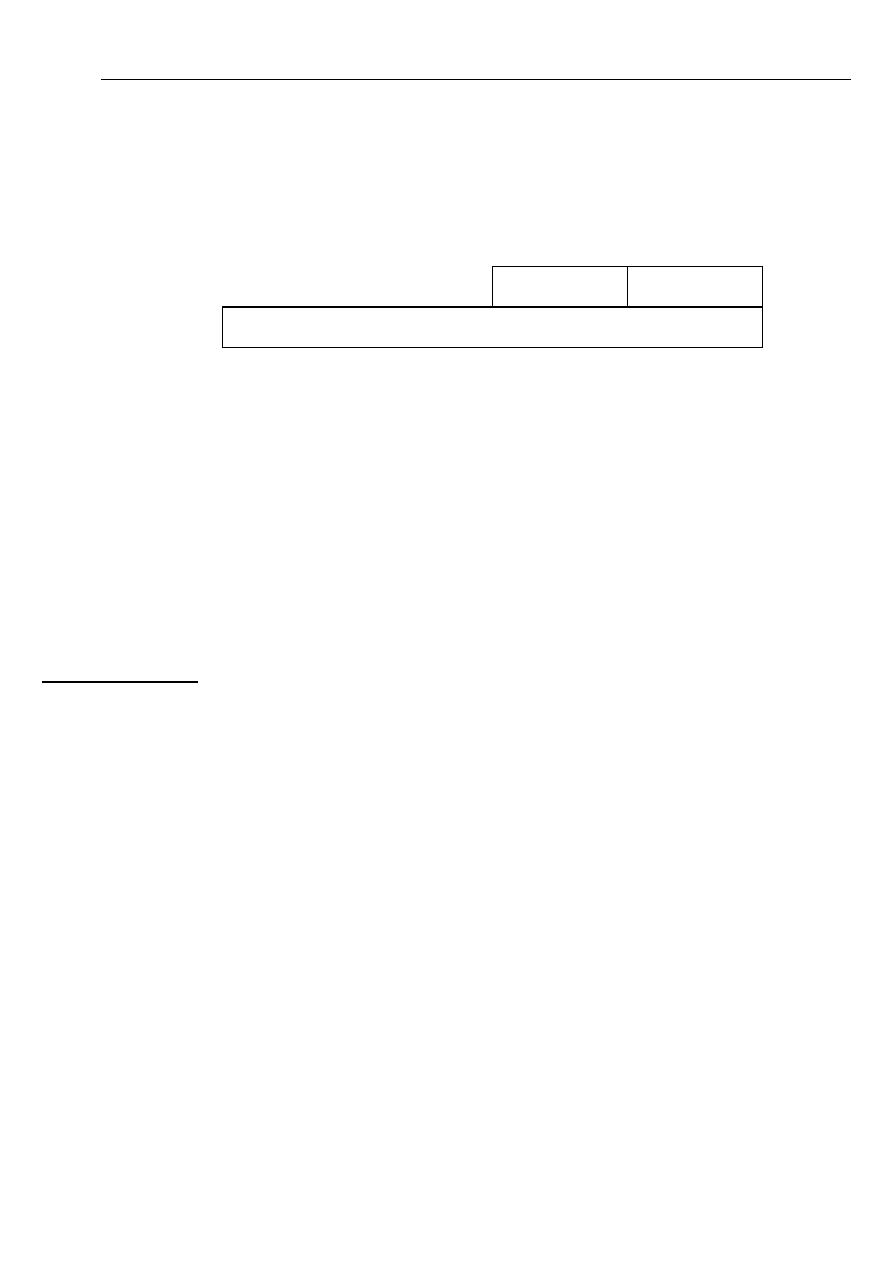
DX register
The DX is known as the data register. Some input / output operations require its use, and
multiply and divide operations that involve large values assume the use of the DX and AX
together as a pair.
ﻴﻌﺭﻑ ﻤﺴﺠل
DX
ﺒﺎﻨﻪ ﻤﺴﺠل ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
ﻭﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻓﻲ ﺒﻌﺽ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ ﻭﻜﺫﻟﻙ ﻓﻲ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻀﺭﺏ،
ﻭﺍﻟﻘﺴﻤﺔ ﻻﻋﺩﺍﺩ ﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ ﺤﻴﺙ ﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﻜل ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻠﻴﻥ
AX
ﻭ
DX
ﻜﻤﺴﺠﻠﻴﻥ ﻤﺯﺩﻭﺠﻴﻥ
.
You may use any of these general – purpose registers for addition and subtraction of 8 - bit,
16 – bit, or 32 – bit values.
ﻭﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺍﻥ ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﺍﻱ ﻤﻥ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺍﻻﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻡ ﻓﻲ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻊ ﻭﺍﻟﻁﺭﺡ ﻭﺒﺎﺤﺠﺎﻡ ﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
٨
ﺒﺕ ﻭ
٦١
ﺒﺕ
ﻭ
٢٣
ﺒﺕ
.
4.Index Registers
The SI and DI registers are available for indexed addressing and for use in addition and
subtraction.
ﺘﺴﺨﺩﻡ ﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ
ﺍﻟﻔﻬﺭﺴﺔ ﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻭﻨﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﻬﺭﺴﺔ ﻭﻜﺫﻟﻙ ﻓﻲ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻊ ﻭﺍﻟﻁﺭﺡ
.
SI register
The 16 – bit source index register is required for some string (character) operations. In this
context, the SI is associated with the DS register, The 80386and later processors support a 32 –
bit extended register, the ESI.
ﺍﻥ ﻤﺴﺠل ﻓﻬﺭﺴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺼﺩﺭ
ﺫﻭ
٦١
ﺒﺕ
ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻤﻊ ﺒﻌﺽ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺴﻼﺴل ﺍﻟﺤﺭﻓﻴﺔ
.
ﻭﻓﻲ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻴﺭﺘﺒﻁ ﻤﺴﺠل
SI
ﻤﻊ
ﻤﺴﺠل
DS
ﻭﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ،
80386
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺒﻌﺩﻩ ﺘﺩﻋﻡ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺴﻊ ﻤﻥ ﻫﺫ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل ﻭﺒﻁﻭل
٢٣
ﺒﺕ ﻭﺒﺎﺴﻡ
ESI
.
DH
DL
DX
EDX

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٢٢
DI register
The 16 – bit destination index register is required for some string (character) operations. In this
context, the DI is associated with the ES register, The 80386and later processors support a 32 –
bit extended register, the EDI.
ﺍﻥ ﻤﺴﺠل ﻓﻬﺭﺴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻘﺭﺫﻭ
٦١
ﺒ
ﺕ ﻴﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻤﻊ ﺒﻌﺽ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺴﻼﺴل ﺍﻟﺤﺭﻓﻴﺔ
.
ﻭﻓﻲ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻴﺭﺘﺒﻁ ﻤﺴﺠل
DI
ﻤﻊ
ﻤﺴﺠل
ES
ﻭﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ،
80386
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺒﻌﺩﻩ ﺘﺩﻋﻡ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺴﻊ ﻤﻥ ﻫﺫ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠل ﻭﺒﻁﻭل
٢٣
ﺒﺕ ﻭﺒﺎﺴﻡ
EDI
.
Flags Register
Nine of the bits of the flags register are common to all 8086 – family processors to indicate the
current status of the computer and the results of processing. Many instructions involving
comparisons and arithmetic change the status of the flags, which some instructions may test to
determine subsequent action.
ﺘﺴﻌﺔ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺘﺘﺎﺕ
ﻟﻤﺴﺠل
flags
ﻫﻲ ﻤﺸﺘﺭﻜﺔ ﻟﻜل ﻋﺎﺌﻠﺔ ﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
8086
ﻭﺍﻟﻜﺜﻴﺭ ﻤﻥ، ﺔﺠﻟﺎﻌﻤﻠﻟ ﺔﻴﻟﺎﺤﻟﺍ ﺔﻟﺎﺤﻟﺍ ﻥﻴﺒﺘ ﻲﺘﻟﺍﻭ
ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﺭﻨﺔ ﺘﻐﻴﺭ ﺤﺎﻟﺔ
flags
ﻭﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻻﺨﺭ ﻴﺩﻗﻕ ﻗﻴﻤﺘﻬﺎ ﻟﻴﺤﺩﺩ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﺴﺎﺱ ﺍﻟﺘﺩﻗﻴﻕ ﺍﺠﺭﺍﺀ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ
ﻤﻌﻴﻨﺔ
.
The following briefly describes the common flag bits:
ﺴﻴﺘﻡ ﺸﺭﺡ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺒﺘﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﻥ
1. OF(overflow). Indicates overflow of a high – order (leftmost) bit following arithmetic, or
indicates a carry into and out of the high order (leftmost) sign bit following a signed arithmetic
operation . JO and JNO test this flag.
ﻴﺒﻴﻥ ﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻭﺠﻭﺩ ﺒﺘ
ﻴﻥ
ﺍﻀﺎﻓﻴ
ﻴﻥ
ﺒﻌﺩ ﺍﺨﺭ ﺒﺕ ﻤﻥ ﺠﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻴﺴﺎﺭ ﺍﻭ ﻭﺠﻭﺩ ﺒﺘ
ﻴﻥ
ﺍﻀﺎﻓﻴ
ﻴﻴﻥ
ﻤﻥ ﺠﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻴﺴﺎﺭ
ﺒﻌﺩ ﺒﺕ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﻓﻲ
ﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﺒﺎﺭﻗﺎﻡ ﻤﻊ ﺍﺸﺎﺭﺍﺕ
.
ﻭﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﻴﻥ
JO and JNO
ﻴﺩﻗﻘﺎﻥ ﻫﺫﺍ
flag
.
2. DF(direction). Determine left or right direction for moving or comparing string (character)
data. When the flag is 0, the string operation performs left – to – right data transfer, when the
flag is 1, the string operation performs right – to – left data transfer.

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٣٢
ﻴﺤﺩﺩ ﺍﺘﺠﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻴﻥ ﺍﻭﺍﻟﻴﺴﺎﺭ ﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻨﻘل ﺍﻭ
ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﺭﻨﺔ ﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﺴﻼﺴل ﺤﺭﻓﻴﺔ
.
ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ
flag
ﻓﺎﻥ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ،ﺭﻔﺼ ﻭﻫ
ﺍﻟﺴﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺭﻓﻴﺔ ﺴﻭﻑ ﺘﻨﻘل
ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻴﺴﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻴﻥ
ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ،
flag
ﻓﺎﻥ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺴﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺭﻓﻴﺔ،ﺩﺤﺍﻭ ﻭﻫ
ﺴﻭﻑ ﺘﻨﻘل ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻴﺴﺎﺭ
.
3. IF(interrupt). Indicates that all external interrupts, such as keyboard entry, are to be
processed or ignored. Which mean all interrupts are disables when 0, and enables when 1.
ﻭﻫ، ﺎﻬﻟﺎﻤﻫﺍ ﻭﺍ ﺎﻬﻌﻤ لﻤﺎﻌﺘﻟﺍ ﻡﺘﻴ ﻑﻭﺴ ﺢﻴﺘﺎﻔﻤﻟﺍ ﺔﺤﻭﻟ لﺒﻗ ﻥﻤ لﺎﺨﺩﺍ لﺜﻤ ﺔﻴﺠﺭﺎﺨﻟﺍ ﺔﻌﻁﺎﻘﻤﻟﺍ ﺕﺎﻴﻠﻤﻋ لﻜ ﺕﻨﺎﻜ ﻥﺍ ﻥﻴﺒﻴ
ﺫﺍ
ﻴﻌﻨﻲ ﻓﺎﻥ ﻜل ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﻁﻌﺎﺕ ﺴﻭﻑ ﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﻫﻤﺎﻟﻬﺎ ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﺘﻜﻭﻥ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﻫﺫﺍ
flag
ﺘﺴﺎﻭﻱ ﺼﻔﺭ
.
ﻭﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﺘﻜﻭﻥ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ
flag
ﺘﺴﺎﻭﻱ
ﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﻓﺎﻥ ﻜل ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﻁﻌﺎﺕ ﺴﻭﻑ ﻴﺘﻡ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻌﻬﺎ
.
4. TF(trap). Permits operation of the processor in single – step mode. Debugger programs such
as DEBUG set the trap flag so that you can step through execution a single instruction at a time
to examine the effect on registers and memory.
ﺘﺴﻤﺢ ﺒﺘﺤﻭﻴل ﻋﻤل ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺨﻁﻭﺓ ﺍﻟﺨﻁﻭﺓ
.
ﻭﺒﺭﺍﻤﺞ ﺍﻟﺘﺼﺤﻴﺢ ﻤﺜل ﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ
DEBUG
ﻴﺤﻭل ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﻫﺫﺍ
flag
ﺍﻟﻰ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﺤﻴﺙ ﻴﺴﻤﺢ ﺒﺘﺤﻭﻴل
ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻤﻥ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺒﺭﻨﺎﻤﺞ ﻤﺘﻜﺎﻤل ﺍﻟﻰ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﻓﻲ ﻜل ﻤﺭﺓ ﻭﺫﻟﻙ ﻟﻔﺤﺹ ﺘﺎﺜﻴﺭ
ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ
.
5. SF(sign). Contains the resulting sign of an arithmetic operation (0 = positive and 1 =
negative) or ( the first bit from left from unsigned number). JG(Jump if Greater) and JL (Jump
if Less) test this flag.
ﻴﺤﺘﻭﻱ ﻫﺫﺍ
flag
ﻋﻠﻰ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﻟﻨﺎﺘﺞ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﺤﻴﺙ ﻴﻤﺜل
)
ﺼﻔﺭ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺠﺒﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﺘﻤﺜل ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺴﺎﻟﺒﺔ
(
ﺍﻭ ﺍﻭل ﺒﺕ ﻤﻥ ﺠﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻴﺴﺎﺭ ﻓﻲ ﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻜﻭﻨﻬﺎ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﻭﻟﻜﻥ ﻻﺭﻗﺎﻡ ﺒﺩﻭﻥ
ﺍﺸﺎﺭﺍﺕ
.
ﻭﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﻴﻥ
JG
ﺍﻗﻔﺯ ﺍﺫﺍ
ﺍﻜﺒﺭ ﻭ
JL
ﺍﻗﻔﺯ ﺍﺫﺍ ﺍﻗل ﻟﺘﺩﻗﻴﻕ
flag
.
6. ZF (zero). Indicates the result of an arithmetic or comparison operation (0 = nonzero and 1 =
zero result ). JE ( Jump if Equal) and JZ( Jump if Zero) test this flag.
ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٤٢
ﻴﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻥ ﻜﺎ
ﻥ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺘﺞ ﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﺍﻭ ﻤﻘﺎﺭﻨﺔ ﻫﻭ ﺼﻔﺭ ﻓﺘﺼﺒﺢ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ
flag
ﻫﻭ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ
.
ﻭﺘﺼﺒﺢ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ
flag
ﻫﻭ ﺼﻔﺭ ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ
ﻭﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﻴﻥ، ﺭﻔﺼﻟﺍ ﺭﻴﻏ ﺩﺩﻋ ﻱﺍ ﺞﺘﺎﻨﻟﺍ ﺔﻤﻴﻗ ﻥﻭﻜﻴ
JE
ﺍﻗﻔﺯ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺘﺴﺎﻭﻱ ﻭ
JZ
ﺍﻗﻔﺯ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺼﻔﺭ ﺘﺩﻗﻕ
ﻫﺫﺍ
flag
.
7. AF( auxiliary carry). Contains a carry out of bit 3 on 8 – bit data, for specialized arithmetic.
It concerned with arithmetic on ASCII and BCD packed fields.
ﺘﺎﺨﺫ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ
carry
ﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﻭﻟﺩ ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﻴﻌﺒﺭ
carry
ﻤﻥ ﺍﻭل ﺍﺭﺒﻊ ﺒﺘﺎﺕ
ﻤﻥ
bit 3
ﺨﻼل ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﺒﻁﻭل
٨
ﺒﺘﺎﺕ
ﻭﻀﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺼﺔ ﻭﻫﻲ
ﻤﺨﺘﺼﺔ ﺒﺎﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺠﺭﻯ ﻋﻠﻰ
ASCII
ﻭ
BCD
.
8. PF (parity).Indicates even or odd parity of a low – order ( rightmost) 8 – bit data operation.
JPO( Jump if parity Odd) and JPE(Jump if parity Even) test this flag.
ﻴﺒﻴﻥ ﺤﺎﻟﺔ
even or odd parity
ﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ
ﻤﻥ
٨
ﺒﺘﺎﺕ ﻭﻓﻘﻁ ﻟﻠﺠﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻨﻰ
.
ﻭﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﻴﻥ
JPO
ﺍﻗﻔﺯ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ
parity
ﻫﻭ ﻓﺭﺩﻱ ﻭ
JPE
ﺍﻗﻔﺯ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ
parity
ﻫﻭ ﺯﻭﺠﻲ ﻴﺩﻗﻕ ﻫﺫﺍ
flag
.
9. CF (carry). Contains carries from a high – order (leftmost) bit following an arithmetic
operation; also, contains the contents of the last bit of a shift or rotate operation. JC and JNC
test this flag.
ﺎﺯﻴﻥــﻌﻴﻻﺍﻭ ﻥﺍﺭﻭﺩ ﻭﺍ ﻑـﻴـﺤﺯﺘ ﺔﻴﻠﻤﻋ ﻥﻤ ﺞﺘﺎـﻨﻟﺍ ﺕﺒﻟﺍ ﻭﺍ ﺭﺎﺴﻴﻟﺍ ﺔﻬﺠ ﻥﻤ ﺕﺒ ﺭﺨﺍ ﺩﻌﺒ ﻲﻓﺎﻀﻻﺍ ﺕﺒﻟﺍ ﺔﻟﺎﺤ ﻲﻫ
JC and JNC
ﺘﺩﻗﻕ ﻫﺫﺍ
flag
.
The flags are in the flags register in the following locations ( which you need memorize):
The flags most relevant to assembly programming are OF, SF, ZF, CF for comparison and
arithmetic operations, and DF for the direction of string operations. The 80286 and later
processors have some flags used for internal purposes, concerned primarily with protected
C
O
D
I
T
S
Z
A
P
1
4
2
3
5
7
8
9
14
11
12
13
15
10
6
0
Flag
Bit no.
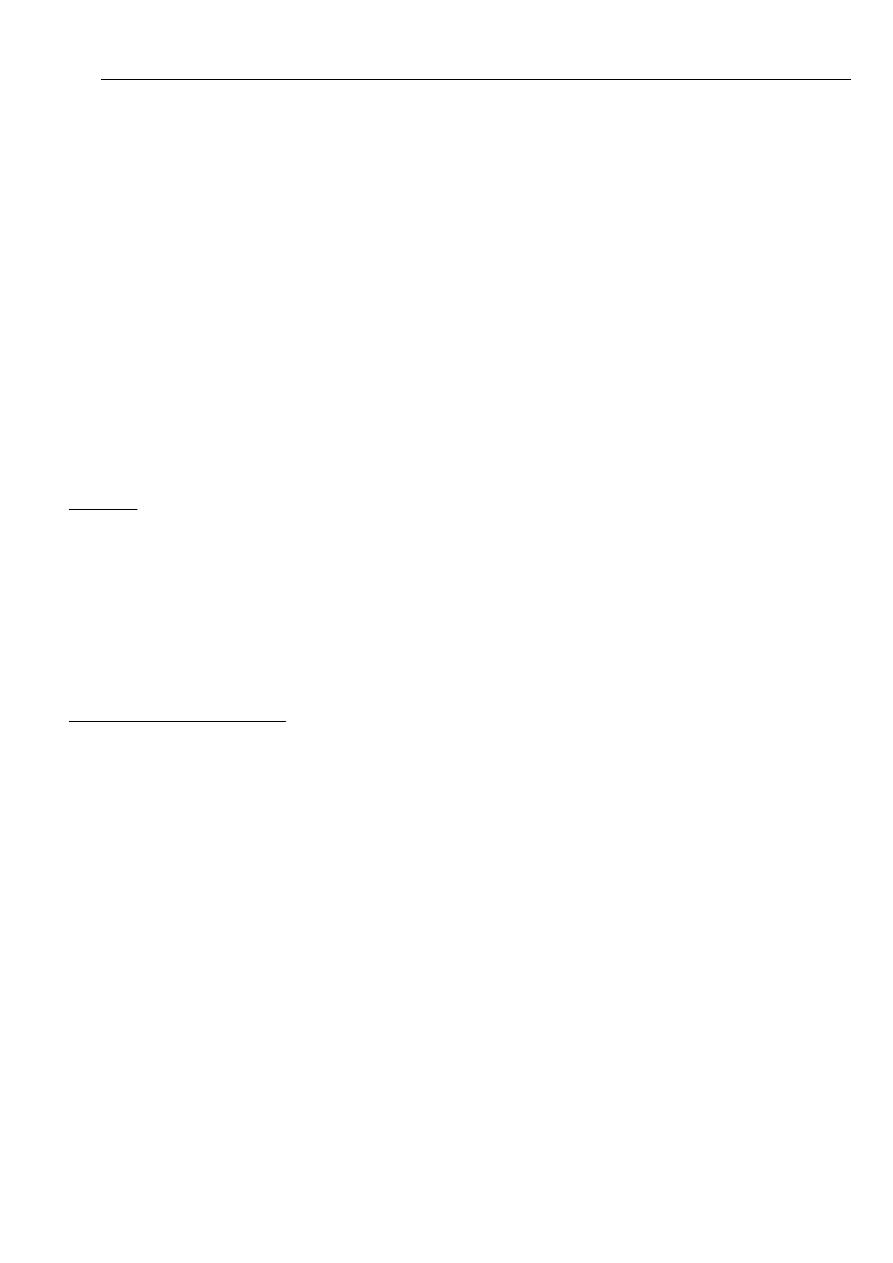
ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜ
ﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٥٢
mode. The 80386 and later processors have a 32 – bit extended flags register known as
Eflags.
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻻﻜﺜﺭ
flags
ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺩﻤﺔ ﻫﻲ
OF, SF, ZF, CF
ﻭ، ﺔﻨﺭﺎﻘﻤﻟﺍ ﺕﺎﻴﻠﻤﻋ ﻭﺔﻴﻀﺎﻴﺭﻟﺍ ﺕﺎﻴﻠﻤﻌﻟﺍ ﻲﻓ ﻡﺩﺨﺘﺴﺘ ﻲﺘﻟﺍﻭ
ﻜﺫﻟﻙ ﻓﺎﻥ
DF flag
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ، ﺔﻴﻓﺭﺤﻟﺍ لﺴﻼﺴﻟﺍ ﻊﻤ لﻤﺎﻌﺘﻟﺍ ﺕﺎﻴﻠﻤﻋ ﻲﻓ ﺕﺎﻫﺎﺠﺘﻻﺍ ﺩﻴﺩﺤﺘﻟ ﻡﺩﺨﺘﺴﻴ
80286
ﻓﻤﺎ
ﺒﻌﺩﻫﺎ ﺘﻤﺘﻠﻙ
flags
ﻭﺨﺎﺼﺔ ﻋﻨﺩﻤﺎ ﺘﻌﻤل ﻓﻲ ﺤﺎﻟﺔ، ﺔﻴﻠﺨﺍﺩ ﺽﺍﺭﻏﺍ ﻲﻓ ﻡﺩﺨﺘﺴﺘ
protected
ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ،
80386
ﻓﻤﺎ ﺒﻌﺩﻫﺎ ﻤﺴﺠل
flag
ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺴﻊ ﻭﺒﻁﻭل
32-bit
ﻭﺒﺎﺴﻡ
Eflags
.
Question Show the effect of below operations on these flags DF,IF,TF,SF,CF,SF,AC,ZF,PF
1. an arithmetic operation as add AH+BH and store result in AL with these numbers
4E
8A +
2. a program deal with four subroutine one of them is Arabic program for bank customer.
SOL:
1. 1
4E 0100 1110
8A 1000 1010 +
1101 1000
DF , IF , TF not effected
ZF=0
SF=1
CF=0
AC=1
PF=1
2. ZF,SF,CF,AC,PF not effected
DF=1
IF=1
TF=0
