
KETOGENESIS
●
Ketogenesis
is the process of formation of ketone bodies ( acetoacetate ,
β-hydroxybutyrate , and acetone ) from mitochondrial acetyl CoA . The
enzymes for the synthesis of ketone bodies are located mainly in liver cell
mitochondria .
Mechanism of Ketogenesis :
● Ketogenesis occurs whenever fatty acid levels are elevated in the blood .
● Ketogenesis occurs under metabolic conditions associated with a high
level of mitochondrial acetyl CoA ( resulting from high rate of partial
oxidation of fatty acid ) ; such metabolic conditions include :
1. fasting & starvation
2. uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
3. high fat / low carbohydrate diet .
● Under these conditions , glucagon/insulin ratio is high which promotes :
Lipolysis : Triglyceride breakdown in adipose tissues and the released
fatty acids enter the liver cell mitochondria and by the process of
β-
oxidation generates increased amount of acetyl CoA , NADH & ATP .
KETOGENESIS PATHWAY :

1
ST
Step
:
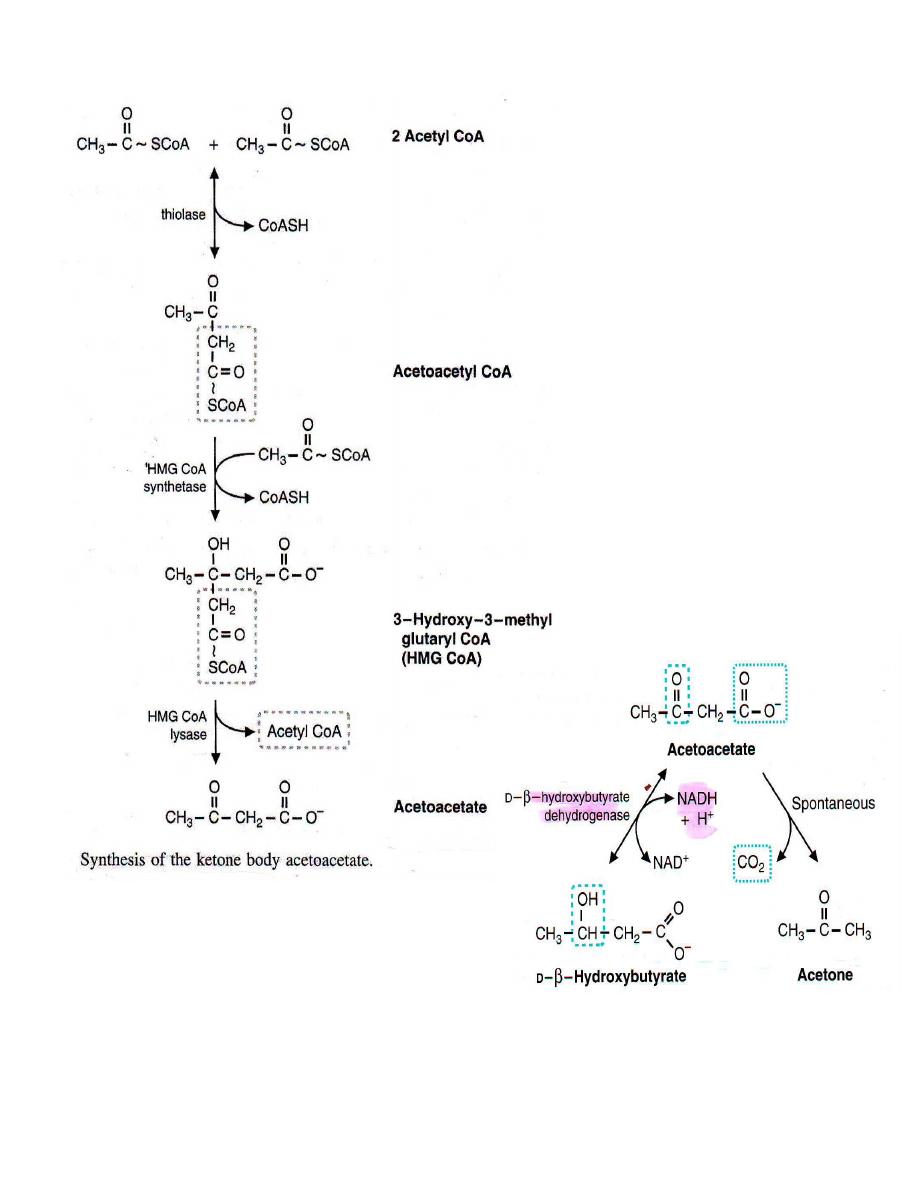
two molecules of acetyl CoA react to form acetoacetyl CoA .
2
nd
Step :
another acetyl CoA reacts with acetoacetyl CoA producing
β-hydroxy-β-
methyl glutaryl CoA( HMG-CoA ) catalyzed by HMG-CoA synthetase-I . This
enzyme is the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of ketone bodies and is
induced as fasting progresses .
3
rd
Step
:
HMG-CoA is then cleaved by the enzyme HMG-CoA lyase ( present only in
liver ) to form acetoacetate ( primary ketone bodies ) .
4
th
Step
:
● acetoacetate can be reduced to β–hydroxybutyrate by a dehydrogenase
enzyme that uses NADH as reducing agent .
● Both , acetoacetate & β–hydroxybutyrate enter the blood and travel from
the liver to extrahepatic tissues where they are oxidized for energy .
● The other fate of acetoacetate is spontaneous decarboxylation in which
nonenzymatic reaction release CO
2
and produces acetone .
■ β-hydroxybutyrate and acetone are termed secondary ketone bodies .
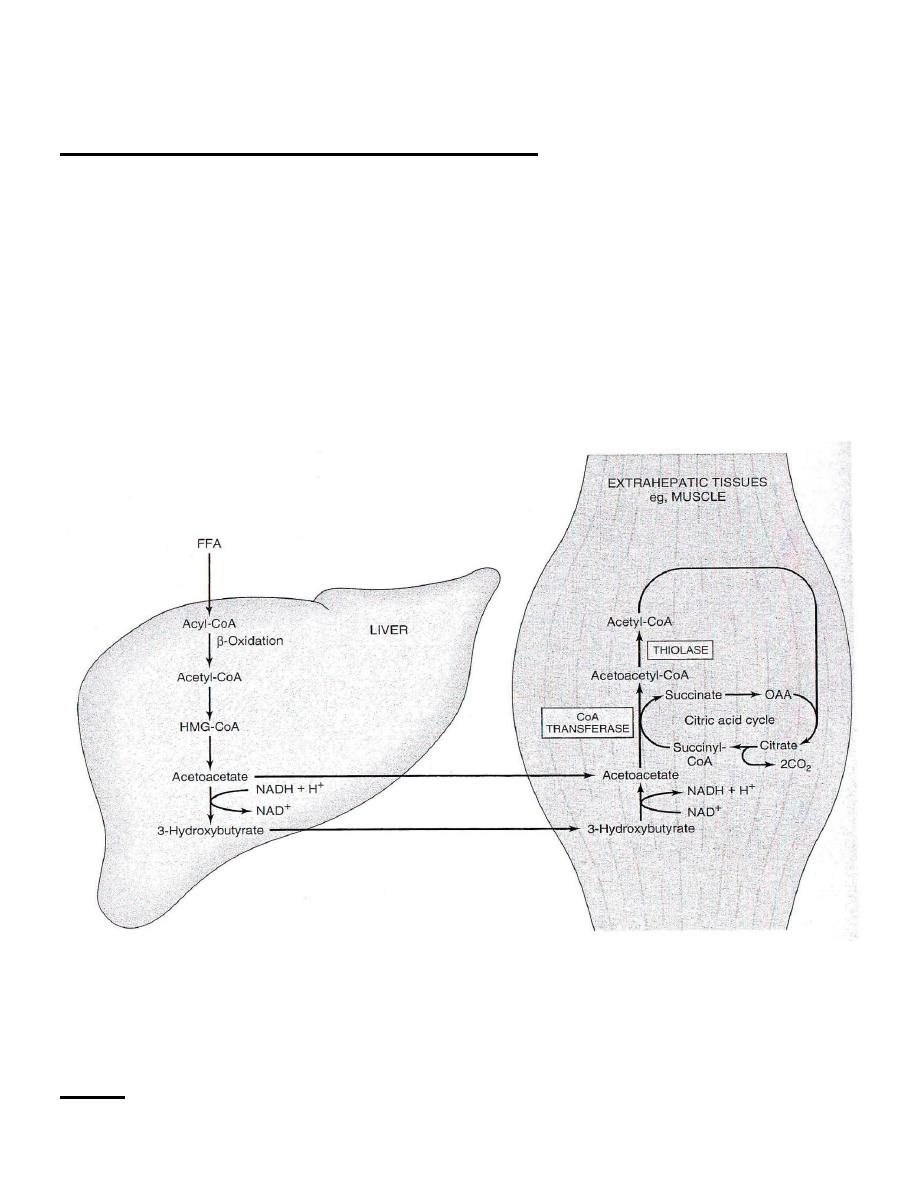
Oxidation of ketone bodies , acetoactate :
●Acetoacetate is activated in the mitochondria , and by enzymatic reactions
it is transformed to acetoacetyl
–CoA.
● Acetoacetyl CoA is then cleaved to two molecules of acetyl CoA catalyzed
by the enzyme thiolase ( same thiolase of β-oxidation ) .
● Acetyl CoA enter TCA cycle and oxidized to generate ATP .
[ Synthesis & Oxidation of Ketone Bodies ]
Notes :

1. Normally , the concentration of ketone bodies in blood rarely exceeds
0.2 mmol /L ; ketone bodies serve as fuels for tissues such as muscle
( cardiac & skeletal ) and kidney during fasting .
2. Ketone bodies are used as a fuel by the brain but only when the
concentration in the blood is elevated ( during starvation ) which
enables them to enter brain cells and other nervous tissue where they
are oxidized .
3. Acetone is difficult to oxidize in tissues ; is volatile and expired by the
lungs . The breath of uncontrolled diabetic patients smells acetone .
ENERGETICS :
Oxidation of one molecule of acetoacetate by extrahepatic tissue yields
23 ATP . The two acetyl CoA derived from acetoacetate generate 24
ATP via the TCA cycle but the net yield is only 23 ATP since one ATP is
used in the activation of acetoacetate .
Advantage gained by ketogenesis :
(a) allows liver to oxidize large amounts of fatty acids .
(b) other tissues use the ketone bodies as fuel .
(c) during starvation , the brain can oxidize ketone bodies . This
reduces its need for glucose , consequently , gluconeogenesis
from muscle protein is reduced ( i.e. degradation of muscle
protein decreases ) .
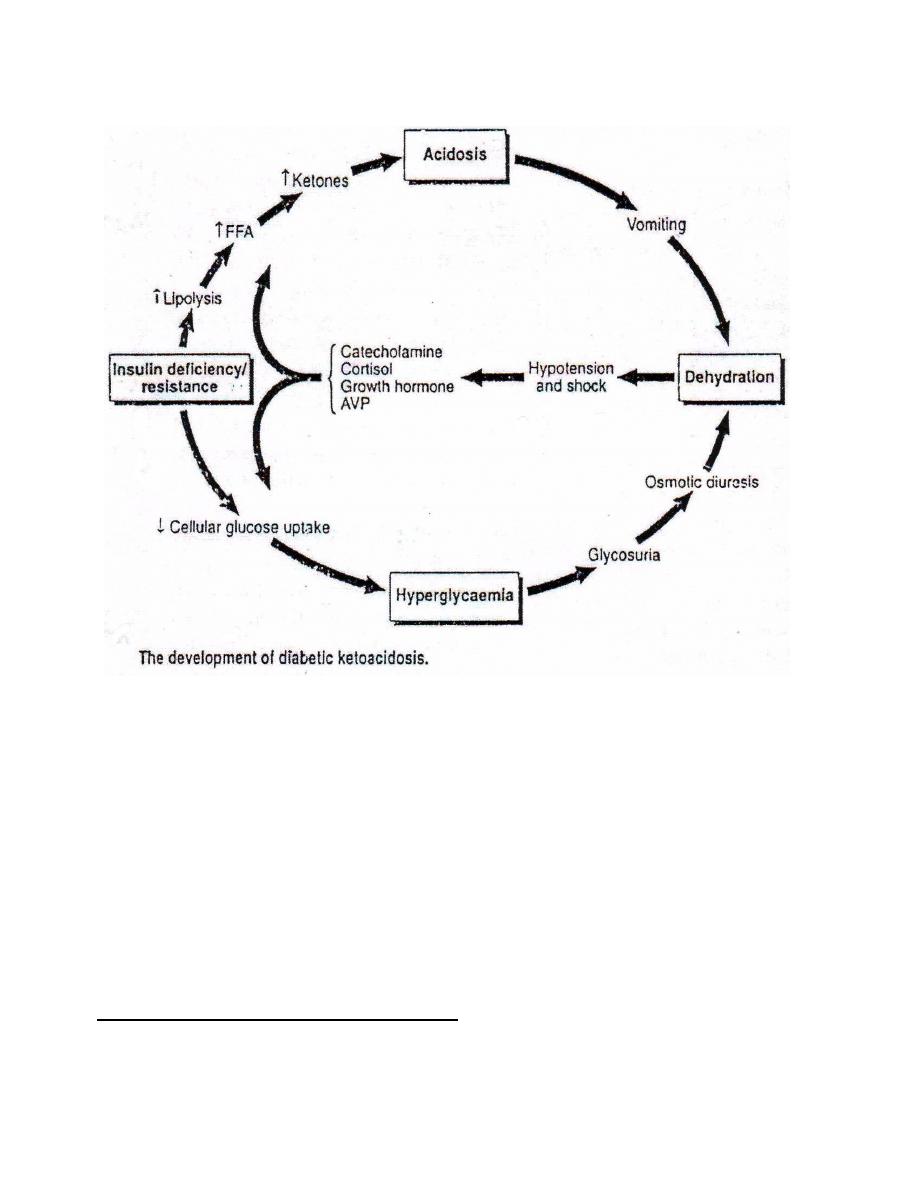
KETOSIS & KETOACIDOSIS :
● A condition develops when the rate of synthesis of ketone bodies exceeds the
ability of extrahepatic tissues to metabolize them ; ketone bodies accumulate
in the blood and levels may reach 12 mmol/ L ( ketonemia ) and excreted in
the urine ( ketonuria ) .
● ketone bodies ( acetoacetate & β-hydroxybutyrate ) are both moderately
strong acids and , when accumulate , will lower the plasma pH leading to
metabolic acidosis ( ketoacidosis ) .
●The body try to compensate acidosis through hyperventilation producing
the rapid deep typical acidotic breath called kussmaul's respiration .
● Osmotic diuresis due to ketonuria lead to water loss & electrolyte depletion
since ketone bodies are excreted in urine as their Na
+
or K
+
salts .
● Frequent vomiting caused by acidosis is usually present and participate in
the loss of more water & electrolytes .
● Electrolyte depletion and water losses lead to dehydration , hypovolemia
and hypotension . This stimulate the secretion of catecholamines , cortisol
and growth hormones which have lipolytic and hyperglycemic effects
creating a viscious circle .
● Finally , the acidosis and dehydration depress consciousness to the point of
coma .
● ketosis may develop in diabetes mellitus and starvation :
■ Ketosis in starvation is due to reduced calorie intake which leads to
decreased blood glucose and insulin levels and an increased glucagon
levels and consequently increased lipolysis and hepatic ketogenesis .
■ In diabetes mellitus , even though glucose level is high , glucagon level is
high because of the deficiency of insulin which causes increased rate of
lipolysis and subsequent ketone bodies production .
**
Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidois ( DKA ) have whole body potassium
depletion which may be severe despite apparently normal plasma K
+
levels . The explanations for this are :
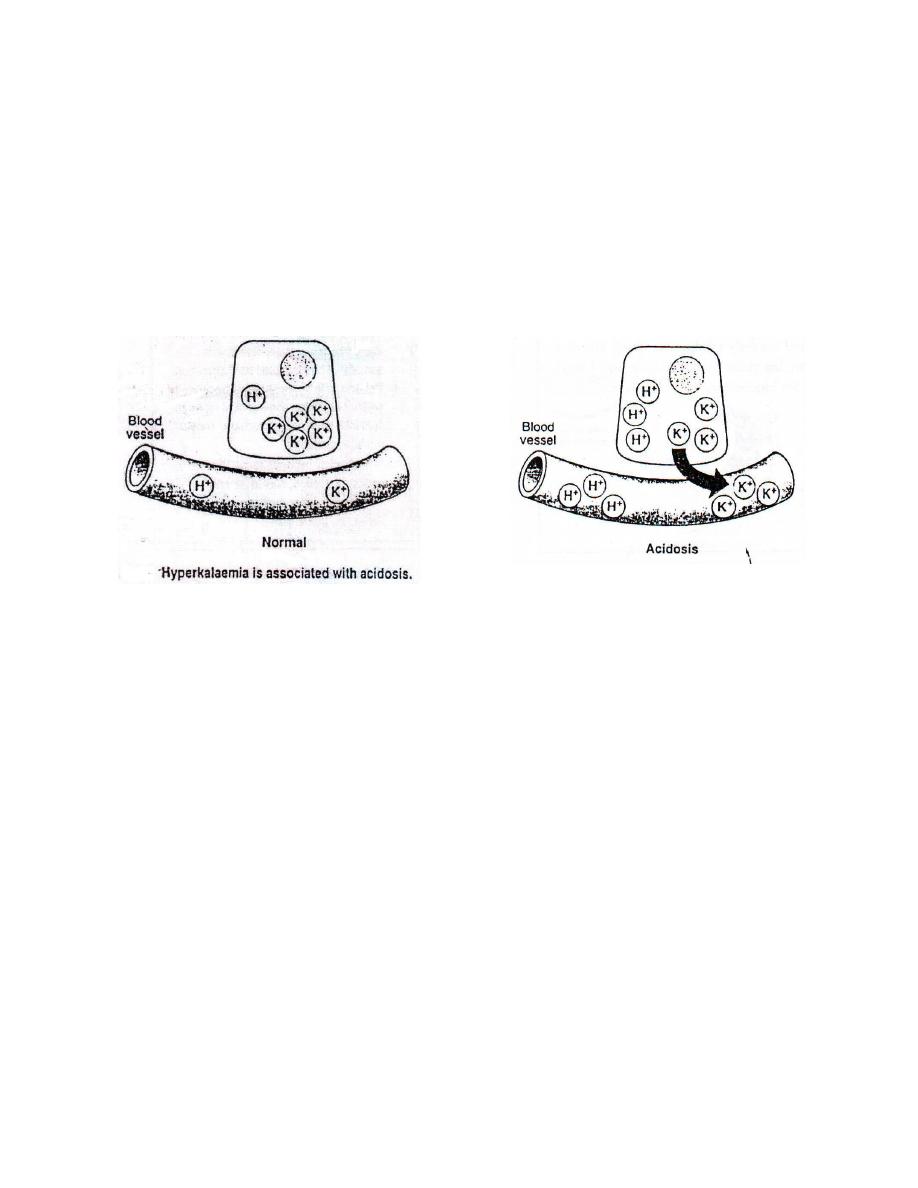
1. Osmotic diuresis : electrolyte depletion accompany water secretion .
2. Ketone bodies excreted as K
+
salt .
3. In acidosis , as the concentration of hydrogen ions(H
+
) increases ,
K
+
ions are moved out of the cell into ECF in order to maintain
electroneutrality .
***************************************************************************

