د.فارس
ردهات
1
Snake bite management
1-Prehospital Care
As with all medical emergencies, the goal is to support the patient until arrival at the
emergency department. The dictum " primum no nocere " (first, do no harm) has significant
meaning here because many poorly substantiated treatments may cause more harm than
good, including making an incision over the bite, mouth suctioning, tourniquet use, ice
packs, or electric shock.
Appropriate field care should adhere to the basic tenants of emergency life support.
Reassure the patient during the implementation of ABCs.
Monitor vital signs and establish at least one large-bore IV and initiate crystalloid infusion.
Administer oxygen therapy. Keep a close watch on the airway at all times in case intubation
becomes necessary.
Restrict activity and immobilize the affected area (commonly an extremity); keep walking to
a minimum.
2-Emergency Department Care
Definitive treatment includes reviewing the ABCs and evaluating the patient for signs of
shock (eg, tachypnea, tachycardia, dry pale skin, mental status changes, hypotension).
3-Surgical Care
Surgical assessment focuses on the injury site and concern for the development of
ndicated only for those patients with objective
. Fasciotomy is i
evidence of elevated compartment pressure. Liberal monitoring of compartment pressure is
warranted. If this is not available, use the physical hallmark of compartment hypertension
(pain with passive range of motion), along with distal pallor, paresthesia, or pulselessness for
the clinical assessment.
Tissue injury after compartment syndrome is not reversible but is preventable.
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/
:
source
Closed # & haematoma formed and amount of blood

د.فارس
ردهات
2
Compound fracture Gustilo
Type I: clean wound smaller than 1 cm in diameter, appears clean, simple fracture pattern,
no skin crushing.
Type II: a laceration larger than 1 cm but without significant soft tissue crushing, including
no flaps, degloving, or contusion. Fracture pattern may be more complex.
Type III: an open segmental fracture or a single fracture with extensive soft tissue injury.
Also included are injuries older than 8 hours. Type III injuries are subdivided into three
types:
Type IIIA: adequate soft tissue coverage of the fracture despite high energy trauma or
extensive laceration or skin flaps.
Type IIIB: inadequate soft tissue coverage with periosteal stripping. Soft tissue
reconstruction is necessary.
Type IIIC: any open fracture that is associated with vascular injury that requires repair
HbA1c-----Give clue for glycemia for the preceding 3 months.
د.فارس
ردهات
3
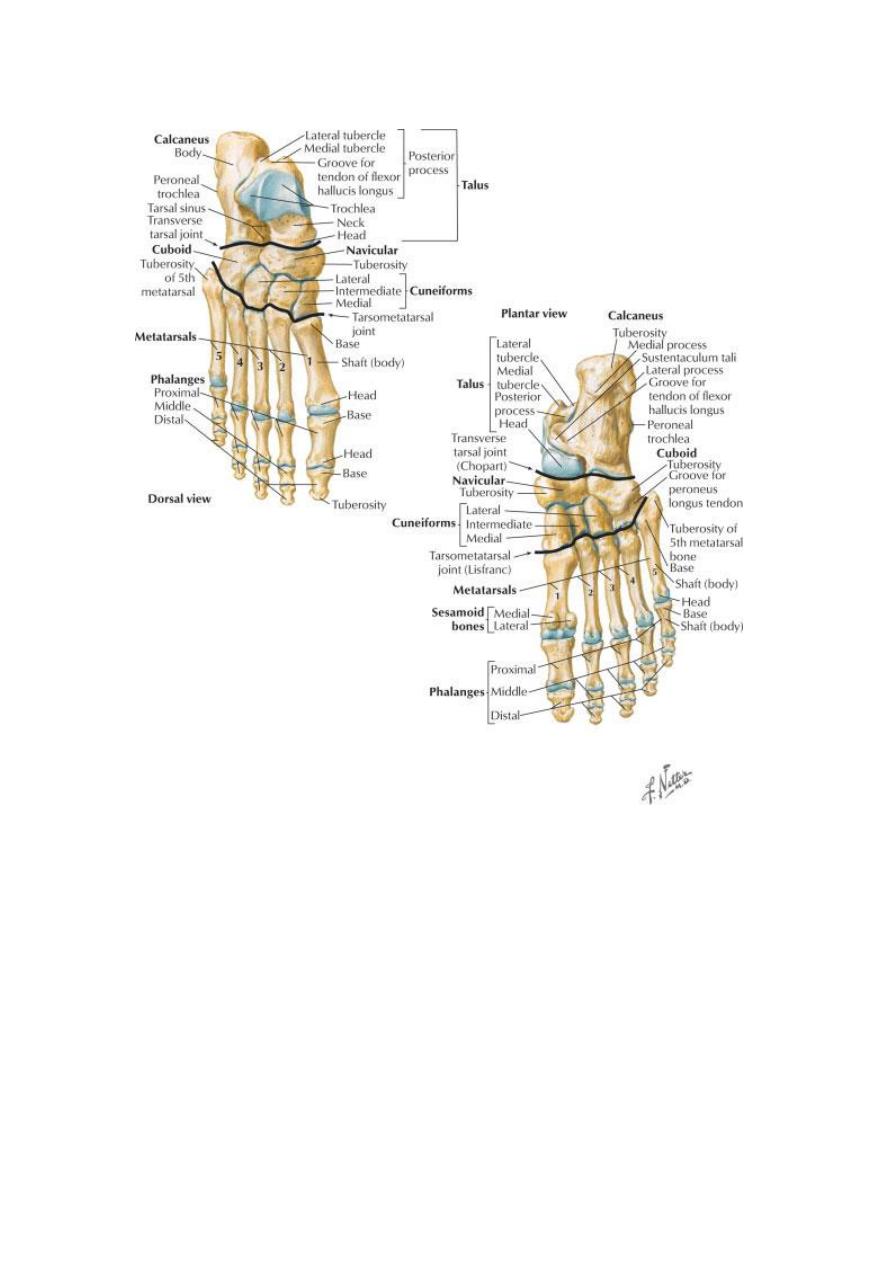
Tarsal bones
-Classification : Salter Harris classification :
Type one : transverse fracture through the growth plate .
Type two : it is similar to type one but it contain triangular piece from the metaphysis .
Type three : the fracture split the epiphysis vertically .
Type four : splitting the epiphysis vertically and extend to the metaphysis .
Type five : compression of the growth plate (crushing) and it result in
growth disturbance of the bone ( baddest type ) .
