
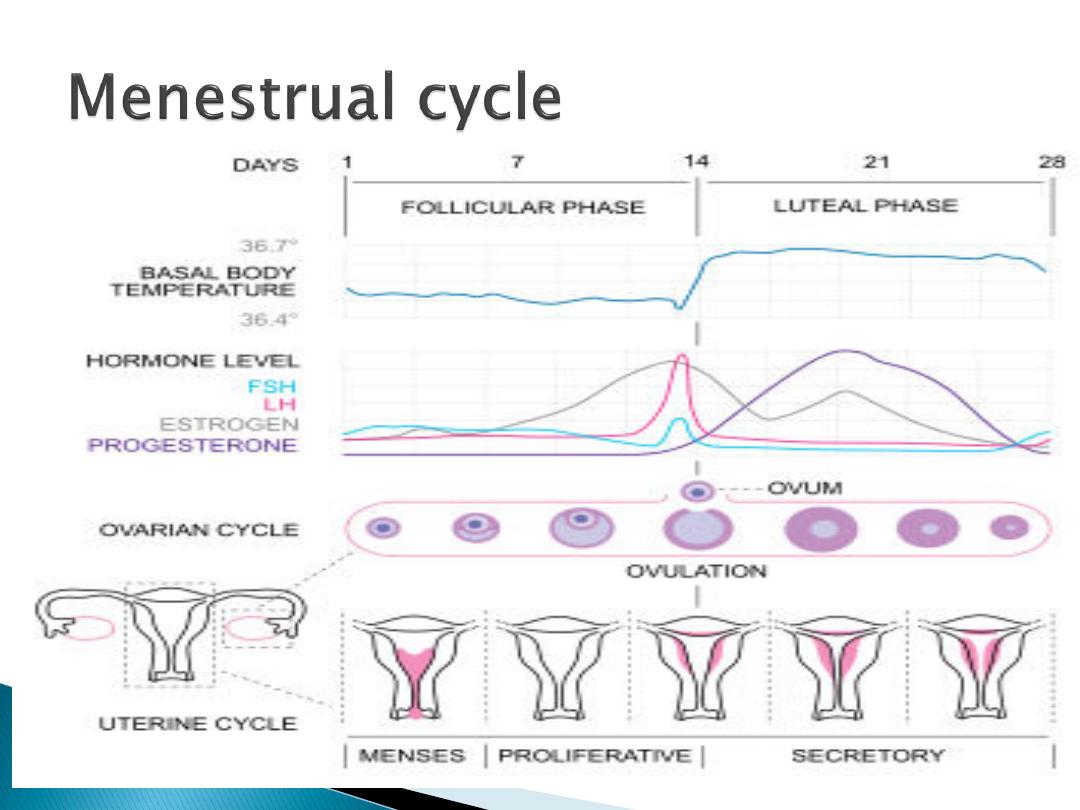
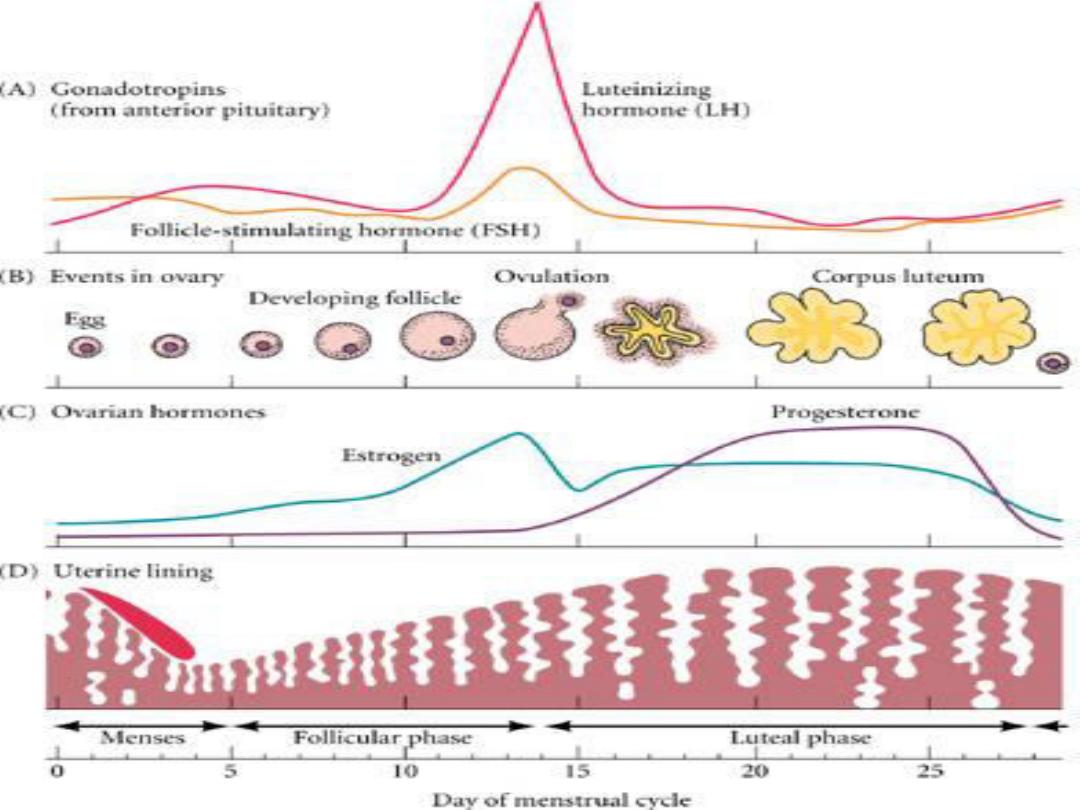
Regular cyclical changes in the
endometrium regarded as a
preparation for fertilization and
pregnancy
Its characterized by periodic
vaginal bleeding that occurs
due to shedding of the
endometrium(uterine mucosa)

In human no new ova are formed after birth
During fetal life the ovaries contain over
7millions
primordial follicles
many undergoes
atresia
(involution)
intrauterine
At the time of birth
2 millions
ova are there
but
50% atretic
At the time of puberty number of ova is less
than
300000
Only
one ova per cycle and 500 ova
are used in
the coarse of reproductive life

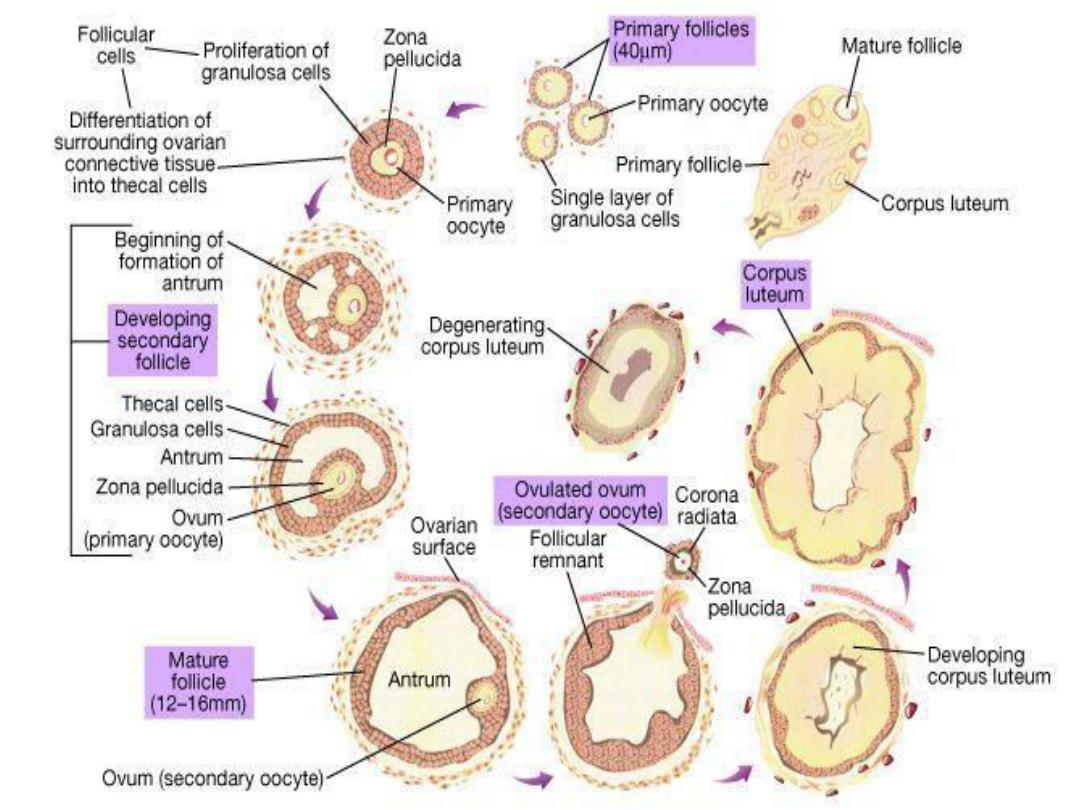
From the time of birth many
primordial follicles are present
under the ovarian capsule,
Each contain an immature ovum
At the start of each cycle many of
these follicles enlarge, a cavity form
inside which is filled with follicular
fluid
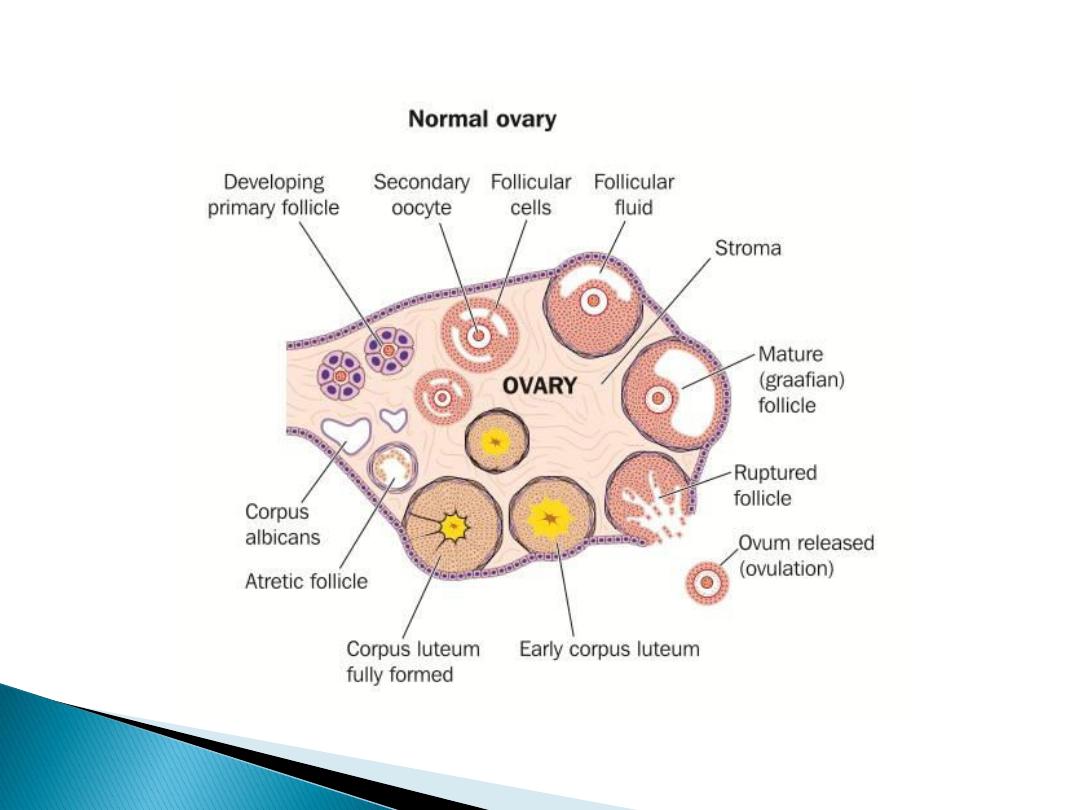

Each follicle is surrounded with
3
layers of cell from inside out word
granulosa cell, theca interna and
theca externa
On about
sixth
day one follicle will
grow and become dominant
follicle(mature grafian follicle)
which become a source of
circulating oestrogen, and others
regress form atretic folliclle
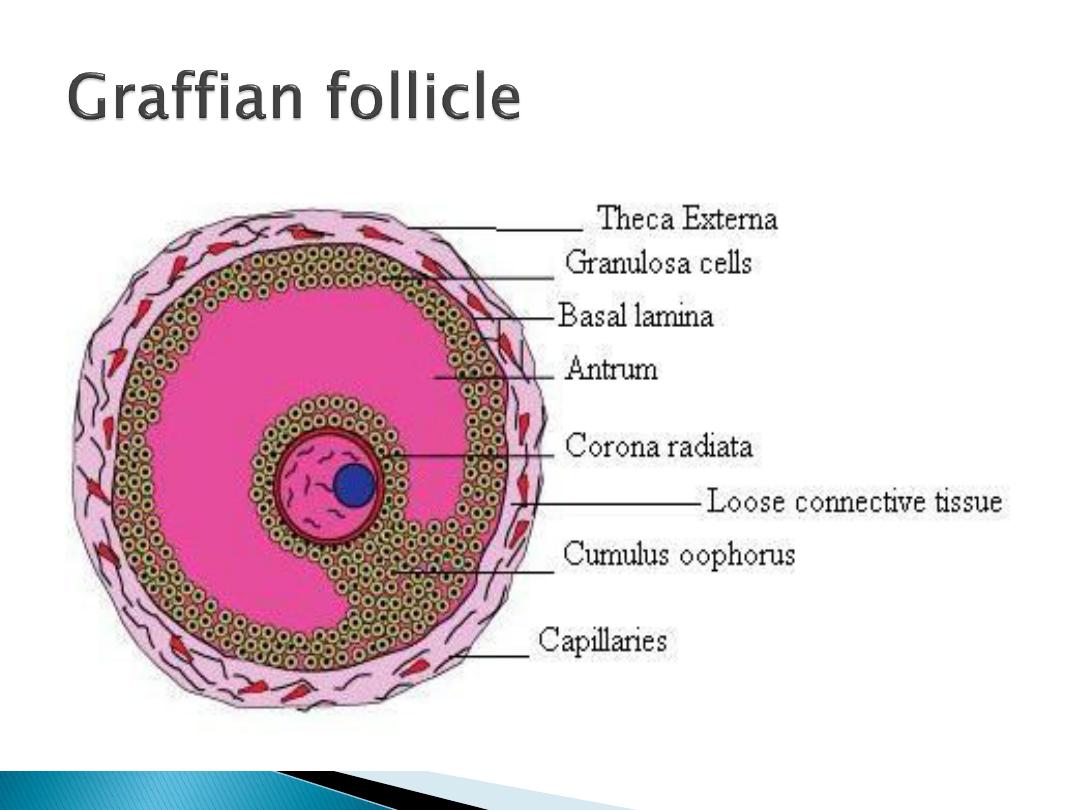

Oestrogen is produced in the
theca interna cells then
aromatized and secreted from
granulosa cell

Is the extrusion of the ovum in to
the abdominal cavity after
rupturing of the distended follicle
It occurs at about
day 14th
of the
cycle after which if fertilization
did not occur the lining of the
follicle will proliferate rapidly and
replaced with lipid rich luteal
cells forming
corpus luteum
.
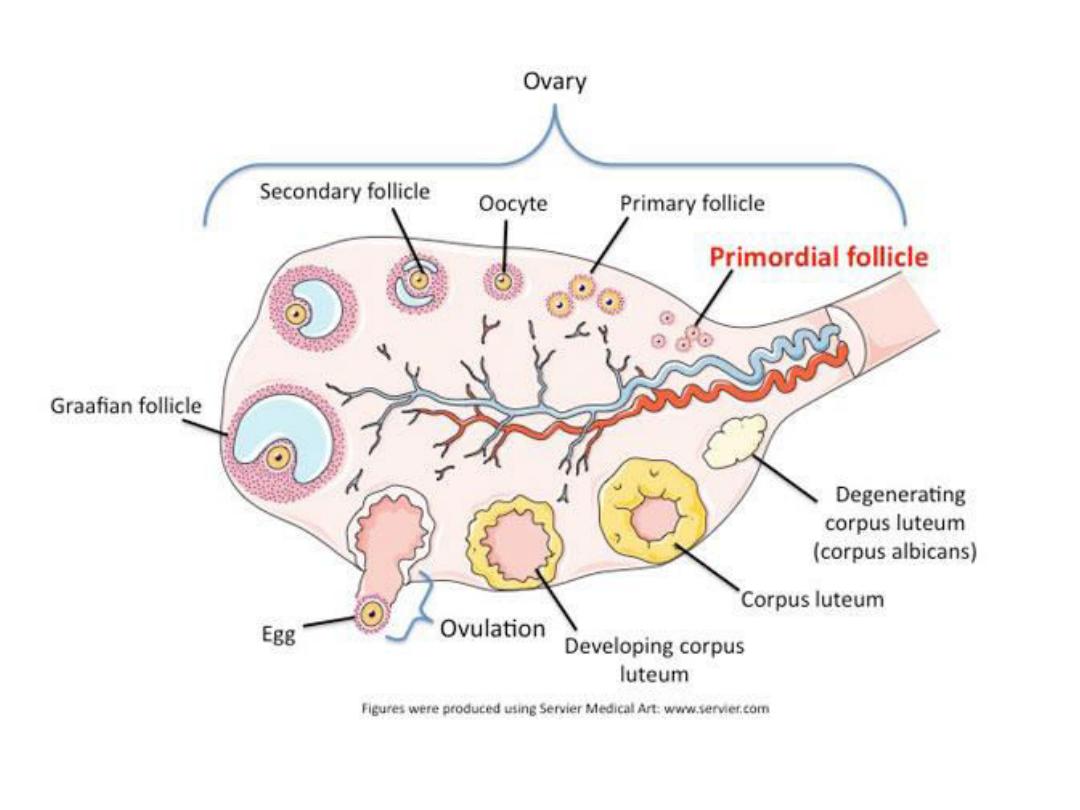

The corpus luteum will initiate the
luteal phase
of the cycle During which
Oestrogen and Progesteron
are
secreted, If pregnancy occur corpus
luteum persist, if not, it begin to
degenerates
about 4 days before the
next cycle
forming corpus albicans

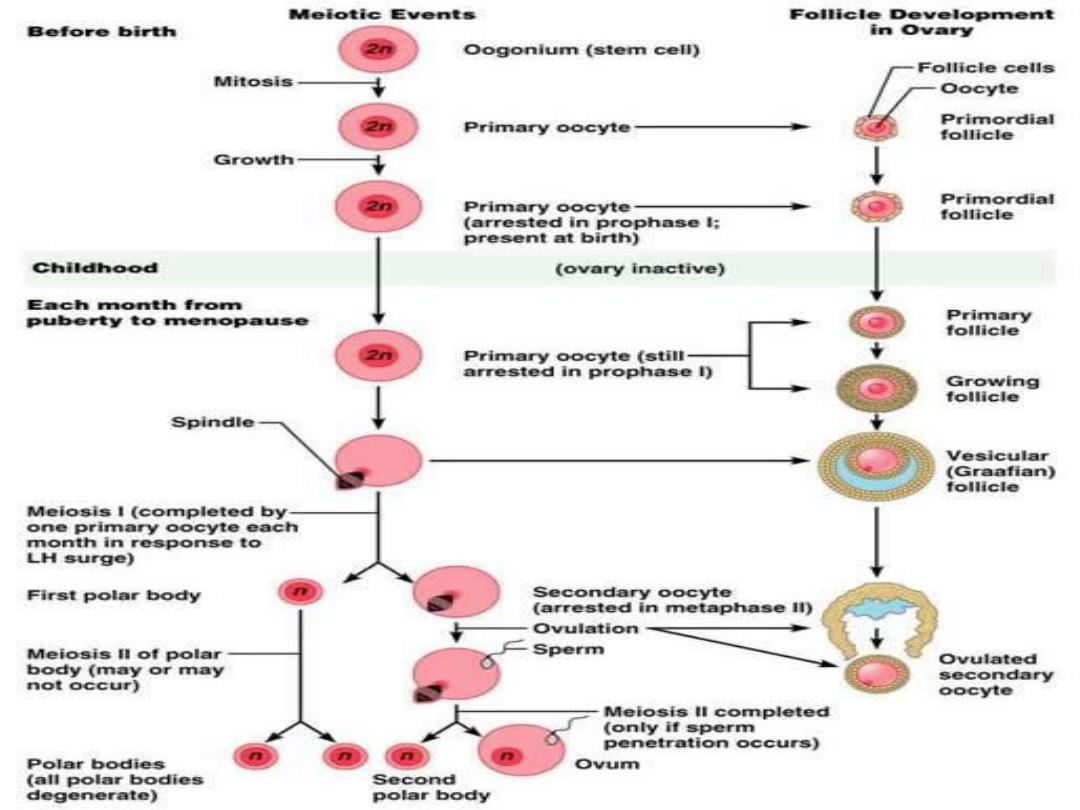
The
first meiotic division
start during the fetal
life and arrest at the
prophase
Just
before ovulation
the first meiotic division is
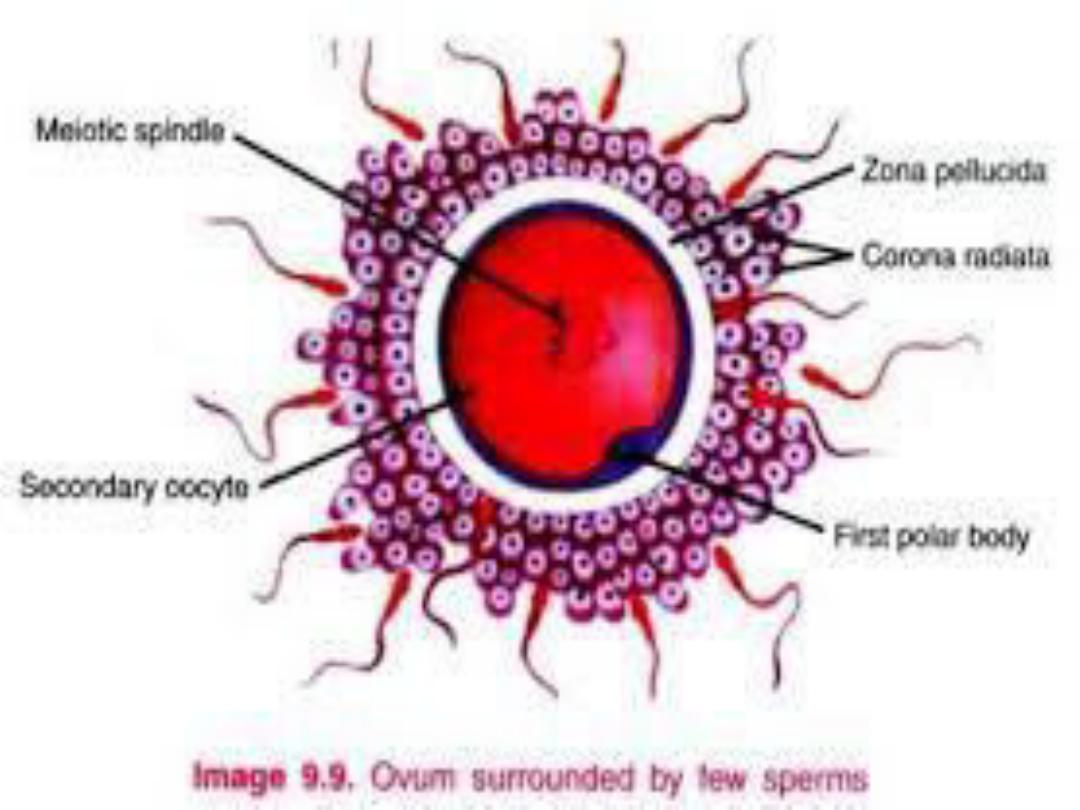
compeleted and the ovum divided in to
secondary oocyte which receive most of the
cytoplasm and 1
st
polar body, which disappear
Immediately the
secondary oocyte start 2
nd
meiotic division and stops at metaphase
and
compeleted only when the sperm enters the
oocytes (after fertilization)

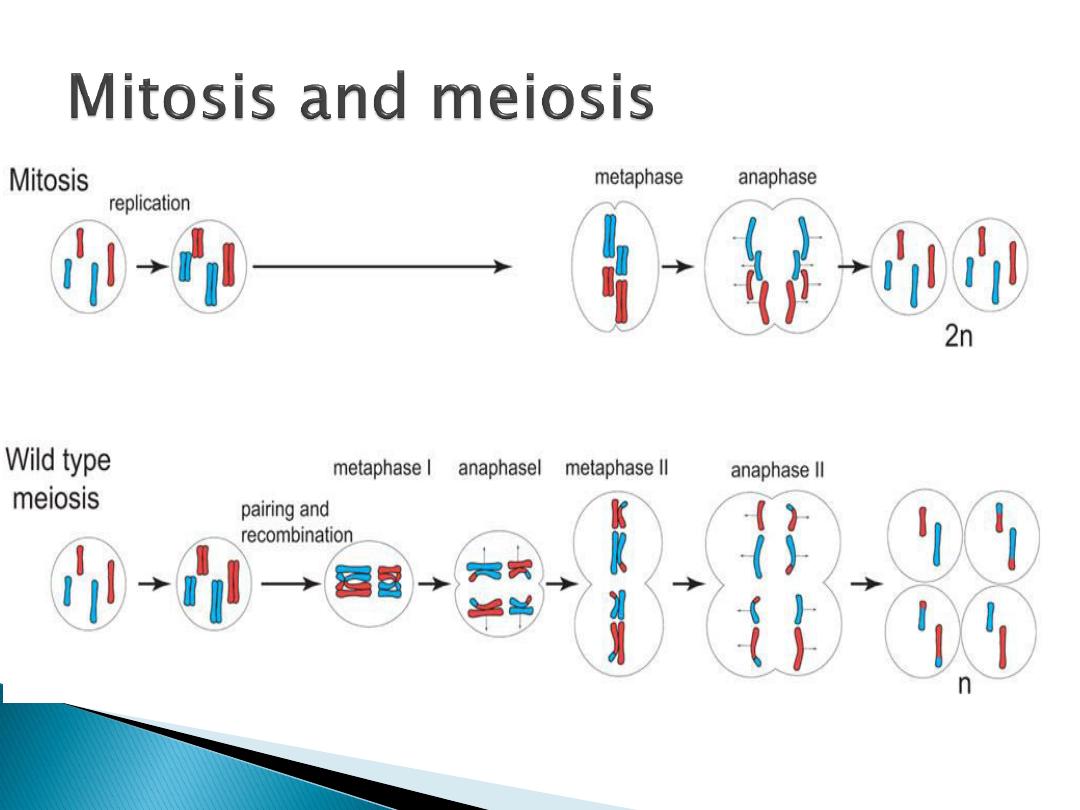
Meiosis I
separates the pairs
of homologous chromosomes,
reduces the cell from diploid to
haploid.
Meiosis II
separates each
chromosome into two chromatids
(chromosome behavior in meiosis
II is like that of mitosis)
.

At the end of menstruation, all but
the deeper layer of the
endometrium sloughed
The developing follicle secretes
estrogen which stimulate re
growing of a new endometrium this
phase of the cycle is called
proliferative or follicular

After ovulation the endometrium
become
more vascular edematous
the glands becomes tortuous
coiled
this phase of the cycle is called
secretory or luteal phase
The proliferative phase is variable
while the secretory phase is fixed
(
14days
)

It consist of
2 layers
, the
superficial
2 third
is called
stratum
functionale
which is supplied by
long coiled spiral arteries
this layer
is shed during menstruation the
deeper layer is not shed is called
stratum basale
is supplied by short
straight basilar
arteries

When the corpus luteum regress
the hormonal support for the
endometrium is withdrawn lead to
more
coiling spasm
and
degeneration of the wall of arteries
and areas of
necrosis
appear in the
secretary endometrium
and
menstrual flow start
The function of the
proliferative
endometrium is to restore the
epithelium from the preceding
menstruation
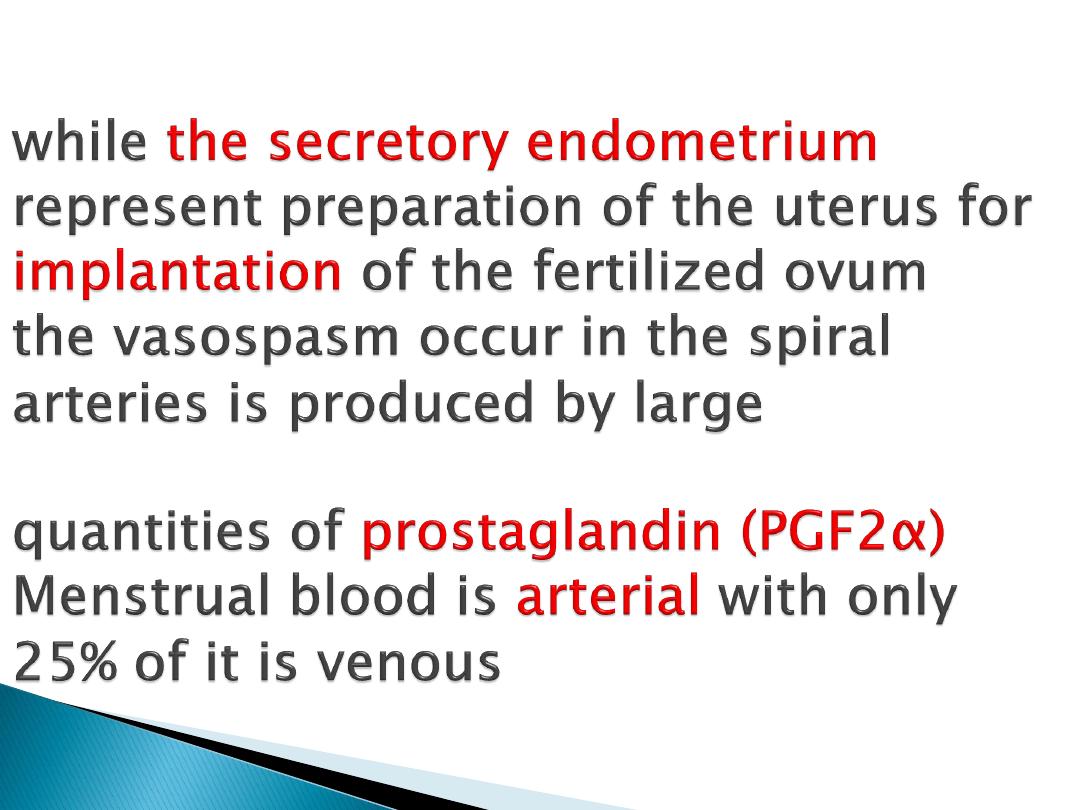

Menestrual blood contains tissue
debris, PG, and large amount of
fibrinolys
in which lyses so that
menestrual flow does not contain clots
unless its excessive
Usual duration is 3 to 5 days , but it
can as short as 1 day and as long as 8
days in normal women
the amount range between slight
spotting to 80ml
The average amount is 30ml

The mucosa of the cervix
does not
undergoes cyclical desequamation but
regular changes in the cervical mucosa,
oestrogen makes the mucus thinner
and
more alkaline which promotes survival and
transport of sperms,
progesteron makes it
thick tenacious
and cellular, at
mid cycle
the
mucous is thin (
spinnbarkeit
) which can be
stretched in to a thin long thread as long as
8-12cm

Oestrogen cause proliferation of the mammary
duct while progesterone cause growth of the
lobules and alveoli

FSH and LH are secreted from the
anterior pituitary,
FSH
is
responsible for early
maturation
of
the ovarian follicle while
FSH,LH
are
responsible for
final maturation
of
the Follicle .
LH
is responsible for
ovulation
and
initial formation of corpus lutium
and stimulate its secretion of
oestrogen and progesteron
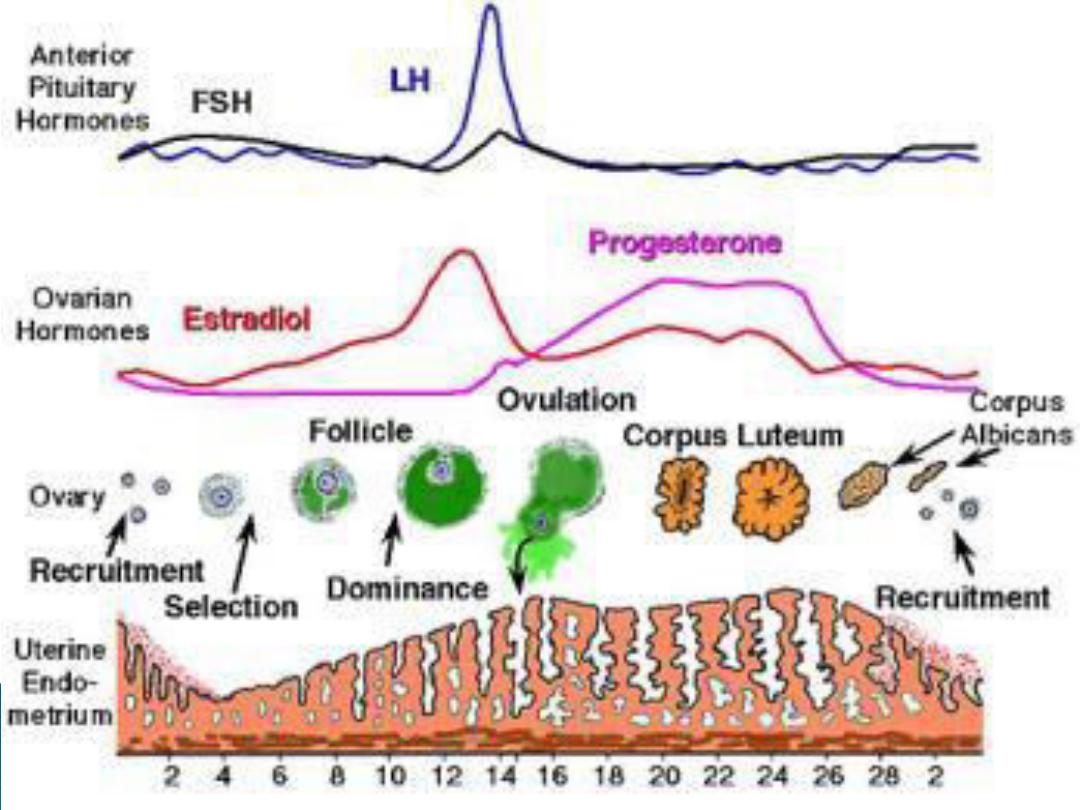

Its exerted by GnRH which is secreted in
the
portal hypophysial vessels
GnRH is secreted in episodic burst at a
rate of one pulse per hr. this will
stimulate the secretion of LH. the
frequency is increased by oestrogen
and decreased by progesterone and
testosterone, constant release of GnRH
lead to down regulation and LH
secretion declines to zero

At 36 to 48 hrs before ovulation the effect of
oestrogen become positive and inhance the LH
surge
Ovulation usually occur
9 hrs
after LH peak
Constant moderate secretion of oestrogen
exert negative feed back effect on LH secretion
, whereas an elevated oestrogen exert positive
feedback effect and stimulate LH secretion
High level of progesteron inhibit the positive
feed back effect of oestrogen

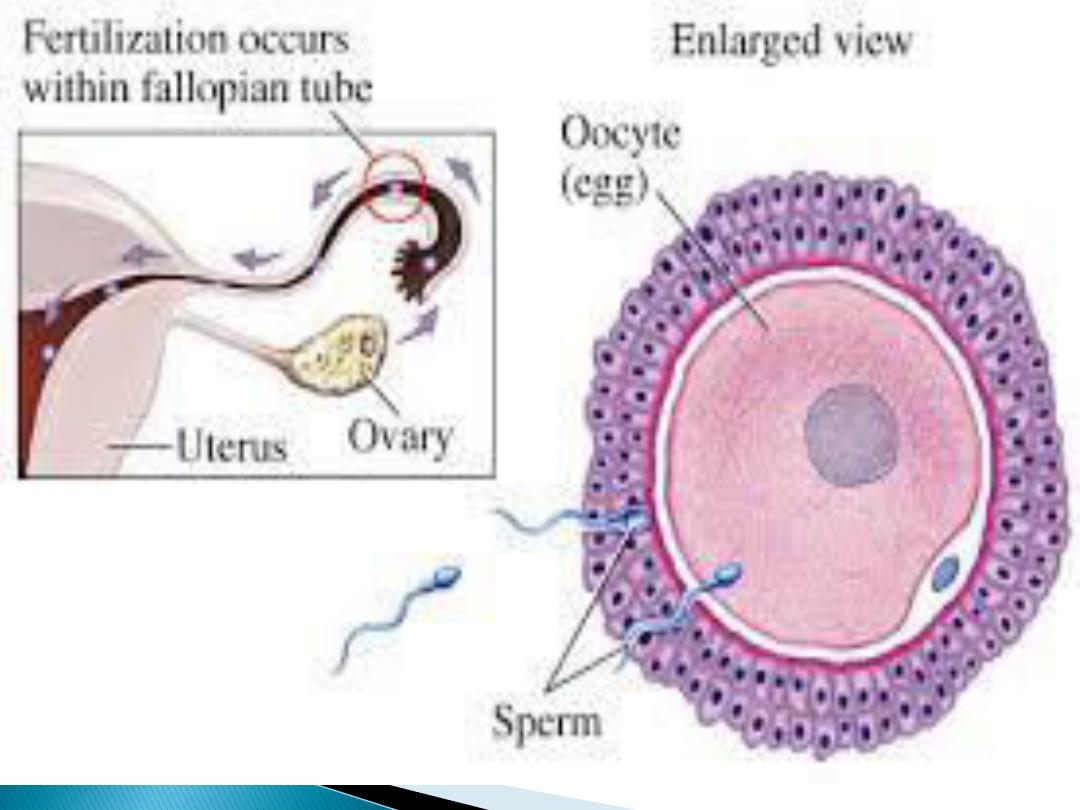
Fertilization of the ovum occur
in the
ampulla
of the uterine
tube It involves
1.
chemoatraction
and
adherence of the sperm to the
zona pellucida
of the ovum by
substances secreted by ovum

2. penetration of the zona
pellucida and acrosome reaction,
3. adherence of the sperm head to
the cell membrane of the ovum,
4. breakdown of the fusion area
5. sperm nucleus will be released
to the cytoplasm of the ovum
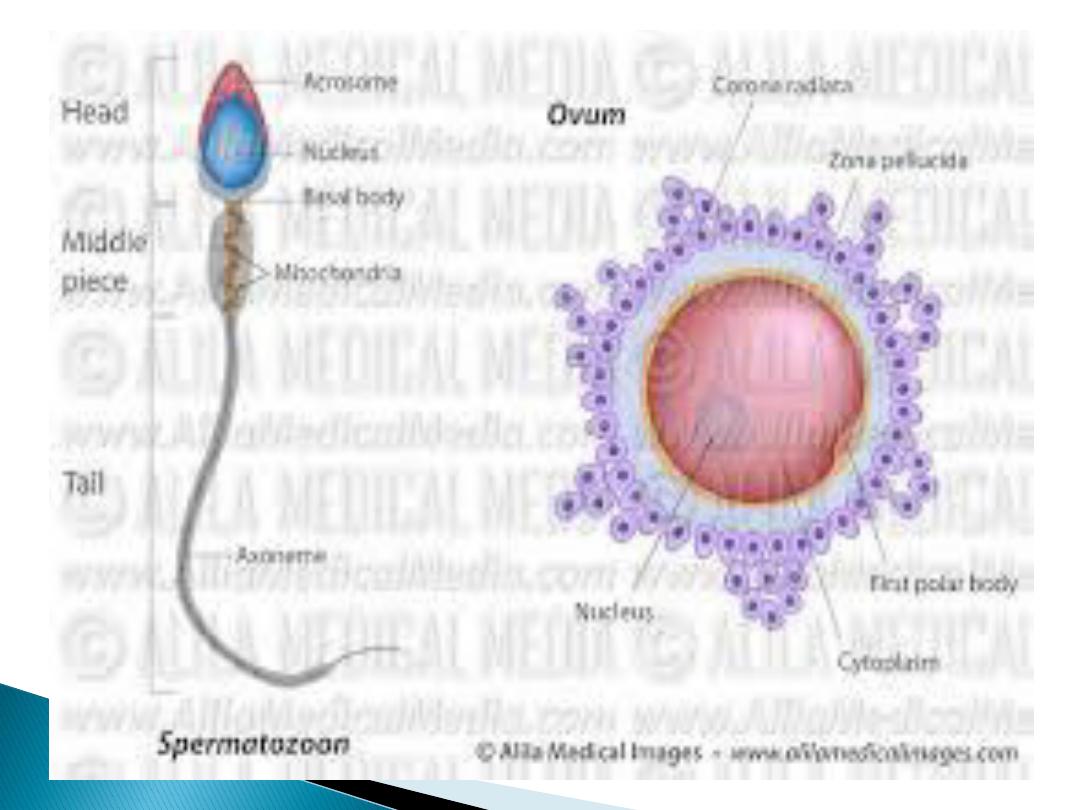
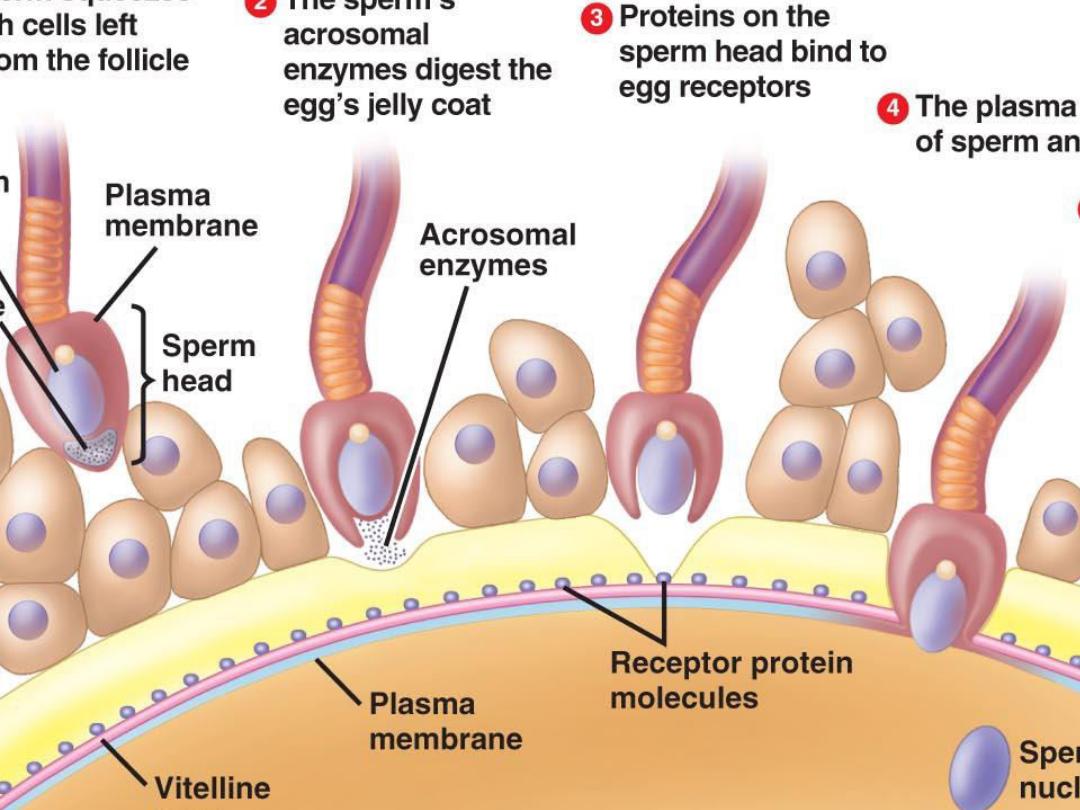

When one sperm enters the cell
membrane of the ovum, fusion of
the membrane occure to avoid
polyspermy
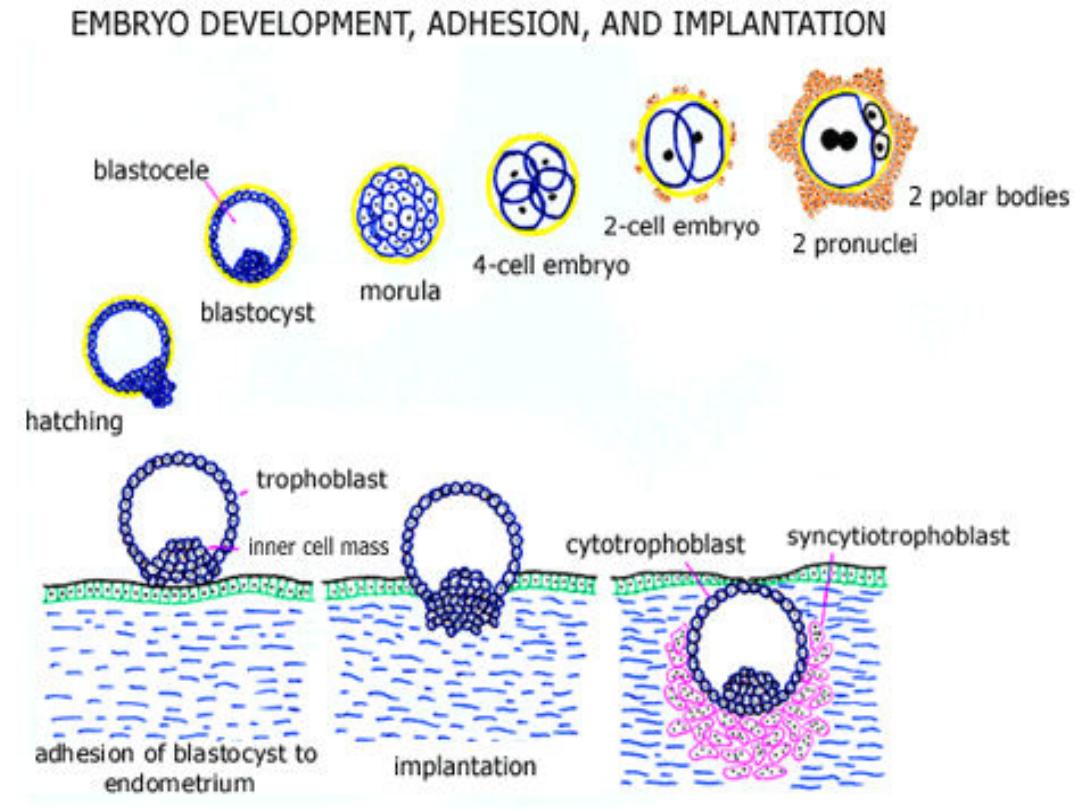
The fertilized ovum continue to
divide until it reaches the stage of
blastocyst
it moves down the tube
in to the uterus, this journy takes
3
days during which it reaches
8-16
cells

The
blastocyst
is surrounded by 2
layers , an
outer
syncytiotrophoblast
(mutinucleated mass with no
discernable cell boundaries) and
an
inner
layer of
cytotrophoblast
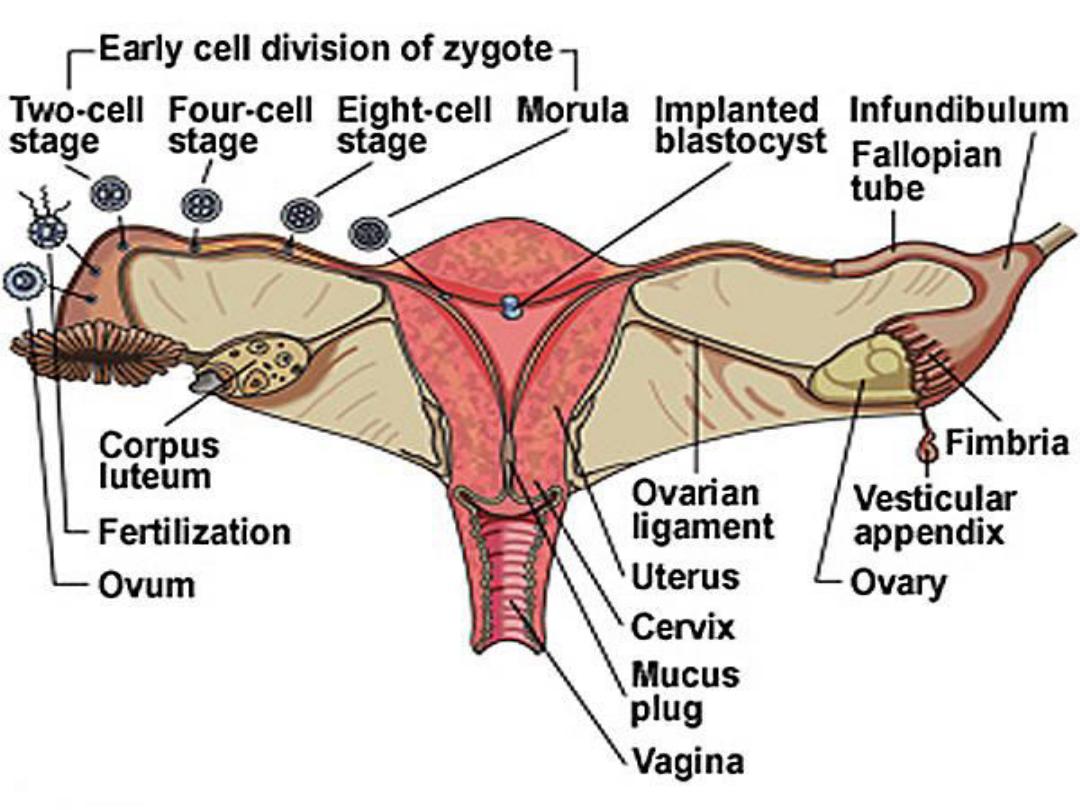
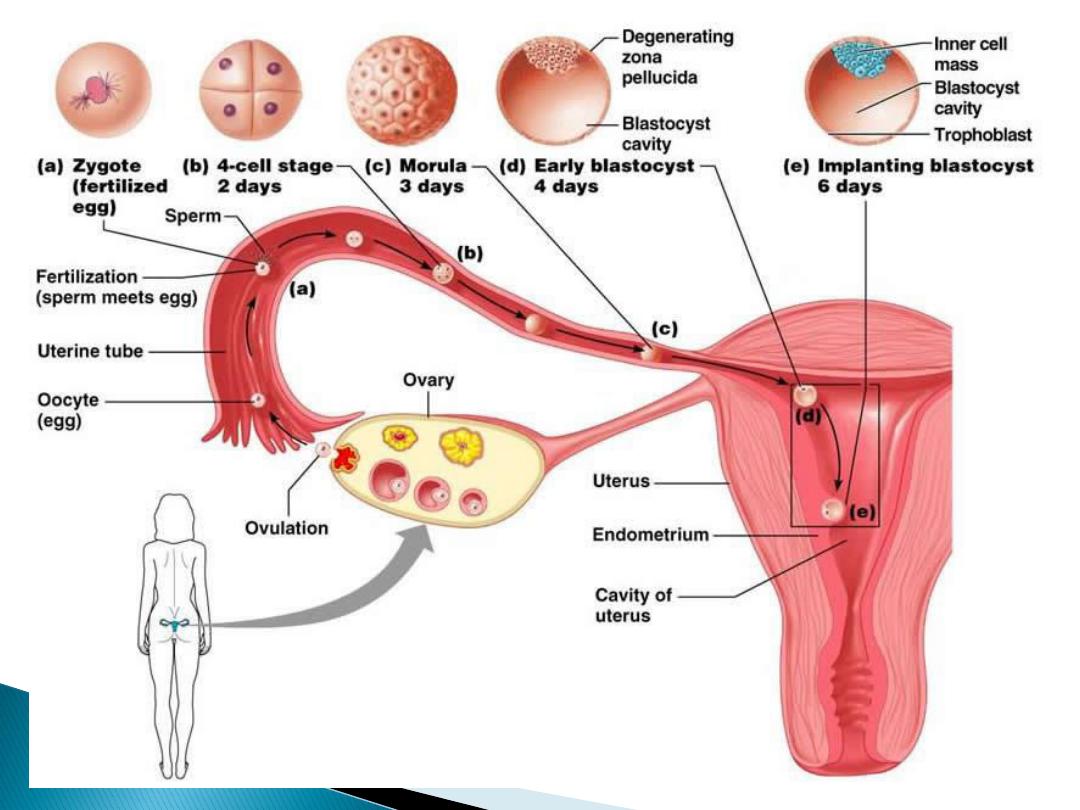

when syncytiotrophoblast erode
the endometrium and the
blastocyst burrows (
implantation
finish) which is on the dorsal wall
of the uterus

Corpus luteum fail to regress
instead it will be enlarges due to
response to stimulation by
gonadotropic hormone secreted by
the placenta which is called human
chorionic gonadotropin
(hCG)
.

The corpus luteum of pregnancy
secretes oestrogen, progesteron
and relaxin
Relaxin help to maintain pregnancy
by inhibiting myometrial
contraction,The function of corpus
luteum persist until 8 weeks

hCG
is a glycoprotien produced by
syncytiotrophoblast , its like any
other pituitary glycoprotien
hormones its made up of and
subunits . hCG
– is identical to
subunit of LH, FSH and TSH
hCG is primarily luteinizing and
luteotropic and little FSH activity
hCG can be detected in the blood
as early as 6 days after conception

The presence of hCG in
urine is the basis for
laboratory test for
pregnancy
hCG is not absolutely
specific for pregnancy
some ovarian and
GIT
tumors secretes hCG

During pregnancy fetus and
placenta interact in the formation of
steroid hormones , some of
placental progesteron enters the
fetal circulation and provide
precursor for cortisol and
corticosterone in fetal adrenal
gland

Some of pregnenolone enters the
fetus with pregnenolone
synthsised in the fetal liver it will
form substrate for the formation
of DHEAS which is a precursor for
oestradiol and 16-OHDHEAS as
aprecursor for estriol

Duration of pregnancy 284 d from
the first day of last menstruation
Increase contraction of utrus in last
month
Cervix softens &dilated
Increase circulatory estrogen
Increase PG
Increase ACTH , CORTSOL
(maturation of respiratory system)
Increase oxytocine receptor

Uterine contraction
Dilated cervix
Increase oxytocin act directly on
uterine muscle.
Stimulate formation of PG
Spinal reflex &voluntary
contraction of abdominal muscle
(bearing down)
؟؟

during pregnancy
prolactine level increase
Milk start from 5th month
Surge 1-3day to come in
After expulsion of placenta ,
decrease in estrogen & progesterone
Initiate lactation
Suckling evoke reflex oxytocine
release milk ejection maintain
secretion of milk by stimulation
prolactine secretion

Prolactin & estrogen in breast
growth
Estrogen inhibit milk production
Woman who do not nurse their
infant , menstruate 6 month after
delivery
If nurse regularly develop
amenorrhea for 25-30 week
Prolactine inhibit GnRH , estrogen
& progesterone , inhibit ovulation
