Physiology of Muscle
Lecture 4
By
Dr. Mufeed Akram Taha
FIBMS Neurology
Clinical Attachment Turkey

Muscle cells, like neurons, can be
excited chemically, electrically, and
mechanically to produce an action
potential that is transmitted along
their cell membrane. Unlike neurons,
they have a contractile mechanism
that is activated by the action
potential.

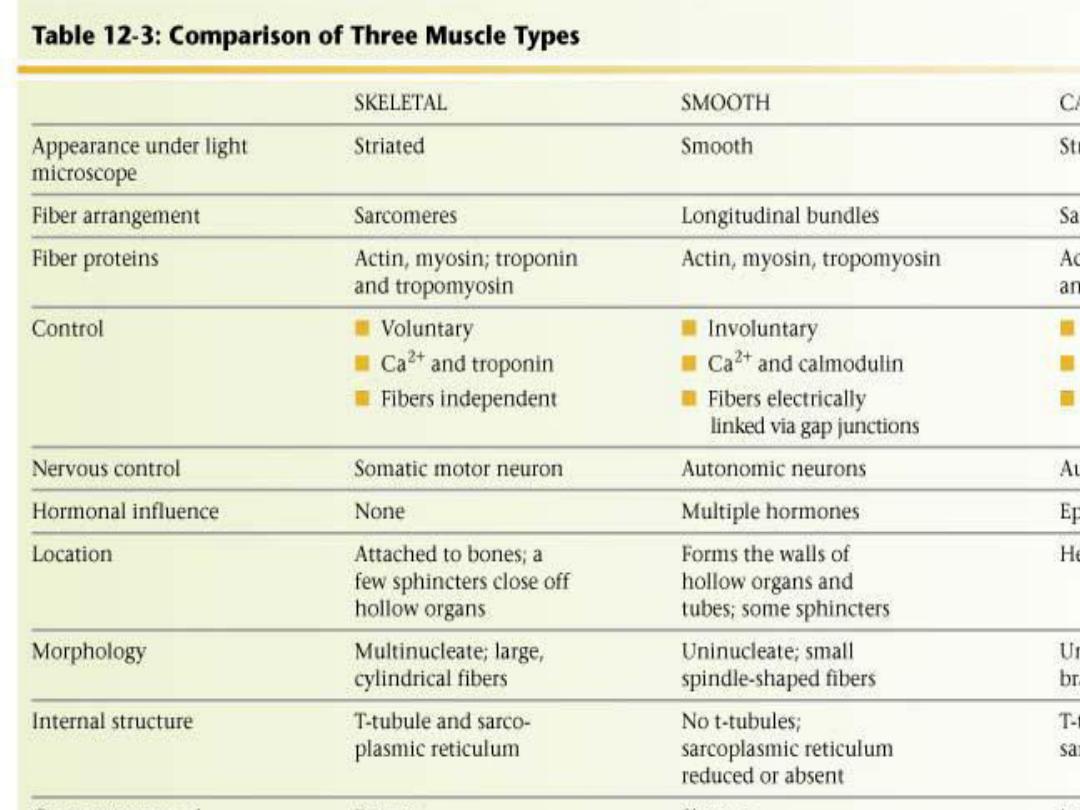
Muscle is generally divided into three
types, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
Skeletal muscle makes up the great mass
of the somatic musculature. It has well-
developed cross-striations, does not
normally contract in the absence of
nervous stimulation, lacks anatomic and
functional connections between
individual muscle fibers, and is generally
under voluntary control.

Cardiac muscle
also has cross-striations, although it can
be modulated via the autonomic nervous
system, it can contract rhythmically in
the absence of external innervation
owing to the presence in the
myocardium of pacemaker cells that
discharge spontaneously.

Smooth muscle
lacks cross-striations and can be further
subdivided into two broad types: unitary
(or visceral) smooth muscle and
multiunit smooth muscle. The type found
in most hollow viscera is functionally
syncytial and contains pacemakers that
discharge irregularly.

SKELETAL MUSCLE
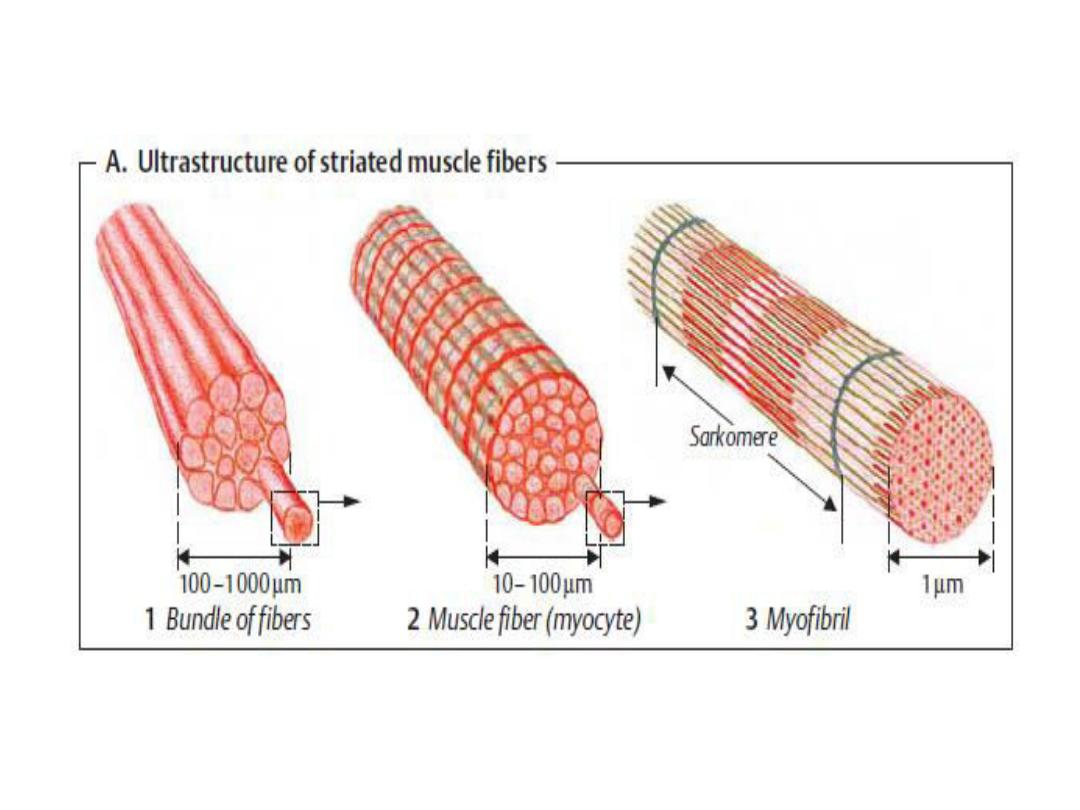
Skeletal muscle is made up of individual
muscle fibers that are the "building
blocks" of the muscular system in the
same sense that the neurons are the
building blocks of the nervous system.
Most skeletal muscles begin and end in
tendons, and the muscle fibers are
arranged in parallel between the
tendinous ends, so that the force of
contraction of the units is additive.

Each muscle fiber is a single cell that is
multinucleated, long, cylindric, and
surrounded by a cell membrane, the
sarcolemma.
There are no syncytial bridges between
cells. The muscle fibers are made up of
myofibrils, which are divisible into
individual filaments. The filaments are
made up of the contractile proteins.

The contractile mechanism in
skeletal muscle depends on the
proteins myosin-II, actin,
tropomyosin, and troponin.
Troponin is made up of three
subunits, troponin I, troponin T,
and troponin C.

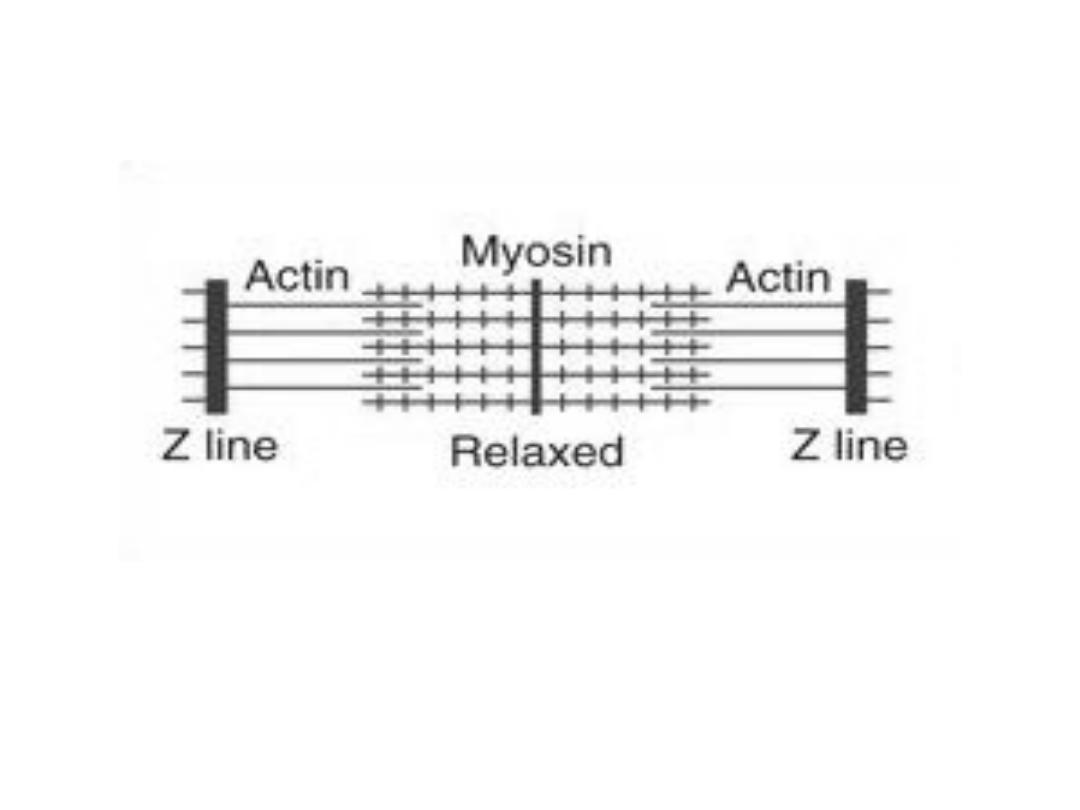
Striations
Differences in the refractive indexes of
the various parts of the muscle fiber
are responsible for the characteristic
cross-striations.The parts of the
cross-striations are frequently
identified by letters.

-There 2 types of filaments in each
myofibril: The thick filaments,
which are about twice the
diameter of the thin filaments,
are made up of myosin; the thin
filaments are made up of actin,
tropomyosin, and troponin.

Parts of cross striation:
-The light I band formed by actin .
-Z line divides I band connects to thin
filaments .
-The dark A band formed by the thick
filaments .

-Lighter H band in the center of A band
they are regions where the muscle is
relaxed ,the thin filament do not
overlap thick filaments .
-Transverse M line in the center of H
band .
- The area between two adjacent Z
lines is called a sarcomere.
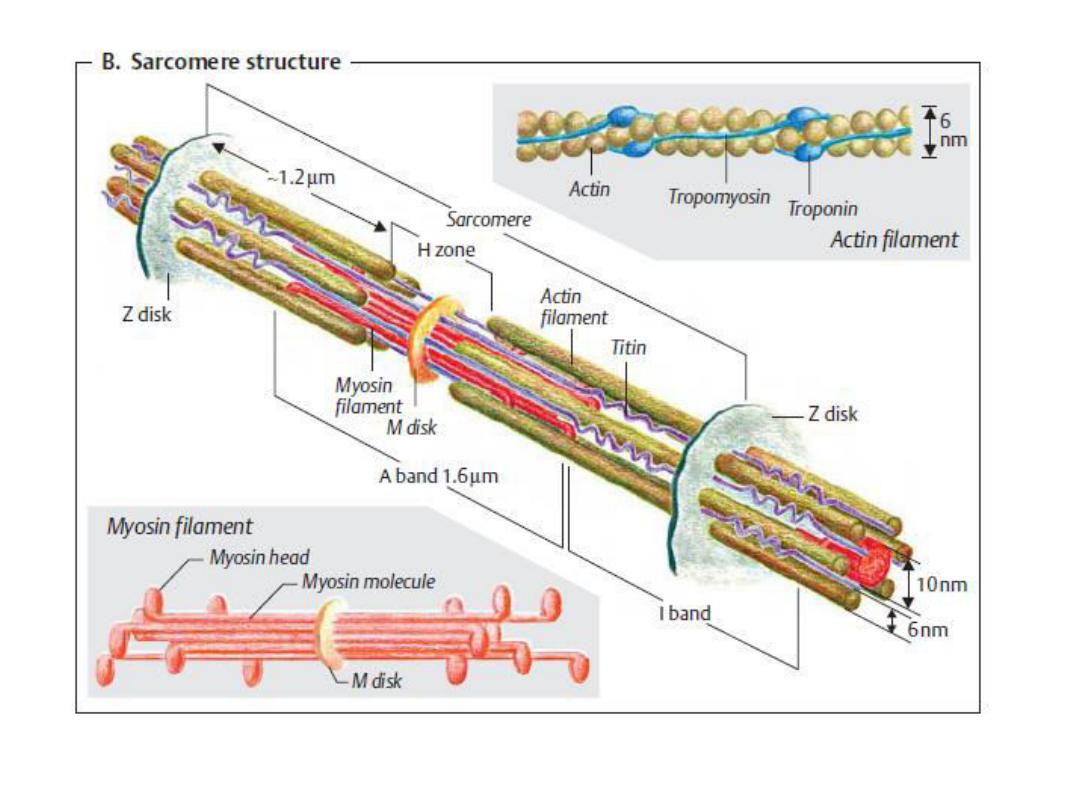

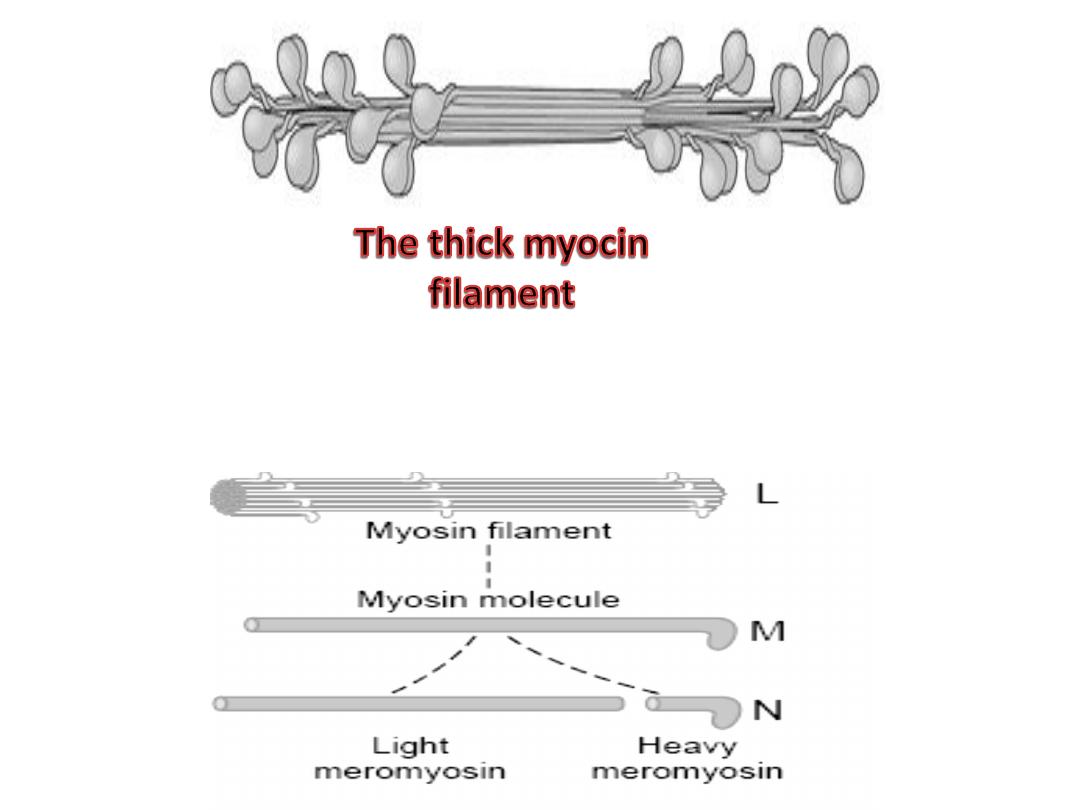
Myosin ( The thick filaments )
The form of myosin found in muscle is
myosin-II, with two globular heads and a
long tail. The heads of the myosin
molecules form cross-bridges with actin.
Myosin contains heavy chains and light
chains, and its heads are made up of the
light chains and the amino terminal
portions of the heavy chains.
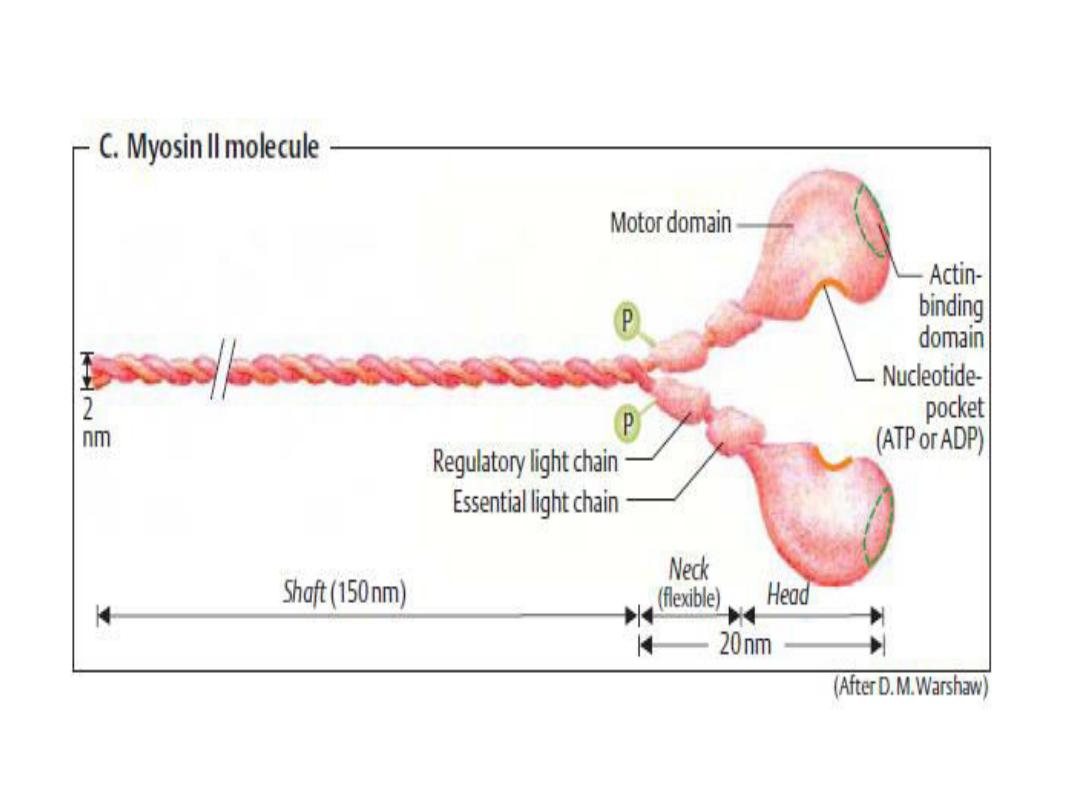

These heads contain an actin-
binding site and a catalytic site
that hydrolyzes ATP. The M line is
the site of the reversal of polarity
of the myosin molecules in each of
the thick filaments. Each thick
filament contains several hundred
myosin molecules.

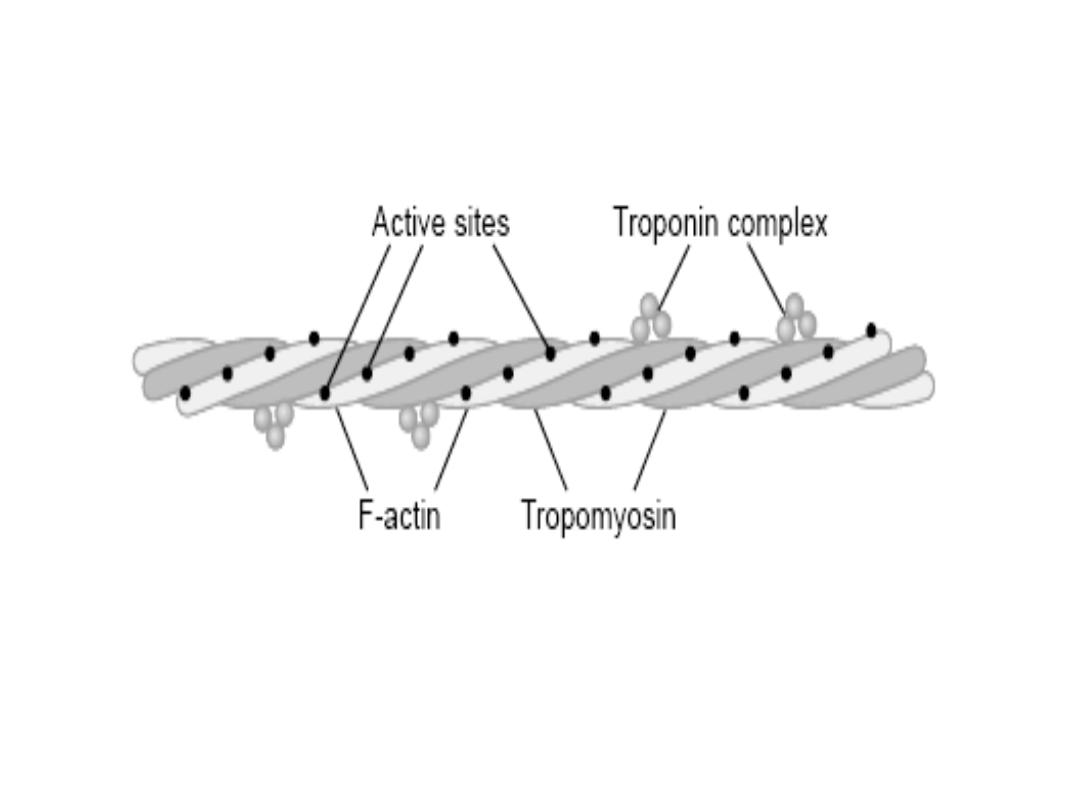
Actin (The thin filaments )
The thin filaments are polymers made up
of two chains of actin that form a long
double helix. Tropomyosin molecules are
long filaments located in the groove
between the two chains in the actin.
Each thin filament contains 300 to 400
actin molecules and 40 to 60
tropomyosin molecules.

Troponin molecules are small globular
units located at intervals along the
tropomyosin molecules. Each of the
three troponin subunits has a unique
function:
Troponin T binds the troponin
components to tropomyosin; troponin I
inhibits the interaction of myosin with
actin; and troponin C contains the
binding sites for the Ca
2+
that helps to
initiate contraction.

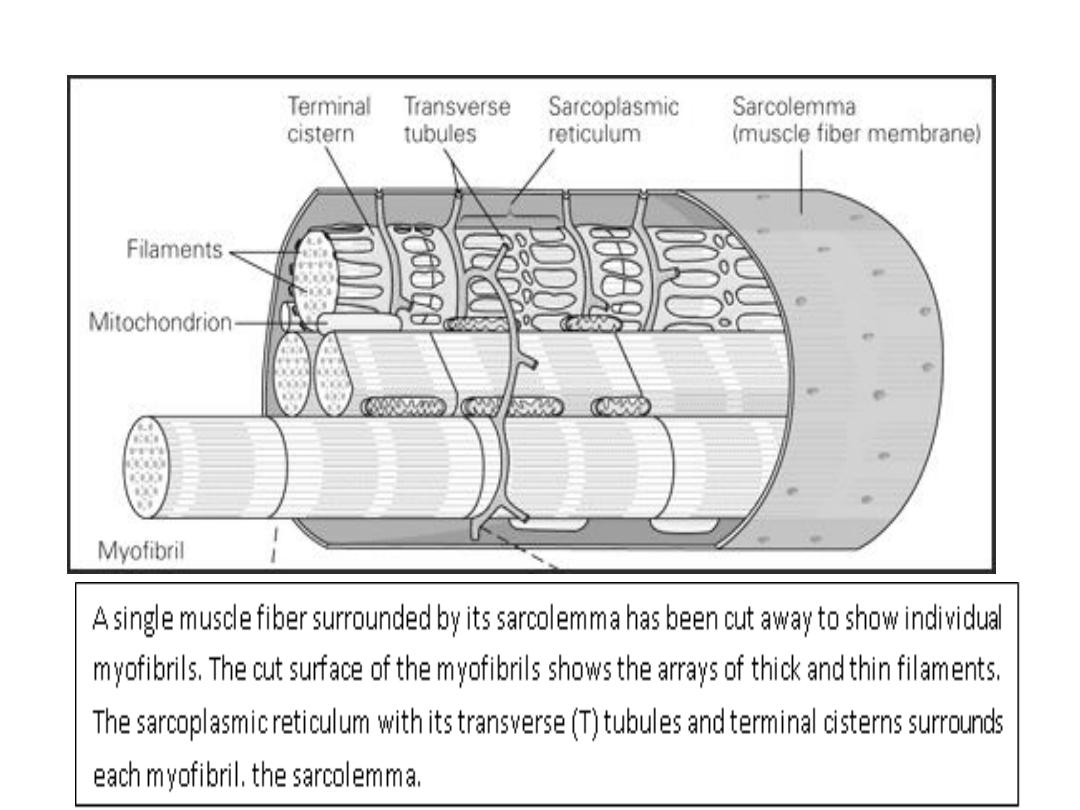
Sarcotubular System
The muscle fibrils are surrounded by
structures made up of membranes that
appear in electron photomicrographs as
vesicles and tubules. These structures
form the sarcotubular system, which is
made up of a T system and a
sarcoplasmic reticulum.

T system
Transverse tubules, which is
continuous with the sarcolemma of
the muscle fiber, forms a grid
perforated by the individual muscle
fibrils. The space between the two
layers of the T system is an extension
of the extracellular space.

The function of T system, which is
continuous with the sarcolemma
,is to provide a path for the rapid
transmission of the action
potential from the cell membrane
to all the fibrils in the muscle.

Sarcoplasmic reticulum
This forms an irregular curtain around
each of the fibrils, has enlarged
terminal cisterns in close contact
with the T system at the junctions
between the A and I bands.
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is an
important store of Ca
2+
and also
participates in muscle metabolism.