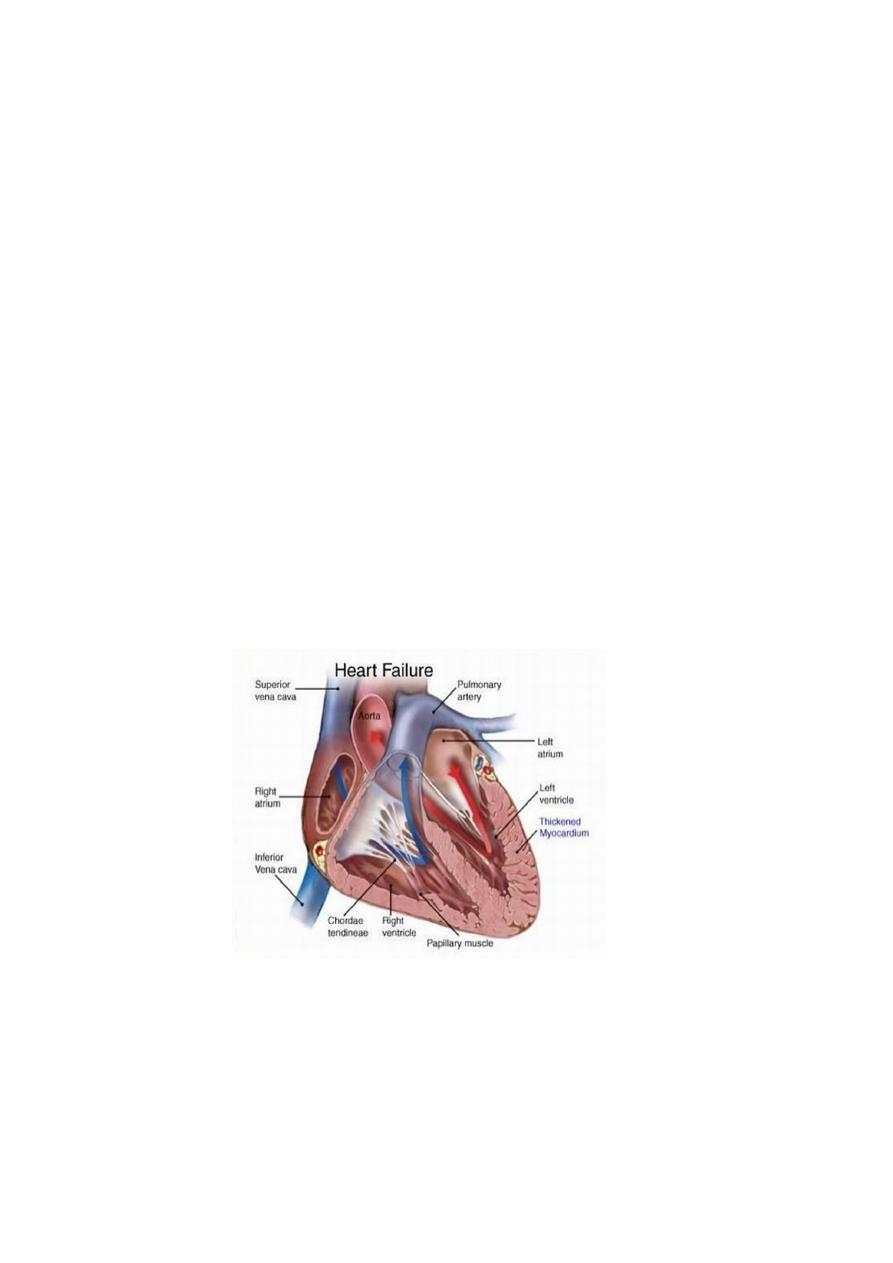
Heart failure
Heart
Cannot maintain an adequate cardiac output or
.Can do so only at the expense of an elevated filling pressure
(Cf.Shock (circulatory failure
(low stroke volume(hypovolaemic & cardiogenic-1
(vasodilatation(septic,anaphylactic &neurogenic-2
Mildest forms = cardiac outputà Adequate=at rest
(Inadequate =during exercise or stress. ( metabolic demand increases
Diagnosis of HF
+ significant heart disease
signs or symptoms of a low cardiac output, &/or-1
(venous congestion (pulmonary or systemic -2
!
TYPES
Acute x Chronic
Right side x Left side
(Systolic x Diastolic (foreward x backward
High output x Low output
!
-Physiology
!
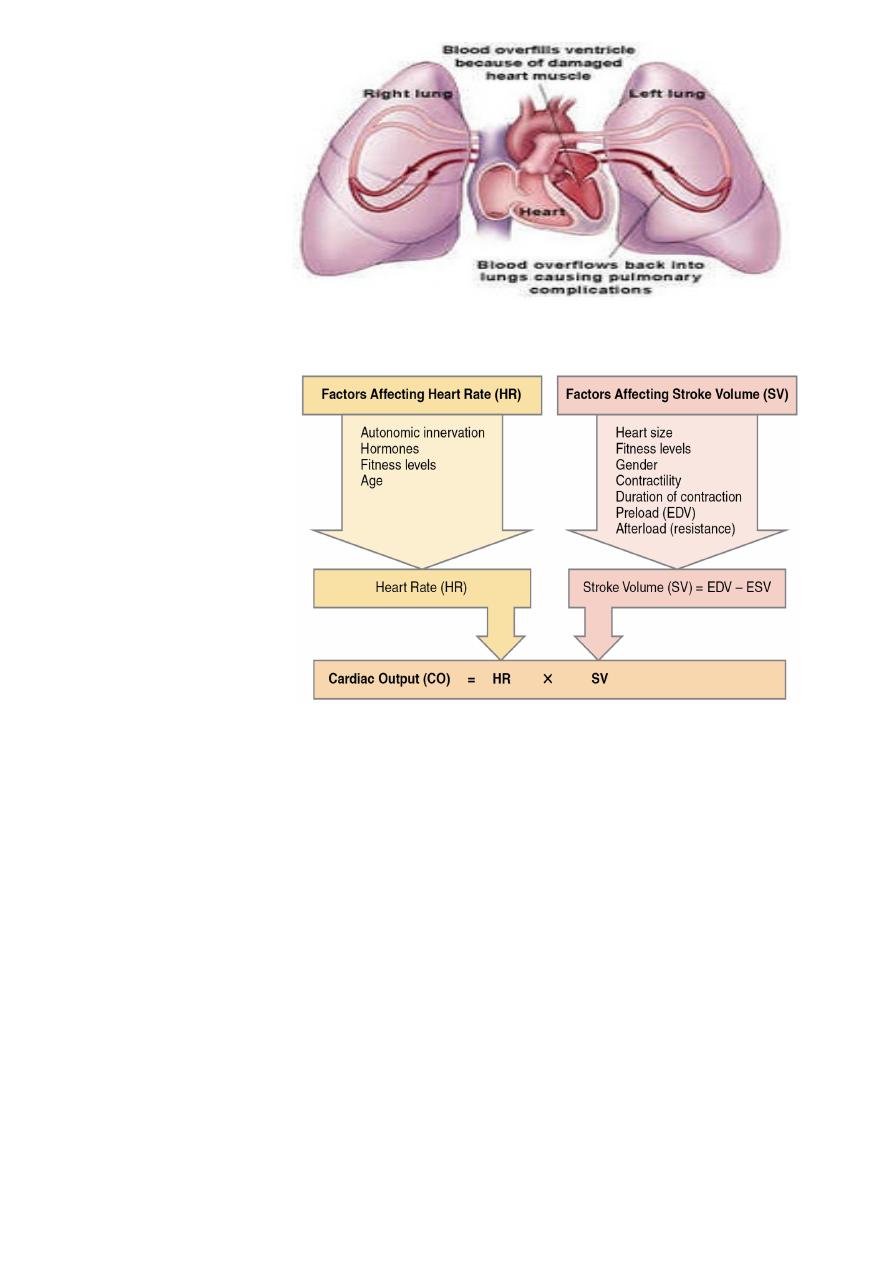
.CO=Volume of blood pumped in one min
CO=Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
SV= volume of blood ejected in each cardiac cycle
SV=Contractility,Preload / afterload
(EDV(130ml) -ESV(50ml) =SV(80 ml
CO=80 ml x 70B/m =5.6 L/m
Afterload
Preload Contractility
!
I. Ventricular Preload = length of muscle at onset of contraction, i.e.,(end-diastolic volume
( and pressure
A. Blood volume
B. Distribution of blood volume 1. Body position 2. Intrathoracic pressure 3.
Intrapericardial pressure 4. Venous tone 5. Pumping action of skeletal muscles
C. Atrial contraction
II. Ventricular Afterload tension that muscle called on to develop during contraction, i.e.,
((systolic aortic pressure
A. Systemic vascular resistance
B. Elasticity of arterial tree
C. Arterial blood volume
D. Ventricular wall tension 1. Ventricular radius 2. Ventricular wall thickness
III. Myocardial Contractility extent and velocity of shortening at any given preload and
.afterload
A. Intramyocardial [Ca2+]
B. Cardiac adrenergic nerve activity
C. Circulating catecholamines
D. Cardiac rate
E. Exogenous inotropic agents
F. Myocardial ischemia

(G. Myocardial cell death (necrosis, apoptosis, autophagy
H. Alterations of sarcomeric and cytoskeletal proteins 1. Genetic 2. Hemodynamic
overload
I. Myocardial fibrosis J. Chronic overexpression of neurohormones
K. Ventricular remodeling L. Chronic and/or excessive myocardial hypertrophy
CAUSES-DISEASES
=LEFT SIDE
Coronary Artery Dis./MI
Hypertension
CardioMyoPathy
.Aortic Valve Dis
Stenosis/Regurgitation)
=RIGHT SIDE
.Lung DIS
.Mitral Valve Dis
Atria Septal Defect
MECHANISMS
Reduced ventricular contractility =Dis .of myocardium
=Ventricular outflow obstruction =pressure overload
Aorta (BP), A. Valve
Ventricular inflow obstruction =Mitral & Tricuspid valve
Ventricular volume overload =VSD,ASD
Arrhythmia
Diastolic dysfunction

PRICPITATING FACTORS
ANAEMIA
ARRHYTHMIAS
Mechanisms of heart failure
CAUSE EXAMPLE
Reduced ventricular contractility
(MI (segmental dysfunction
Myocarditis/cardiomyopathy
Ventricular outflow obstruction
(pressure overload)
Hypertension, aortic stenosis
Pulmonary hypertension, PV stenosis
Ventricular inflow obstruction
,Mitral stenosis
tricuspid stenosis
Ventricular volume overload
Ventricular septal defect
RV volume overload (ASD)
Increased metabolic demand
Arrhythmia
Atrial fibrillation
Tachycardia cardiomyopathy
Complete heart block
Diastolic dysfunction
Constrictive pericarditis

Restrictive cardiomyopathy
LV hypertrophy and fibrosis
Cardiac tamponade
Compensatory changes
StarlIng Law-STRETCH-1
Neuro-humoral-2
change in size , shape and mass of ventricle-3
(dilatation/hypertrophy & remodelling)
Starling’s Law-1
Basis =>Cardiac output =function of
,(preload (volume and pressure of blood in ventricle at end of diastole -1
(afterload (volume and pressure of blood in ventricle during systole -2
myocardial contractility -3
.Ventricular performance related to = degree of myocardial stretching
;in preload àenhance function ↑
overstretching è marked deterioration.
In heart failure ,curve moves to right and becomes flatter
Stretch of cardiac muscle (from increased end-diastolic volume) causes an increase in force of
contraction, producing a greater stroke volume= SL
!

Starling's Law. Normal (A), mild (B), moderate (C) and severe (D) heart failure. Ventricular
.performance is related to degree of myocardial stretching
increase in preload (end-diastolic volume, end-diastolic pressure, filling pressure or atrial
;pressure) =enhance function
.overstretching causes= marked deterioration
In heart failure curve moves to right and becomes flatter. An increase in myocardial
contractility or a reduction in afterload will shift the curve upwards and to the left (green
.(arrow
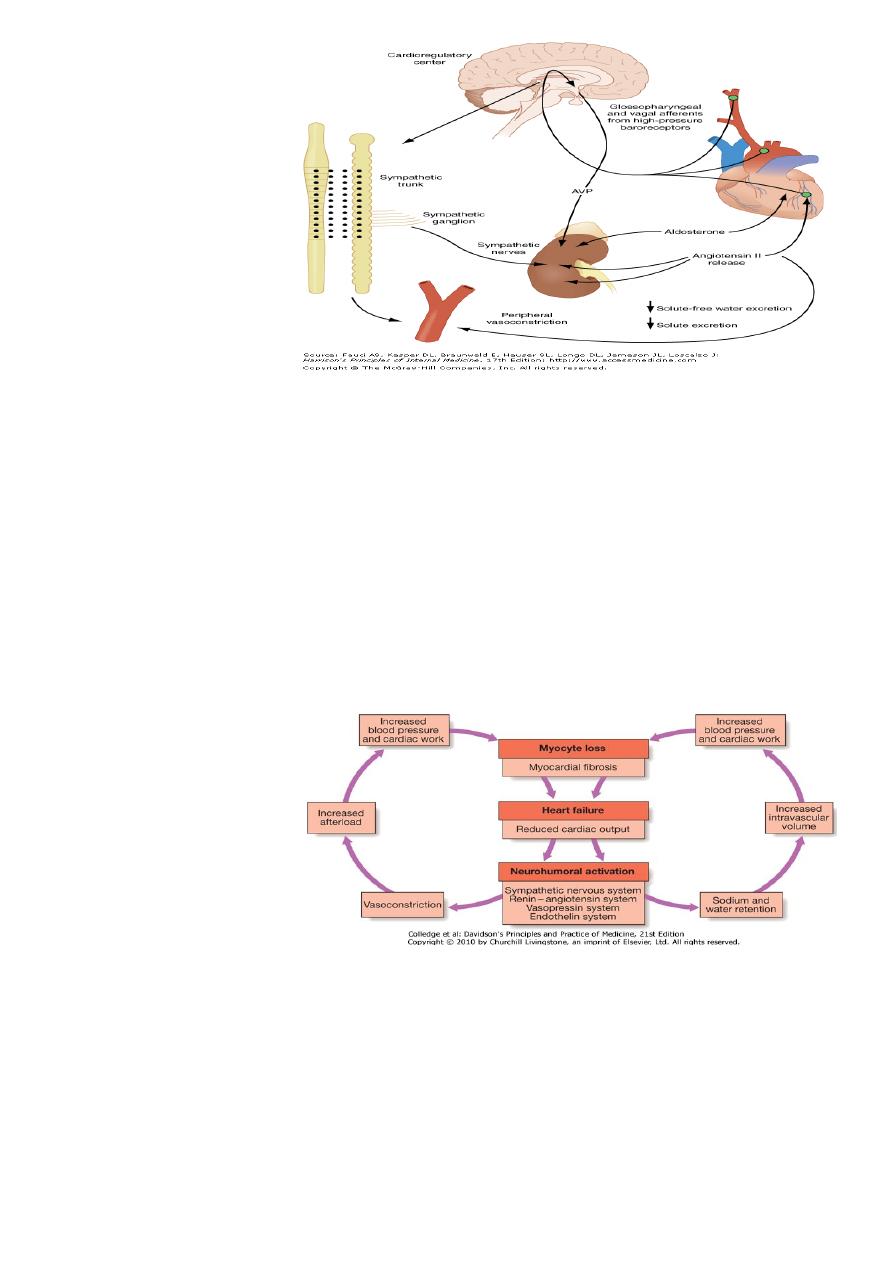
neuro-humoral-2
Stimulation of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system à
,Vasoconstriction= angiotensin II-1
Activation of sympathetic nervous system-2
.Initiallyà increase Myo contractility, heart rate and peripheral vasoconstriction
.Laterà cardiac myocyte apoptosis, hypertrophy and focal myocardial necrosis
Salt and water retention = by-3
Aldosterone, Endothelin-1
Antidiuretic hormone
Natriuretic peptides atrial stretch
.physiological antagonists to fluid-conserving effect of aldosterone
SUMMARY
in normal physiological circumstances =support cardiac function, but -1
in impaired ventricular function èdeleterious increase in afterload and preload-2
!
.impairment of ventricular function leading è fall in cardiac output
without valvular disease) ècounter-regulatory neurohumoral mechanisms that)
in normal physiological circumstances would support cardiac function, but-1
in setting of impaired ventricular function èdeleterious increase in both afterload and-2
preload).è
vicious circle =established (any additional fall in cardiac output will cause further
(.neurohumoral activation and increasing peripheral vascular resistance
!
change in size , shape and mass of ventricle-3
Myocyte loss or HD load =>hypertrophy of viable myocyte-1
A-volume overload à↑ cell length (eccentric) =vent .dilatation
B-pressure overload à↑cell width, thickening, concentric hypertrophy
After myocardial infarction, cardiac contractility impaired and neurohormonal activation è-2
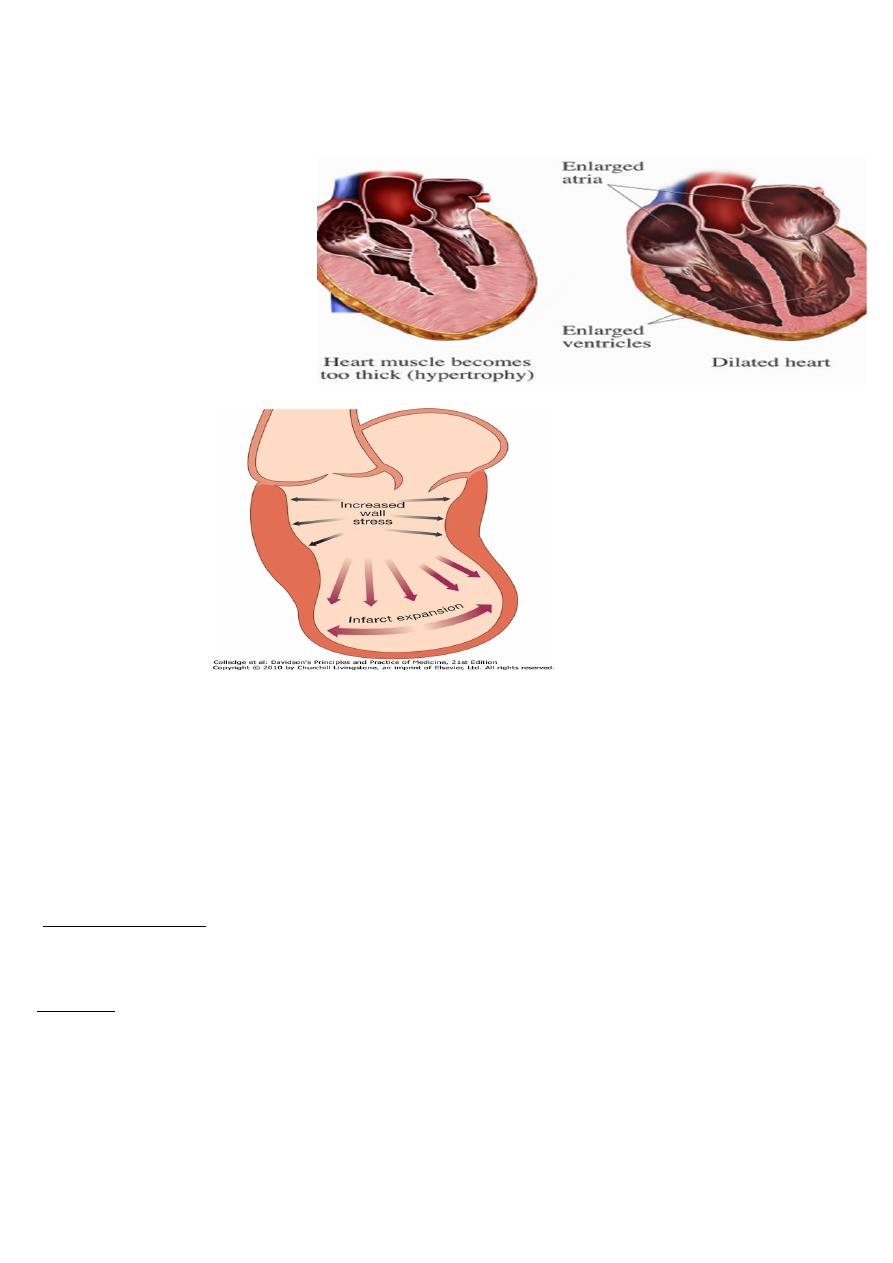
+,A-hypertrophy of non-infarcted segments
B-thinning, dilatation and expansion of infarcted segment (remodelling,). èfurther deterioration
.in ventricular function and worsening heart failure
!
!
Types and Clinical presentation
Acute and chronic heart failure
Left, right and biventricular heart failure
Diastolic and systolic dysfunction
(backward-congestive x foreward-output)
High-output failure
By:brwa
