
Tuesday, August 23, 2016
DR.Ahmed (urology 5)
1
هذه مالحظات على السشن يرجى الرجوع لملزمة ال
urology
لتكملة المعلومات
Associated symptom with renal colic ---GIT symptoms
1-The most imp. One ---nausea (typical symptom )
2-freq. vomiting
3-appetite -----is preserved In pure stone wlt out
infection
Pathogenesis of GIT symptom
1-sort of venisity(by near) adjacent GIT structures
affected
2-Sharing of Nerve supply(sympathetic + vagus)
-----constitutional
1-feeling of tiredness
2-fever—if there is infection ((alarming sign in pt with
colic =may be pyonephrosis)
How to approach a patient with a renal renal colic ?
1-Hx
2-EX:---General examination = vital signs
Hydration status= bz of vomiting and we need it in Mx & Px
--Local ex. Of abd.
1-inspection(movement with respiration)
2-palpation
-Tenderness in costorenal angle (Murphy pinse sign).
-any palpable mass (hydronephrosis )
-palpable bladder(due to irritable bladder-retention –destension)+dull note on
percussion
- Genitalia=external meatus of penis + any stone in urethra
PR exam in male & pv in female
-
- Back(renal angle tenderness)
Indication of admission in renal colic
1-dehydrated pt
2-suspected pyonephrosis
3-bilateral obst.
4-refractory pain
5-features of uremia
6-pt with solitary kidney
7-pt with comorbidity
8-extreme of age
9-pregnancy(relative)
10-specific condition like passenger to distant
area

Tuesday, August 23, 2016
DR.Ahmed (urology 5)
2
Instigations
Note :before invasigation : make pt pain-free by analgesics
1-Lab. ect
2-imaging ect
PH is imp.
-acidic urine mean (ca-oxalate & uric stone & cysteine stone)
-alkaline =MAP & ca-phosphate
Adv. Of u/s
1-
exclude extra-renal problem, site, hydronephrosis, radiolucent
stone (uric acid, xanthine, drug stone).
2-doppler for jet of urine to blader from ureter(normally =2jet /min)
Drug of choice is NSAID
-diclofeac inj(IM)
C/I
1-absolute:asthma +PU
2-relative :uncontrolled HT
HF
RF
*SE:impairment of renal function
line is Nargotic :pethidine
nd
2
C/I :Resp. failure mau pass to apnea
-Analgesia
pethedin because it has no antispasmodic
action
stone clerance
،،
اللي نعتمد عليها بل
if not useful give
tramadol if not useful give morphine
(analgesia + ant spasmodic action)
كلهم معاهم
الزم نعطي
anti emmitics..acetaminophine
usful in maintinance only
بعد كل هاي من يقل ال
pain
نبدي
inv.
ال
stone
اللي ما تبين بل
ct
هيه
some drug
stones such as antiretroviral drugs
INVx of choice is plain CT-SCAN
-
-advantage of CT
1-stone seen 90%
2-Exrarenal pathology
3-state of kidney(grade of hydronephrosis)
4-rapid 5-cost-effective 6- no contrast
needed
Shape
-enveloped
spiky needle shaped
-
-hexagonal
also there is
coffin shape
amorphous or non specific
shapes
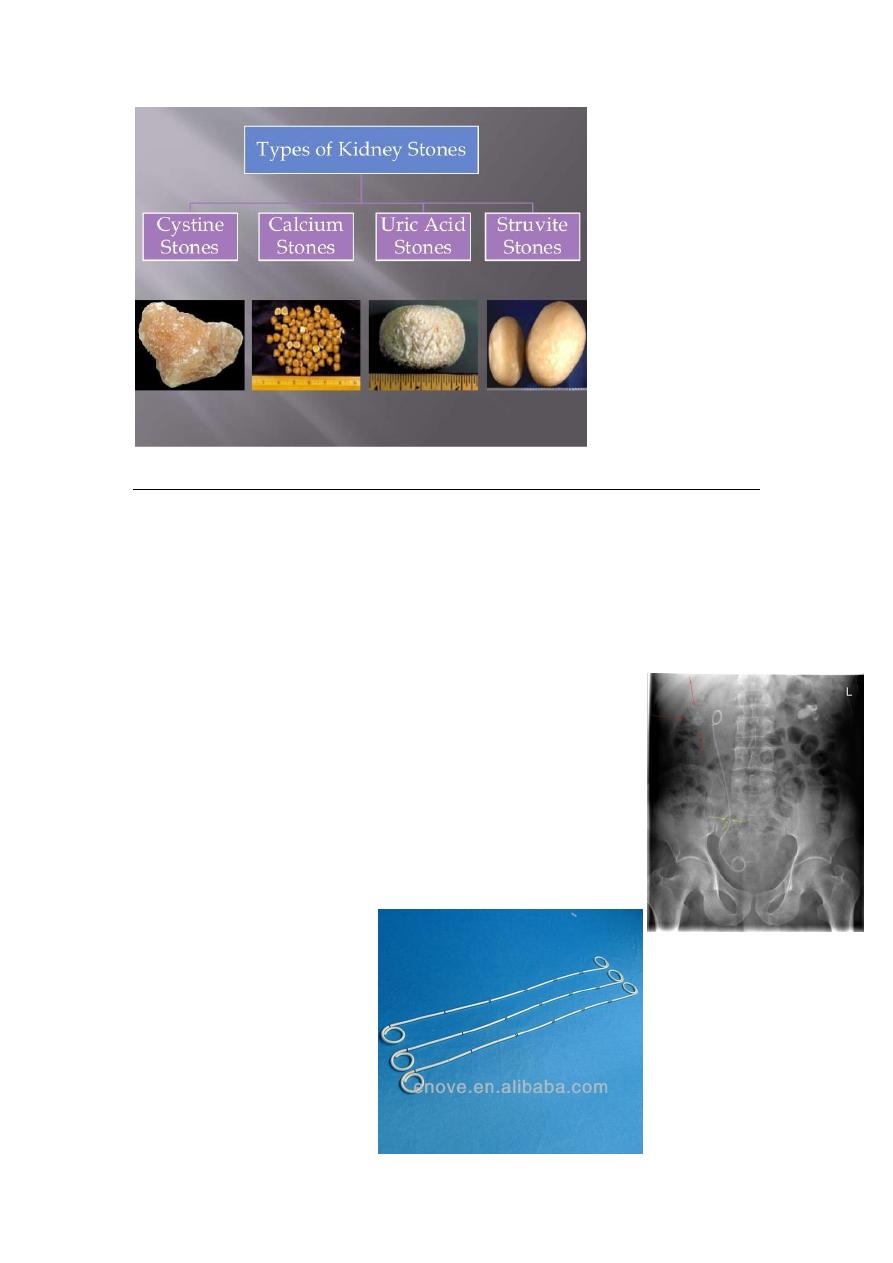
Crystal types
1-oxalate=
uric acid
-
2
crystals
3-cystein
4-MAP
Tuesday, August 23, 2016
DR.Ahmed (urology 5)
3
Rx
Notes: 1-expolsive therapy
expulsive therapy
encourage to drink plenty of water e.g(patient 70k=3_4 lt/24 hr)
movement also will help and alpha 1 blocker
NSAIDs for pain
ca channel blocker
steroid inj. methylprednisolone( depo medrol)
and antibiotics not used unless there is infection.
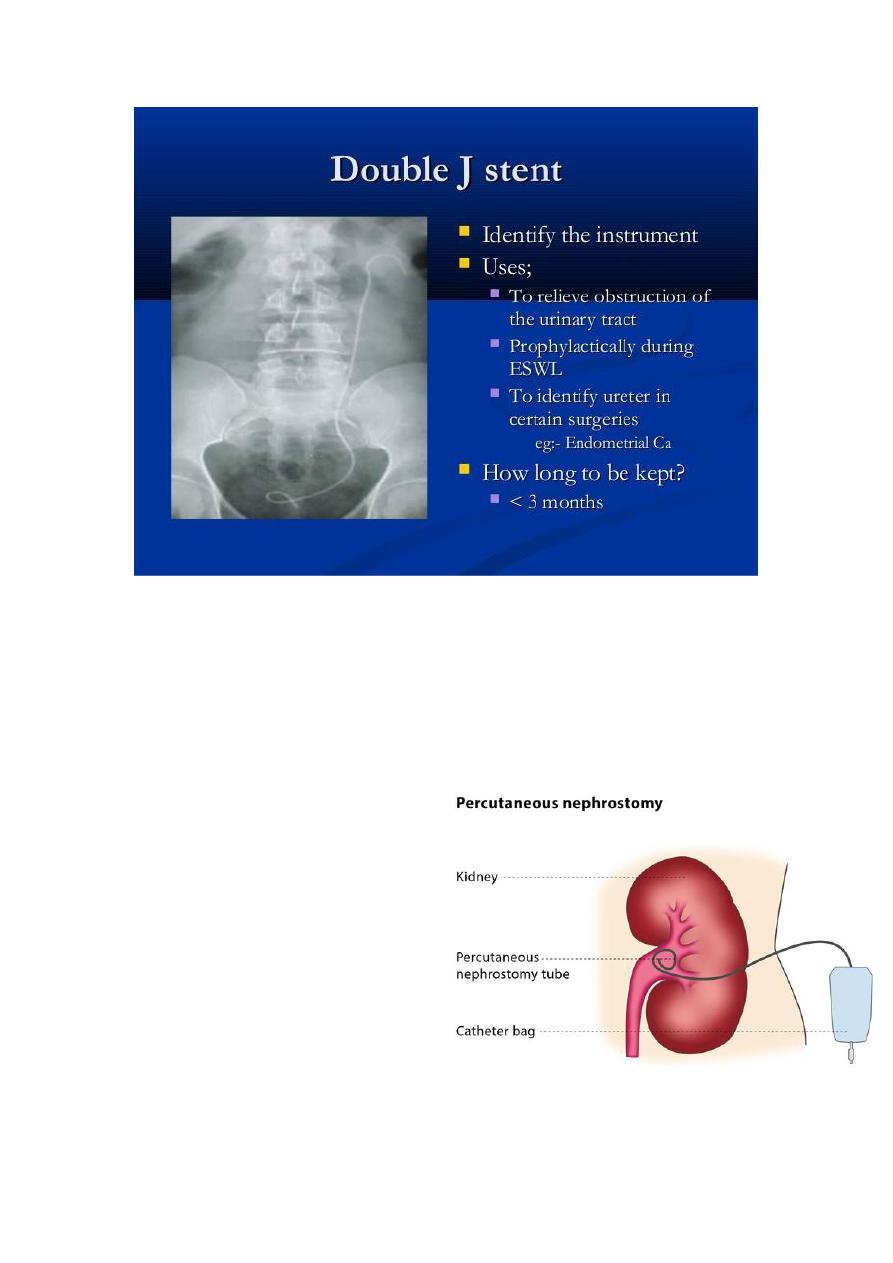
2-temporary diversion -either internal or external
Internal=Double JJ ( J stent,double J stent or pig-tail stent).
Indx : but to relieve pain and drainage of fluid above obstructing stone
Adv. =no open to outside
Disadvantage –stone formation + removal under anaestheasia
Tuesday, August 23, 2016
DR.Ahmed (urology 5)
4
External =Nephrostomy
-A nephrostomy is an artificial opening created between the kidney and the skin which
allows for the urinary diversion directly from the upper part of the urinary system.
Adv.=done under local anaesthesia + return of peristalisis and passage of stone + removal
need no GA
Disadv.=open to outside so risk of
infection
3-Definitive Rx
Indication of Double JJ ??
Indication of Double JJ in ESWL
1-infection 2-large stone 3-solitory
kidney
*permminnt DJJ only in malignancy
8in preg. Change it freq. ly to avoid ca-
stone formation
Complication of DJJ

Tuesday, August 23, 2016
DR.Ahmed (urology 5)
5
1-perforation of ureter
2-crastetic =neuclus of stone formation(esp. in preg.)
3-infection
4-irritative
5-needs GA+endoscopy for removal & insertion
