
Embryology
Lecture -3-
2
nd
Week of Development
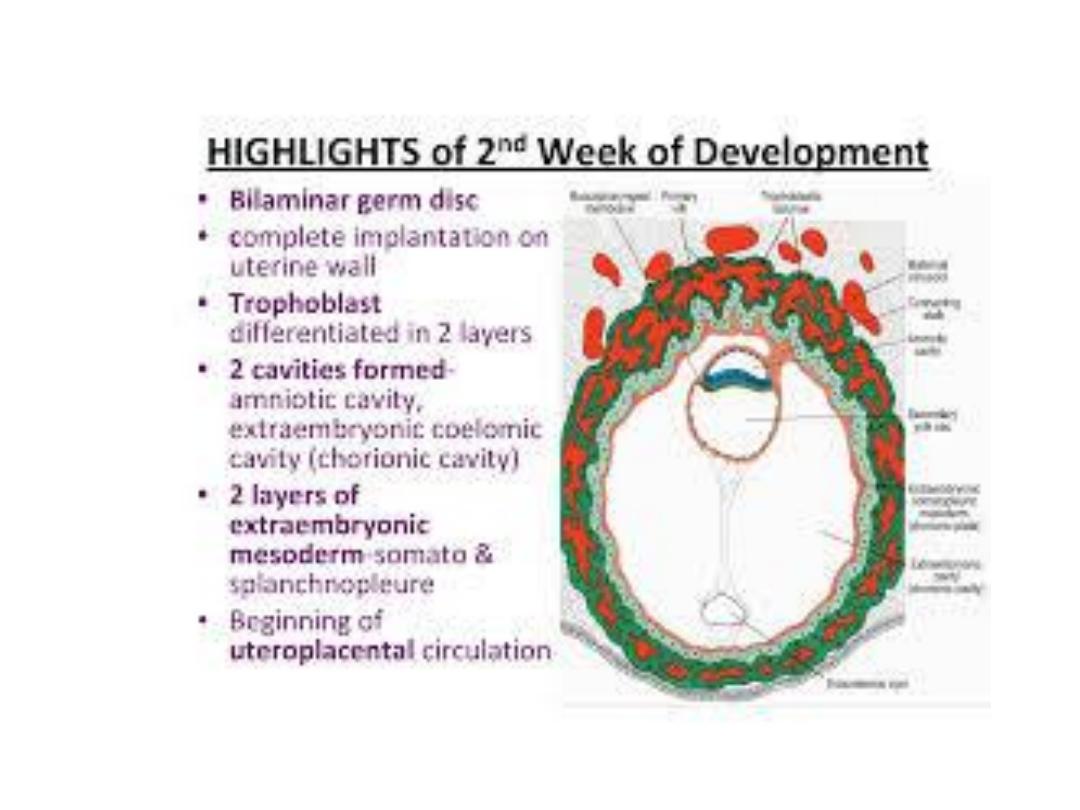
Bilaminar Germ Disc

The uterus at ^ time of implantation is in ^
secretory phase, & ^ blastocyst implants in ^
endometrium along ^ ant. or post. wall, during
which time uterine glands & arteries become
coiled & ^ tissue become succulent.

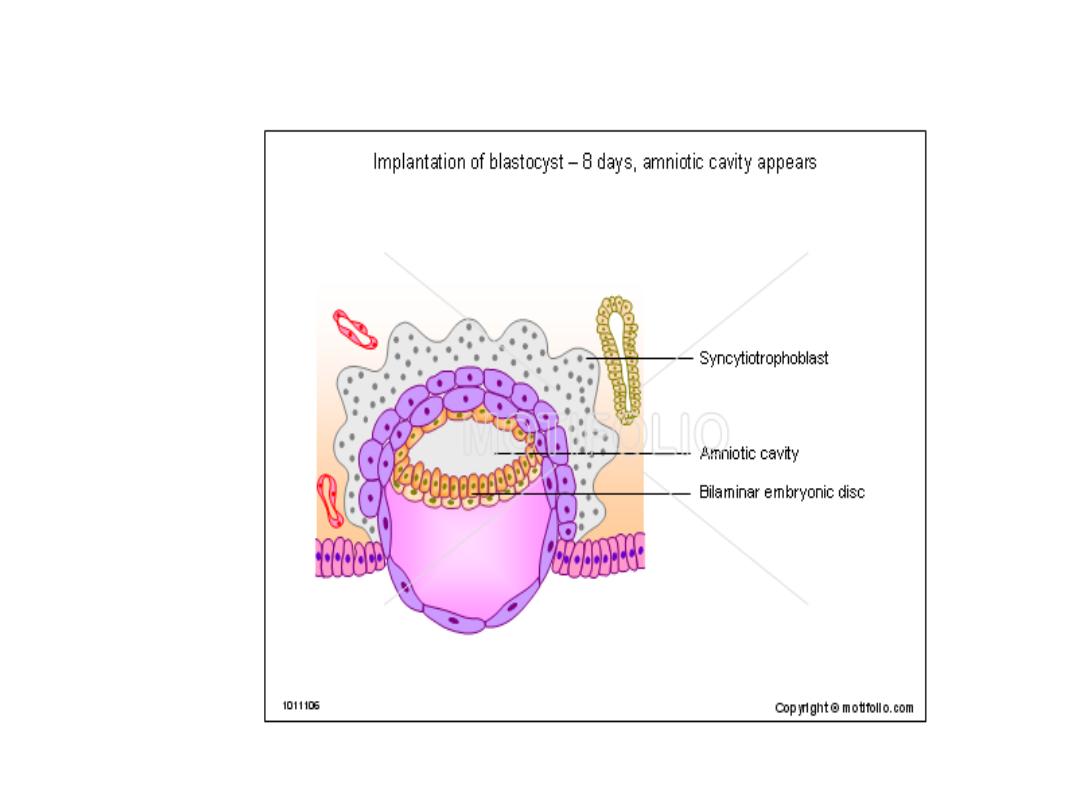
DAY 8
*^ Blastocyst is partially embedded in ^ endometrial stroma.
*^
trophpoblast
has differentiated into 2 layers:
_an inner layer of mononucleated cells, ^
cytotrophoblast
&
_ an outer multinucleated zone without distinct cell boundaries, ^
syncytotrophoblast.
* Cells in ^ cytotroph. divide & migrate into ^ syncytio.
*Cells of ^ inner cell mass (
embryoblat
) also differentiate into 2
layers:
_ a layer of small cuboidal cells adjacent to ^ blastocyst cavity, called
^hypoblast layer
.
_ a layer of high columnar cells adjacent to ^ amniotic cavity, ^
epiblast layer.

• Together, ^ layers form a flat disc.
• A small cavity appears within ^ epiblast which enlarges &
become ^
amniotic cavity.
• Epiblast cells adjacent to ^ cytotroph. r called
amnioblasts,
together with ^ rest of ^ epiblast they line ^ amniotic cavity.
• The endometrial stroma adjacent to ^ implantation site is
edematous & highly vascular.

DAY 9
• ^ Blastocyst I more deeply embedded in ^ endometrium, & ^
penetration defect is closed by a fibrin coagulum.
• Vacuoles appear in ^ syncytium--- this phase called
lacunar
stage.
• At abembryonic pole, meanwhile, flattened cells probably
originated from ^ hypoblast form a thin membrane, ^
exocoelomic ( Heuser’s) memb.
• This memb. together with ^ hypoblast forms ^ lining of ^
exocoelomic cavity, or (primitive yolk sac).
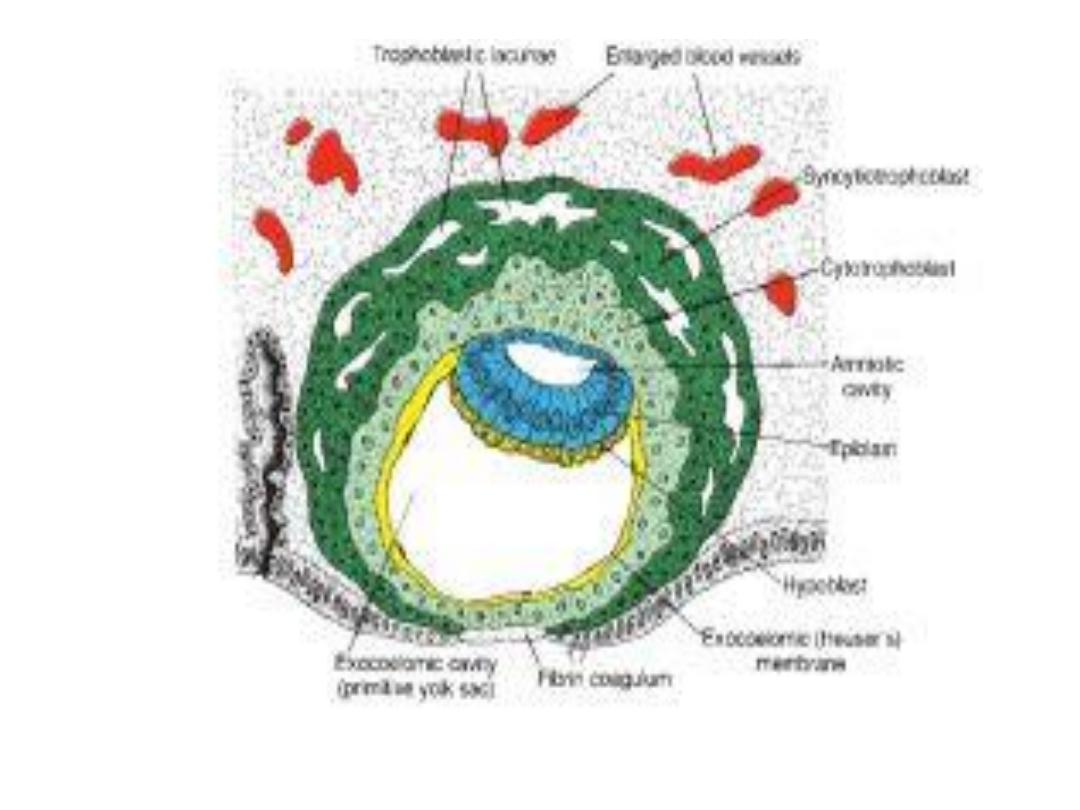

DAY 11 & 12
• Completely embedded in ^ endometrium.
• ^ Blastocyst now produces a protrusion into ^ lumen of ^ uterus.
• ^ Trophoblast is characterized by lacunar spaces in ^ syncytium
forming an intercommunicating network at ^ embryonic pole.
• The abembryonic pole consists mainly of cytotrophoblast.
• The syncytiotrophoblast penetrate deeper into ^ stroma & erode ^
endothelial lining of ^ maternal capillaries, which are congested &
dilated known as
sinusoids.
• The syncytial lacunae become continuous with ^ sinusoids, &
maternal blood enters ^ lacunar system, establishing ^
uteroplacental circulation.

• A new population of cells appears between ^ inner surface of
cytotroph. & outer surface of exocoelomic cavity, which r derived
from yolk sac cells,
^ extraembryonic mesoderm.
• Soon, large cavities develop in ^ extraembryonic mesoderm, when
they become confluent , they form a space known as
^
extraembryonic coelom, or chorionic cavity.
This cavity surrounds ^
primitive yolk sac & ^ amniotic cavity, except where ^ germ disc is
connected to ^ trophoblast by ^ connecting stalk.
• ^ Extraembryonic mesoderm lining ^ cytotrophoblast & amnion -
extraembryonic somatopleuric mesoderm.
• ^ lining covering ^ yolk sac
extraembryonic splanchnopleuric
mesoderm.

• Growth of ^ bilaminar disc is relatively slow compared with
that of ^ trophpblast.
• Cells of ^ endometrium become polyhedral & loaded with
glycogen & lipids & ^ tissue is edematous, known as
decidua
reaction,
at ^ site of implantation then occur throughout ^
endometrium.
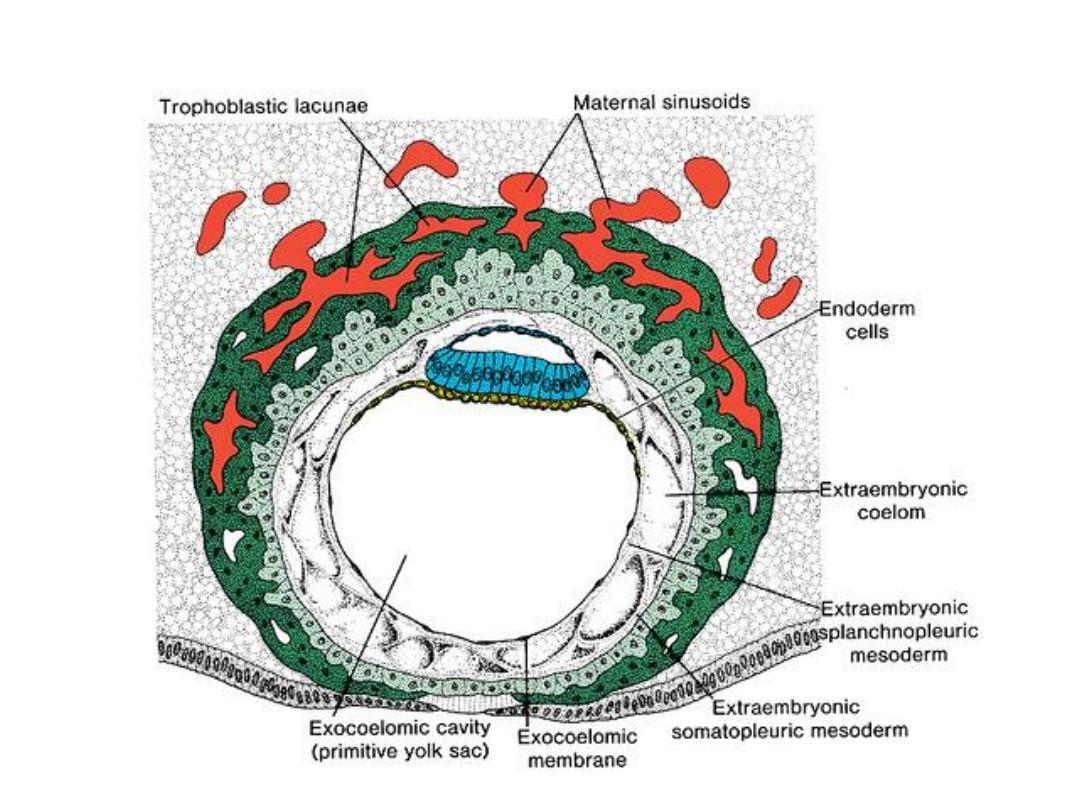

DAY 13
• Here ^ surface defect in ^ endometrium is healed.
• Bleeding occurs at ^ site of ^ implantation as a result from
increased blood flow into ^ lacunar spaces ( because this
bleeding occurs near ^ 28
th
day of menstrual cycle, it may be
confused with normal menstruation).
• Cells of ^ cytotrophoblast proliferate locally & penetrate into ^
syncytium forming cellular columns surrounded by syncytium
(
primary villi
).
• Hypoblast produces cells migrate along ^ inside of ^
exocoelomic membrane forming a cavity within ^ exocoelomic
cavity called
secondary or definitive yolk sac.

• During this period,
^ exocoelomic cysts
produced in ^
extraembryonic coelom or
chorionic cavity.
• The extraembryonic mesoderm lining ^ inside ^ cytotrop. is
known as
chorionic plate.
• The only place where extraembryonic mesoderm traverse ^
chorionic cavity is in ^ connecting stalk (become umbilical
cord).

Thank you for your listening
