Seminar 3
DR. Bassam Al-AbbasiFirst photo:
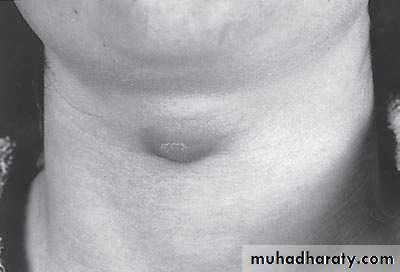
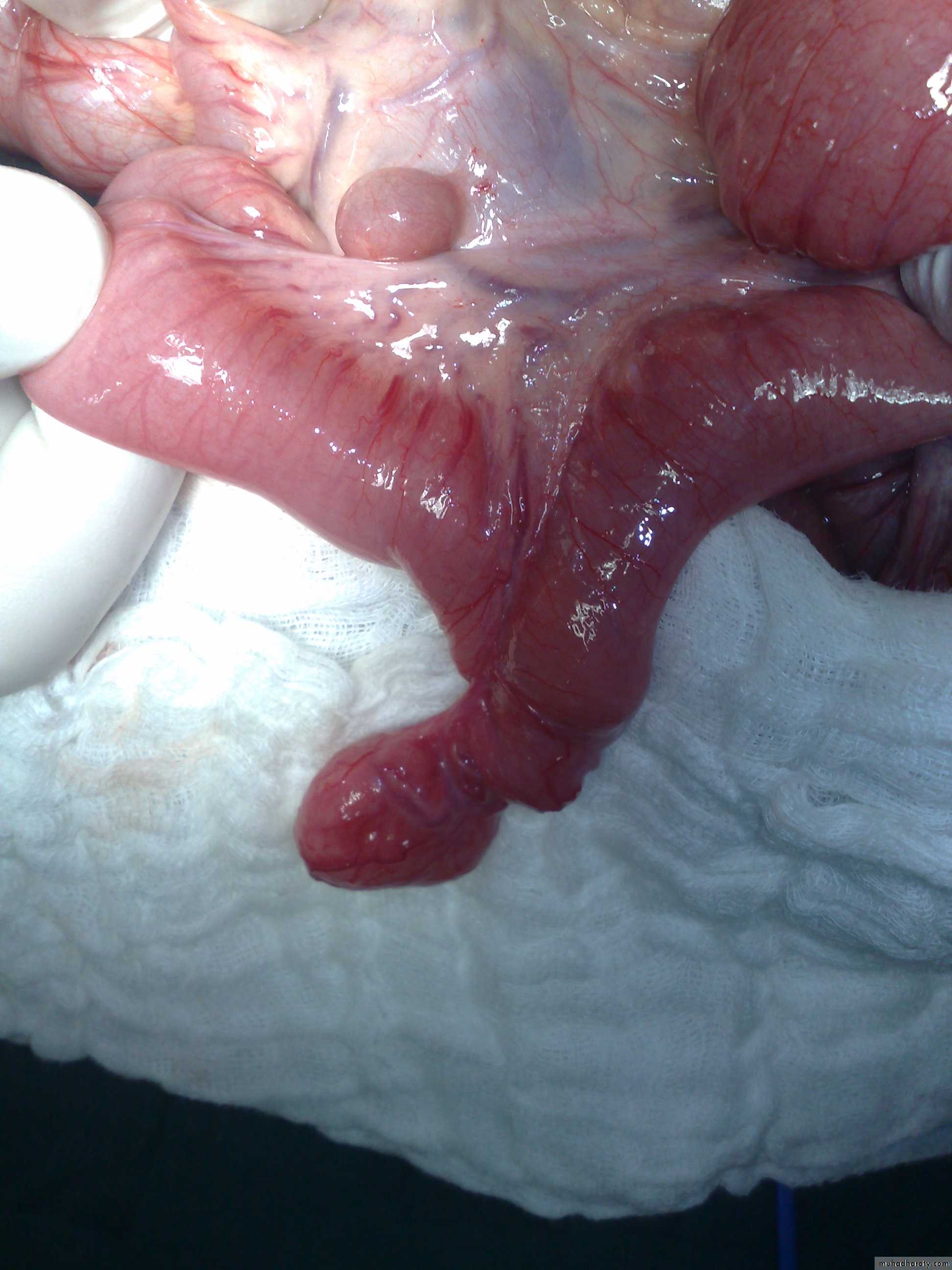
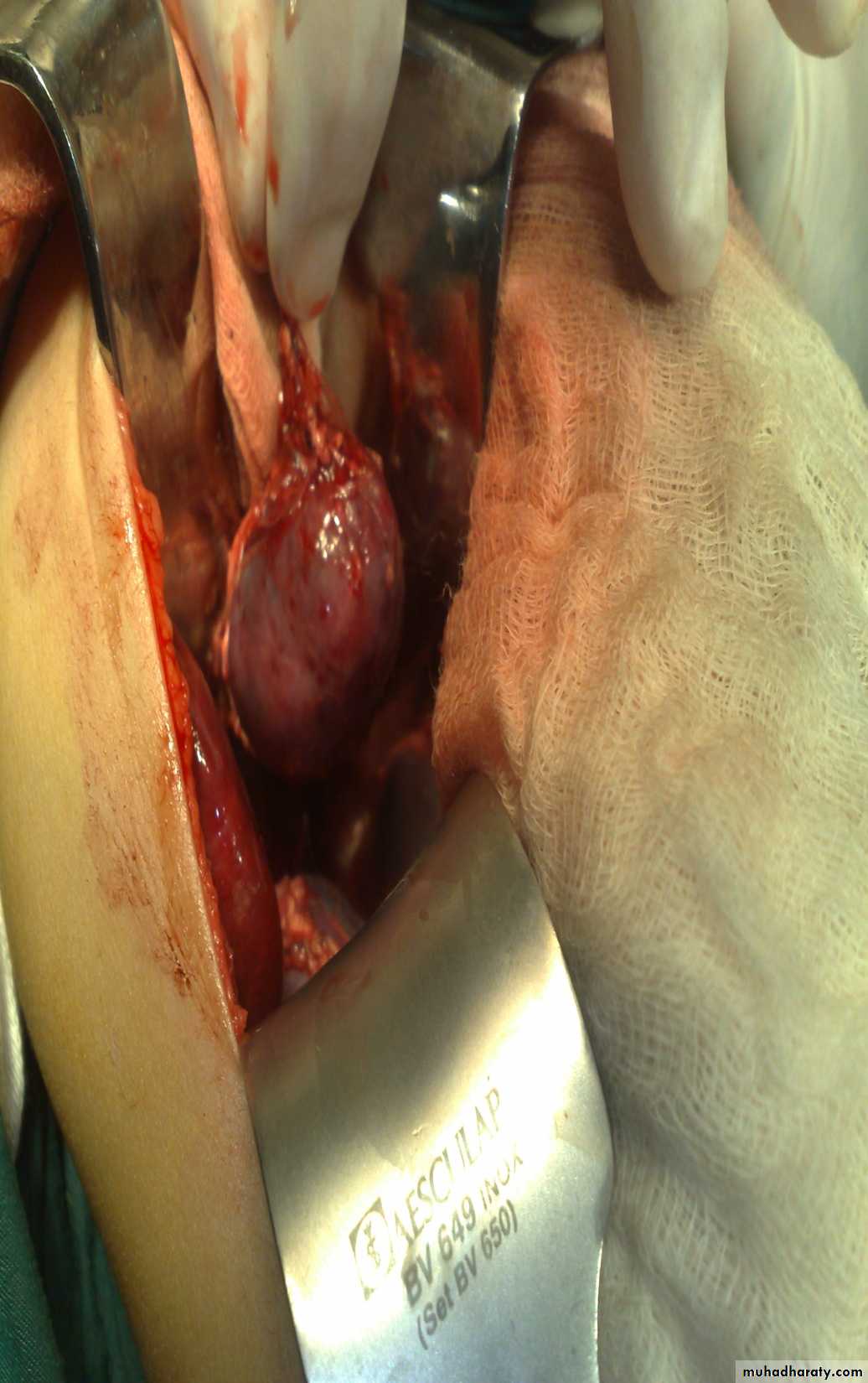
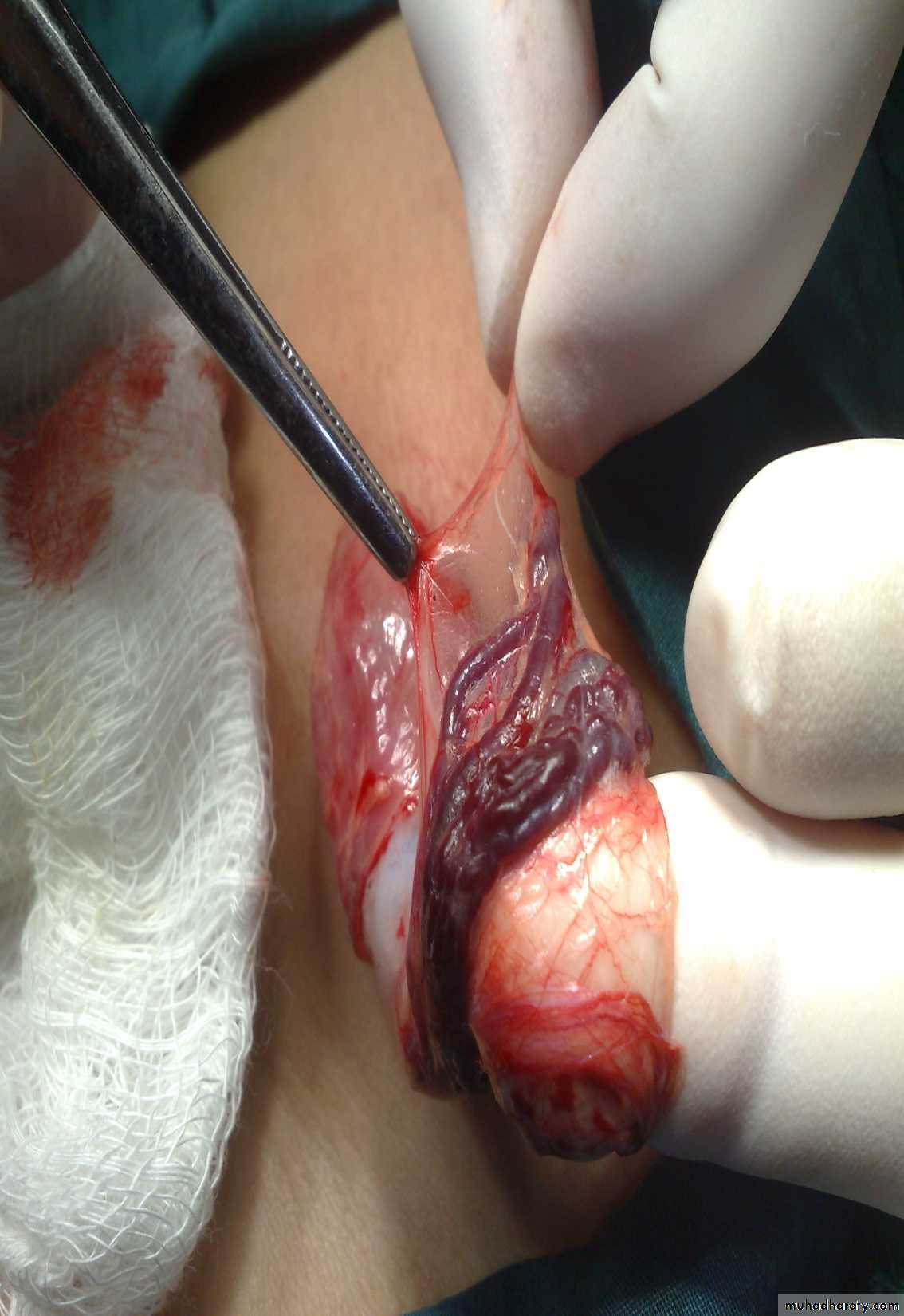
Diagnosis: thyroglossal cystContent : gelatinous fluid
Problems:
• Lead to infection
• Lead to fistula
• Could convert to malignancy
Need surgery remove the fistula tract + remove the hyoid bone to
prevent recurrenceSecond photo:
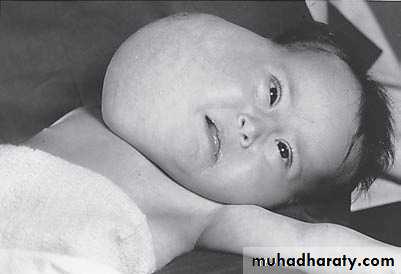
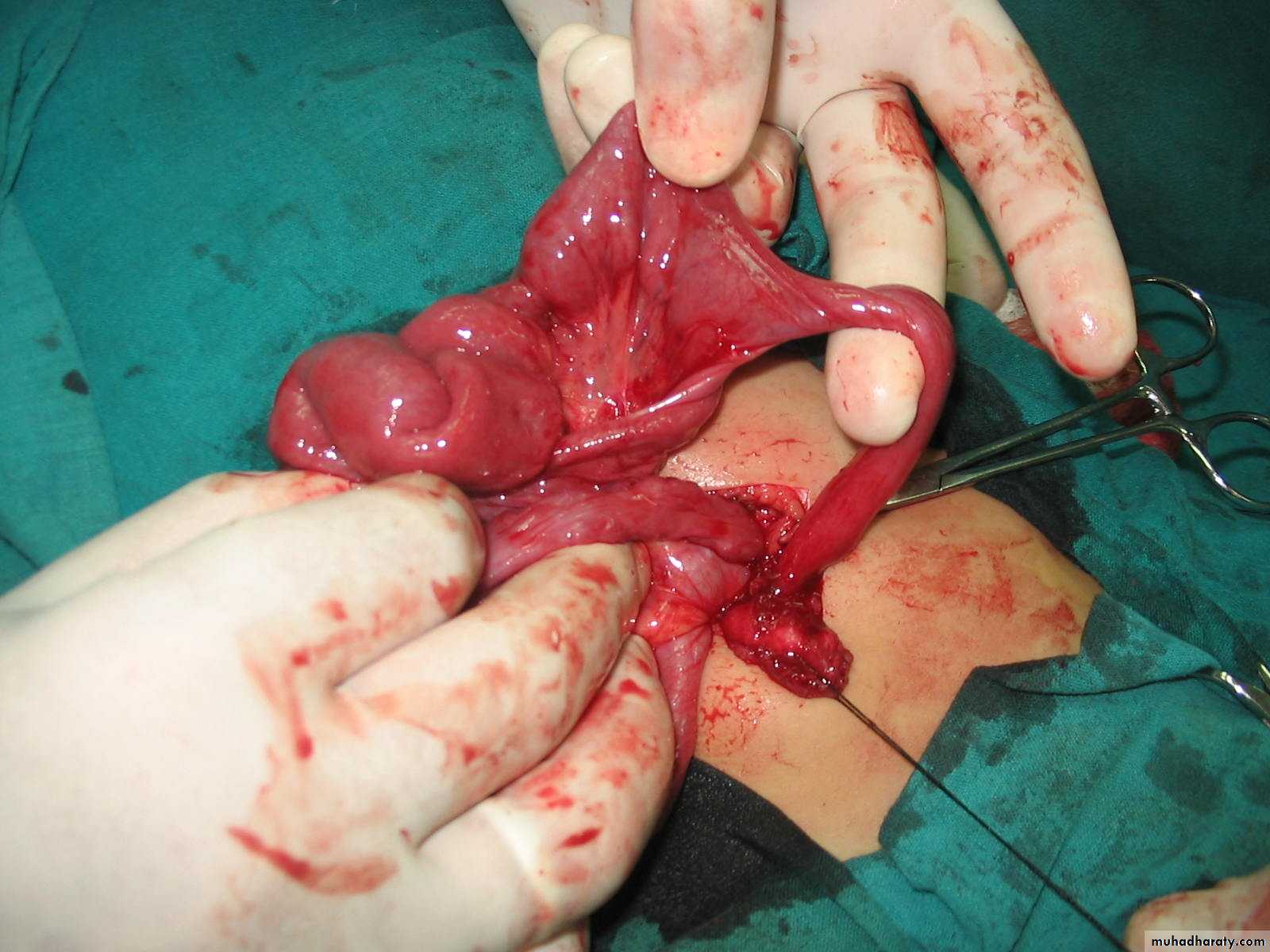
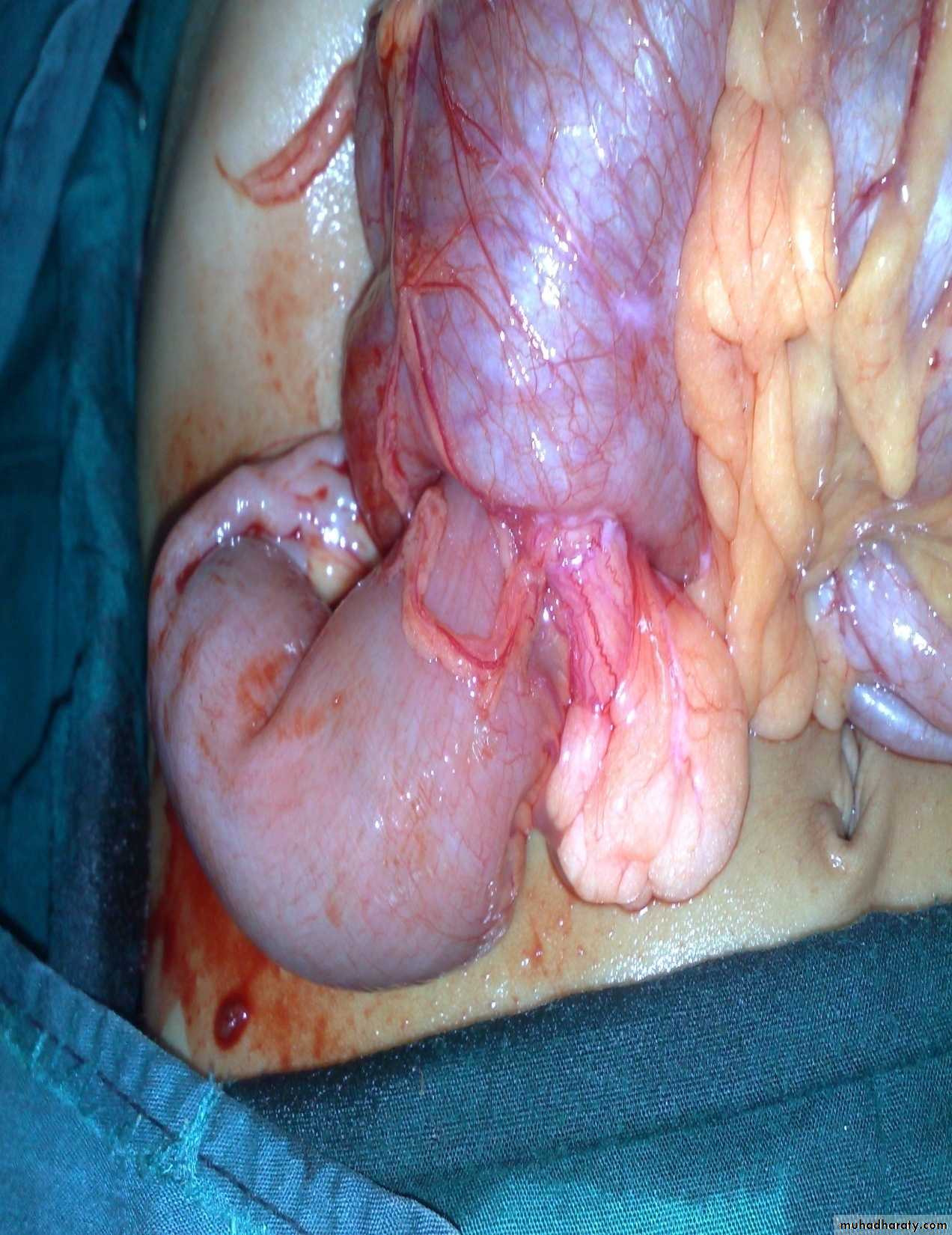
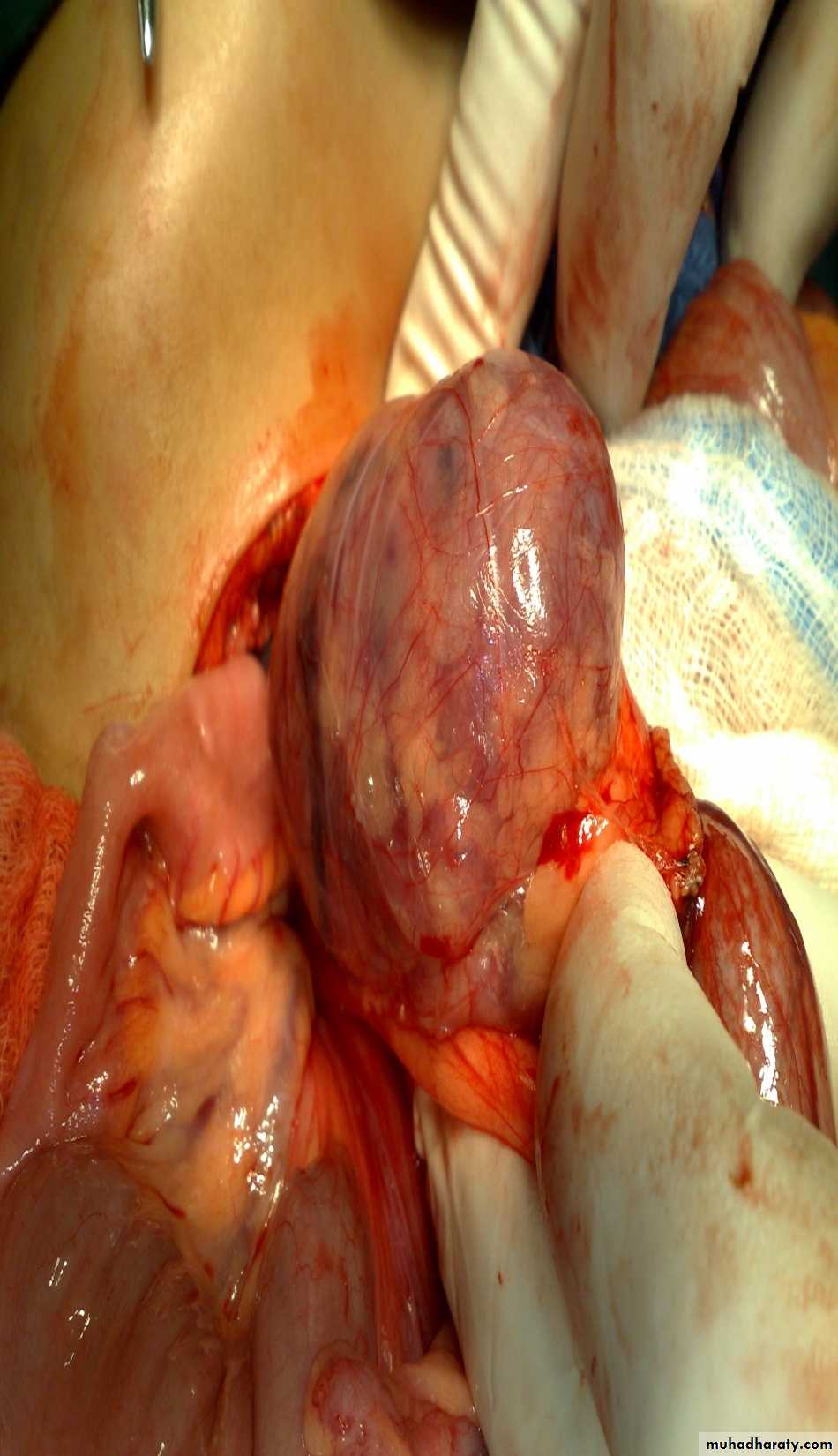
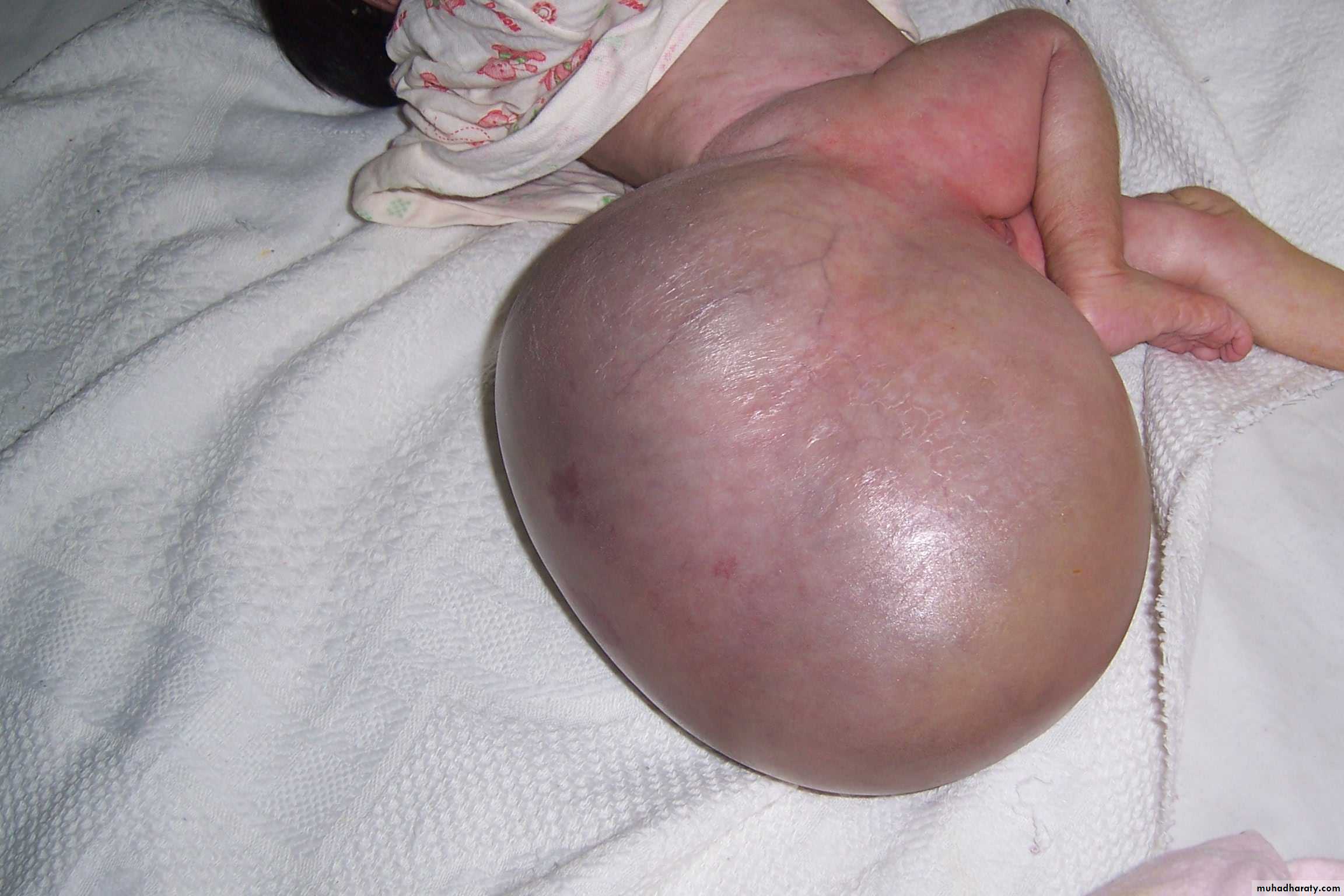
Diagnosis: cystic hygroma
Notes:
• It is due to lymphatic obstruction
• Common at the sites of communication between the trunk and the extremities
like cervical region, axilla, groin.
Treatment:
• By surgery: it depends on presence of complications like compression, infection
bleeding (rapid increase in size and become pale and shock)
• During surgery be careful to some nerves like hypoglossal never, spinal
accessory nerve, mandibular branch of facial nerve
Thyroglossal cyst
-assessment of Thyroglossal cyst: -assess the thyroid gland (present or not)-ask the pt to protrude his tongue
complication : 1-Infection 2-Fistula 3-Malignant transformation after 20 -30 years
Surgery : Sistrunk operation (remove the cyst and the tract completely ) + removal of the central part of hyoid bone or sometimes completely(if didn't done properly –recurrence)
-thyroid tissue can be detected by AITS in cyst
How u know u reached the base of tongue in operation?-
-in operation room I ask the assistant to compress on tongue
-avoid rapture of this jelatinian fluid containing cyst bz it may be missed .
Cystic Hygroma
-It may contain thousands of cysts within –how many cysts present how many its surgery difficult .
-Rx—1-conservative :inj. Of sclersing agent like lyomycin --indx:-few cysts
Or ok-432 –in multiple sessions
2- surgery:-N. inj.----use of nerve st-imulator to see if it's nerve and try to avoid it.
Common sites; groin, neck ( posterior triangle ) axilla.
Complication. InfectionsCompression ( on trachea )
Bleeding
Surgical complication nerve injury as hypoglossal nerve
Spinal accessory
(And to avoid it use nerve stimulator )
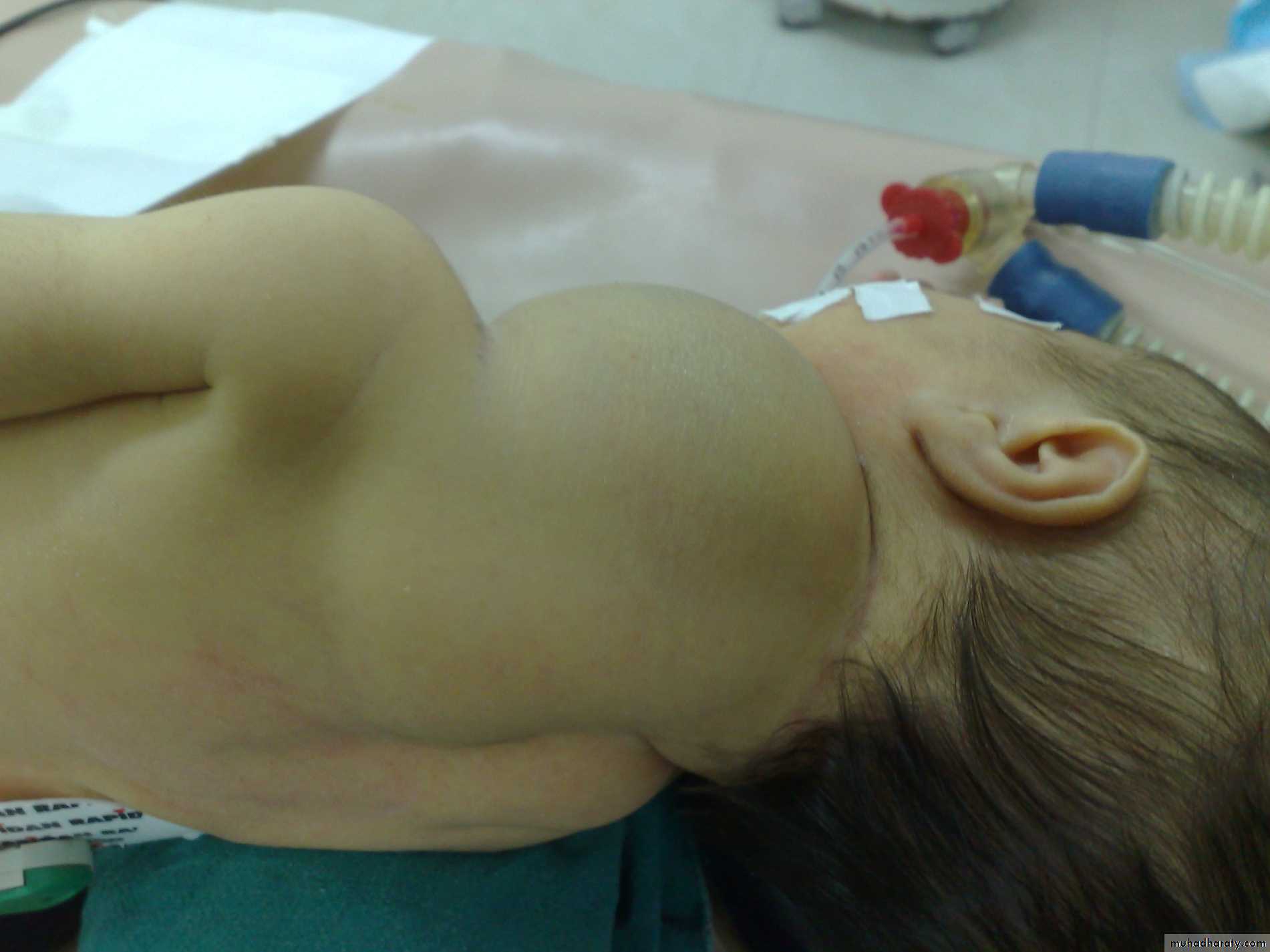
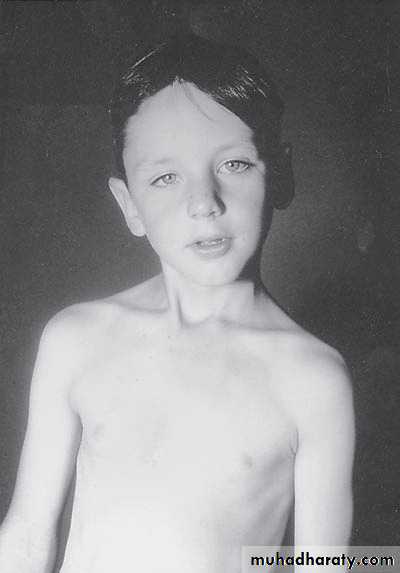
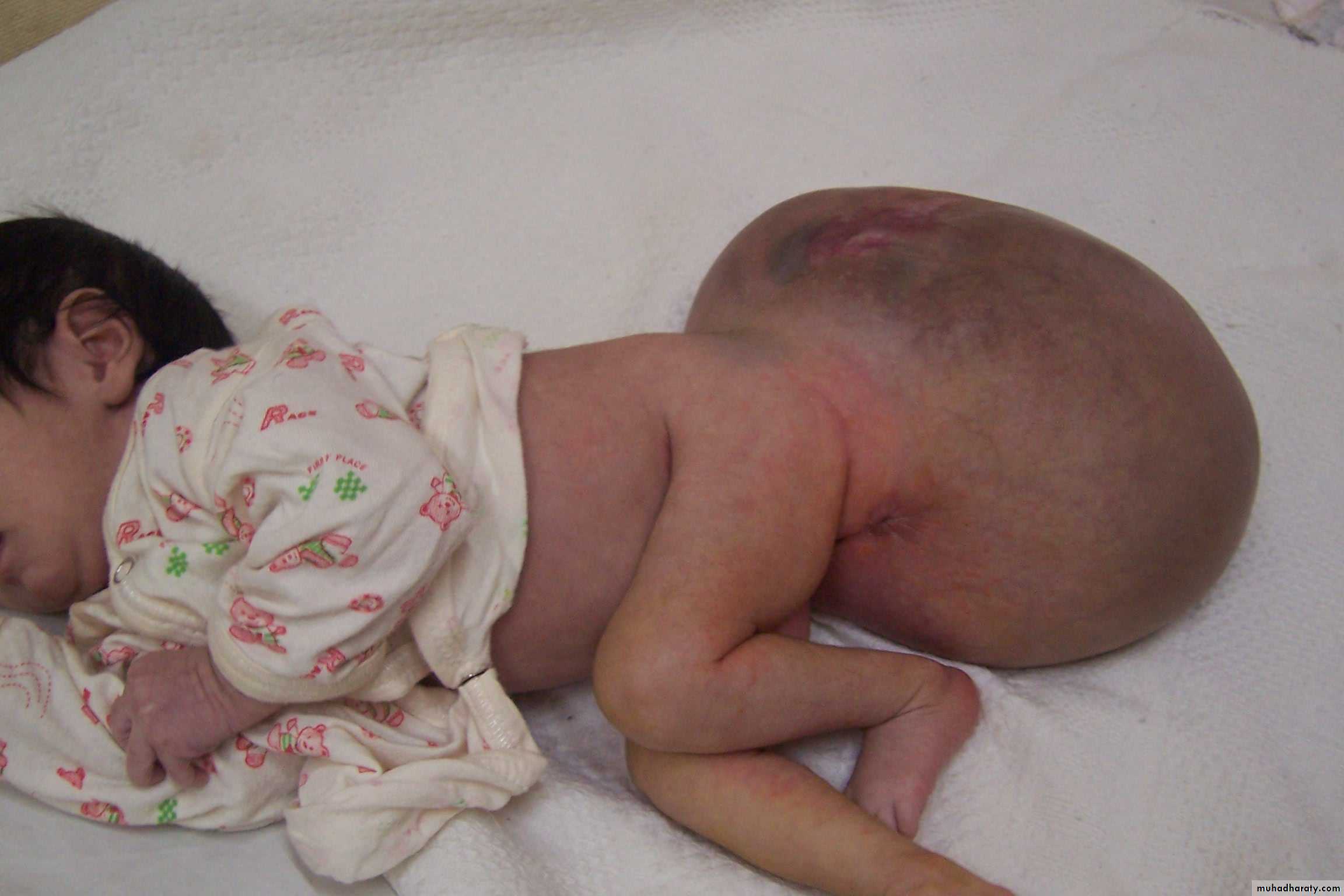
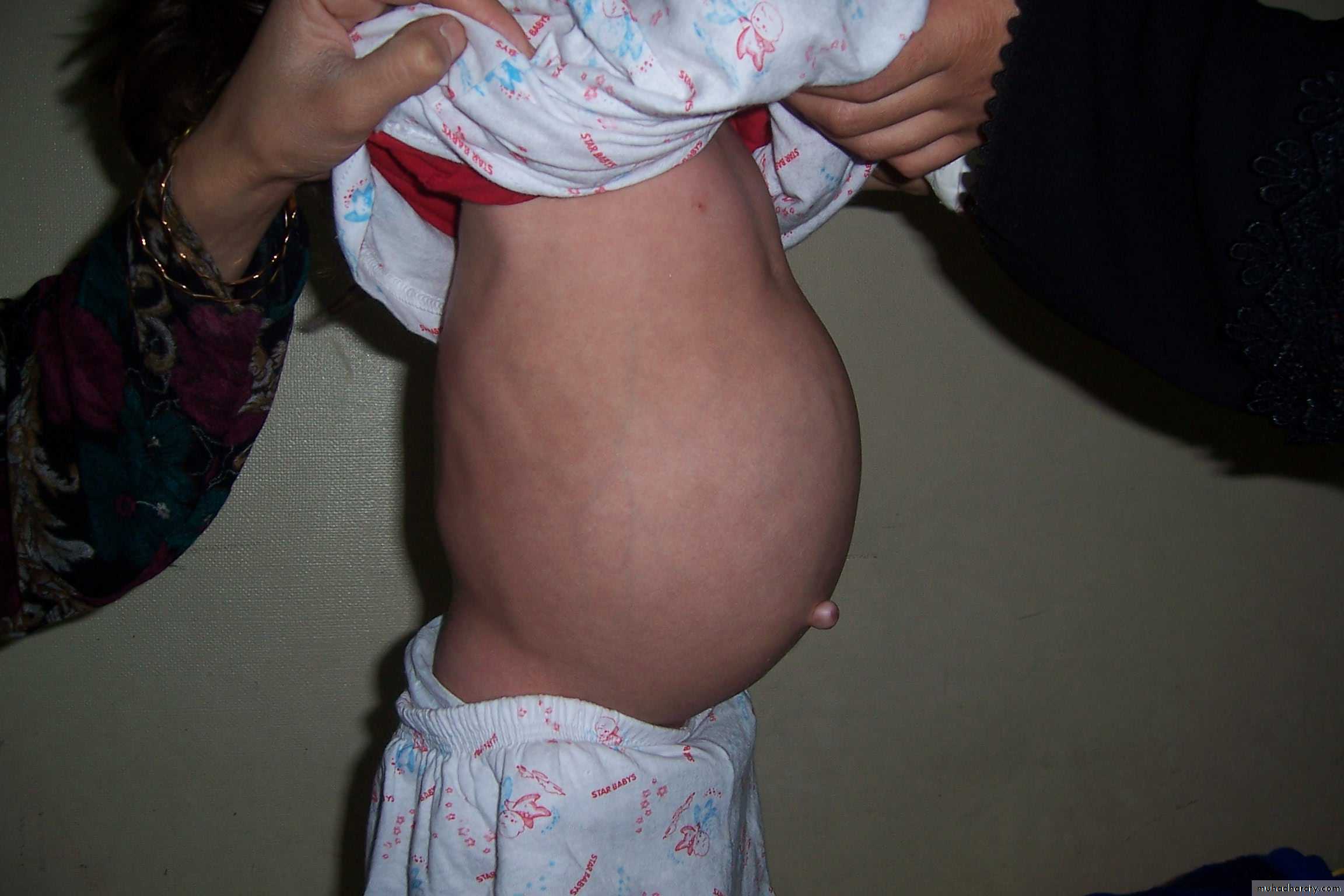
Diagnosis:
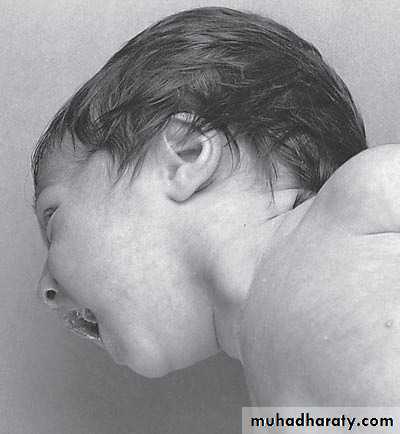
sternocleidomastoid torticollis (first photo)sternocleidomastoid mass (second photo)
Notes:
• Ask about breech presentation and obstructed labor• If not treat the mass it could be converted to torticollis
• Treatment of mass is by physiotherapy by twisting the chin and movement of
earlobule and massage 90% will disappear if not treated do surgery by
cutting the mass and muscle.
• Treatment of torticollis is by surgery.
Torticulus; --ask about breach presentation ----most imp.
Facial hypoplasia * surgery : incision 2 finger above the clavicle and realse it and continue PhysiotherapyFirst photo:
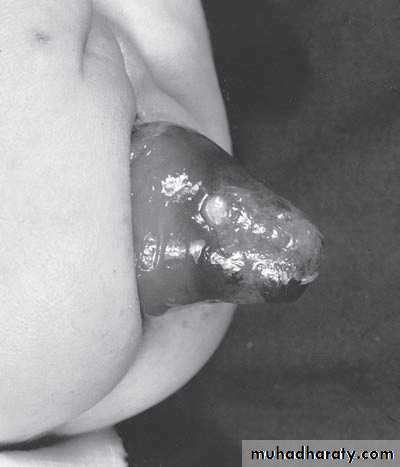
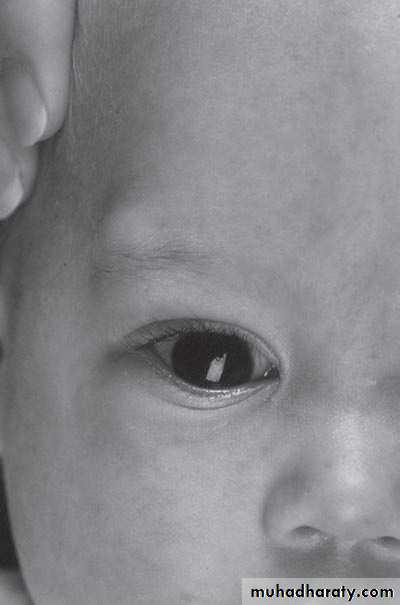
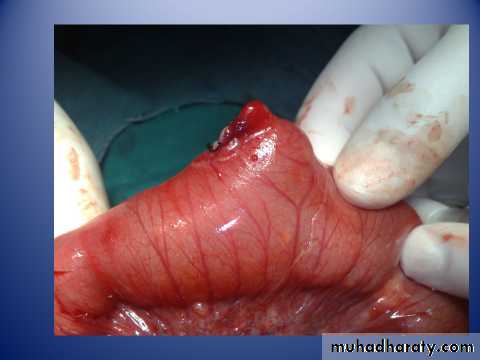
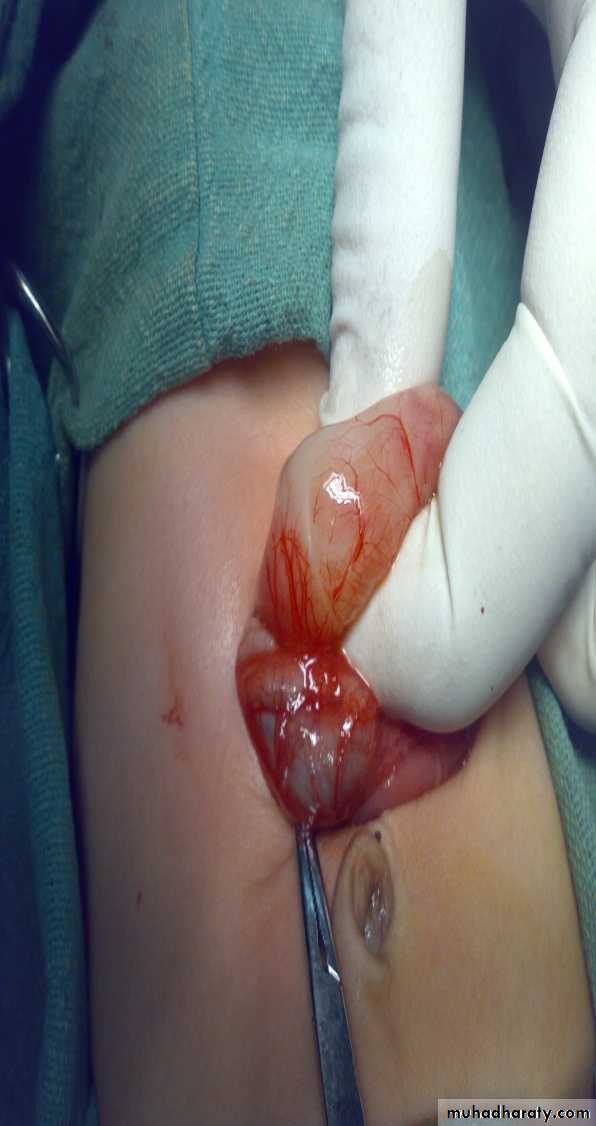
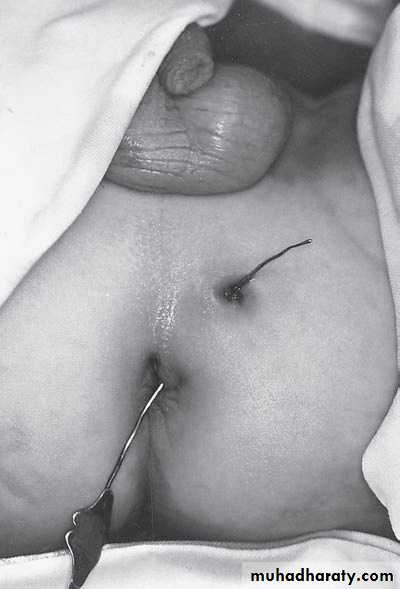
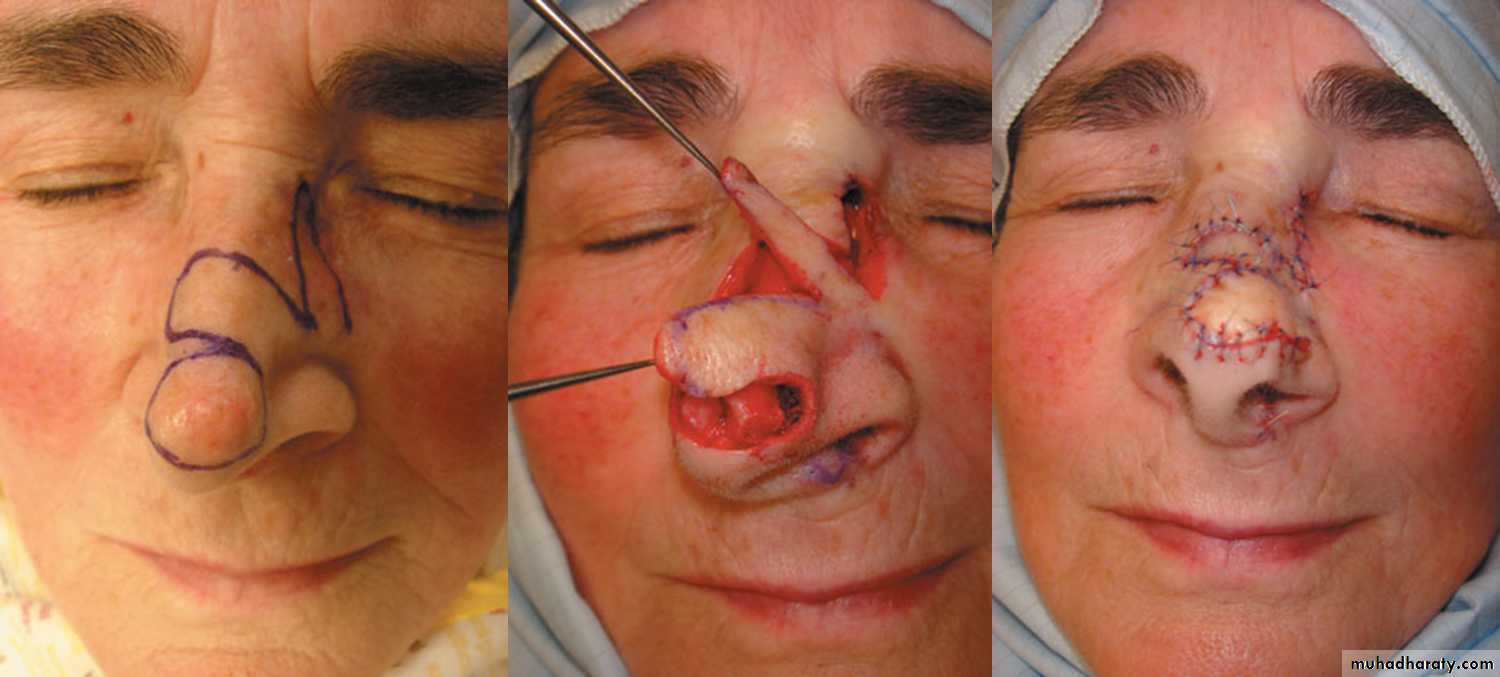
Diagnosis: External angular dermoidNotes:
• Treated by surgery excision and complete remove & don’t shieve the eyebrow hair• Problems infection, trauma, cosmetic
• Liable to trauma
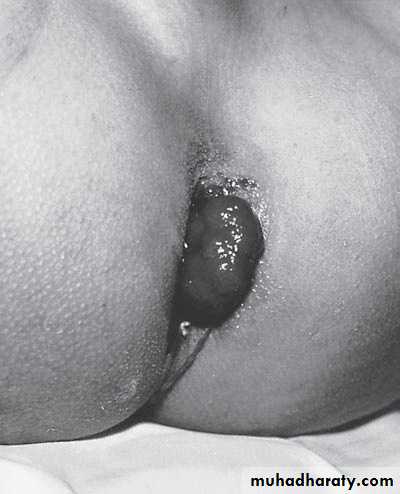
Second photo:
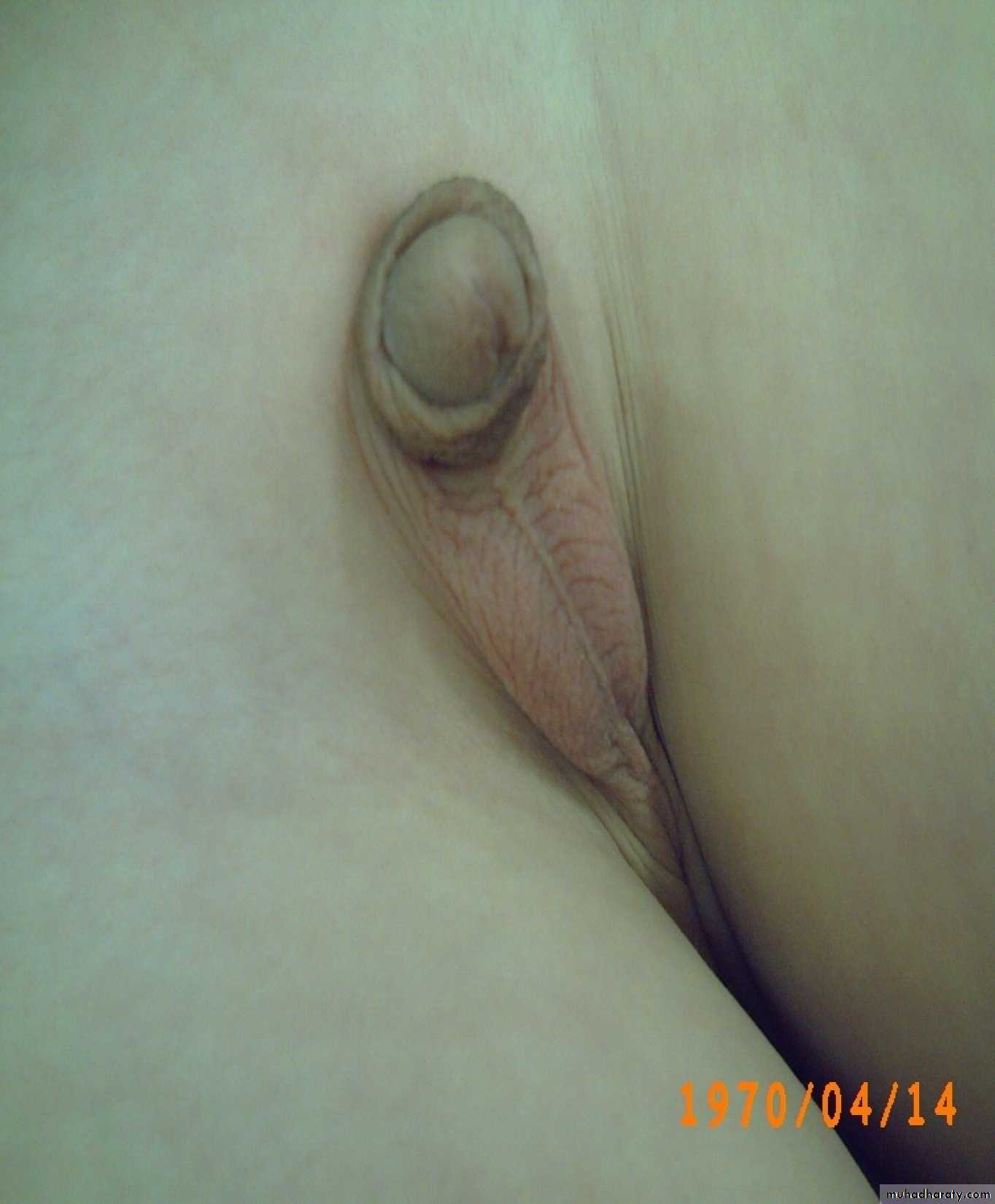
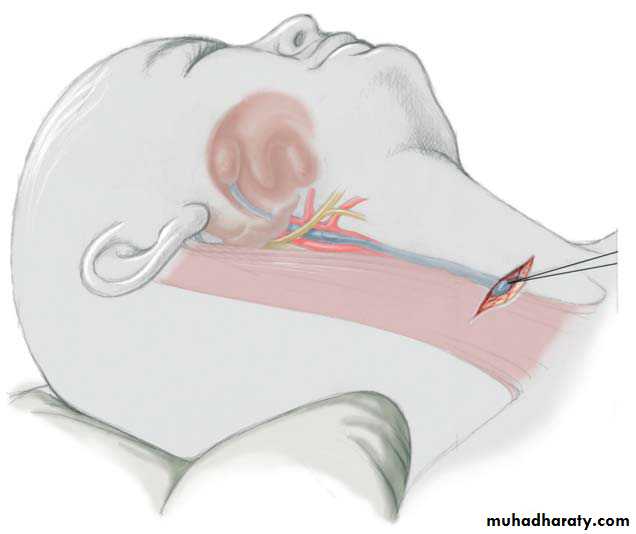
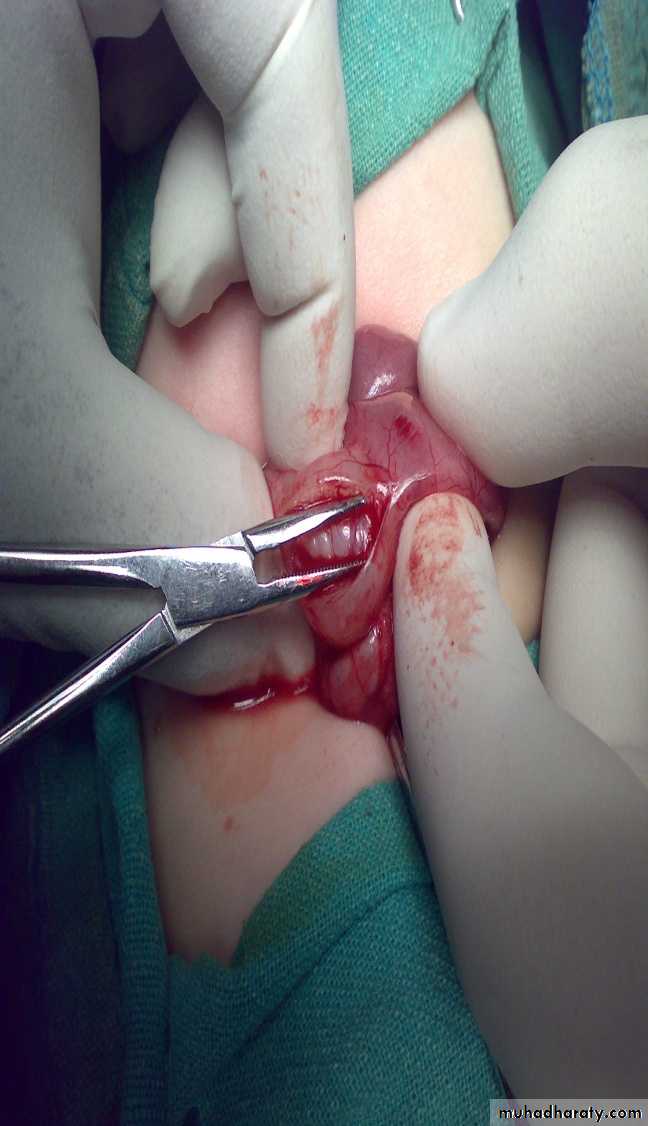
Diagnosis: remnant of second branchial arch branchial cyst or fistula
Hx; Whitish sticky discharge from pin-point opening.
Site: anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle between tonsil
and lower two third of sternocleidomastoid muscleProblems: infection – malignancy
Treatment: surgery (excision)-when baby is one yearProblem during Surgery;-inj. To bifurcation of carotiod & hypogossal n.
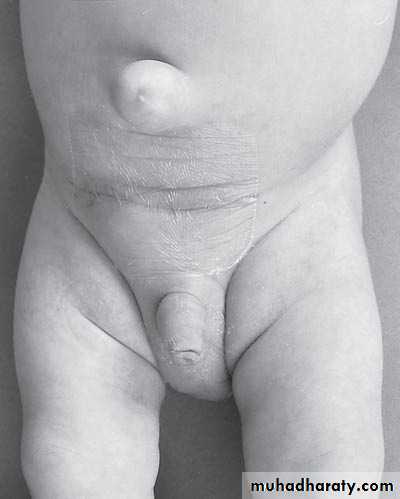
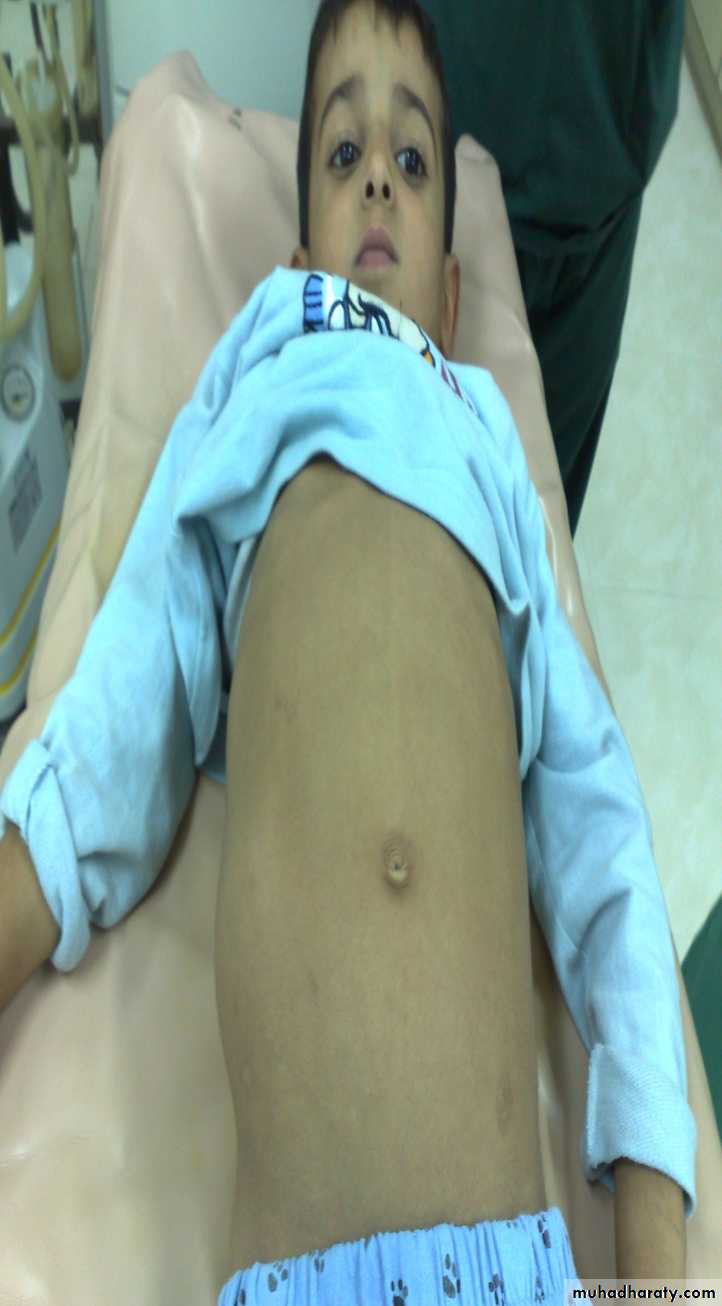
The Umbilicus
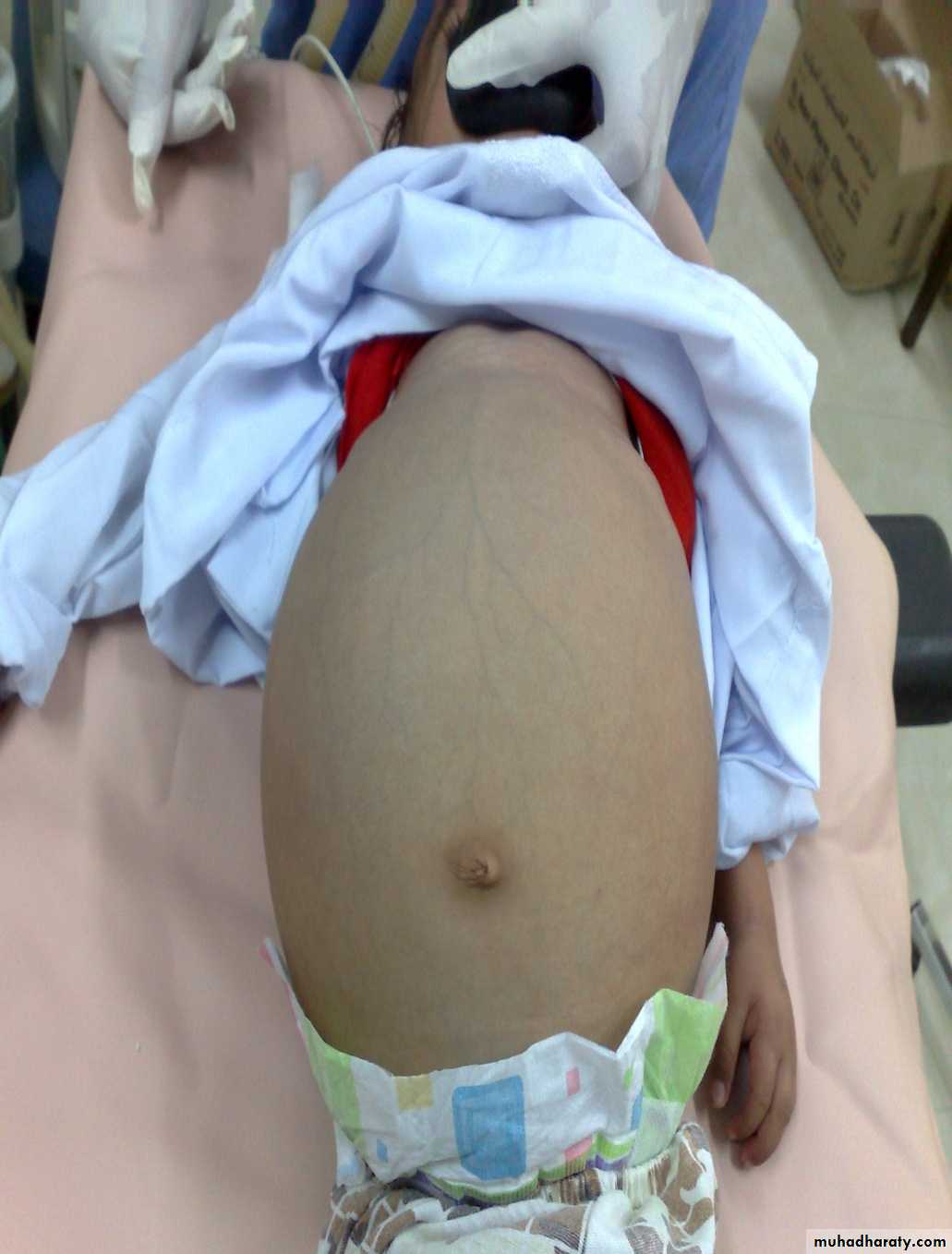
First photo:
Diagnosis: umbilical herniaTreatment: could resolve spontaneously or by surgery
Indication for surgery;1-obstructed H. 2-Age >3-5y.o3-size >3-4cm 4-any problem increase intra-abd. pressure
Second photo:
Omphalo-mesenteric duct connection between umbilicus and bowel
1-Complete communication between skin and bowel = fistula 2- Cyst
3-Meckles diverticulum
*patent uricus—blader to umbilicus tract
-Rx;-probing –catheter and see where contrast appear in bladder or intestine
to determine type of anomaly
Diagnosis: Michaels diverticulum
Role of 2:• 2% of population.
• 2 type of mucosa(ectopic gastric mucosa).
• 2 feet from iliocecal valve.
• 2 inches in length.
Presentation:
• Bleeding per rectum (painless – bright red – profuse)• Infection (lead to abdominal pain)
• Complication intestinal obstruction, volvulus, intussusception
• Incidental finding
Diagnosis:
• Use isotope (bind to gastric tissue (parietal cell) within the Michaels)• Laparoscope (diagnostic and therapeutic)
Wider neck ----obstruction by band
1 y.o infant with effortless vomiting since birth
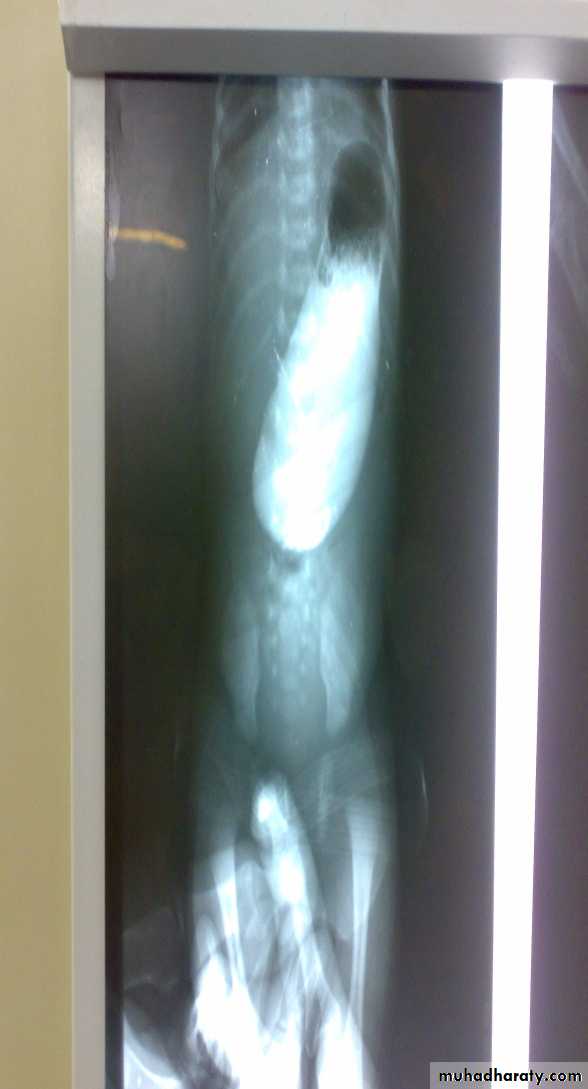
Growth within normalDx:-Hiatus Hernia(above diaphragm)
Types:-sliding -Roling -Mixed(commonest in pediatrics)
*it’s associated with bleeding—often
-it’s subtype of D.H
Surgery:Fundiplication
Vomiting in the First Months of Life
Diagnosis: pyloric stenosis(IHPS infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis—this name should be mentioned)
Presentation:
• Projectile vomiting (not present in first two weeks)• Olive mass in the abdomen
• Positive prestalsis(visible)
• FTT
Diagnosis:
• Clinically
• Ultrasound(width>14mm-length>16mm)
• Ba-meal dilated stomach – failure to pass to intestine – string sign
Treatment: in ER : resuscitation the pt(electrolyte+fluid)
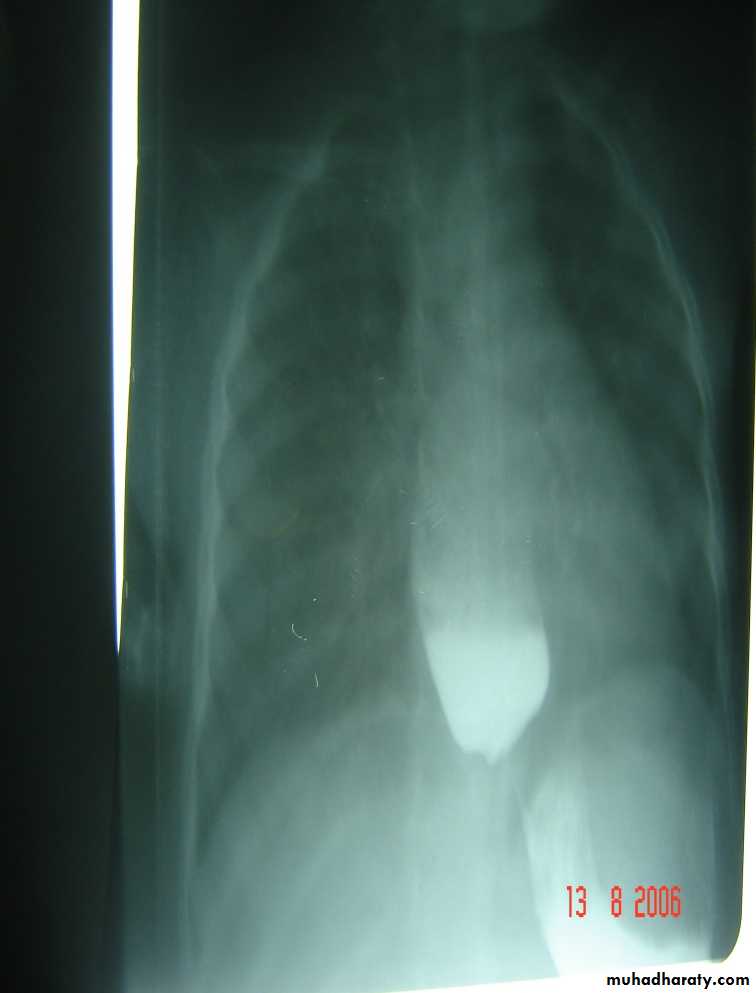
surgery pyloromyotomy (rami stick surgery)Diagnosis: achalasia cardia
Presentation:• Hailtosis
• Vomiting (not projectile)(bad odor)
• Wheezing
• Chest infection(recurrent)
Ba-swallow dilatation of esophagus with narrowing of lower part.
Treatment cardiomyotomy +fundoplication(by abd. Approach)
(heller operation)• **role of conservative by CCB or bochlenium toxin –not applicable today
The Child with an Abdominal Mass
5 years child, presented with mass in the flank.
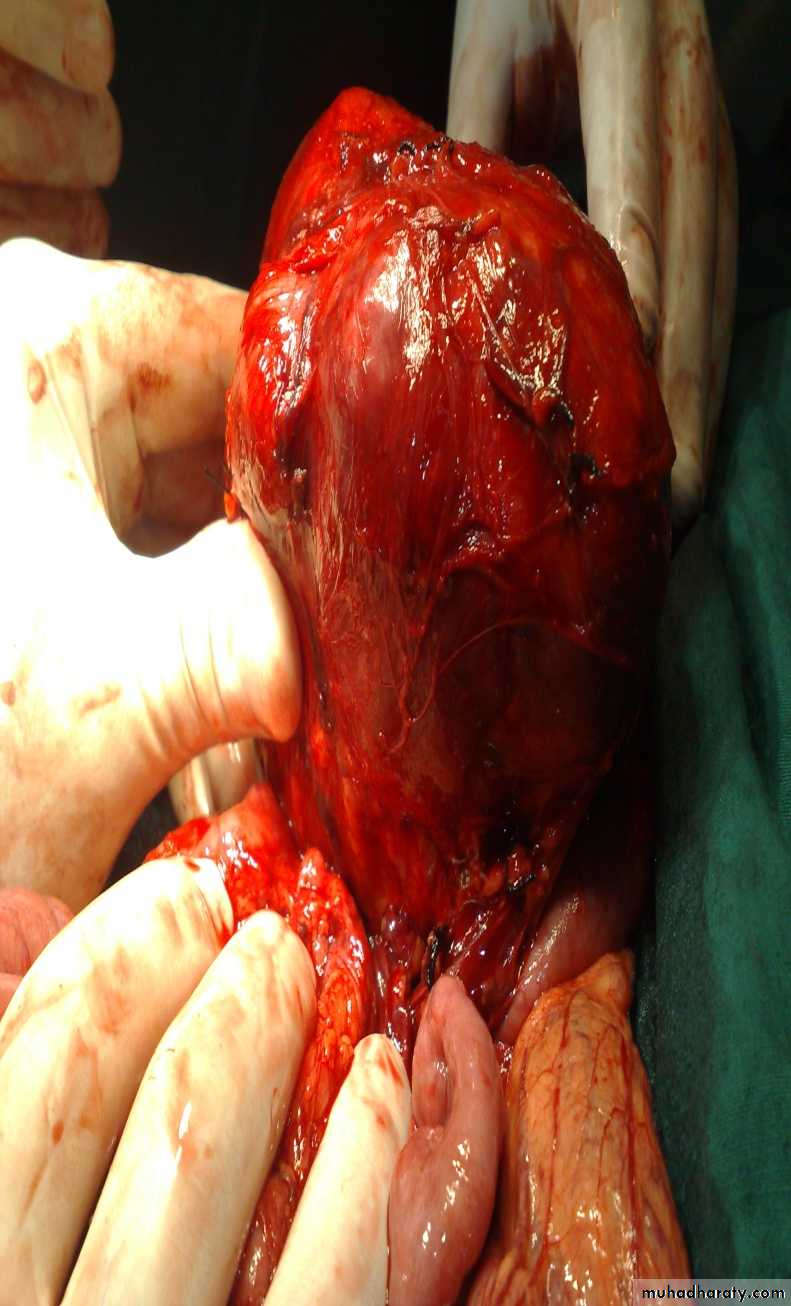
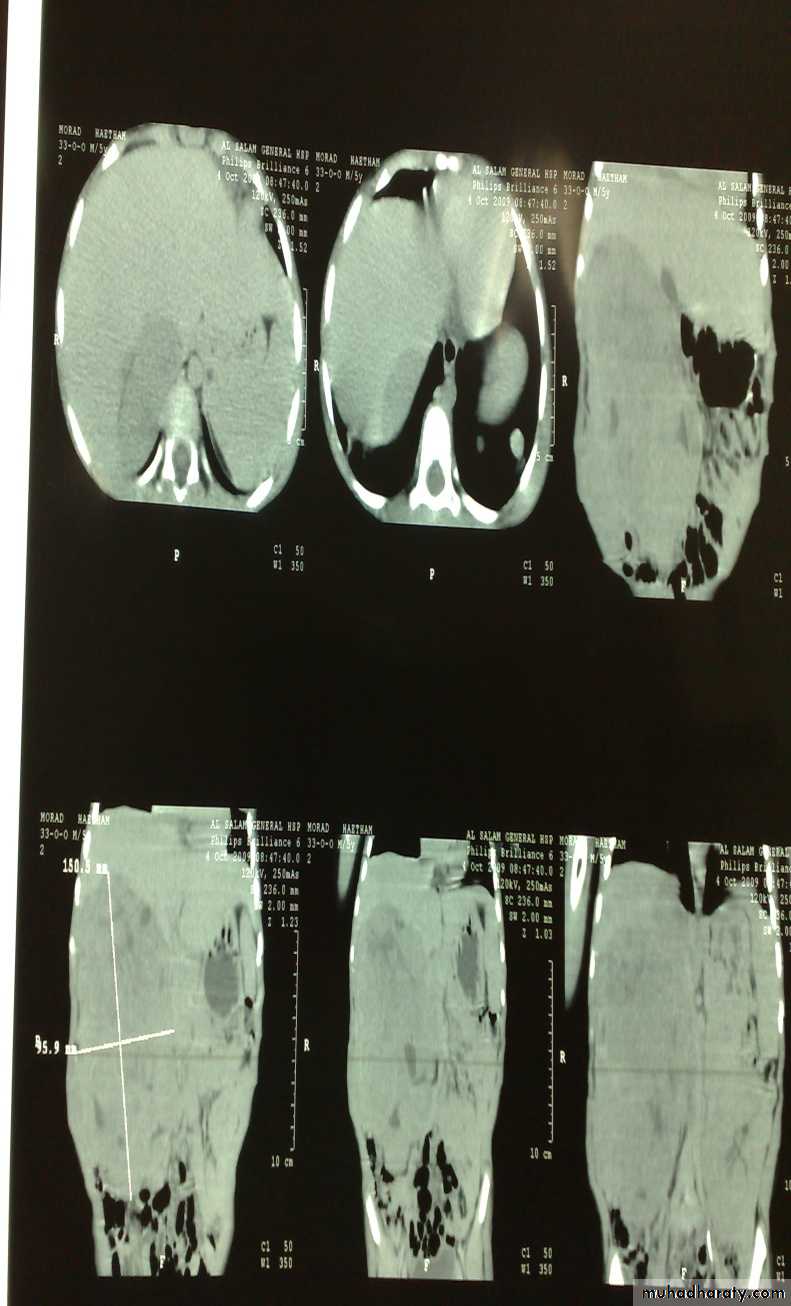
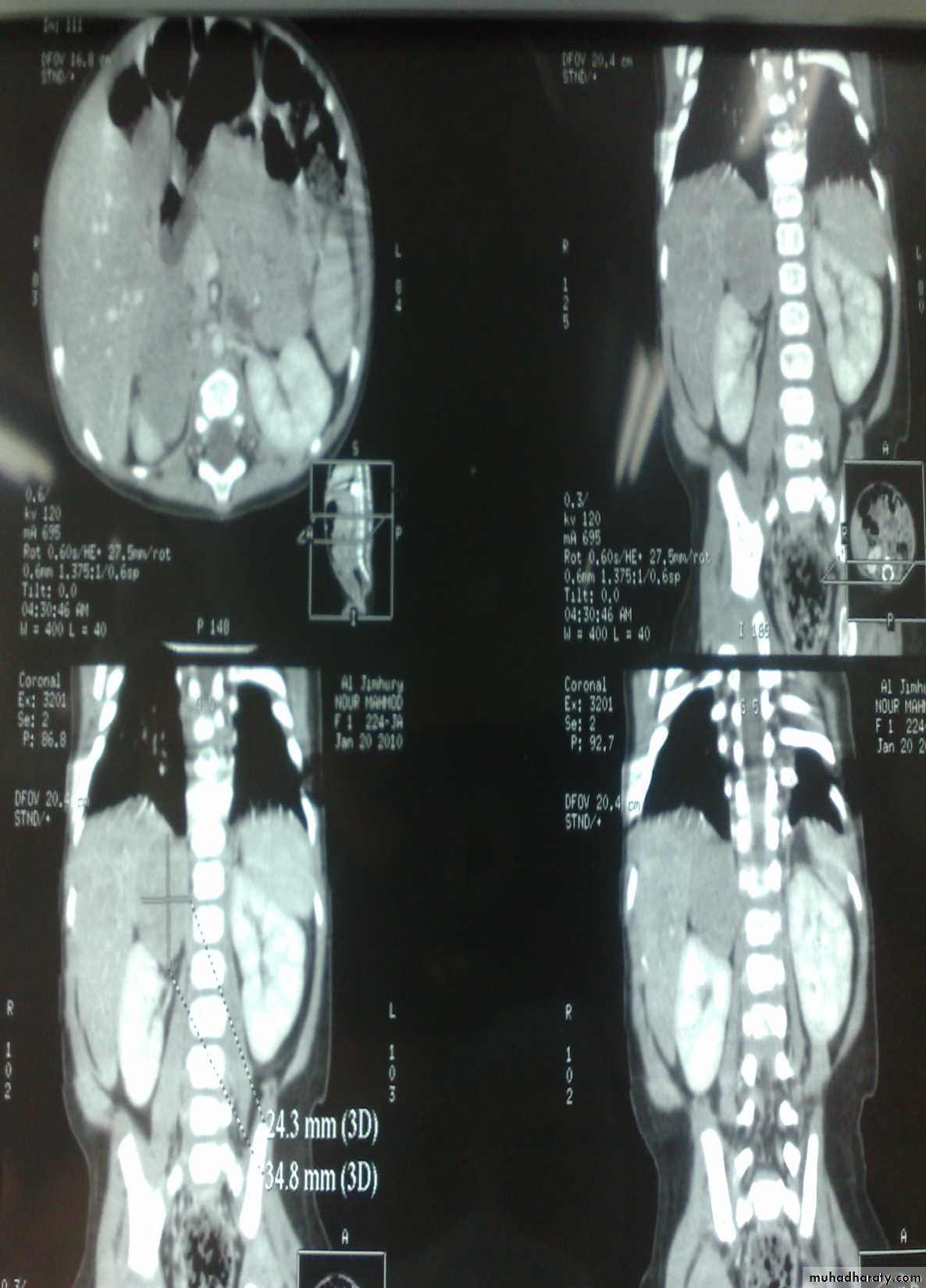
Dx: nephroblastomaDDx of mass in the flank:
1- Wilms tumor2- Neuroblastoma
3- Neglected PUJ obstruction
Presentation:
1- Mass2- hematuria
3- hypertension(1/3pt)
4-Incidental finding
Treatment by surgery remove the kidney + chemotherapy
The most common of pediatric renal tumor is Wilms tumor(second is neuroblastoma) (third is lymphoma non-hogkins),Neuroblastoma in the adrenal gland
Presenation : abd. Pain & mass &HT &incidental finding &recon eyeDansing eye syndrome
-diarrhea &flushing bz of catecolamines secreted
Dx: by fenyl mandilic acid in urine
Sites ;1-mediastinum2-Abd. Mass2/3 (supra-renal)
3-cervical
4-Pelvic
Diagnosis: non-Hodgkin lymphoma(burkit lymphoma)
Presentation:
1- Mass2- Intussusception(2ry type –10 year ---no role for conservative Rx)
The problem in lymphoma:1-emergency due to it is rapid growth(doubling dialy)
2-Tumor lysis syndrome-(with manipulation or chemotherapy or surgery
Bz uric acid which will cause renal shut down.
Investigation: FNA
Treatment: surgery + chemotherapy (for one year)
-chemo---debulking is used when there is no GIT complication like Itussusception
-surgery;-when there is complicationDiagnosis: Sacro-coccygeal teratoma
Problems:
1-obstructed labor
2- Malignancy (if neglected for 2-3 months)
3-bleeding:may cause death(middle sacral a.—from aorta)
Teratoma;more common in rapid growing structure like ovary& testes& stomach &brain
misDx as twin.
Treatment: surgery + remove the coccyx to prevent recurrence
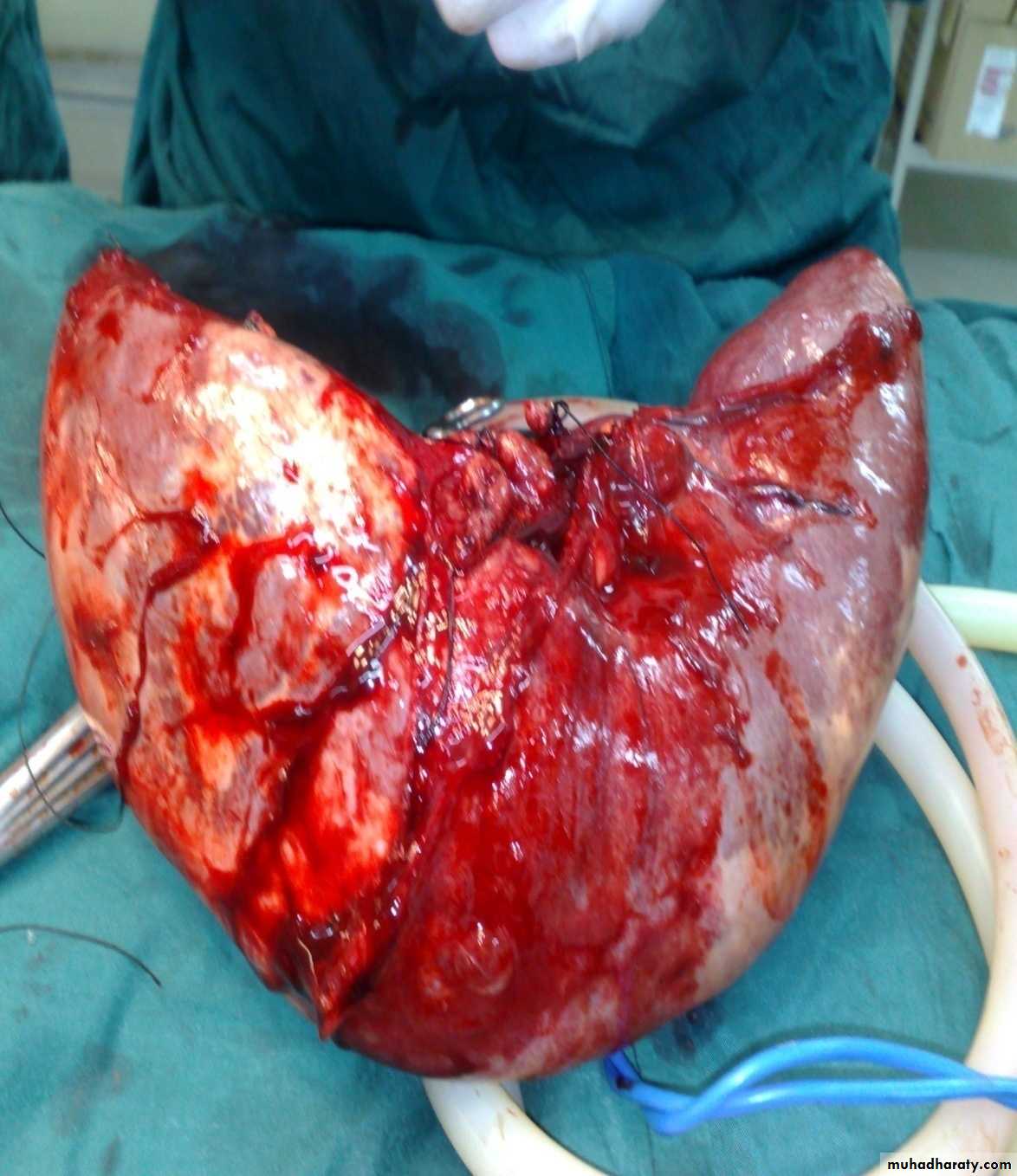
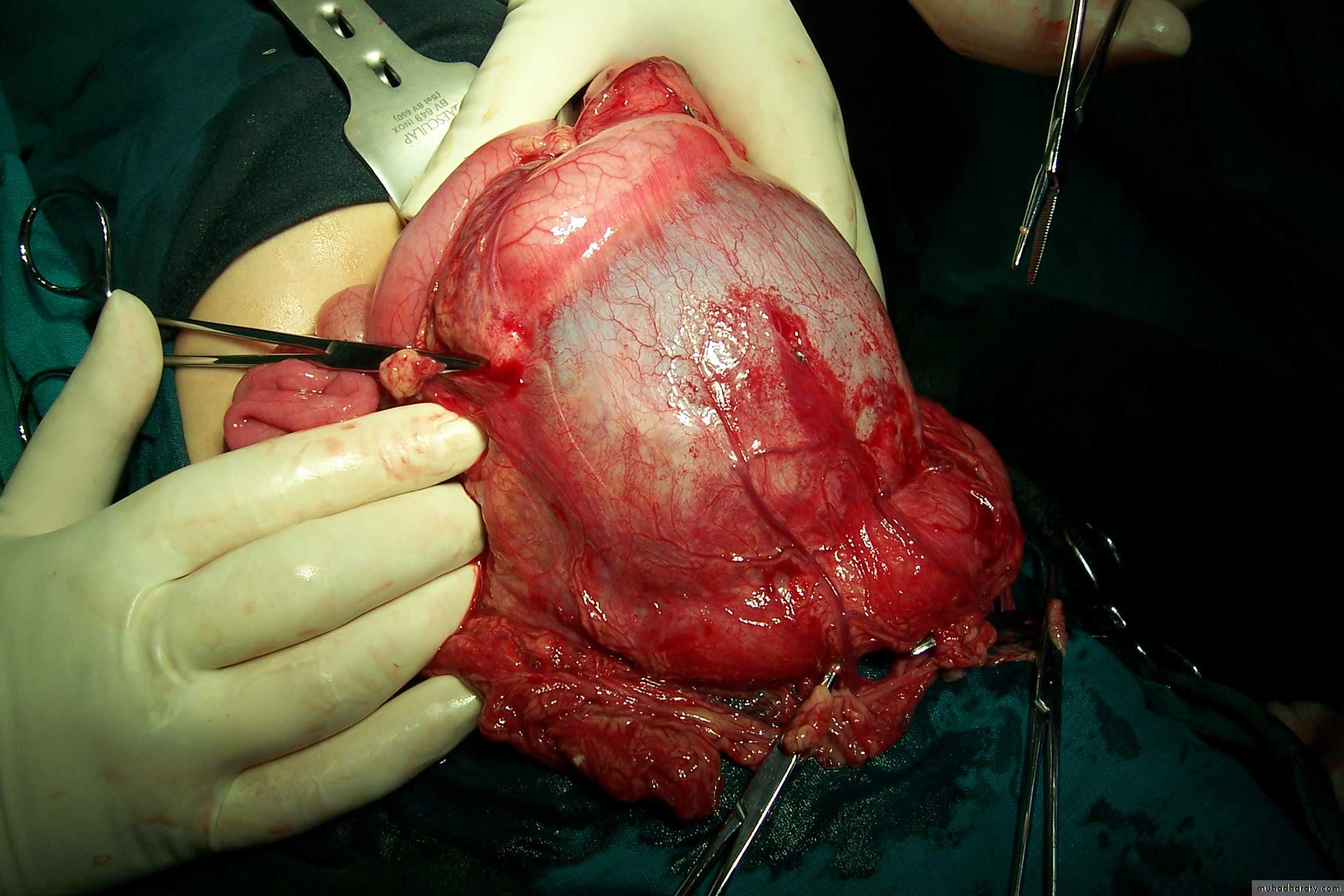
Spleen, Pancreas and Biliary TractSplenomegaly
Indication of splenectomy:-Blood dz:1-thalassemia 2-ITP 3-malaria 4-CML 5-gowsher dz—mecopolysacharide storage dz6-lymphoma 7-H.cyst
غير مطلوب
Pancreatic pseudocystPresentation: abd. Destension after trauma
causes
-chronic pancreatitis
Causes of acute pancreatitis -Trauma
-congenital stenosis
-asacaris
-drugs –corticosteroids
Rx;surgery—Follow-up
---drainage uder us-guided---cystogastrostomy
First photo:
Diagnosis: rectal prolapseCauses:
• Constipation or chronic diarrhea
• Weak pelvic muscles –in spina bafida
• Worm (trichuris trichiura)
Grades:
• Grade1 يطلع ويرجع conservative treatment by taping
• Grade2 يطلع ويحتاج الى دفع للدخول surgery (Therach operation)
• Grade3 يطلع وما يرجع ابد surgery (Therach operation)
Second photo:
Diagnosis: Perianal fistula
Causes infection
Presentation as Abscees
Treatment: surgery (fistulectomy or fistulotomy)
Third photo:
Diagnosis:juvenile rectal polyp
Cause in infection
Red-bleed mass + bleeding per rectum+PRE can detect it(90%)
Treatment: excision-polypectomy directly (use sigmoidoscope)
other type as familial polyposis coli(100% malignant potential)
Hernia
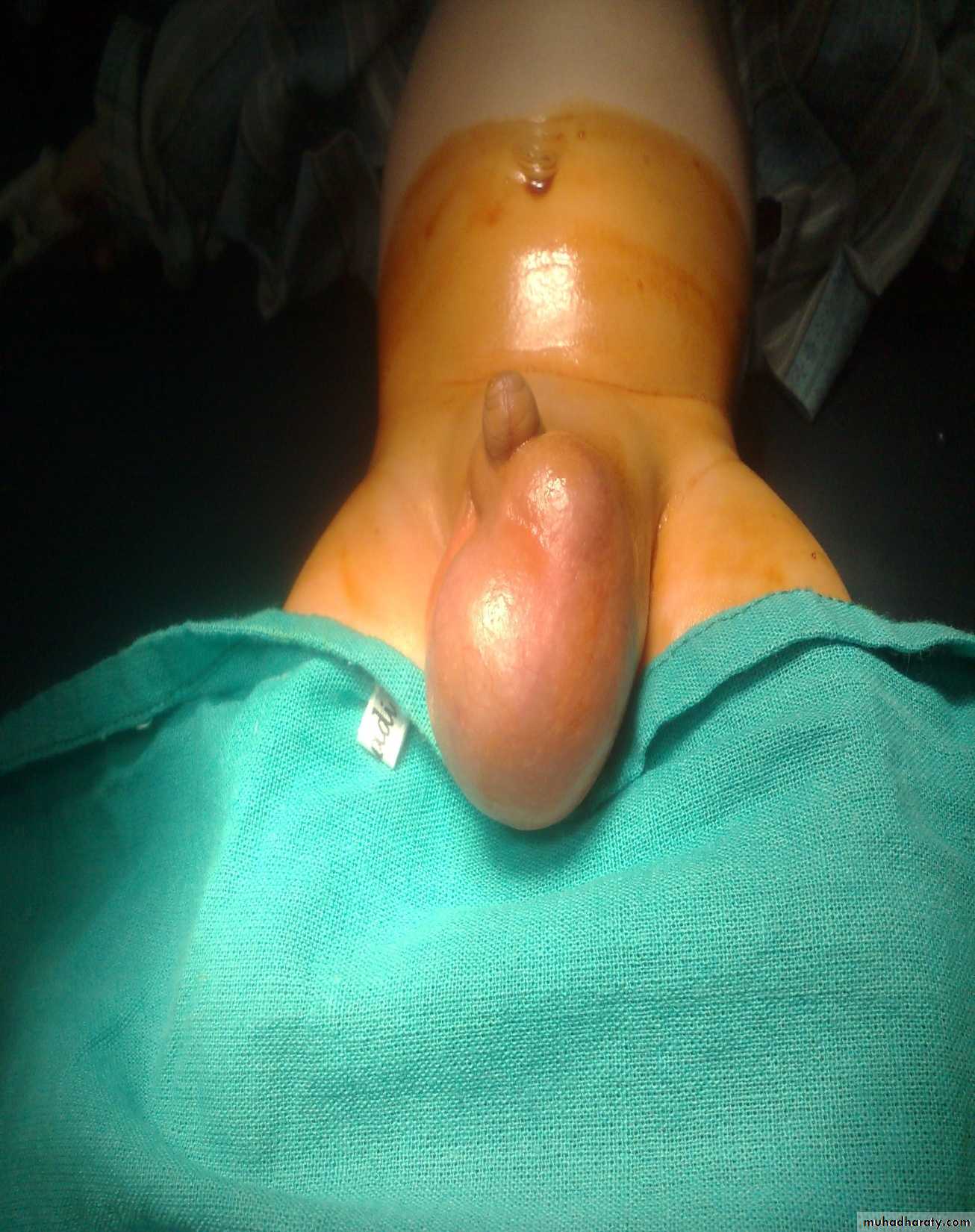
VaricoceleDiagnosis: undescended testes
Problems:• Tumor
• Sterility
• Infection
• Orchitis (like appendicitis)---in abd.
Treatment:
• If palpable do fixation
• If not palpable do laparoscopy
• If not present do nothing
Time of surgery:-6month-1y
>1y. Decrease benifet
>2y. No benifet
*Ex. On 3 position
Squatting
Lying
Standing
Dx. Laparoscopy
*Complication : trauma, Infertility, ca , psychological problem.
* surgery : 6 month _ 1 year ( best time)
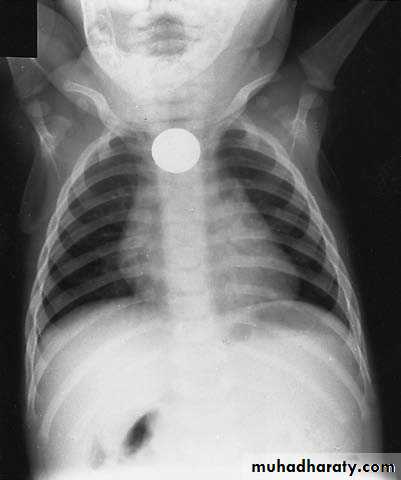
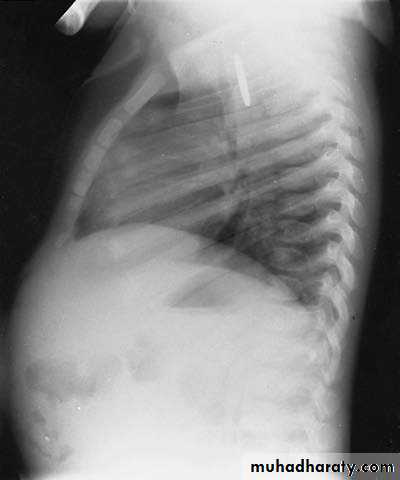
Esophageal F.B
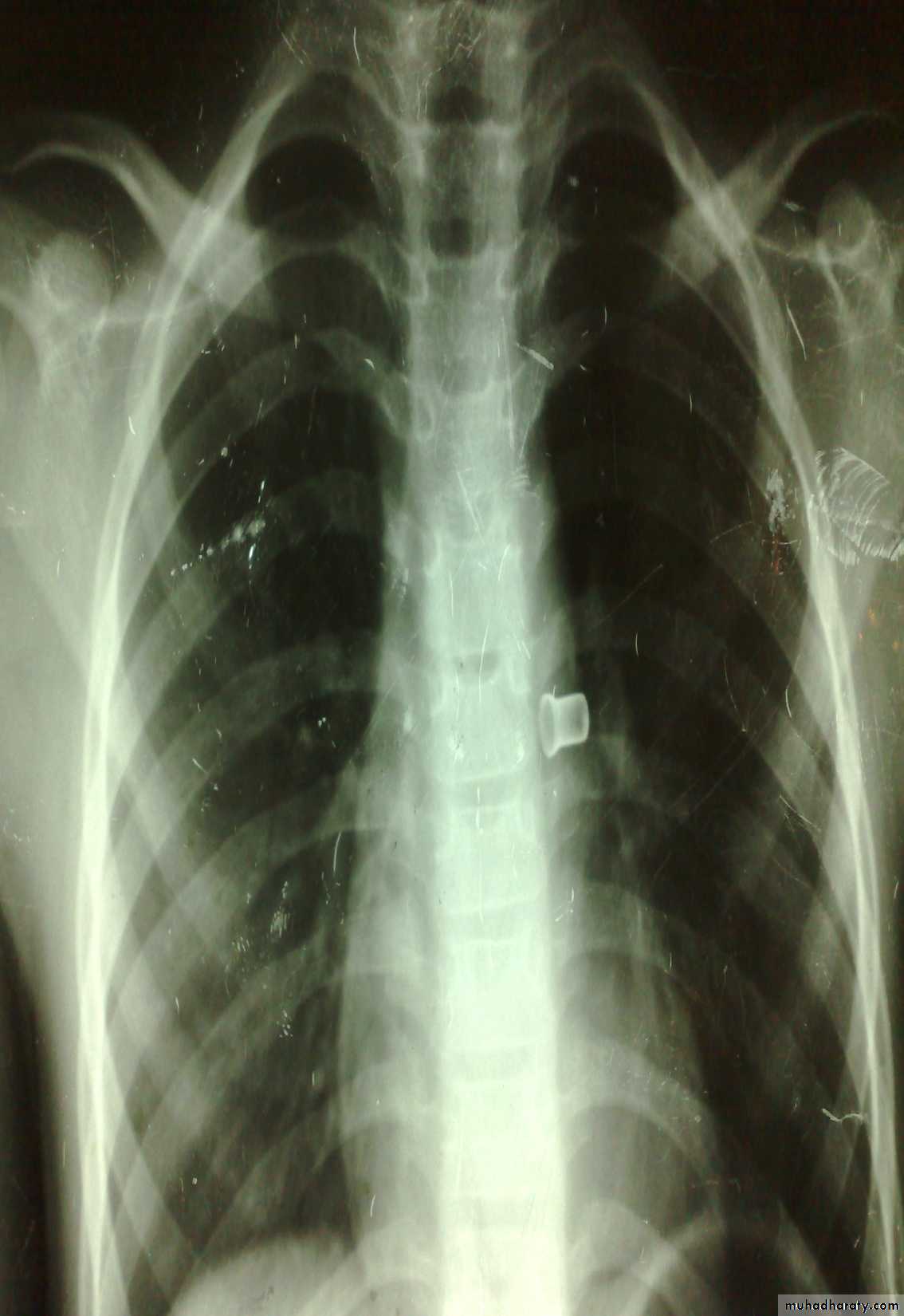
Clinically:salivation +no strioder1st F.b in Lt main bronchus removed by bronchoscopy
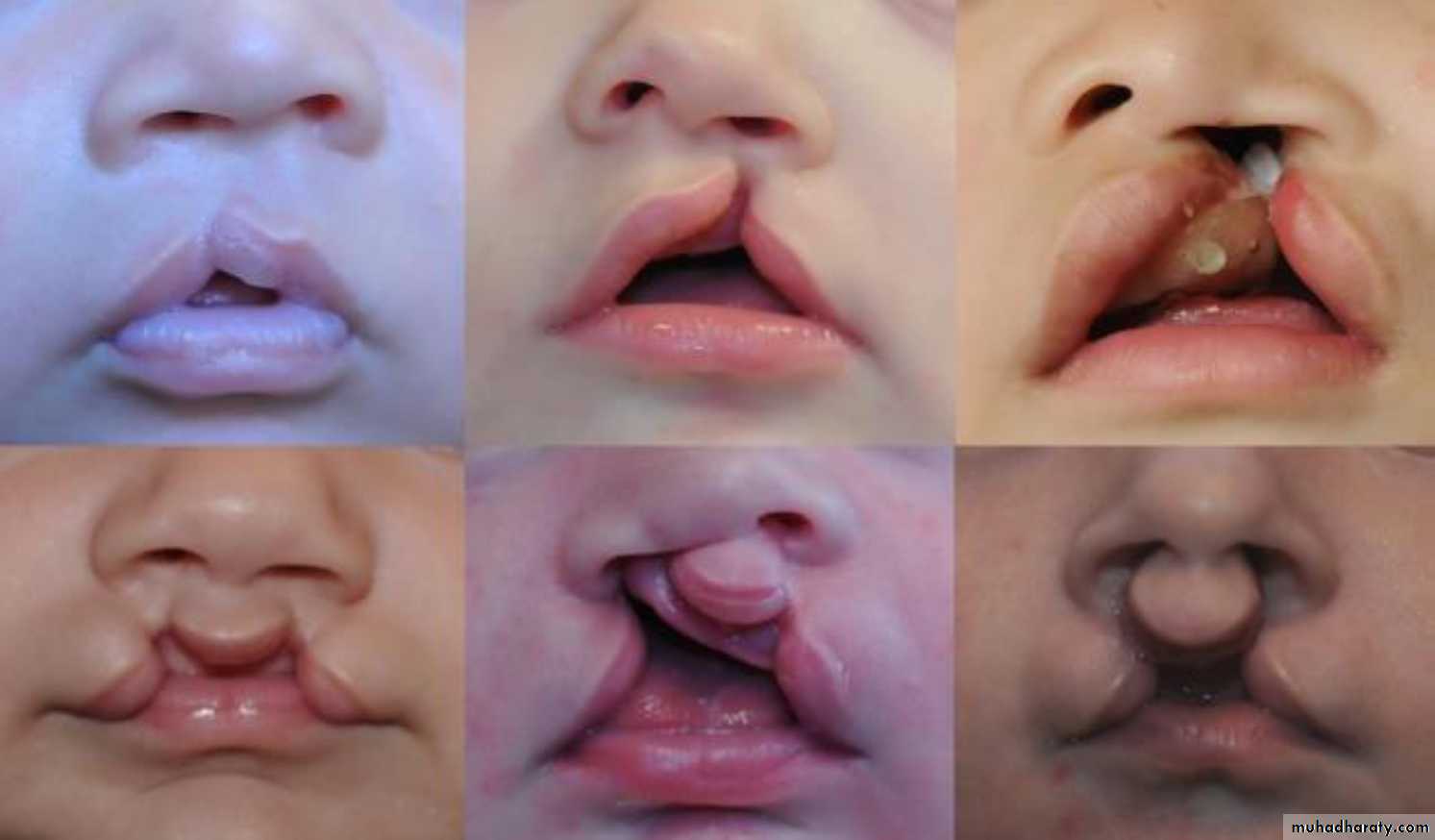
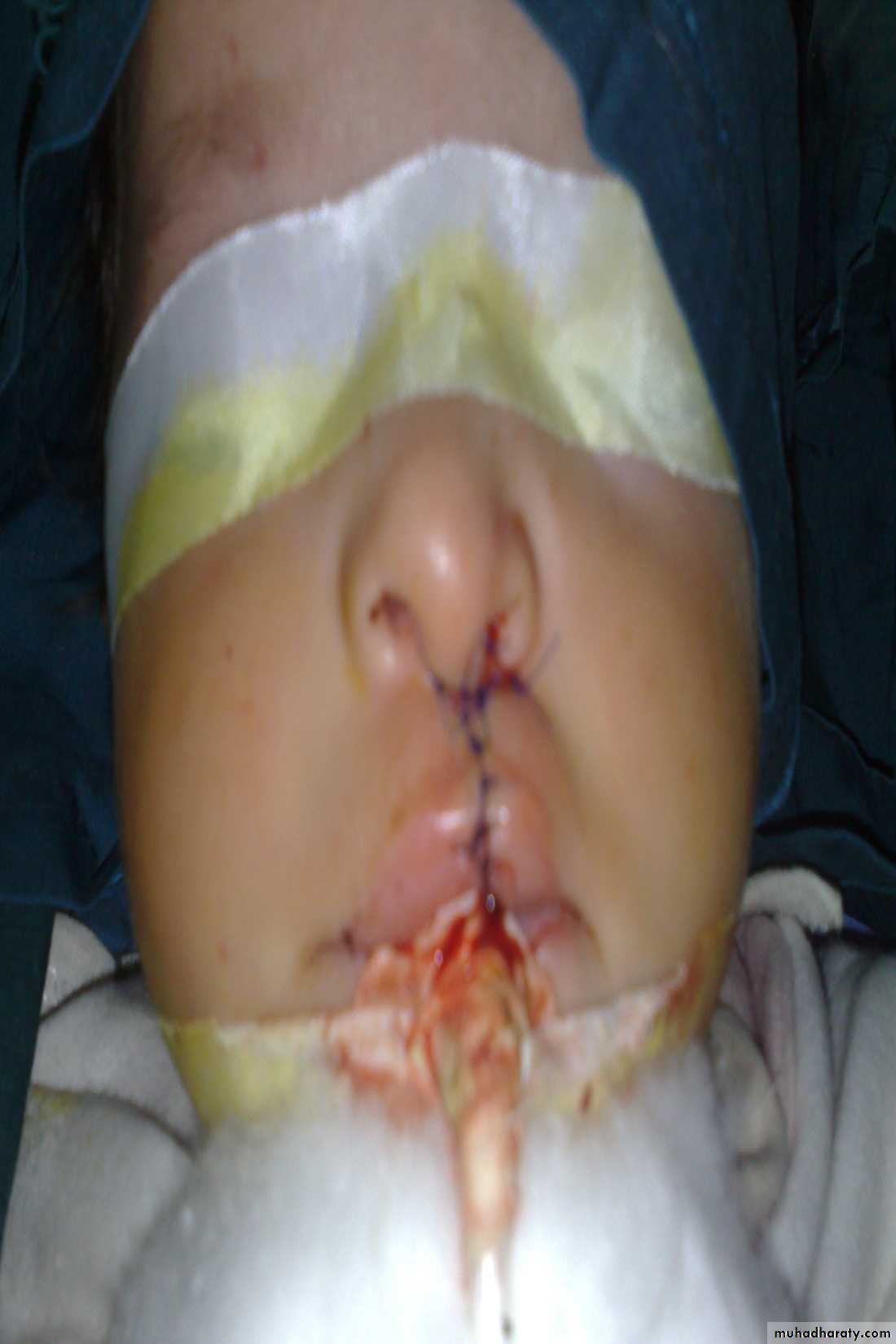
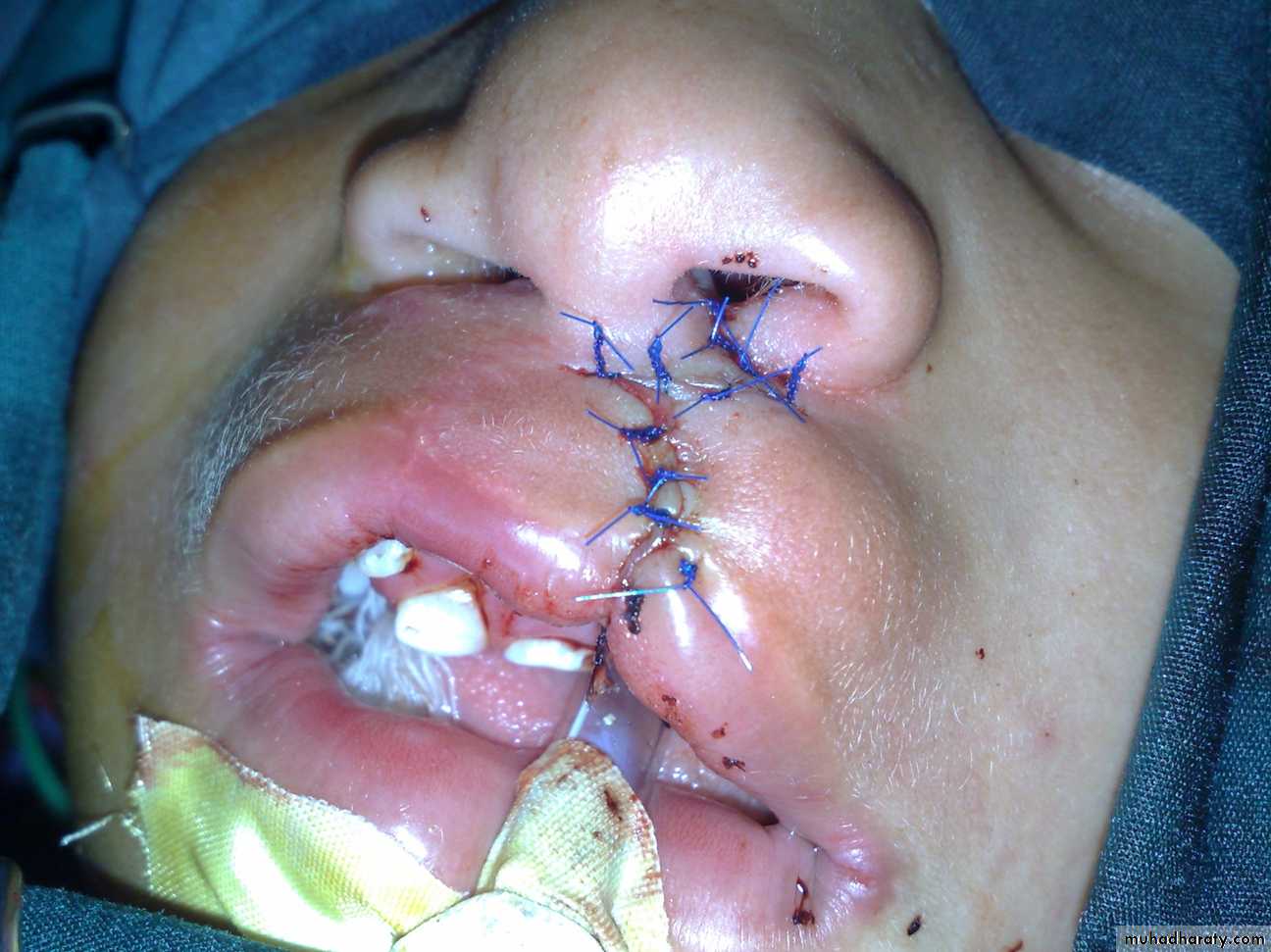
2nd needle of haijab in tracheaCleft lip repair (cheiloplasty)
Lethal teeth should be removed
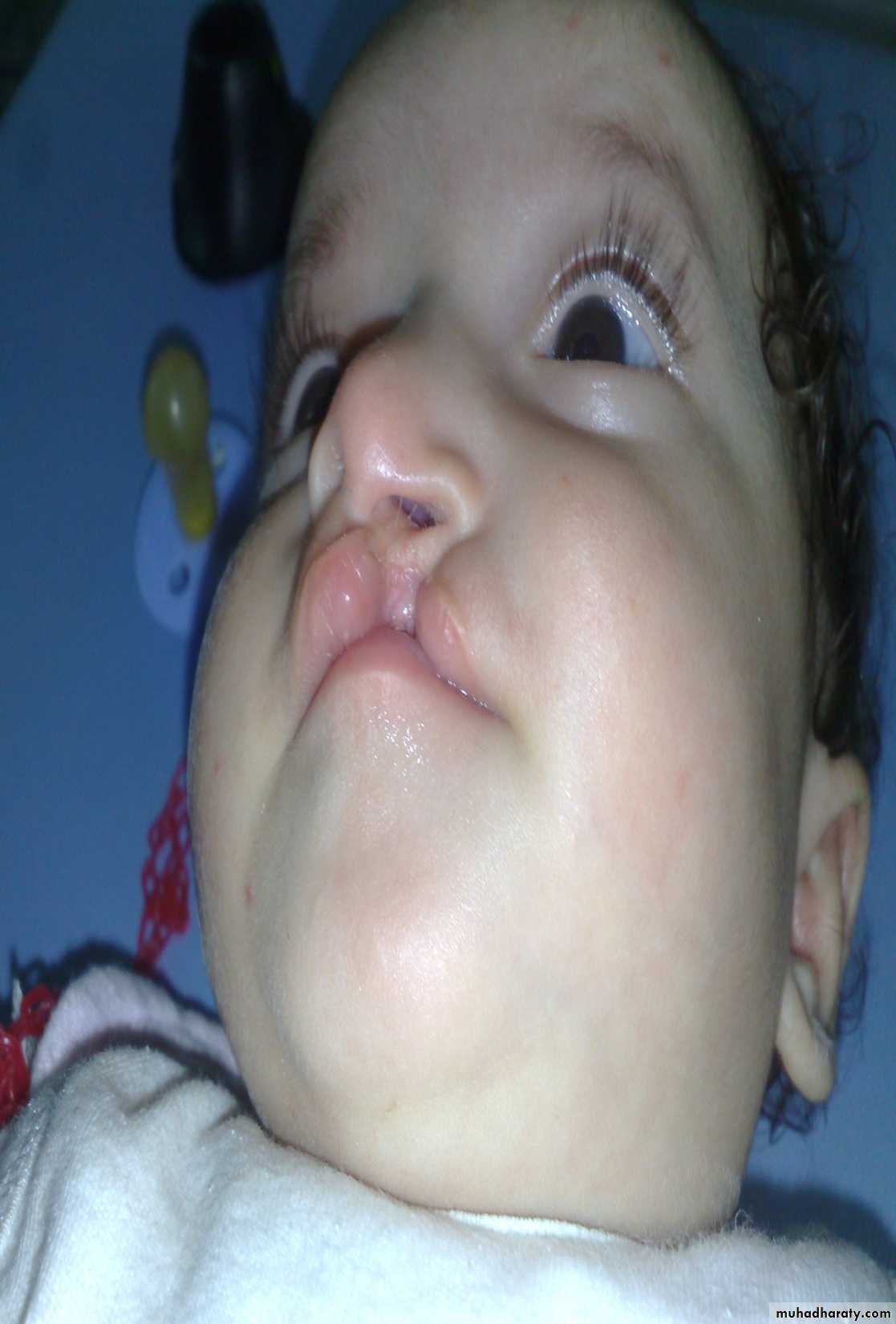
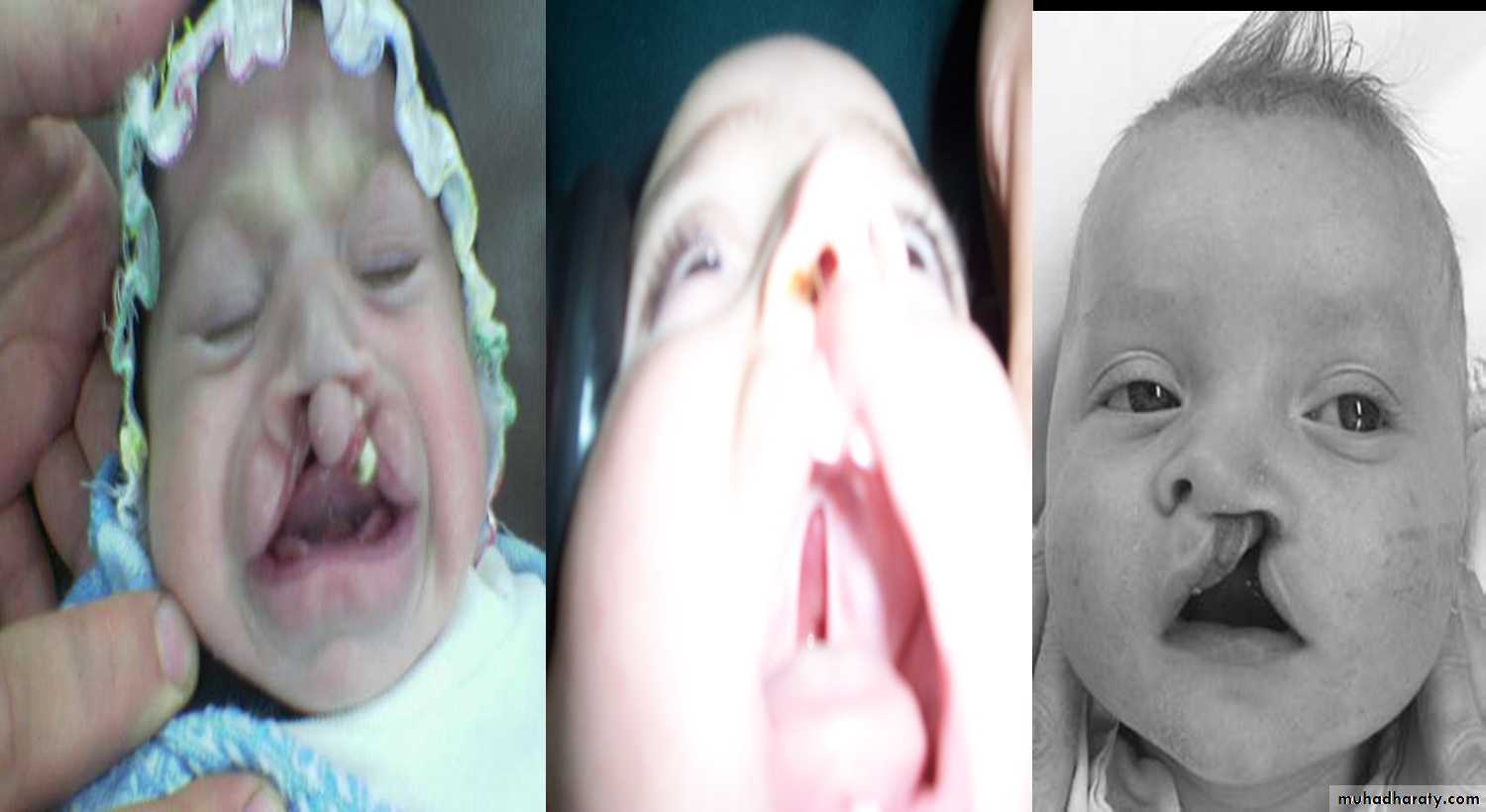
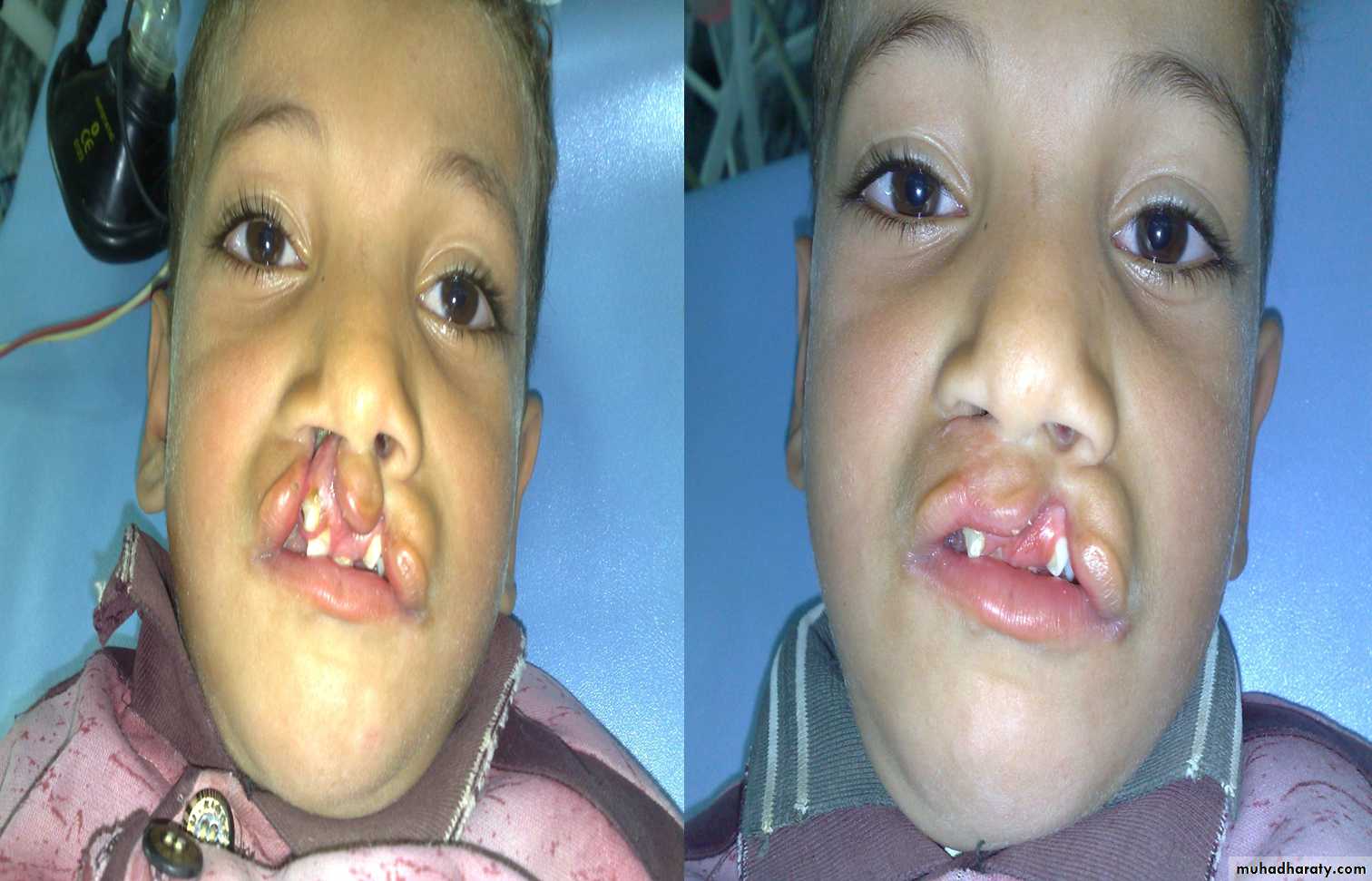
1st :bilateral complete cleft lip and palate2nd : unilateral complete cleft lip and palate.
Cleft lip and palate
Problems:• Aspiration during feeding
• Nasal speech
• Cosmetic problems
• Affect the hearing (glue ear)
• Lead to recurrent chest infection
Surgery:
• In 6 months to 1 year for cleft palate
• In 3 months for cleft lip
Feeding:
• Use special bottle tit
• In setting position
Highly associated with heart disease
After 1st surgery
Z-shaped surgery
Cleft lip and palate: Cleft palate lead to feeding problems, recurrent otitis media, speech problems (nasal speech).
Do surgery in first year of life.
Cleft lip cosmetic problem do surgery before 3 months.
Types:
1- Complete or incomplete.
2- Bilateral or unilateral.
3- Lip + palate or only lip.
advise to mother
-Specific bottles
-Feeding on siting position
-Decrease amount of feeding & increase frequency. )
What is feeding advise to the mother
What are you going to say to mother has a child born with cleft lip ± palate = feeding instructions1. The child is abnormal and different from previous children and need special care.
2. The feeding should be in upright position not lying
3. The normal child need a feed every 2hr but your child need more frequent feeds
4. If normal child need 15 minutes to complete his feed your child will take longer time to complete his feeding
5
5. In cleft palate and some cleft lip patients it is contraindicated to breast feed the child but mother can suck her milk and use bottle to feed the child.
6. The opening of the nipple of the milk bottle is too small to feed the child so either we increase it`s size by hot needle or we choose a special kind of nipples for cleft patients.
7. Inform that choking from milk is dangerous but unavoidable so we should reduce it as much as possible because it causes repeated chest infections.
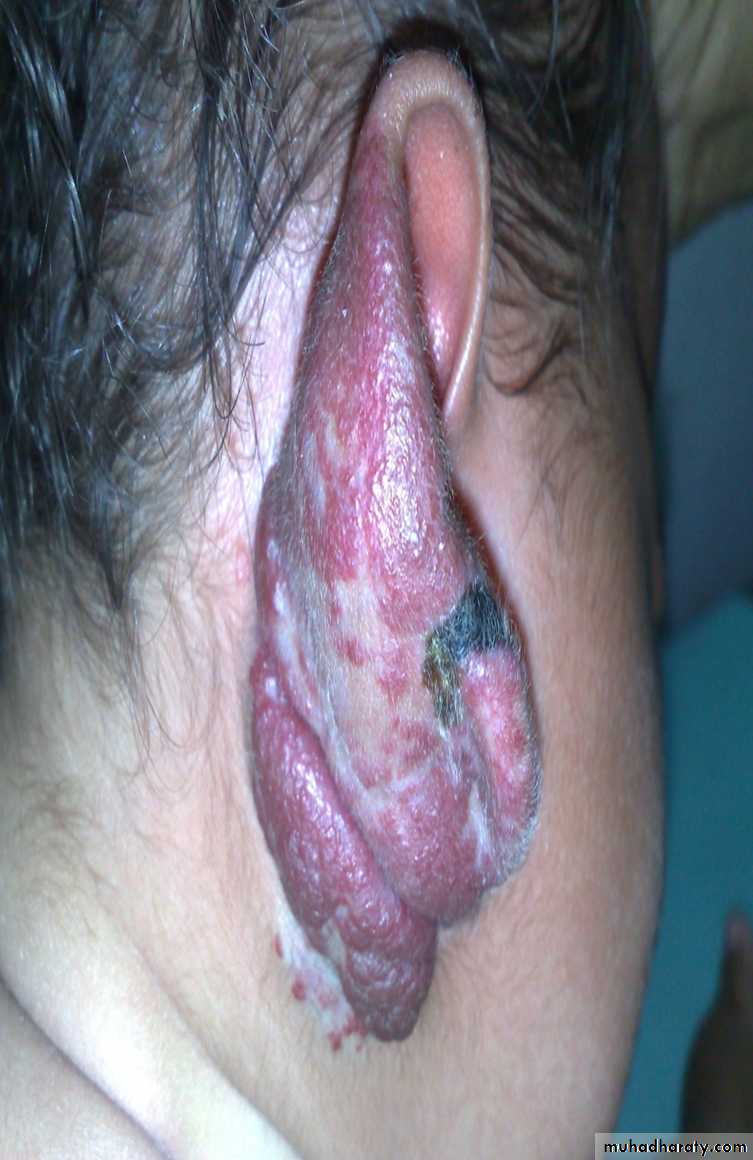
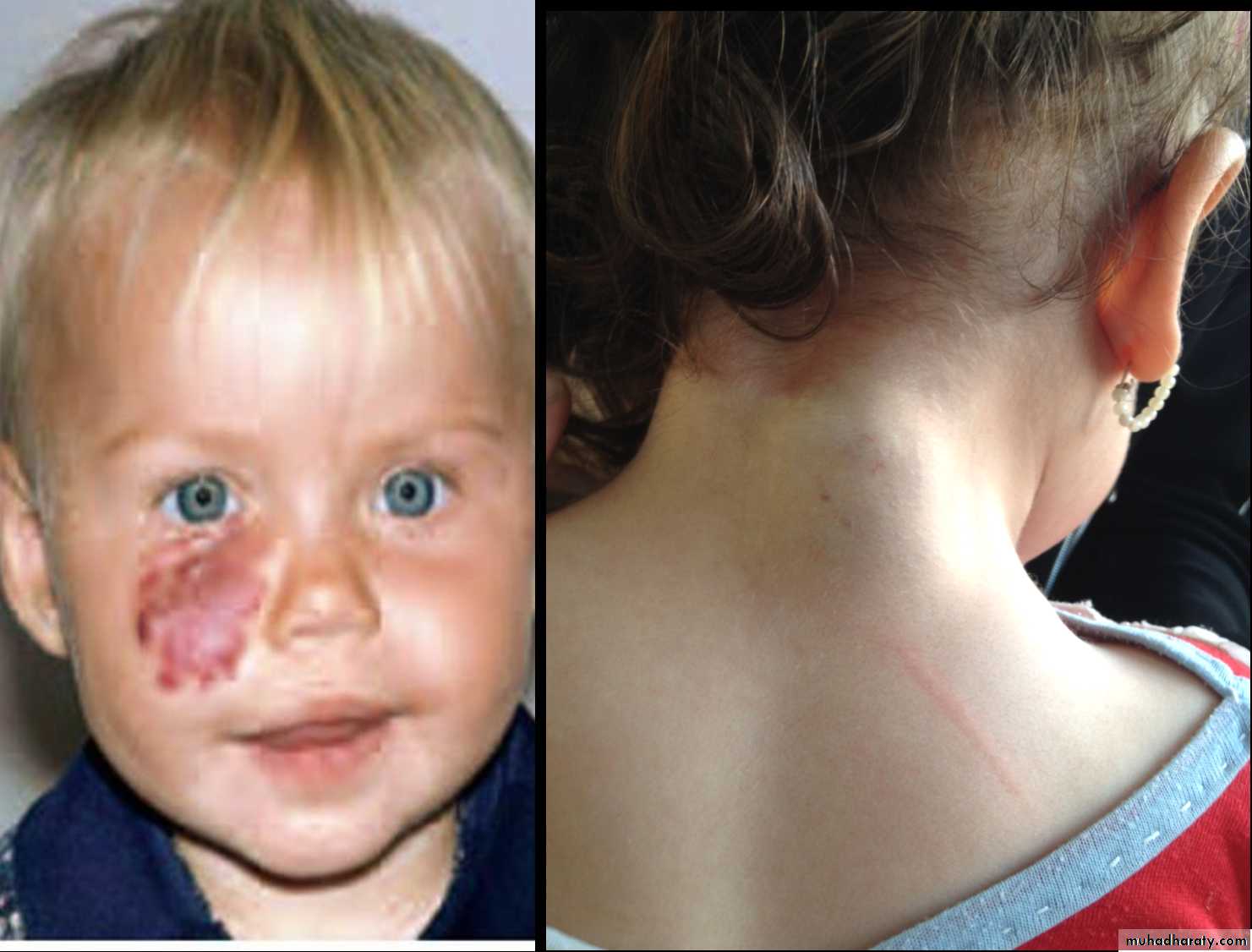
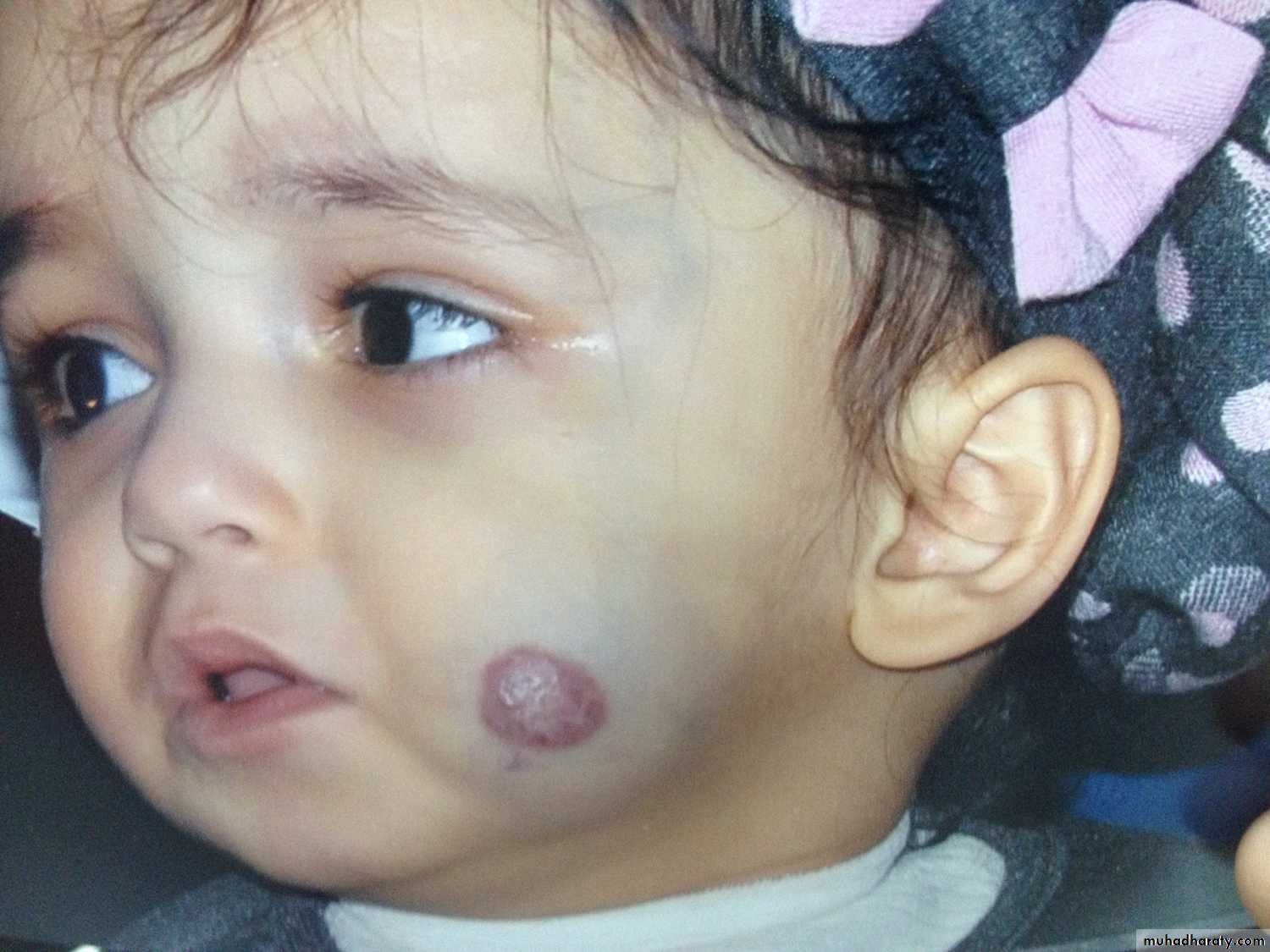
Cavernous Hemangioma.
Complication: 1-bleeding 2-Ulcer 3-Infection 4-Pressure effect according to site e.g. eye affect vision, ear may cause deafness. 5-consumptive coagulopathy due to hemolysis inside the hemangioma = activation of clot mechanism = consumption = DIC = Casabach syndrome.On exam: compressibility, can be compressed and refill after removal of pressure.
Treatment; Small red spot increases in size rapidly within 2-3 month Up to 1 or 2 increase in size then become stable( Platue phase) till the 5 year start to decrease and within 7 years it involute mostly by itself according to the type and site.
hemangioma
. Affect vision may cause blindnessCHL conductive hearing loss
Tinnitus
Hx. Small spot on 3 month & gradually increase in size until 2 years then stopped.
* Complication
Bleeding
Infection
Ulceration
Cosmotic
* on liver can cause heart failure
Mx. Removal
Systemic steroids if liver involved very effective
Cryotherapy ( not dangerous and stop the growth)
Interferon
B. Blocker very effective.
1-superfacial Haemangioma
-cord one-associated w/t uderlaying dz: stuge one dz
Mixed capilocavernous H.
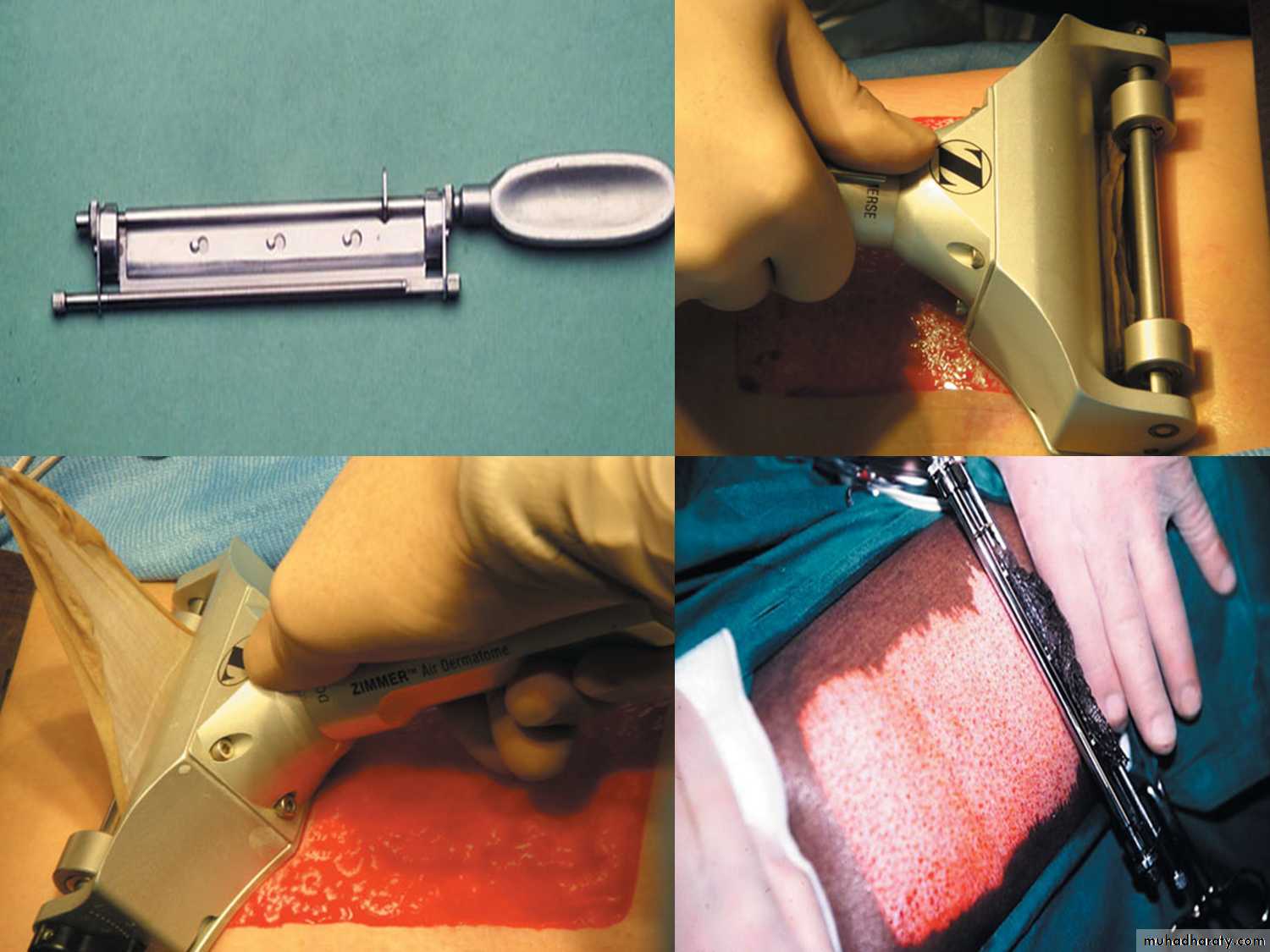
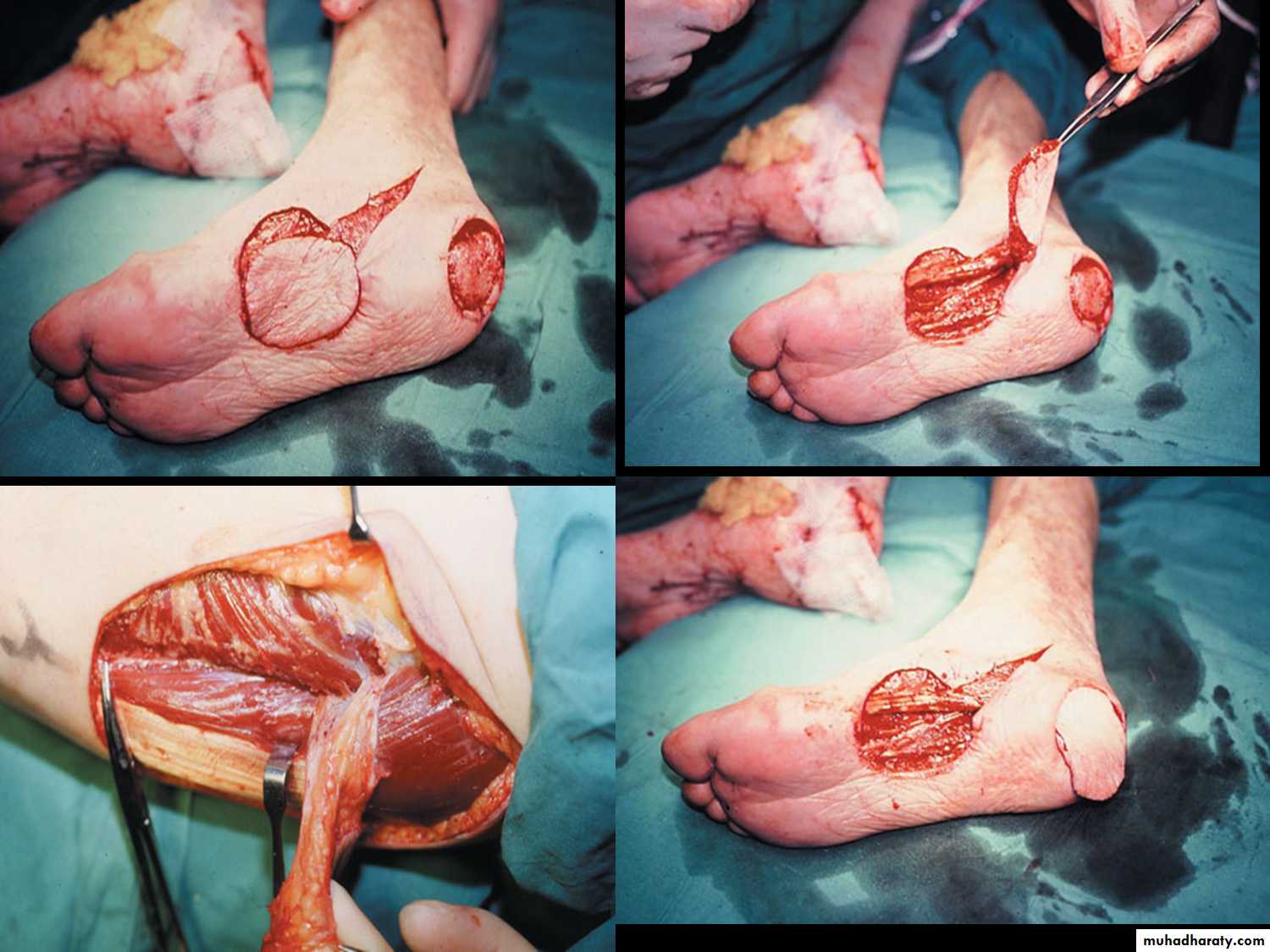
HUMBY knife
Used in 1-skin graftingIndication of graft:1-burn 2- ulcer
3-malignancy
Graft; without blood supply
Flab : with blood supply*Indication
Burns
Ulcer
Trauma
Ca
Flab ( Cosmotic)
* most common donor Site is the lateral aspect of thigh .
* causes of failure of graft
1_ infection
2 _ thin graft
3 _ tension on graft
4_General conditions of ths patient
* causes of flab failure
Technical problems