
Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
1
Bleeding
in early pregnancy
(Miscarriage)
Causes of bleeding in early pregnancy
• Miscarriage
• Ectopic pregnancy
• Gestational trophoblastic disease
• Cervical lesions (erosion and/or polyp)
Miscarriage
Spontaneous loss of pregnancy before viability(at or before24 weeks of
gestation or<500gm birth wt)
The incidence in a clinical recognized pregnancy is10-20% decreasing
to3%if a viable fetus has been recognized on ULS.

Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
2
Causes
Fetal:
Chromosomal abnormalities
More than 80 percent of abortions occur in the first 12 weeks of
pregnancy at least half result from chromosomal anomalies
Maternal:
Advanced maternal age: due to decreased number of good quality
oocytes.
Medical diseases of the mother :SLE, anti- phospholipid syndrome,
inherited thrombophilia
Endocrinal abnormalities :PCOs,hypothyroidism un controlled D.M,CL
insufficiency
Uterine defects :uterine leiomyomas ,congenital abnormalities
,Asherman’s syndrome, cervical incompetence.
Infections:Listeria monocytogenes ,Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma
urealyticum, TORCHS
Toxic chemicals ,drugs, radiation
Immunological rejection of the fetus
Incompetent cervix
Painless dilatation of cervix in the 2
nd
or early in the 3
rd
trimester
Diagnosis :Hysterography or Acceptance without resistance at the internal os of
specifically sized cervical dilators
In pregnant women:
The use of transvaginal ultrasound for Cervix showing progressive shortening
& dilatation(Funneling)
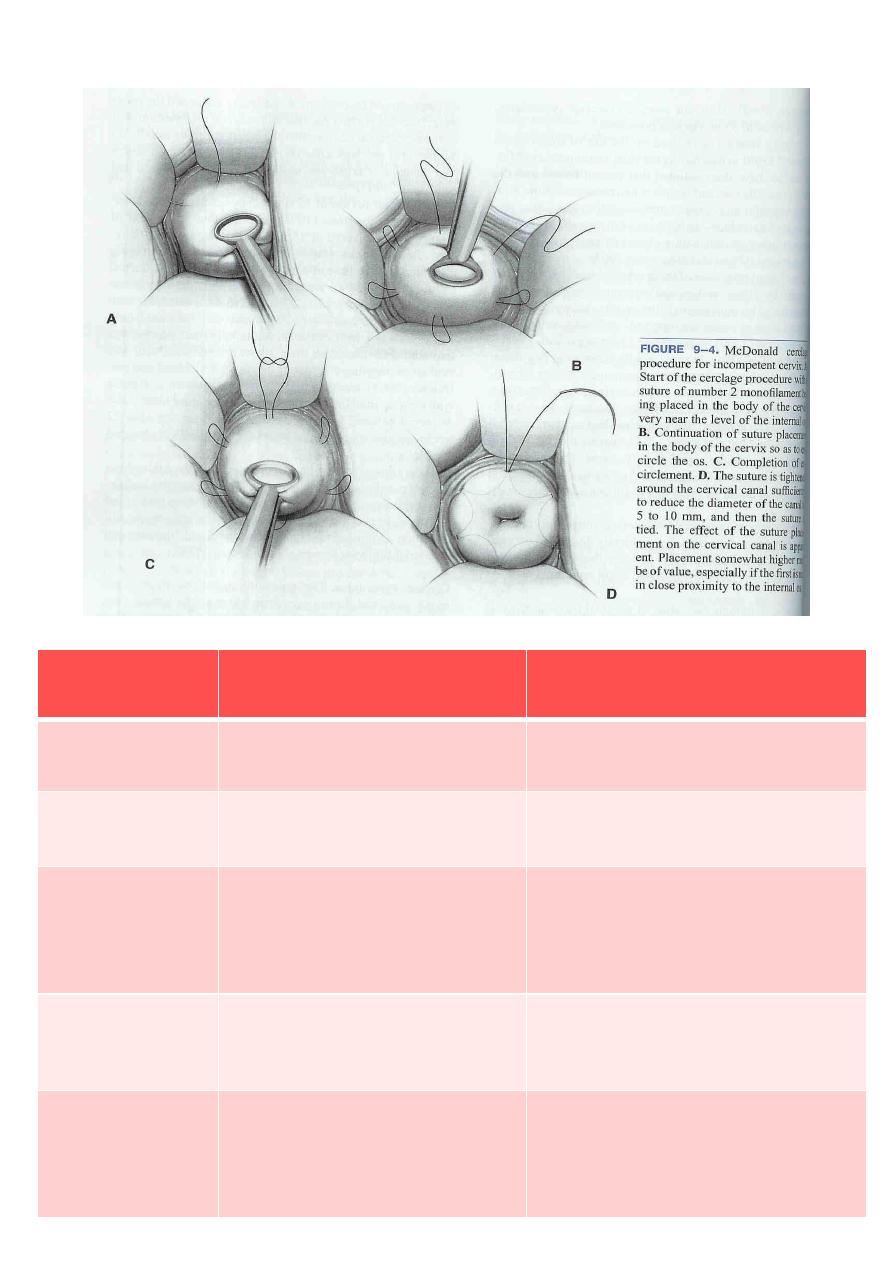
Treatment: surgically Reinforcement of weak cervix by some type of purse
string suture ( Cerclage )performed between 12 & 14weeks
Types of operations commonly used:
McDonald
Transabdominal cerclage(Shirodkar)
Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
3
Clinical presentation
Ultrasound findings
Types of
miscarriage
Milde vaginal bleeding & pain
Ex.cervical os close
Viable intrauterine
pregnancy
Threatened
miscarriage
Per vaginal bleeding & pain
Ex.cervial os open
Intrauterine pregnancy
Inevitable
miscarriage
vaginal bleeding & pain
Ex.cervical os open, products
of conception located in
cervical os
Retained products of
conception
Incomplete
miscarriage
Expultion of conceptus Pain
&bleeding resolved
Ex.cervical os closed
No retained products of
conception (empty uterus)
Complete
miscarriage
With or without pain &
bleeding uterus smaller than
expected mamary changes
regress,DIC
Fetal pole present, but no
fetal heartbeat identified
Gestational sac present
but no fetal pole identified
Missed
miscarriage

Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
4
Categories of spontaneous abortion
Recurrent miscarriage is 3 or more consecutive, spontaneous pregnancy
losses, before viability &in the same pattern.
Septic abortion
Most often associated with criminal induced abortion
Metritis is usual outcome, but parametritis, peritonitis, endocarditis, and
septicemia may all occur
Therapeutic abortion
Done if continuation of pregnancy may threaten the life of women or seriously
impair her health e.g heart disease , advanced hypertensive vascular disease ,
invasive carcinoma of the cervix, or in case of sever congenital abnormality of
fetus incompatible with life.
History and examination
History
LMP
Duration of amenorrhea
Nature of bleeding
Pain
Cause if present
Examination
BP, pulse rate ,temp.
Abdominal palpation
Speculum examination
Vaginal examination

Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
5
Investigations
Urine – MSU/PT in urine or blood
FBC
Quantitative βHCG
USS (transvaginal or abdominal)
Bd group and cross match if patient is severely compromised)
Management options
Expectant management
Medical evacuation
Surgical evacuation
Expectant Management
Watch and wait
Serial scans and HCG
bleeding may stop &pregnancy continue (if viable) , completely abort&
bleeding stops or may have prolonged bleeding which can need to convert
at anytime to medical/surgical especially if bleeding is heavy
Medical induction of abortion
Prostaglandins are used in single or divided doses administered orally
(misoprostol) or vaginally (Gemeprost). Misoprostol is cheap & effective in
oral & vaginal forms& in both 1
st
&2
nd
trimester.
Antiprogesterone RU 486
Oral agent used alone or in combination with oral
PG to induce abortions in early gestation

Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
6
Oxytocin
Successful induction of 2
nd
trimester abortion is
possible with high doses of oxytocin administered
in small volumes of IV fluids
Women under going medical management of miscarriage may need surgical
treatment if medical treatment fails.
Surgical techniques for abortion
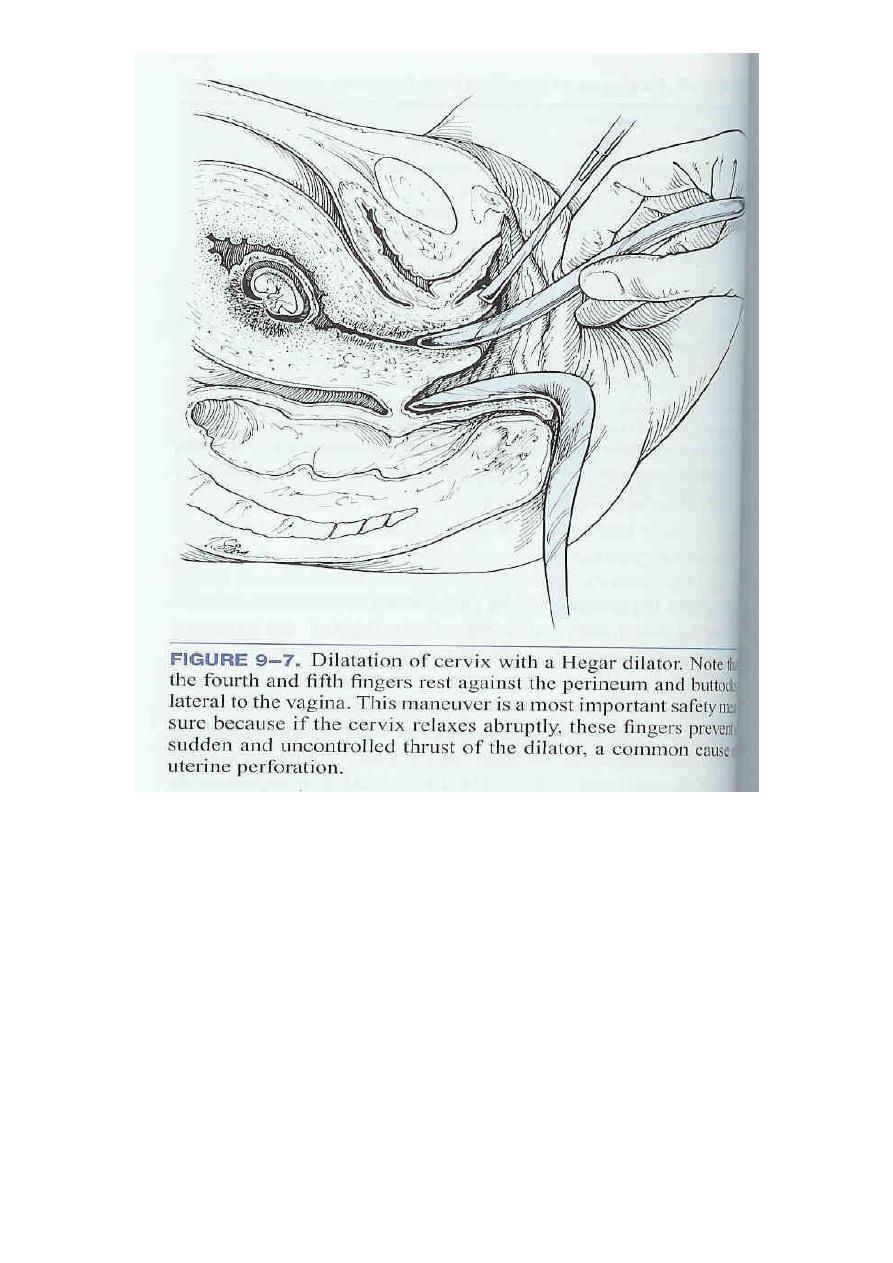
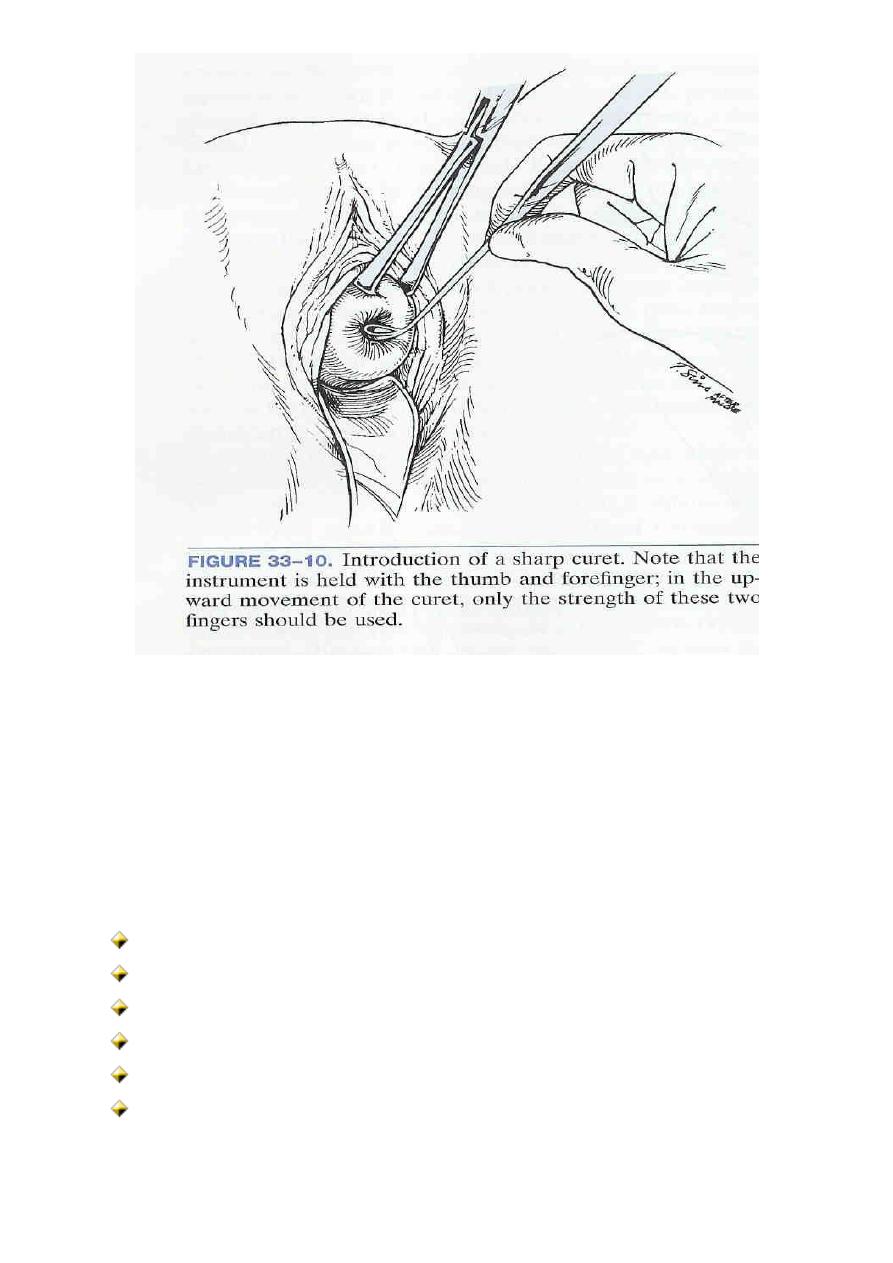
Dilatation and curettage
Before 14 weeks, D&C or vacuum aspiration can be performed
Performed first by dilating the cervix & then evacuating the product
of conception either by
Mechanically scraping out of the contents (sharp curettage)
Or Vacuum aspiration (suction curettage)
Complications :
uterine perforation ,cervical incompetence , uterine synechiae & even sub
fertility.
Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
7
Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
8
Surgical techniques for abortion
– Abdominal hysterotomy
Failure of medical induction during the late 2
nd
trimester
Further management
Psychological support – information
Contraception
Future pregnancies
Recurrent miscarriag should be investigated
Folic acid
Anti D
Obstetrics Lec 12 Dr. Aseil
9
Surgical abortion
Medical abortion
Invasive procedure & usually
requires anesthesia
Avoids invasive procedure
& anesthesia
Usually requires one visit only
done in hospital/clinic
Requires two or more visits
in hospital/clinic or in
home
Completes in predictable short
time
Days to weeks to complete
Available in early pregnancy
Available in early & late
pregnancy
Higher success rate (99%)
High success rate (95%)
Does not require follow up in all
cases
Requires follow up to ensure
completion of abortion
Requires patient participation in
a single step process
Requires patient participation
throughout multi step process
Not
Contraindicated in asthma &
cardiac disease
Hemorrhage, infection, uterine
perforation, cervical damage
Complication:hemorrhage,
Infection ,failure to remove
pregnancy
