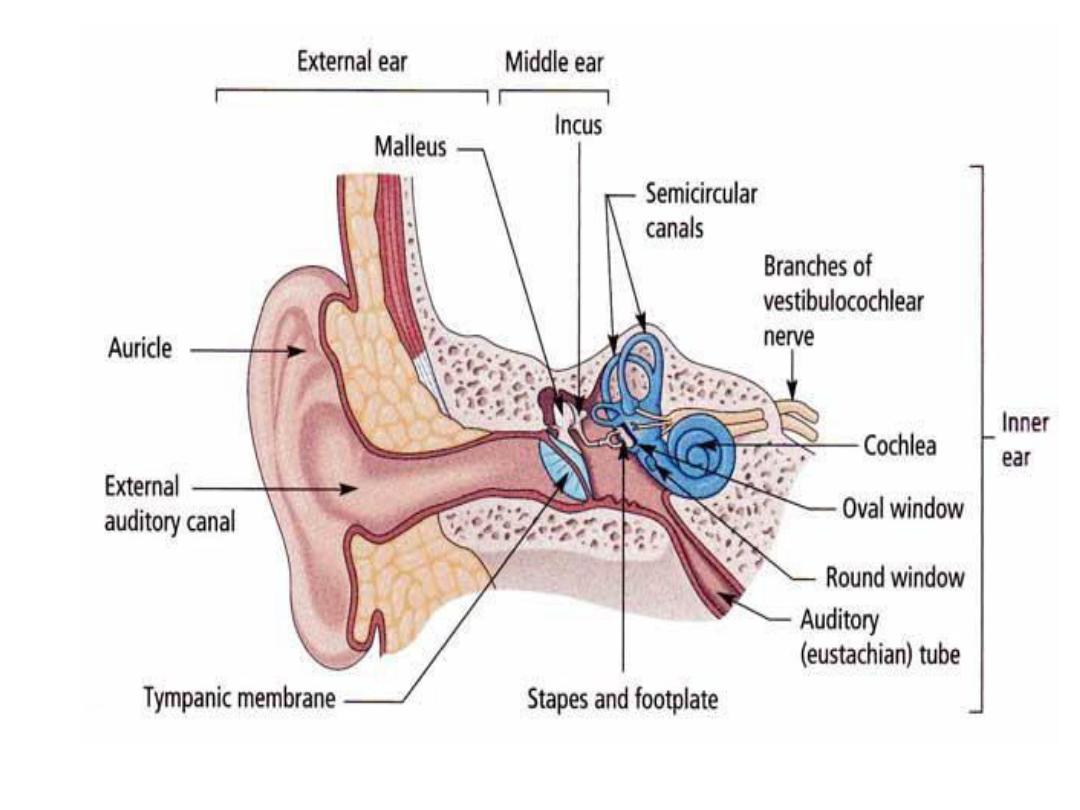
Ear & Eye

• The ear consists of three parts that have different
origins but that functions as one unite.
• The internal ear originates from ^ otic vesicle
which in ^ 4
th
week of development detaches
from surface ectoderm.
• This vesicle divides into a ventral component,
which gives rise to ^ saccule & cochlear duct and
a dorsal component, which gives rise to ^ utricle,
semicircular canals, & endolymphatic duct.
• The epithelial structures thus formed are known
collectively as ^ membranous labyrinth.

• Except for ^ cochlear duct, which forms ^ organ of
Corti, all structures derived from membranous
labryrinth are involved with equilibrium.
• The middle ear, consisting of ^ tympanic cavity &
auditory tube, is lined with epithelium of
endodermal origin & derived from 1
st
pharyngeal
pouch.
• ^ auditory tube extends between ^ tympanic cavity
& nasopharynx.
• The ossicles, which transfer sound from ^ tympanic
membrane to ^ oval window, are derived from ^ 1
st
(malleus & incus) & 2
nd
(stapes) pharyngeal arches.

• ^ external auditory meatus develops from ^ 1
st
pharyngeal cleft & is separated from ^ tympanic
cavity by ^ tympanic membrane (eardrum). ^
eardrum consists of (a) an ectodermal epithelial
lining. (b) an intermediate layer of mesenchyme,
(c)an endodermal lining from ^ 1
st
pharyngeal
pouch.
• ^ auricle develops from six mesenchymal hillocks
along ^ 1
st
& 2
nd
pharyngeal arches. Defects in ^
auricle are often associated with other congenital
malformations.

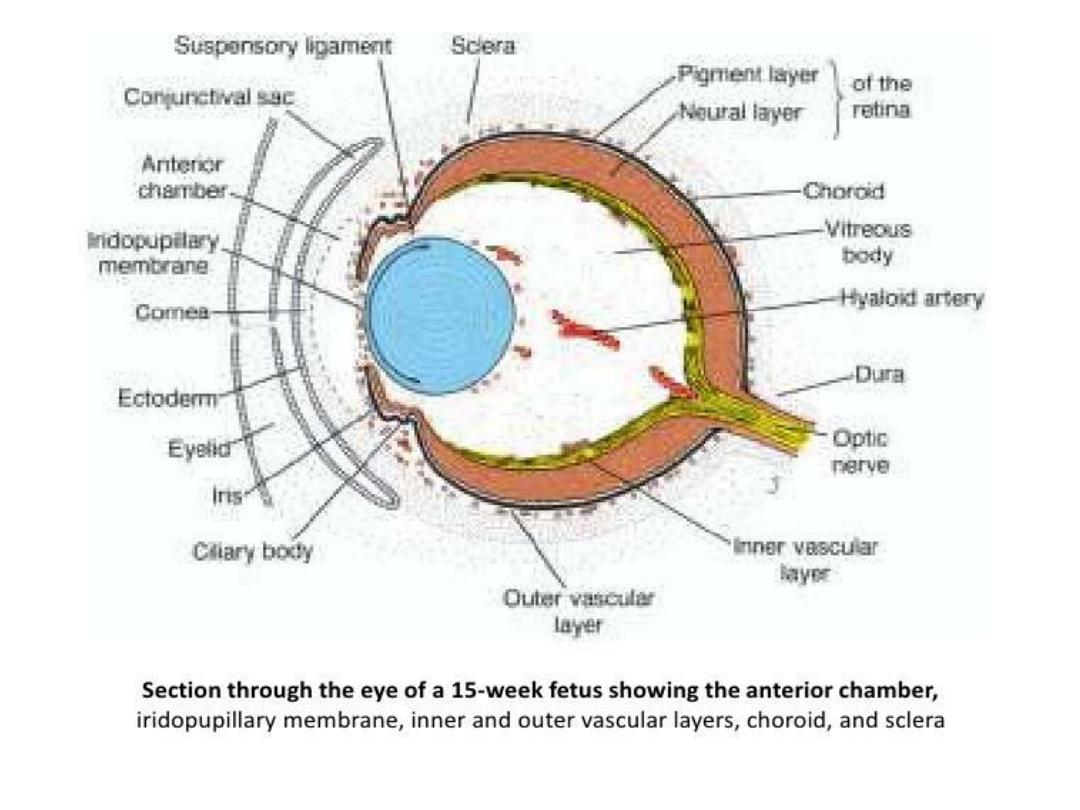
Eye
• The eyes begin to develop as a pair of out-
pocketings that will become ^ optic vesicles on
each side of ^ forebrain at ^ end of ^ 4
th
week of
development.
• ^ optic vesicles contact ^ surface ectoderm &
induce lens formation.
• When ^ optic vesicle begins to invaginate to form
^ pigment & neural layers of ^ retina, ^ lens
placode invaginates to form ^ lens vesicle.

• Through a groove at ^ inferior aspect of ^ optic
vesicle, ^ choroid fissure, ^ hyaloid artery (later ^
central artery of ^ retina)enters ^ eye.
• Nerve fibers of ^ eye also occupy this groove to
reach the optic areas of ^ brain.
• The cornea is formed by (a) a layer of surface
ectoderm, (b) ^ stroma, which is continuous with
the sclera, & (c ) an epithelial layer bordering the
anterior chamber.

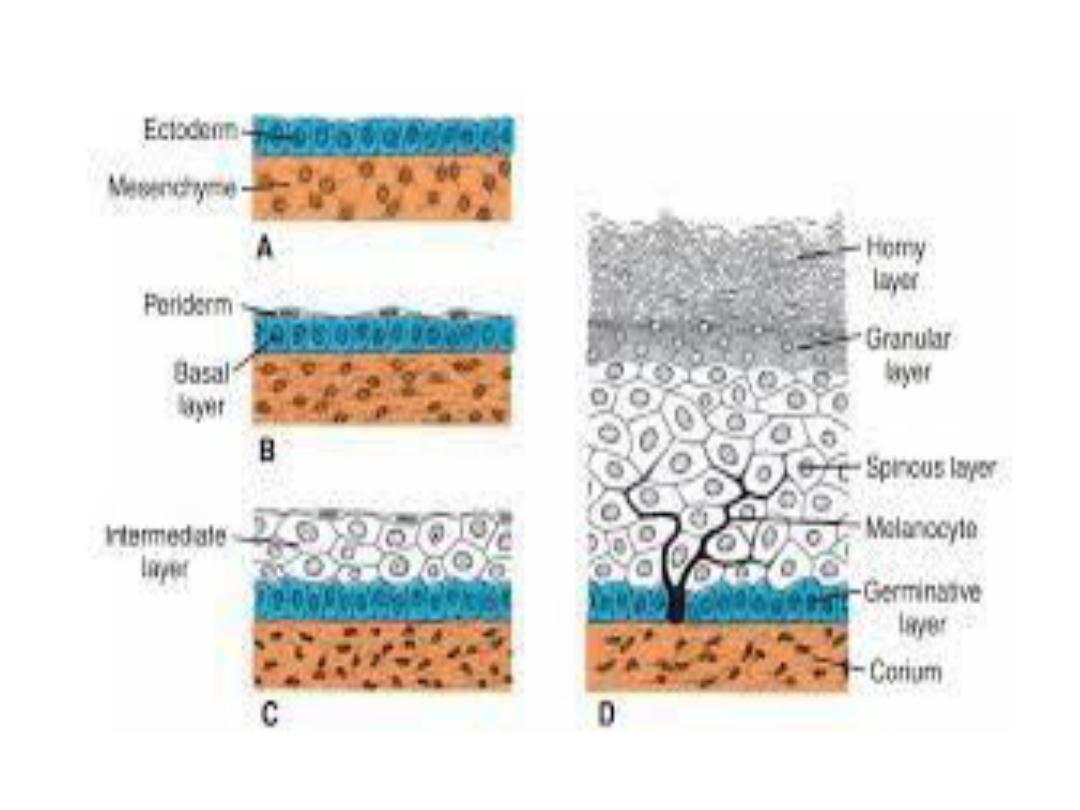
Integumentary system
• ^ skin & its associated structures, hair, nails
glands, are derived from surface ectoderm.
Melanocytes, which give ^ skin its color, are
derived from neural crest cells, which migrate
into ^ epidermis. ^ production of new cells occurs
in ^ germinative layer. After moving to ^ surface,
cells sloughed off in ^ horny layer.
• ^ dermis, ^ deep layer of skin, is derived from
lateral plate mesoderm & from dermatomes of ^
somites.

• Hairs develop from downgrowth of epidermal
cells into ^ underlying dermis. By about 20
weeks, ^ fetus is covered by downy hair,
lanugo hair, which is shed at ^ time of birth.
• Sebaceous glands, sweet glands, & mammary
glands all develop from epidermal
proliferations.
• Supernumerary nipples (polythelia) & breasts
(polymastia) are relatively common.