Chapter 3 – Epidemiology of infectious diseases (Parasites & Scabies)
196
“” Helminthes infection (In general) “”
Introduction
Infection:
The entry and development or multiplication of an infectious agent in the body
of man or animals.
Infestation:
Development and reproduction of arthropods on the surface of the body, e.g.
lice, itch mites, or gut parasite e.g. Ascariasis.
The word "helminth" is derived from the Greek "helmins" (worm). Helminthology is
the study of parasitic worms
Important parasitic infection, world-wide distribution: Ascaris, Ancylostoma, Hydatid
cyst & schistosoma are most important
They affect man by:
1- Physical presence in organ. e.g. Fasciola hepatica.
2- Produce lesion by their mass effect. e.g. Hydatid cyst.
3- Competition for nutrition. 4- Loss of blood. 5- Allergy.
Helminth: A worm classified as a parasite. (A parasite is a disease-causing organism that
lives on or in a human or another animal and derives its nourishment from its host.)
Lice are examples of parasites that live on humans; bacteria & viruses are examples of
parasites that live either on humans or in humans; helminthes are examples of parasites
that live in humans. Helminth eggs contaminate food, water, air, feces, pets and wild
animals, and objects such as toilet seats and door handles. The eggs enter the body of a
human through the mouth, the nose and the anus. Once inside the body, helminth eggs
usually lodge in the intestine, hatch, grow & multiply. They can sometimes infest other
body sites.
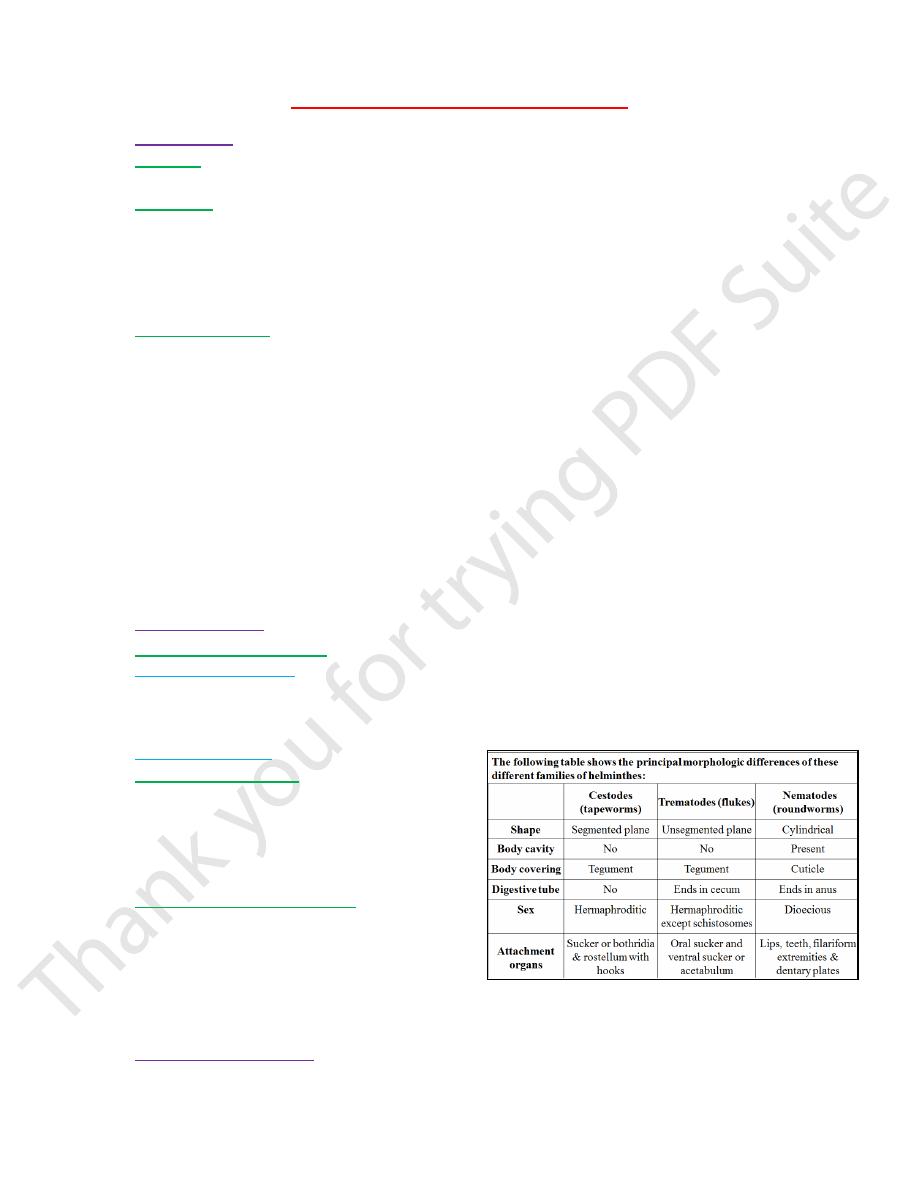
Classified into:
1) Nematodes (Round worm):
A) Intestinal nematode;
- Ascaris. - Hook worm (Anchylostoma and Necator American).
- Trichuriasis, Tricurus Trichura (Whip worm). - Strongyloides.
- Entrobiasis (Thread worm, Pin worm, Oxyuriasis). - Trichinosis (Trichinella Spiralis).
B) Tissue nematode;
E.g Fliariasis
2) Cestodes (Tape worm):
- Taena saginata (Beef tape worm).
- Taeni Solium (pork tape worm).
- Echonococciasis (Dog tape worm, Hydatid cyst).
E.g. E. granulosus, E. multilocularis.
- Diphyllobotheriasis latum.
3) Tramatode (Flat worm, Fluke).
- Blood fluke (Schistosomaiasis, Bilharziasis). E.g.
S. haemotobium, S. Mansoni, S. Japonicum.
- Intestinal fluke. E.g. Fasciolopsis buski.
- Liver fluke. E.g. Fasciolahepatica.
- Lung fluke. E.g. Paragonimus westermani.
Intestinal helminthes
are a type of intestinal parasite that resides in the human GIT. They represent one of the
most prevalent forms of parasitic disease. Scholars estimate that over a quarter of the

Chapter 3 – Epidemiology of infectious diseases (Parasites & Scabies)
197
world’s population is infected with an intestinal worm of some sort, with roundworm,
hookworm, and whipworm infecting 1.47 billion people, 1.05 billion people & 1.30
billion people, respectively Furthermore, the World Bank estimates that 100 million
people may experience stunting or wasting as a result of infection.
Because of their high mobility and lower standards of hygiene, school-age children are
particularly vulnerable to these parasites.
Overall, it is estimated that 400 million, 170 million, and 300 million children are
infected with roundworm, hookworm & whipworm. Children may also be particularly
susceptible to the adverse effects of helminthes infections due to their incomplete
physical development & their greater immunological vulnerability.
Dx, Treatment & prevention of helminth diseases
Dx of helminth diseases in humans
Usually requires a medical hx & physical examination, a laboratory analysis of stools &
sometimes other tests.
Treatment in most cases
involves the use of highly effective anti-worm drugs known as
vermifuges that kill the worms.
Prevention of helminthes diseases
usually requires frequent washing of hands, frequent
cleaning of bathrooms and kitchens, and thorough cooking of the foods they infest --
mainly beef, pork, sausage & bear meat. Water supplies should be chlorinated, if possible.
Common helminths & the problems they cause include the following:
1) Nematodes (Roundworm):
Hatch and live in the intestines. Eggs usually enter body through contaminated water or
food or on fingers placed in the mouth after hands have touched a contaminated object.
Symptoms of their presence include fatigue, weight loss, irritability, poor appetite,
abdominal pain and diarrhea. Treatment with medication results in a cure in about a
week. Without treatment, anemia and malnutrition can develop.
Intestinal Nematodes:
o
Ascariasis
: Transmission by eating eggs of Ascariasis that contaminate in the ground.
Habitation of Acariasis is in the small intestinal. The patients will present the symptoms
in the diseases of intestinal obstruction, liver abscess, billary ascariasis and ascaris
pneumonia. diagnose include: stomach X-ray, examine the eggs & mature of Acariasis in
stool. The medications for treatment are albendazole, mebendazole, and levamisol
o
Pinworm:
Also called seat worms and threadworms, pinworms hatch and live primarily
in the intestines. The eggs usually enter the body through the anus, through the nose or
mouth via inhaled air, or through the mouth on fingers that have touched a contaminated
object. Symptoms of their presence include anal itching and sometimes pale skin and
stomach discomfort. If pinworms enter the vagina in females, discharge and itching may
develop. Pinworms do not cause serious complications. Treatment with medication
results in a cure within days
o
Trichurisis:
mature of Trichurisis is found in large intestine. Transmits to the body by eat eggs of
Trichurisis. It would be no symptom if it is light infection but in heavy infection may
present the symptoms of hemorrhage, mucopurulent stool, dysentery with rectal
prolapsed. Diagnosis Trichurisis infection by examine stool of patients and proctoscopy.
Medication should be taken are mebendazole 100mg, 3 times a day for 3 days. Or the
single dose of albendazole 400 mg.
