
Obstetrics Lec 10 Dr. Aseil
1
Malposition of
the fetal head
When the head is presented with vertex posterior “OP” it will be deflexed and
the longitudinal diameters will be will change to:
Sub-occipito frontal 10.5cm
Or
Occipito frontal 11.5cm
Occipito Posterior Position OP
Diagnosis
Antenatal
Diagnoses is important at least to rule out any major causes which may be a
contraindication to leave the patient inter into labour
Suspicion during antenatal examinations raise when:
○ High head &large amount of head is palpable abdominally
○ flattening of the abdomen below the umbilicus
○ fetal back is placed posterior &the limbs are felt anteriorly
Diagnosis During Labour
vaginal examination during labour:For assessment of descent,flexion&position
○ High presenting part
○ Anterior fontanel felt near to the symphysis
○ Posterior fontanel felt near to the sacral promontory
○ Frontal sutures and Frontal bones

Obstetrics Lec 10 Dr. Aseil
2
Possible Etiological causes
Maternal
Bicornoate uterus
Septet uterus
Fibroid
Pelvic tumor
Non gynaecoid pelvis
(Anthropoid)
contracted pelvis
Fetal
Prematurity
Multiple gestation
Polyhydramnios
Oligohydramnios
Large Fetus
Large Fetal head
Congenital Abnormalities
Cord around the neck
Neck tumer
Complication
Fetal
Premature rupture of fetal membranes
marked molding &fetal injuries
cord prolapsed → fetal distress →fetal death
Maternal
prolonged and complicated labour
Maternal distress
Infection
obstructed labour → uterine rupture
→ ( PPH ) →maternal death
Operative delivery: vacum extraction, forceps &C/S increased
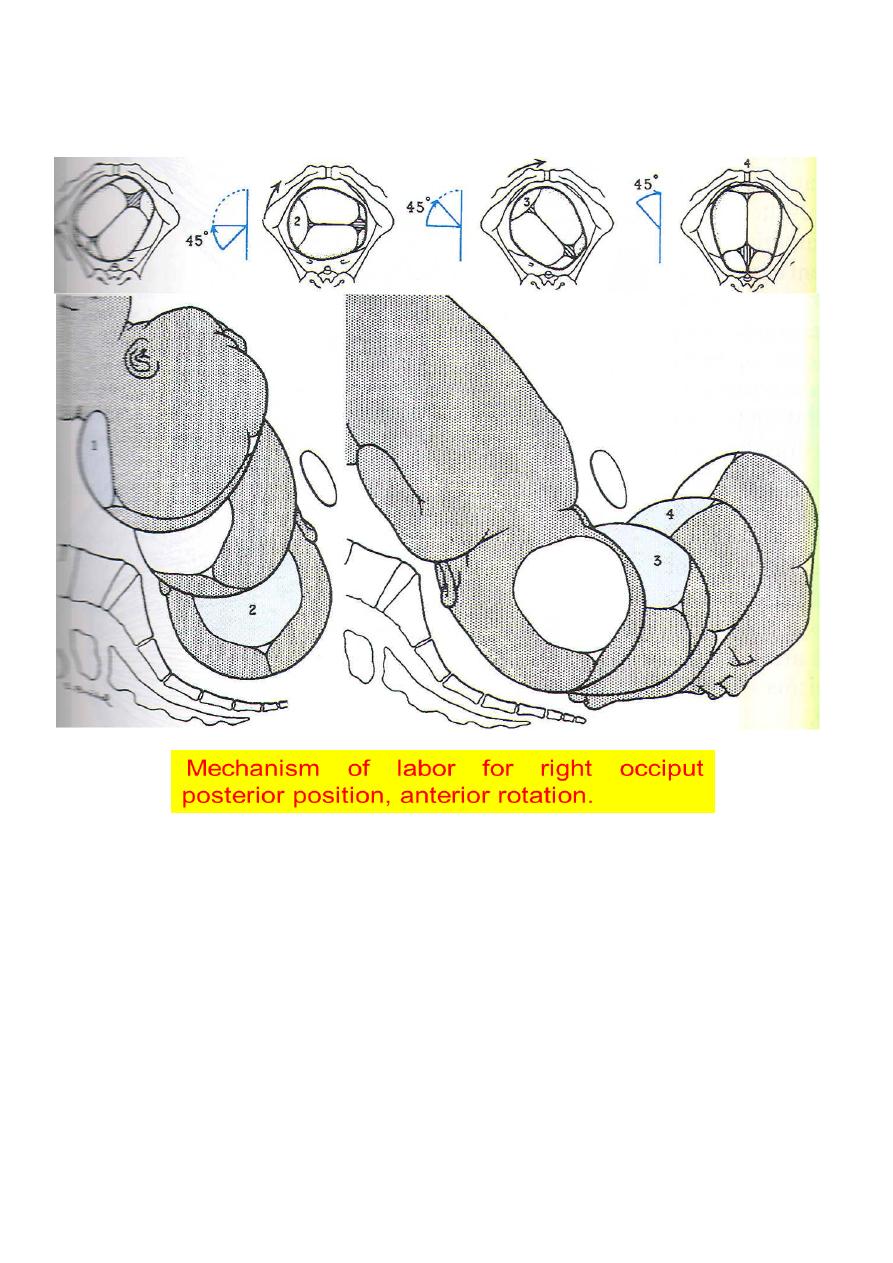
Mechanism of labour in OP
Mechanism of labour is identical to OT & anterior varieties
75 % of the cases flexion increases & the occipt rotates when it reaches the
pelvic floor from the posterior to anterior position through 135º instead of 90º
or 45º in OT &OA positions and deliver as OA&this long journy in rotation
explains the prolonged labour associated with this position.
Obstetrics Lec 10 Dr. Aseil
3
○ 5 % of the cases deflexion persists or increase & the pregma will be the part
which reaches the pelvic floor first &rotates forwards causing a direct
occipitoposterior position and in some cases the presenting part descends
further &delivers as face to pubis with high incidence of severe perineal tears.
○ 20% will end as deep transverse arrest of the head.
Obstetrics Lec 10 Dr. Aseil
4
PERSISTENT OCCIPITO- POSTERIOR POSITION
• The possible management for vaginal delivery
1. Await spontaneous delivery &slow progress in 1
st
stage should be treated
with a titrated oxytocin infusion &if satisfactory progress is not achieved C/S is
indicated.
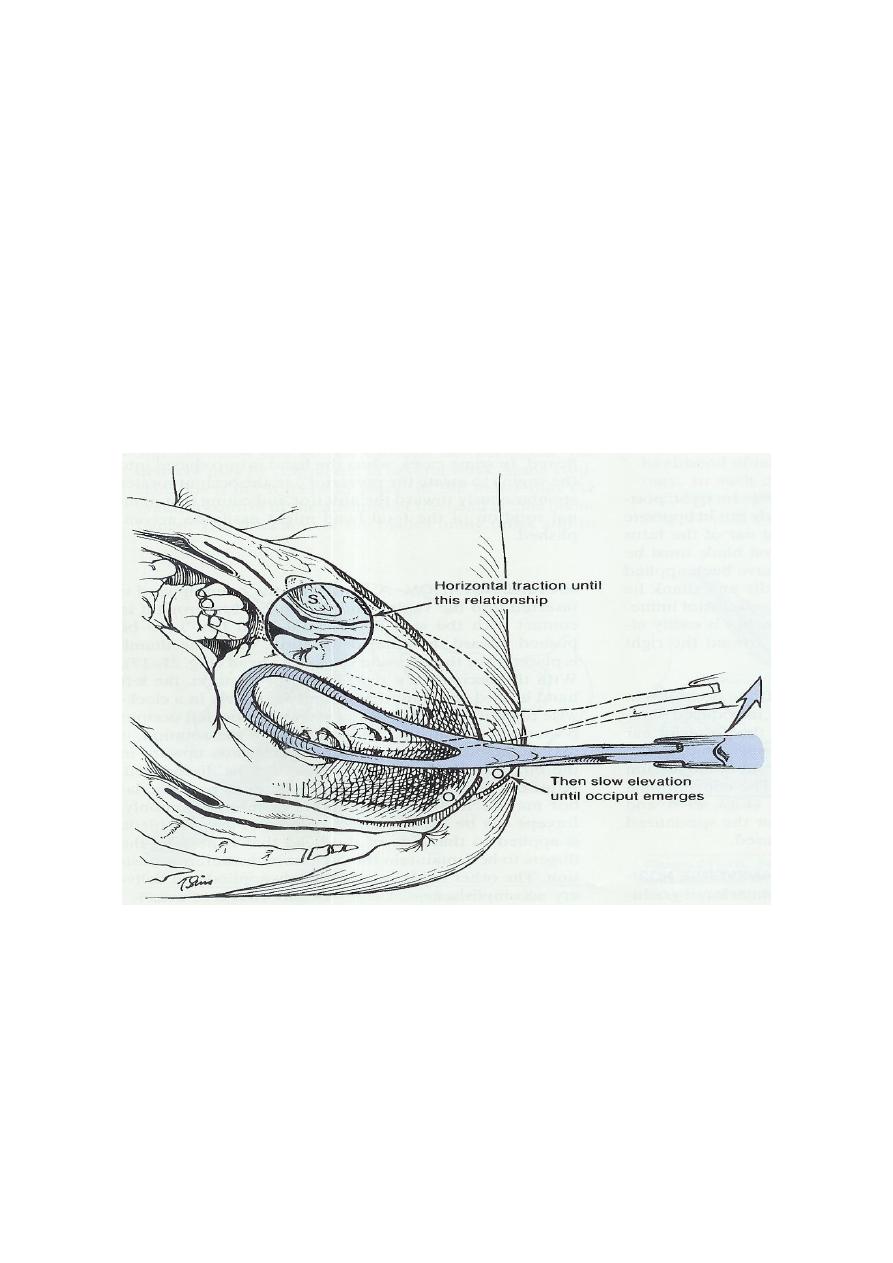
2. Forceps delivery with the occiput directed posterior for delay or fetal
distress in the 2
nd
stage.
3.or forceps &vacum rotation of the occiput to the anterior position and then
delivery
*generous episiotomy is usually needed.

Obstetrics Lec 10 Dr. Aseil
5
PERSISTENT OCCIPUT TRANSVERSE POSITION
• In the absence of a pelvic architecture abnormality it is most likely a
transitory one rotate spontaneously to the anterior position
if failure of spontaneous rotation is caused byhypotonic uterine dysfunction
without CPD oxytocin may be infused with close observation
If there is platypelloid(anteroposteiorly flat) orandroid(heart-shaped) pelvis,
rotation is arrested at the level of ischeal spines a condition called deep
transverse arrest of the head so C/S will be needed.
