
Dr.Aseel
Labour and delivery (part 1)
Passenger (cont.)
The fetal position and the mechanism of normal labour
Certain terms used to describe the position of fetus in relation to the uterus and
the pelvis.
1.Lie:
By the lie of the fetus is meant the relation which the long axis of the fetus
bears to that of the uterus. The lie may be longitudinal, oblique or transverse.
2.Presentation:
the presentation part of the fetus is that part which is in or over
the pelvic brim and enters the pelvis first.
When the head occupies the lower segment of the uterus the presentation is
termed cephalic. If the head is flexed on the spine the vertex presents
If the head is fully extended in the spine there is a face presentation, and if it is
partly extended a brow presentation.
If the breech occupies the lower segment the presentation is termed podalic.
If the fetus lies obliquely the shoulder generally lies over the cervix and this is
called a shoulder presentation.
Any presentation other than a vertex presentation is described as a
malpresentation.
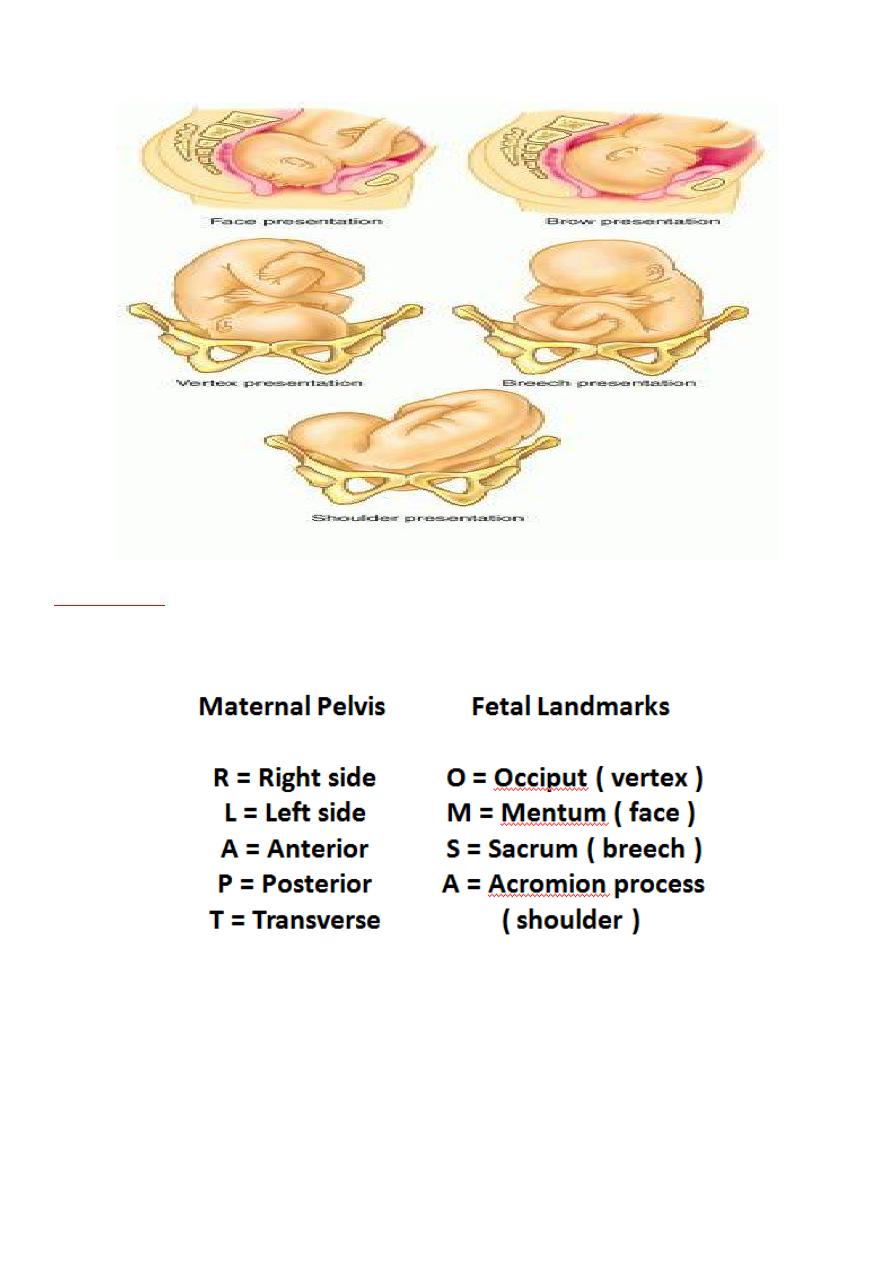
Examples of presentations
3- Position:
is the relation of selected part of fetus chosen according to
presentation (denominator ) to the maternal pelvis.
*Most common position is LOA
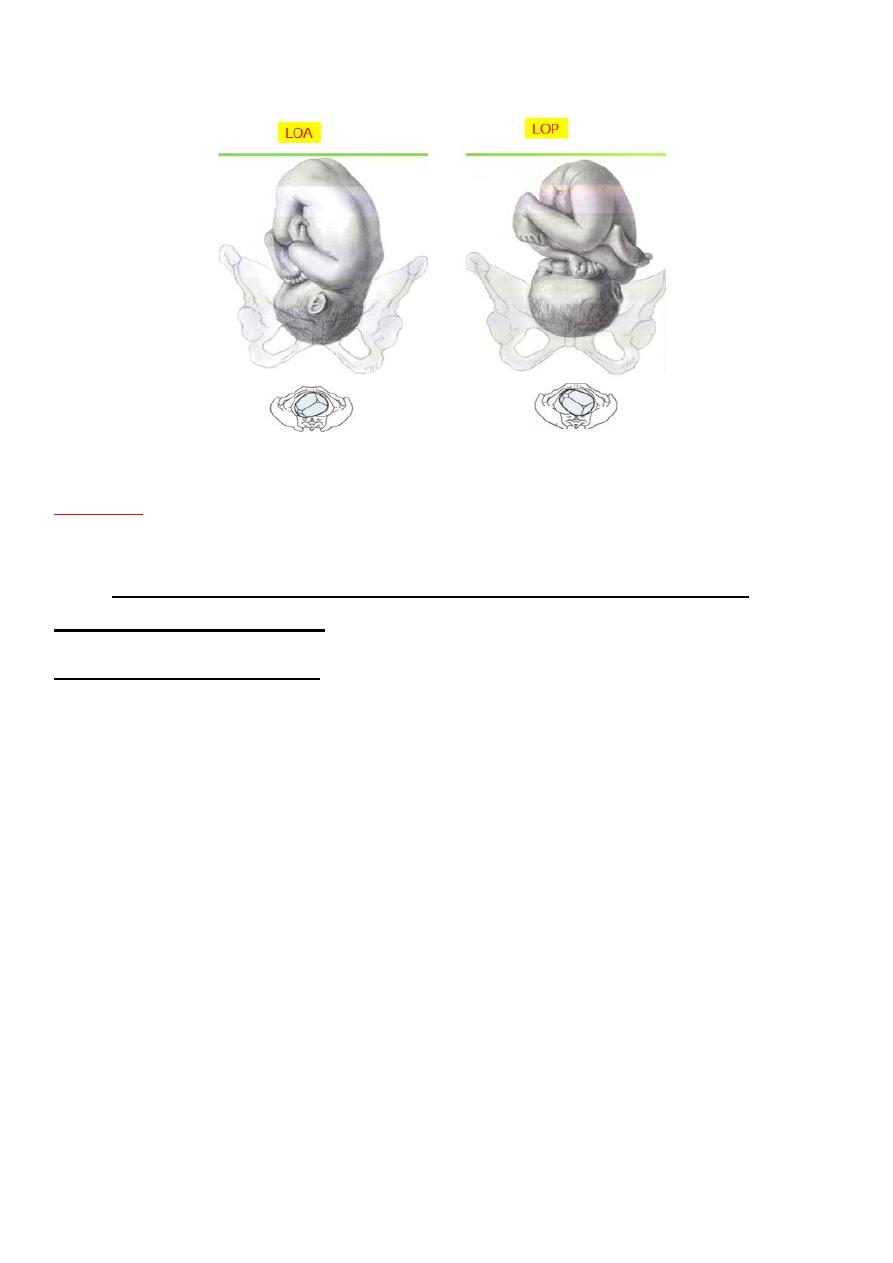
LONGITUDINAL LIE VERTEX PRESENTATION
4-Station
It refers to the descent of presenting part of the fetus through the birth
canal. Estimated by measuring the relationship of the presenting part
to an imaginary line drawn
between the ischial spines
The ischial spines as a landmark have been designated as zero station (the
exact point of engagement)
If the presenting part is higher than the ischial spines, a negative number is
assigned, noting cm above zero station
Positive numbers are used to indicate that the presenting part has passed the
ischial spines

Power
Uterine contractions
Power refers to the force generated by the contraction of the uterine
myometrium
Activity can be assessed by the palpation of the fundus, or external
tocodynamometry.
Contraction force can also be measured by direct measurement of
intrauterine pressure using internal manometry or pressure transducers.
Generally 3-5 contractions in a 10 minute period is considered adequate in
labor
Strength measured in Montevideo units
Adequate 200-250 MVUs
Normal labour:
Spontaneous expulsion, through the natural passages (birth canal) of a single,
mature (37-42 completed weeks of pregnancy) alive fetus, presenting by
vertex, within a reasonable time, without fetal or maternal complications.
Labour becomes abnormal when there is poor progress &/ the fetus shows
signs of compromise. Also, if there is fetal malpresentation , multiple
gestation , uterine scar , or if labour has been induced.
By: Sama Adeeb
