Obstetrics Lec 8 Dr. Aseil
1
Abnormal Labour
(Prolonged Labour)
Dysfunctional labor: (Prolonged labour)
1-Prolonged 1
st
stage.
2-Prolonged 2
nd
stage.
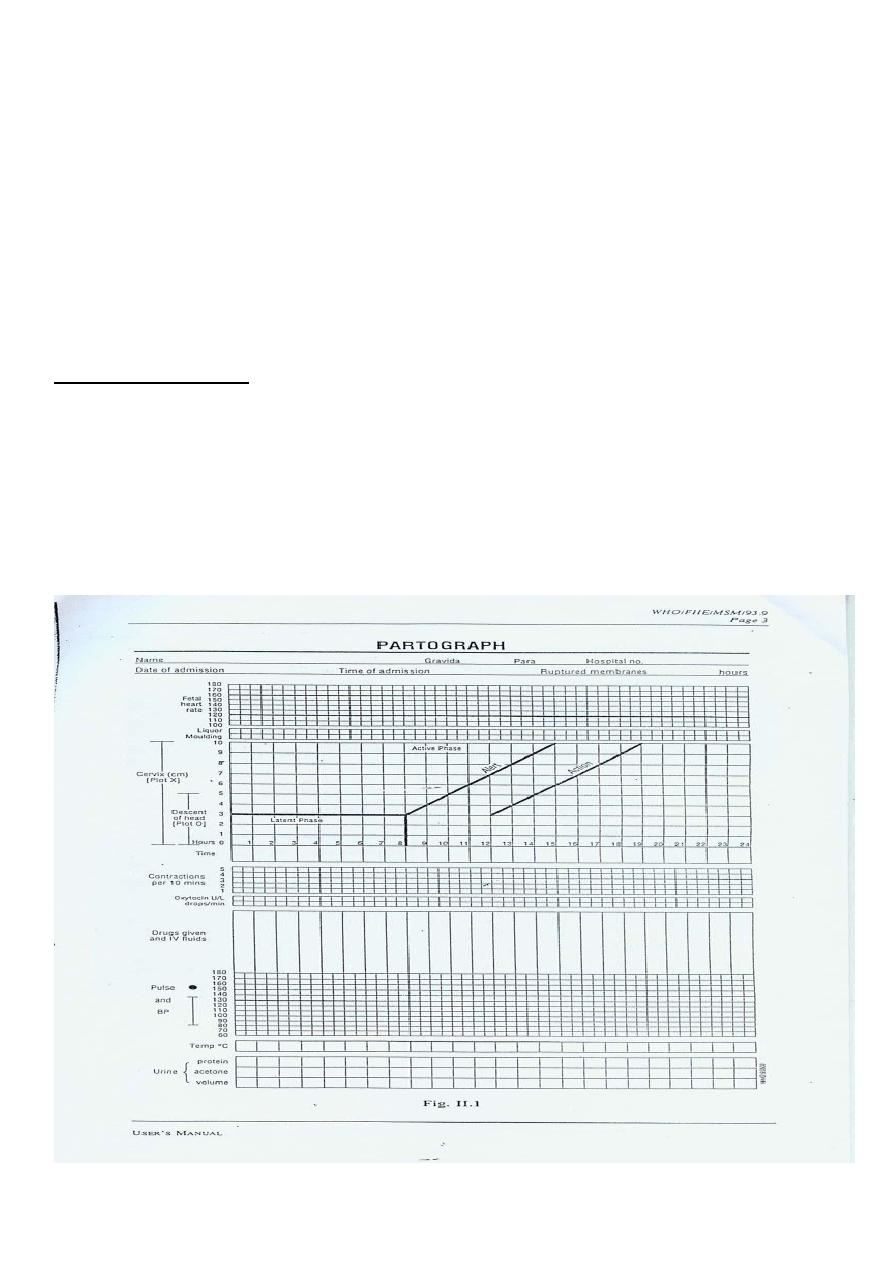
Any deviation in normal progress of labor , either in cervical dilatation or in
descent of the presenting part. this can be judged by partogram
WHO partogram
Obstetrics Lec 8 Dr. Aseil
2
Etiology
1.Abn.of power (uterine contraction & maternal expulsive effort) Malfunction
in the myogenic, neurogenic, or hormonal mechanisms of uterine activity.
2.Abn.in the passenger (Malpresentation ,Malposition ,Macrosomia ,fetal
anomalies)
3-Abn.in the passeges(abn.of the bony pelvis i.e CPD),abn.in the soft tissue of
birth canal (uterine malformation, pelvic tumors , fibroid , cervical dystocia).
4. Extrinsic factors: sedation, anxiety, anesthesia.
Patterns of abn.progress in labour
1.Disorders of dilatation:
a. Prolonged latent phase
b. Protracted active phase (primary dysfunctional labour)
c. Secondary arrest
2.Disorders of descent:
a. Failure of descent
b. Protracted descent
c. Arrest of descent.
Obstetrics Lec 8 Dr. Aseil
3
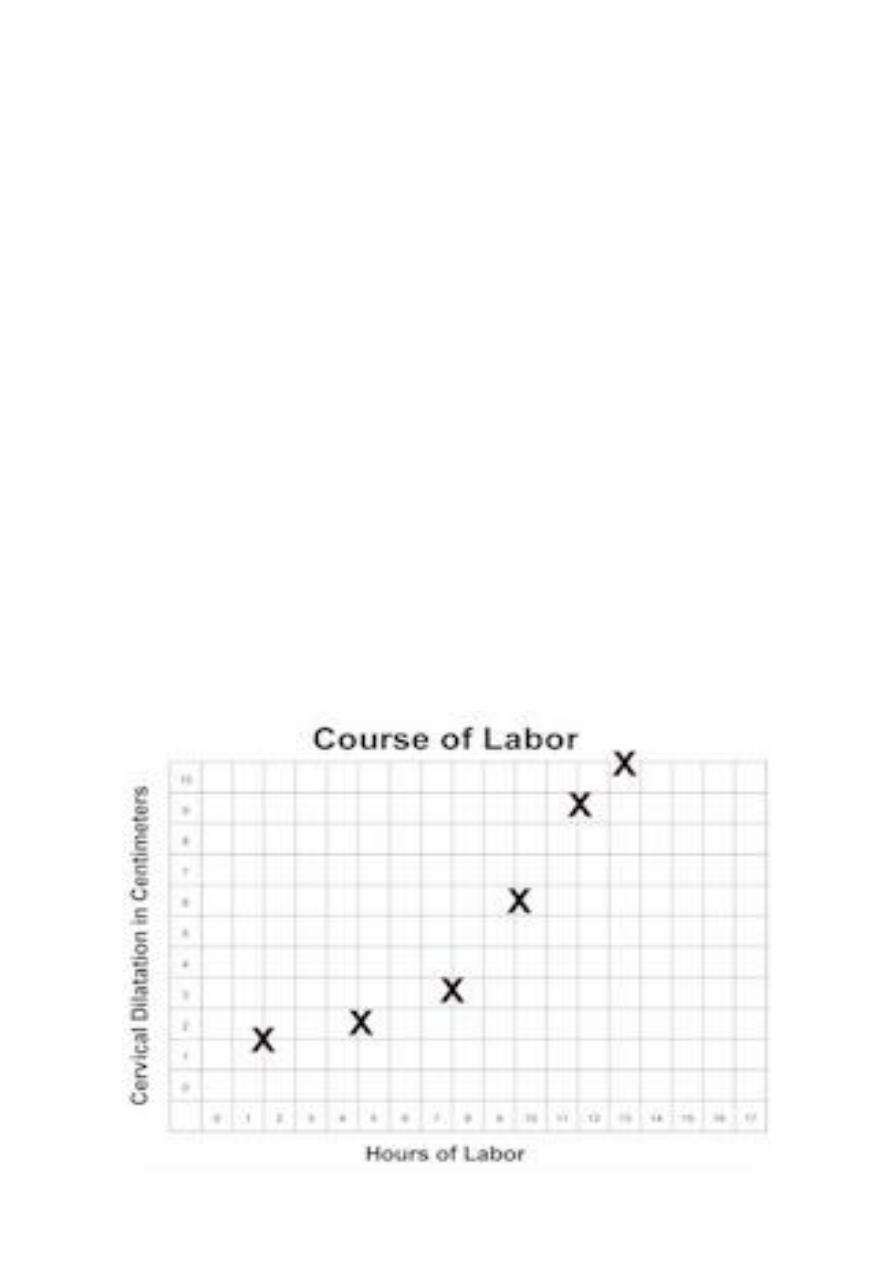
Prolonged Latent Phase Labor
If after 8hr from the onset of regular contractions cervical dilatation still<4cm
the Dx. Of prolonged latent phase is made.It is more common in primiparous
women
Primary dysfunctional labour
– Active phase:
• cervical dilation rate at least 1cm/hr.
• (Protracted Active Phase)
– it means poor progress in the active phase of labour (<2cm
dilatation/4hr)
– More common in primiparous commonly caused by inefficient
uterine contractions, but can also result from CPD&malposition of
the fetus.
Obstetrics Lec 8 Dr. Aseil
4
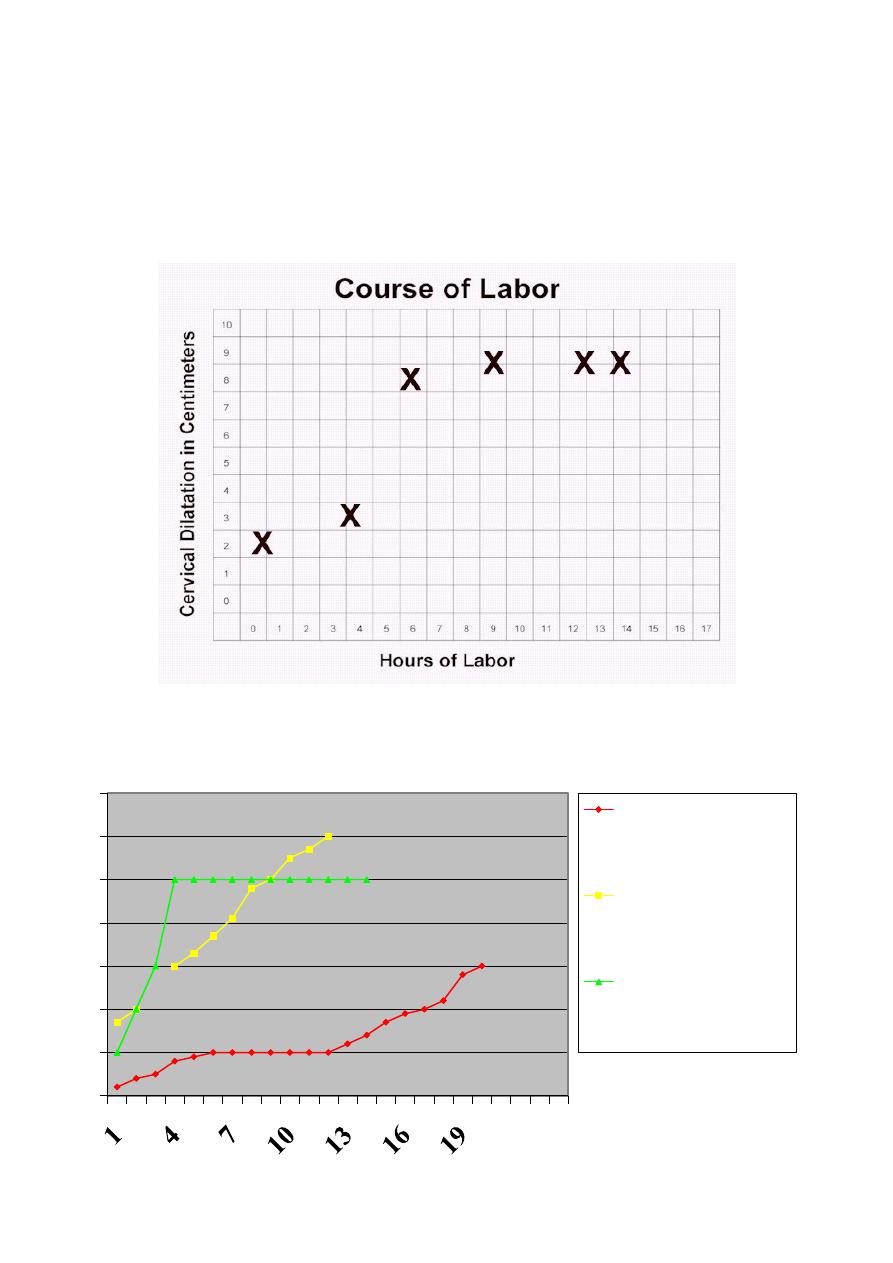
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Prolonged latent
phase
Primary
dysfunctional
labor
Secondary
arrest
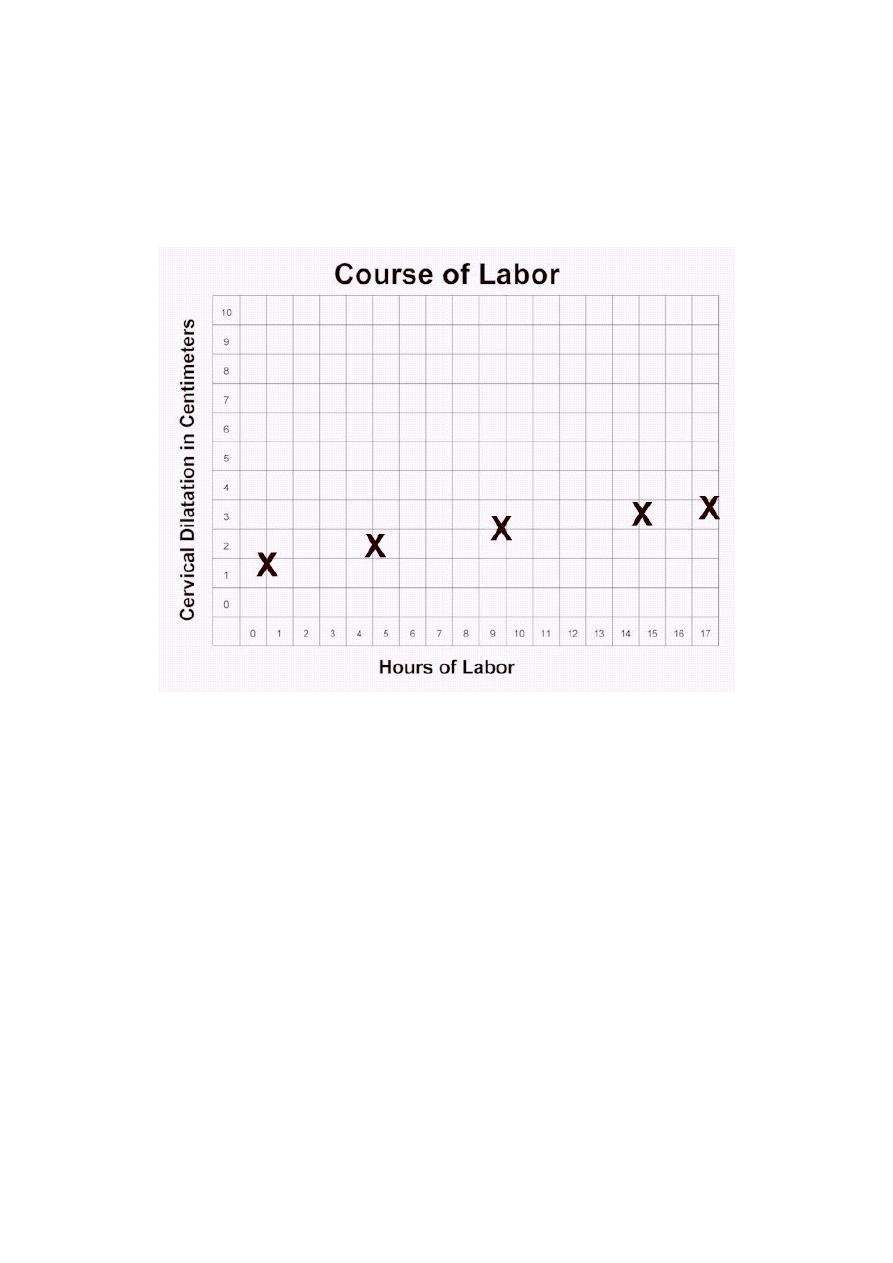
Secondary arrest
Arrest: occurs when progress in the active phase of 1
st
stage is initially good but
then slows ,or stops altogether, typically after 7cm
(2 hours with no cervical change)
Although inefficient contractions may be the cause , fetal malpositions ,
malpresentations& CPD are more common
Arrest of Active Labor
Cervical dilatation (cm)Types of dysfunctional
Time (hours)

Obstetrics Lec 8 Dr. Aseil
5
Prolonged second stage
• Max. duration of 2
nd
stage for nullips: 2hr
Max. duration for multips: 1hr
• Abnormal progress of labourmay occur either due to slow descent or
secondary arrest of descent or failure of descent of fetal head.
Management of prolonged labour
1-Careful history
2-Asses and examine the woman to identify the cause and to determine the
maternal and foetal conditions, include: general , abdomen( asses the
contraction ,lie, presentation of fetus, size, fetal heart assessment)
The pelvic examination ( assessment of bony pelvis, soft tissue, progress of
labour, meconium).
Treatment of prolonged labour
Either allow the labour to continue OR Undertake an operative delivery
Allowing thelabour to continue
1- in the absence of fetal distress
2- in the absence of maternal distress
3- no severe cephalopelvic disproportion
BY Rupturing of membrane
If ineffecientcontraction (oxytocin)2m unit/min , max. dose 32m unit/min
Adequate analgesia,Good maternal fluid balance. If no progress after 4hr C/S
Operative delivery if there is:
Fetal distress
Maternal distress
Frank cephalopelvic disproportion
Arrest of cervical dilatation in spite of good uterine contraction
Operative delivery either by caesarean section, or by ventouse extraction
or forceps delivery

Obstetrics Lec 8 Dr. Aseil
6
Obstructed labour
Arrest of cervical dilatation or descent of presenting part inspite of good uterine
contraction with large caput, severe moulding, cervix poorly applied to
presenting part, oedematous cervix, ballooning of lower uterine segment,
formation of retraction ring, maternal & fetal distress
Causes
1-Maternal:
Contraction or deformity of bony pelvis
Pelvic tumors: fibroid,ovarian tumor, Pelvic kidney
Abnormalities of uterus or vagina
Stenosis of cervix or vagina
2- Fetal:
- Large fetus
- Malposition or malpresentatio
- Congenital abnormalities of fetus :Hydrocephalus , fetal ascitis ,hydropsfaetalis
,conjoined twin
Treatment
rehydration
antibiotics
emergency caesarean section
Maternal complications :
– Intrapartum infection– especially in the setting of ROM
– Uterine rupture– esp with prior C/S
– Fistula formation
– Pelvic floor injury
