
Lec.4
Pediatrics
6
th
stage
2016/8/28
Session notes
د.ربيع الدبوني
Werdnig-hoffmann disease(SMD):
Progressive degeneration of AHC (anterior motor horn cell ) .
3 types(early type WHD) , (late type Kugelberg-Welander syndrome) ,
intermediate type).
Autosomal recessive.
WHD:start as progressive proximal weakness , ↓spontaneous
movement , floppiness , atrophy of muscles , loss of head control ,
drooling , ↓ facial expression ,loss of reflex , eyes remain bright open ,
engaging , tongue fasciculation(sleep) normal mentality , language ,
sensation
Cause of death: respiratory infection , respiratory failure.
Diagnosis:CPK↑, EMG.
TREATMENT :CONSERVATIVE
Hypotonia occur in :
1-Surgical cut of nerve
2-Diabetes mellitus
3- B complex deficency
4- myaesthania gravis
In the first week hypotonia is unusual
In case of cerebral palsy hypotonia can occur at first early life
And then changed to either spastic paralysis or still in hyopotonic
pattern
The death is due to respiratory failure infantile death
All lesion result in hypotonia + hyporelfexia
In case of UMNL it result in hypotonia + hyporeflexia
On Exam :
-hypotonia in ventral suspension
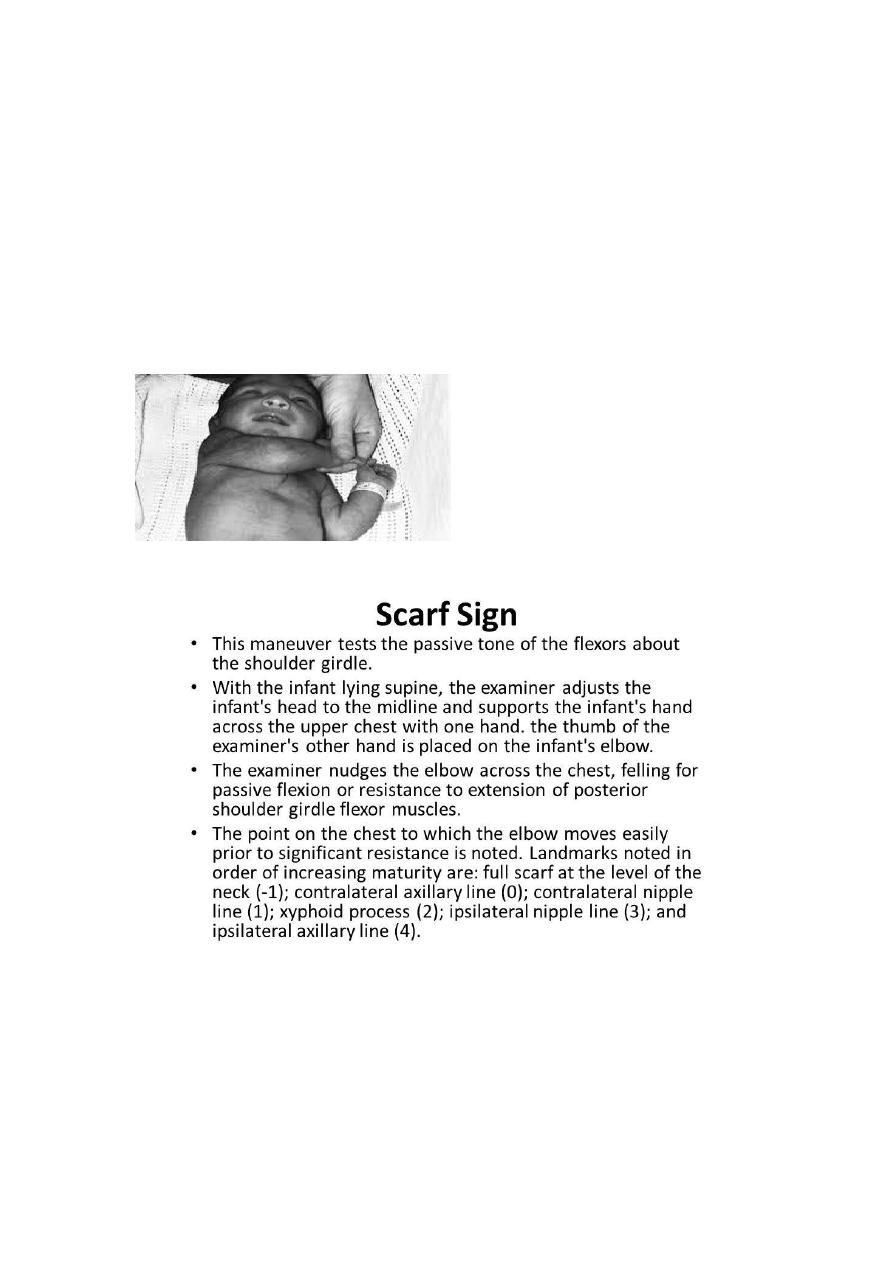
- scarf sign
Both Elbow meet on the back
-heel reach and touch the ear lobule ( Heel – Ear test )
- Sun set sign during hands rising up
Prognsis : it is lethal disease
25% of sbling affected , 50% carrier , 25 % normal
Adivce family to avoid conaguinity marriage
Notes :
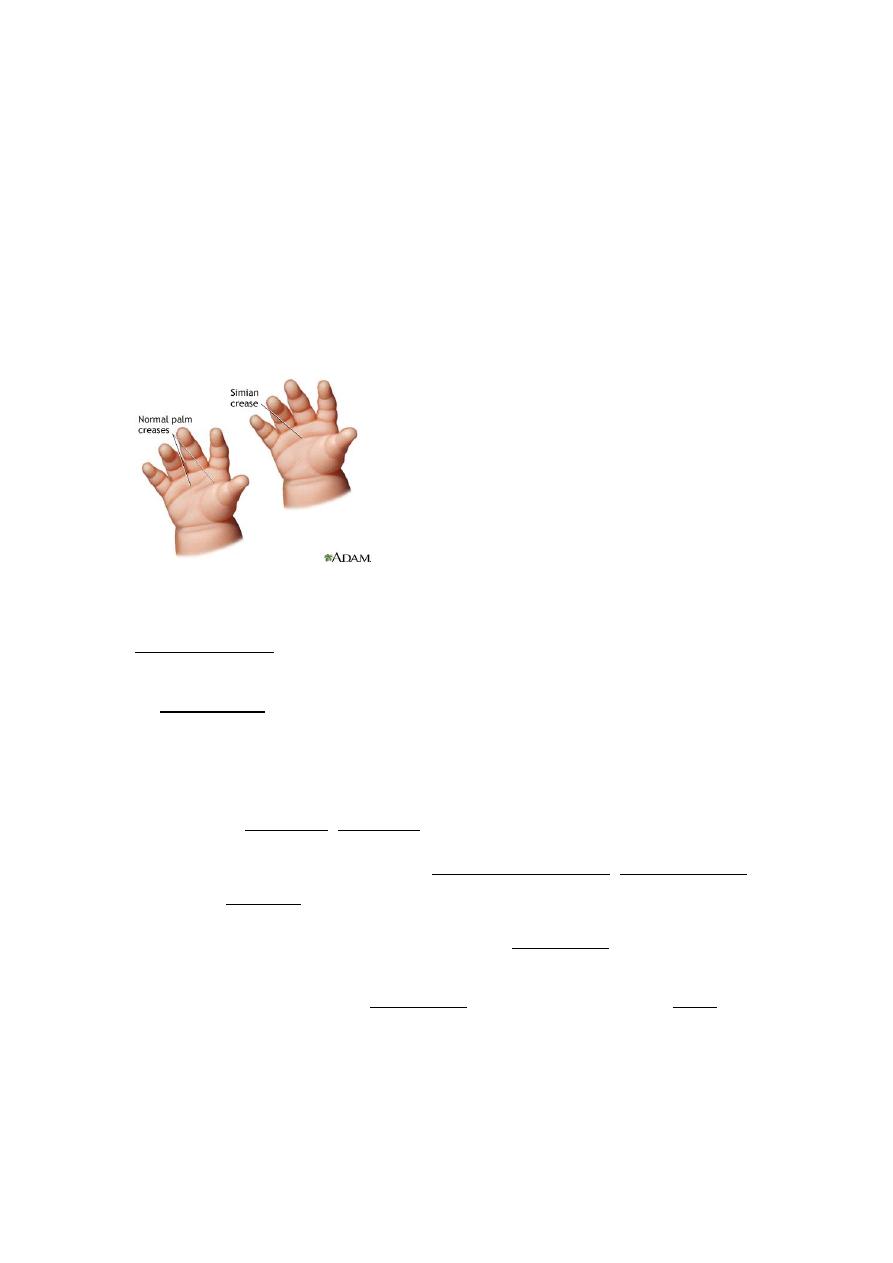
Simian creases is a normal finding
# Heat exhaustion
Heat exhaustion is a heat-related illness that can occur after you've been
exposed to high temperatures, and it often is accompanied
by dehydration.
There are two types of heat exhaustion:
Water depletion. Signs include excessive
thirst, weakness, headache, and loss of consciousness.
Salt depletion. Signs include nausea and vomiting, muscle cramps,
and dizziness.
Although heat exhaustion isn't as serious as heat stroke, it isn't
something to be taken lightly. Without proper intervention, heat
exhaustion can progress to heat stroke, which can damage the brain and
other vital organs, and even cause death.
Symptoms of Heat Exhaustion
The most common signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion include:

Confusion
Dark-colored urine (a sign of dehydration)
Dizziness
Muscle or abdominal cramps
Pale skin
Profuse sweating
Rapid heartbeat
Treatment for Heat Exhaustion
If you, or anyone else, has symptoms of heat exhaustion, it's essential to
immediately get out of the heat and rest, preferably in an air-
conditioned room. If you can't get inside, try to find the nearest cool and
shady place.
Other recommended strategies include:
Drink plenty of fluid (avoid caffeine and alcohol).
Remove any tight or unnecessary clothing.
Take a cool shower, bath, or sponge bath.
Apply other cooling measures such as fans or ice towels.
If such measures fail to provide relief within 15 minutes, seek emergency
medical help, because untreated heat exhaustion can progress to heat
stroke.

After you've recovered from heat exhaustion, you'll probably be more
sensitive to high temperatures during the following week. So it's best to
avoid hot weather and heavy exercise until your doctor tells you that it's
safe to resume your normal activities.
Notes on general exam :
Check for :
-position
-consiounesss
-respiratory condition
-color :
1-pale : check the eye and palm
2-cyanosis : central and peripheral , clubbing , heart
3-rash : distrunution , nature of rash
4-jaundice
-reaction to examiner
-state of hydration
- state of nutrition
- vital sign
Cervical and inguinal LN is recurrently enlarged in the infancy
Due to infection
Axillary LN is impt. During exam if there is any LAP , sometimes is
enlarged due to BCG vaccine

Notes :
Dont mix egg with iron it will be non-absorbable in the intestine
Milk + iron = non-aborbable complex
Green leafy vegetable contain iron but is non-absorbable
Because it is ferric
Physiological need of iron :
On Exam check for nutritional status by :
Fat and carbohydrate check for wasting
Protein check for edema
Mineral and vitamins check for rickets
Water check for dehydration

Anemia :
Normal retics is 0.2-2%
When increase indicate BM compensation
Differential diagnosis of Anemia :
1-iron def. Anemia ( serum ferritin test )
2-Thalassemias Hemoglobin electrophoresis with quantitative
hemoglobin A2 and hemoglobin F
3-sidroblastic anemia
4-lead poisoning porphyrin in urine test
5-anemia of chronic disease
6-Hodgkin dis take biobsy
7-Atransferrin anemia ( congenital loss of iron binding protein )
Ancylostoma Duodenale :
If pateint has iron def anemia and not respond to Tx check
Ovum is D-shape / Tx :
