1
ARRHYTHMIAS
DISEASE OF HEART RATE, RHYTHM AND CONDUCTION
PHYSIOLOGY
MECHANISM
TYPES-
CLINICAL MANIFESTAIONS
ECG DIAGNOSIS
TREATMEMT
PREVENTION
DISORDERS OF HEART RATE, RHYTHM AND CONDUCTION
TACHY-ARRHYTHMIAS
1-SINOATRIAL RHYTHMS
2-ATRIAL TACHYARRHYTHMIAS
3-'SUPRAVENTRICULAR‘-JUNCTIONAL TACHYCARDIAS
4-VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIAS
Atrio-ventricular block and
Bundle branch block
2
Physiology
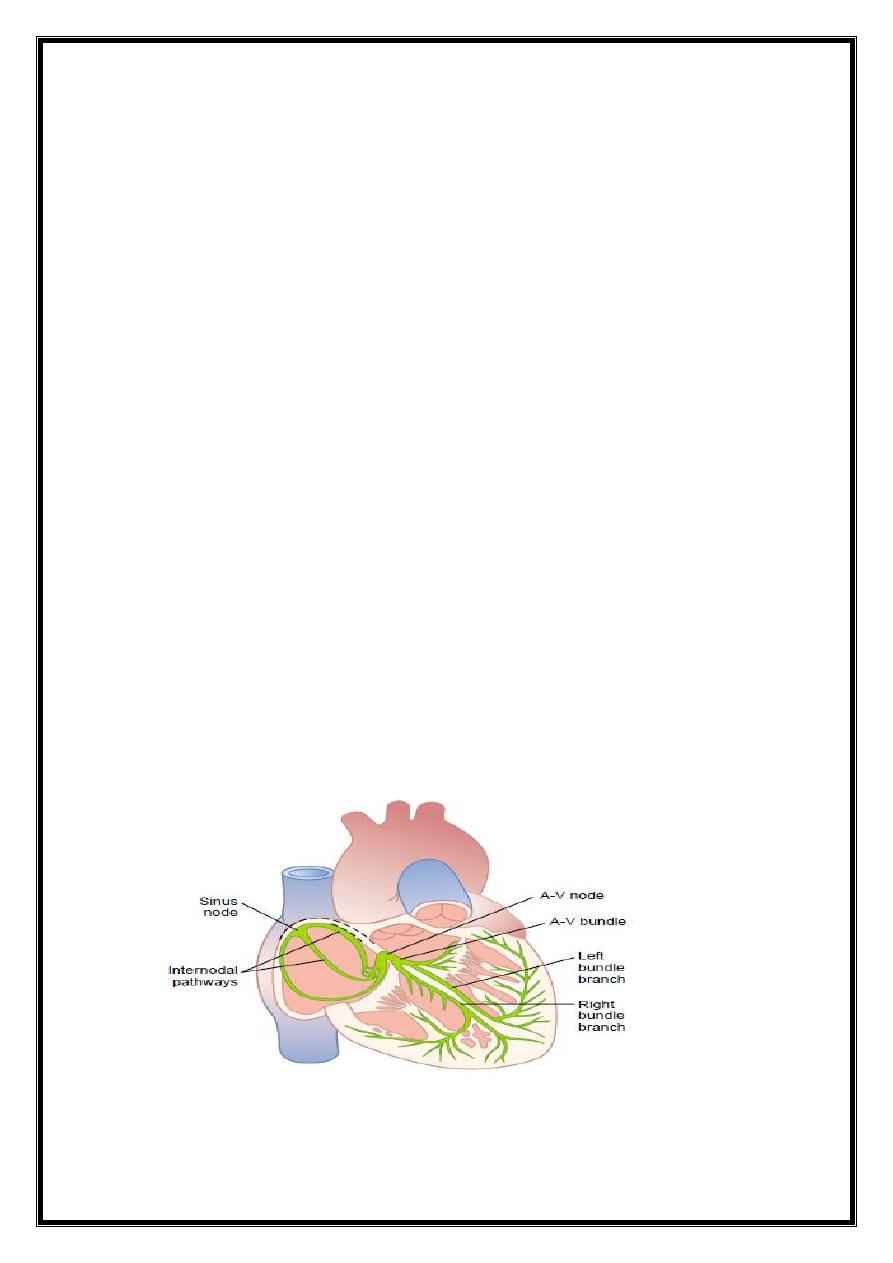
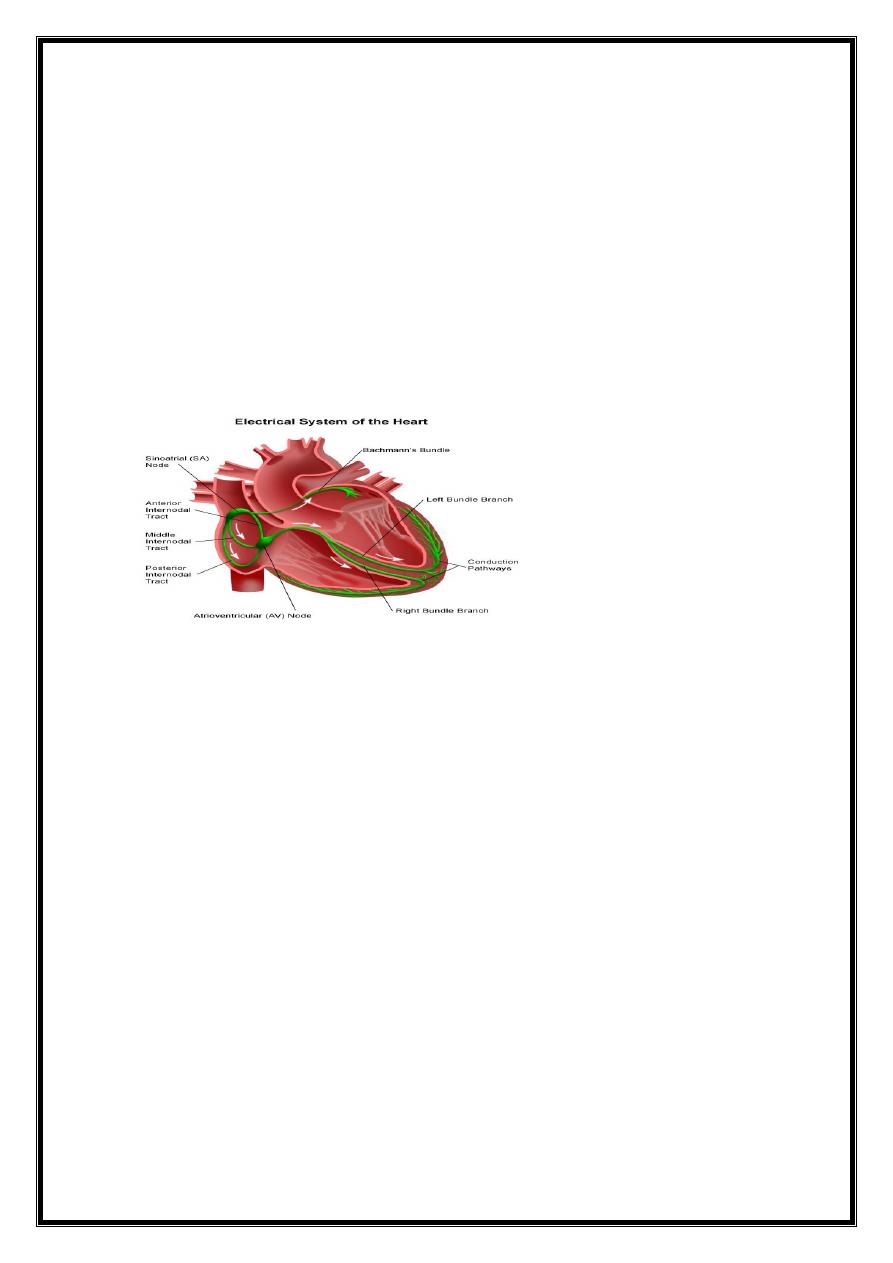
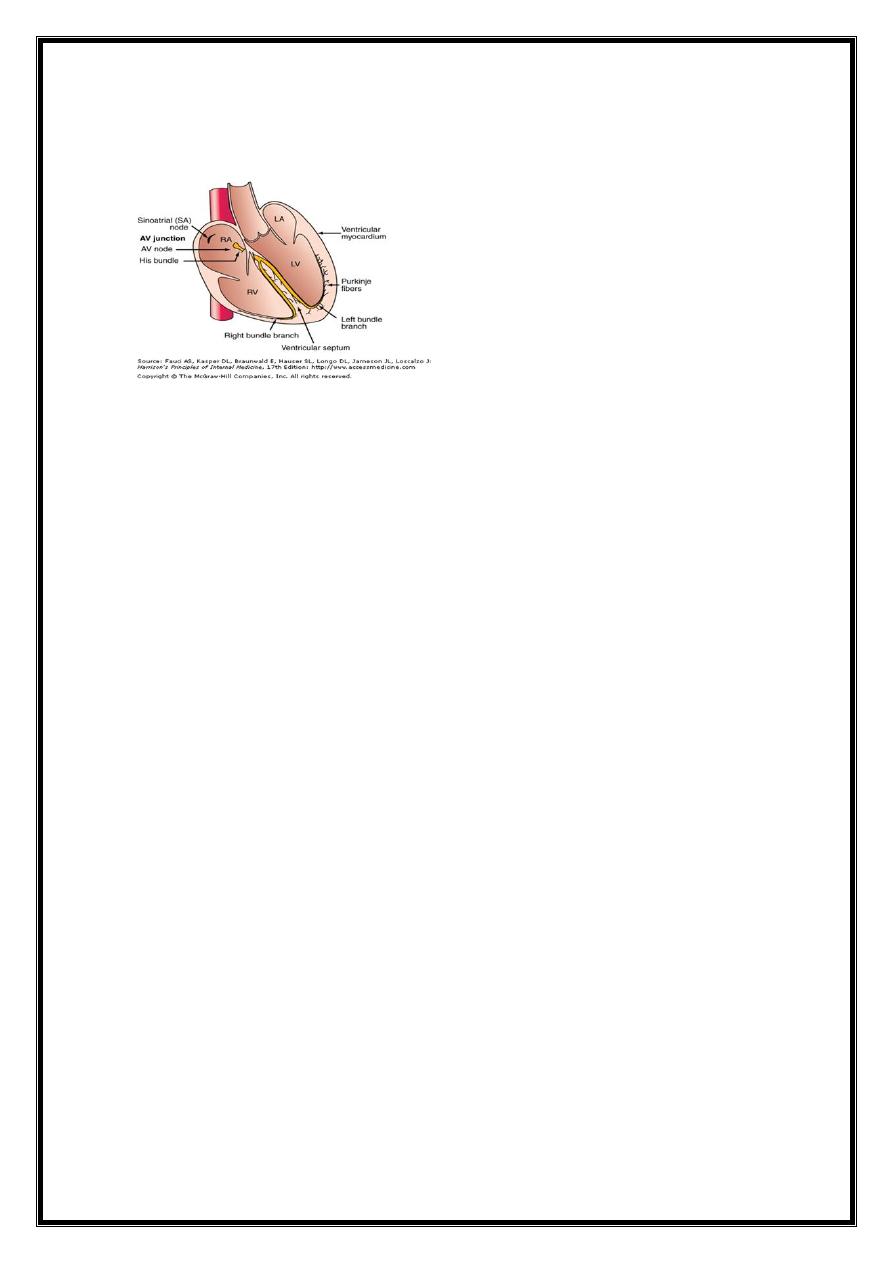
Heart beat - initiated electrical discharge from sinoatrial (sinus) node.
electrical depolarisation passes through specialised conducting tissues Atria and
ventricles depolarise sequentially
sinus node =pacemaker and its intrinsic rate is regulated by the autonomic nervous
system;
vagal activity slows heart rate
sympathetic activity accelerates ( via cardiac sympathetic nerves and circulating
catecholamines.)
Definition
Tachycardia=heart rate > 100/min
Bradycardia=rate < 60/min
escape rhythm (If sinus rate becomes unduly slow, a lower centre may assume the role
of pacemaker )
1- AV node or His bundle (junctional rhythm) or
2- ventricles (idioventricular rhythm).
Cardiac arrhythmia =disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart.
Cuases :
1- often a manifestation of structural heart disease
2-healthy heart (abnormal conduction or depolarization
3
TYPES
Extra-systole(Ectopics-premature)
Tachycardia
Flutter
Fibrillation
SITE OF ORIGIN
Above ventricles=SupraVentricular
-----Sinus
-----Atria
-----Juntional(AV)
Ventricular
Supraventricular rhythms = narrow QRS complexes (ventricles depolarised normally
through AV node and bundle of His).
Ventricular rhythms =broad, bizarre QRS complexes (ventricles activated in an abnormal
sequence).
(occasionally a supraventricular rhythm can produce broad or wide QRS complexes due
to coexisting bundle branch block or the presence of accessory conducting tissue) .
ARRHYTH
MIAS
TACHY-A
ECTOPIC
S
TACHYC
ARDIA
FLUTTER
FIBRILLA
TION
BRADY-
A
AV
BBB
4
How
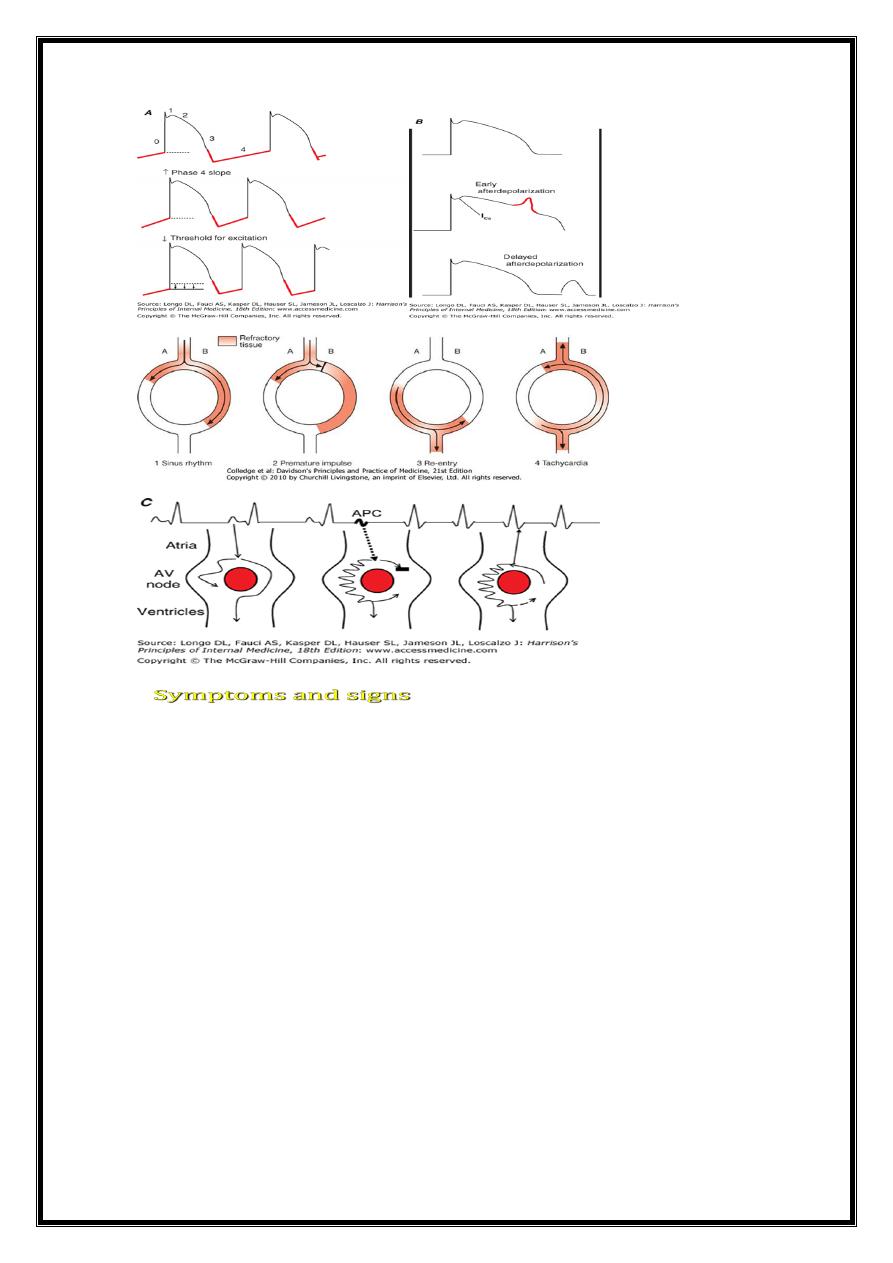
Mechanism:
Tachyarrhythmias
1- Increased automaticity
2-Re-entry
3-Triggered activity
BRADYARRYTHMIAS
Bradycardia=
1-Reduced automaticity, e.g. sinus bradycardia.
2-Blocked or abnormally slow conduction, e.g. AV block.
1- Increased automaticity. repeated spontaneous depo. of an ectopic focus,- in response
to catecholamines.
2-Re-entry
tachycardia initiated by an ectopic beat
sustained by a re-entry circuit .
3-Triggered activity
a form of sec.depol. arising from incompletely
repol. cell mem.-v.arrhythmias CAD
5
Tachycardias=
rapid palpitation//dizziness
//chest discomfort or SOB
Can trigger HF or
Sudden death
Extreme tachycardias
syncope
Bradycardias =
symptoms of low cardiac output: fatigue,
lightheadedness and syncope
Extreme bradycardias or tachycardiasSDor cardiac arrest.
6
Diagnostic approach to arrhythmias
TYPES extra-systole
tachycardia
flutter
fibrillation
Anatomical origin
SA node,
Atria
AV node-Juntional
Ventricles
3-Conduction sequence –
2-1 AV block,
complete AV block
7
TACHYARRHYTHMIAS
SUPRAVENTRICULAR
SINUS---------Tachycardia
ATRIAL----------Ectopics
----------Tachycardia
----------flutter
----------fibrillation
JUNCTIONAL---Ectopics
---Tachycardia
VENTRICULAR-Ectopics
-Tachycardia
-Fibrillation
SINUS RHYTHMS
1-SINUS TACHYCARDIA
sinus rate >100/min
Physiological =increase in sympathetic activity
exercise, emotion, pregnancy
Young adults- up to 200/min, during intense exercise.
Pathological Causes
Anxiety Fever Anaemia
Heart failure Thyrotoxicosis Phaeochromocytoma
8
Drugs, e.g. β-adrenoceptor agonists-bronchodilaters
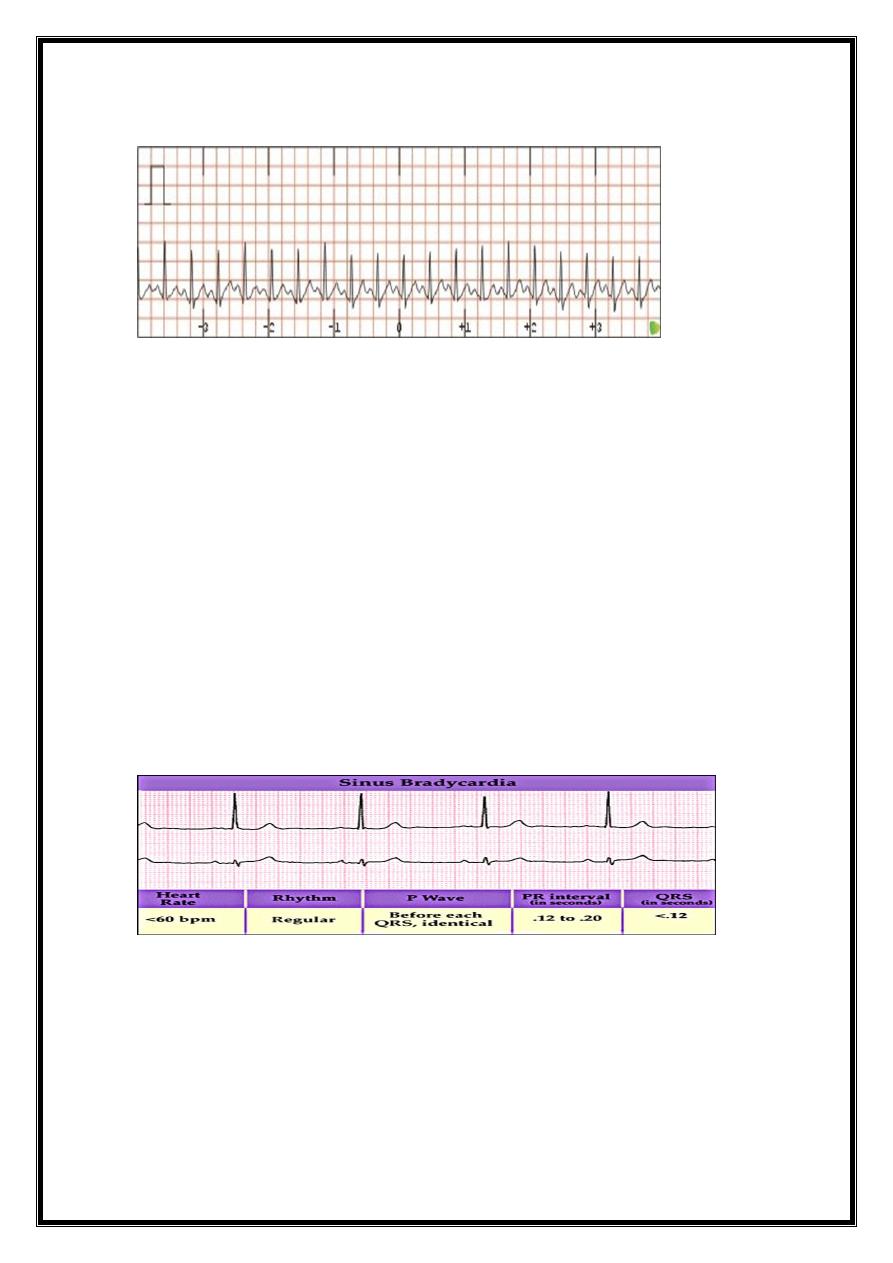
2-SINUS BRADYCARDIA
sinus rate of <60/min
Physiological causes
healthy people at rest *common finding in athletes.
Pathological causes
Myocardial infarction *Sinus node disease (sick sinus syndrome)
Hypothermia *Hypothyroidism *Cholestatic jaundice
Raised intracranial pressure *Drugs, e.g. β-blocker, digoxin, verapamil
Treatment
Asymptomatic =no treatment.
Symptomatic =usually responds to i.v. atropine 0.6-1.2 mg.
3- SINUS ARRHYTHMIA
Phasic alteration of heart rate during respiration
sinus rate increases during inspiration and slows during expiration)
consequence of normal parasympathetic NS activity
pronounced in children.
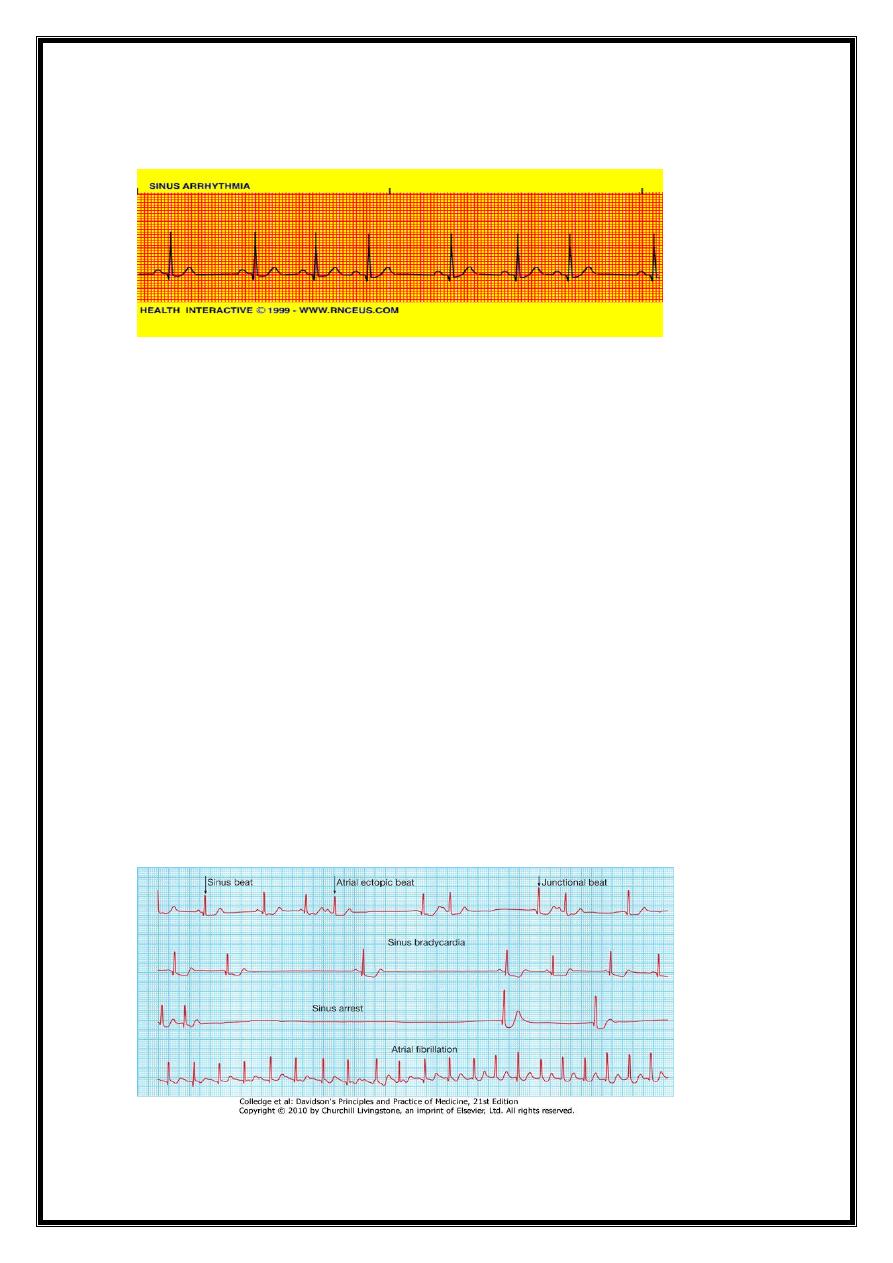
9
Absence of this normal variation in heart rate with breathing or with changes in posture
= feature of autonomic neuropathy
Sinoatrial disease(sick sinus syndrome)
can occur at any age -most common in older people.
underlying pathology = fibrosis, degenerative changes or ischaemia of SA (sinus) node.
characterised by a variety of arrhythmias and may present with palpitation, dizzy spells
or syncope{intermittent tachycardia, bradycardia, or pauses with no atrial or ventricular
activity (SA block or sinus arrest)}
Common features of sinoatrial disease
Sinus bradycardia
• Sinoatrial block (sinus arrest)
• Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
• Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
• Atrioventricular block
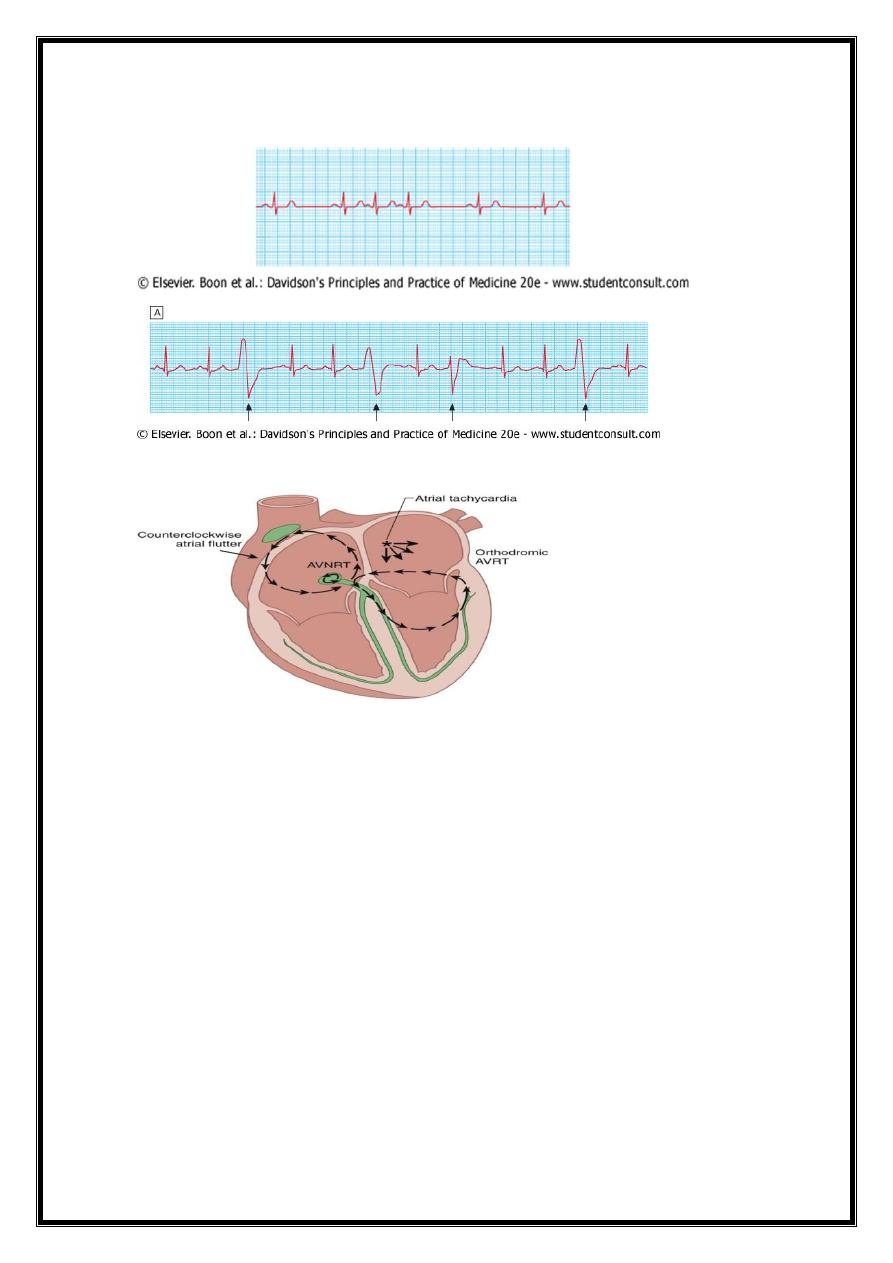
Sinoatrial disease (sick sinus syndrome). continuous rhythm strip from a 24-hour ECG tape
recording illustrating periods of sinus rhythm, atrial ectopics, junctional beats, sinus
bradycardia, sinus arrest and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation

11
B-ATRIAL TACHYARRHYTHMIAS
1-atrial extrasystoles(ectopics)
2-atrial tachycardias
3-atrial flutter
4-atrial fibrillation
A-AT WITH 2:1 AND VARIABLE AV CONDUCTION
B-MULTIFOCAL AT C-AF D-Afib
1-ATRIAL ECTOPIC BEATS
Symptoms=
usually no symptoms
sensation of a missed beat or an abnormally strong beat.
ECG= premature but otherwise normal QRS complex;
if visible, preceding P wave has a different morphology (atria activate from an abnormal
site).
Consequences=
Most no consequence
very frequent atrial ectopic beats -may herald onset of atrial fibrillation.
Treatment rarely necessary
11
Compare with VE
2-ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA
AETIOLOGY 1-increased atrial automaticity
2- sinoatrial disease or
3- digoxin toxicity.
ECG=
narrow complex tachycardia with abnormal P-wave morphology, (sometimes associated
with AV block if atrial rate is rapid).
Treatment=
β-blockers( reduce automaticity) or
class I or III antiarrhythmic drugs
rapid atrial tachycardias controlling ventricular response = AV node-blocking drugs.
recurrent or drug-resistant atrial tachycardia =Catheter ablation therapy

12
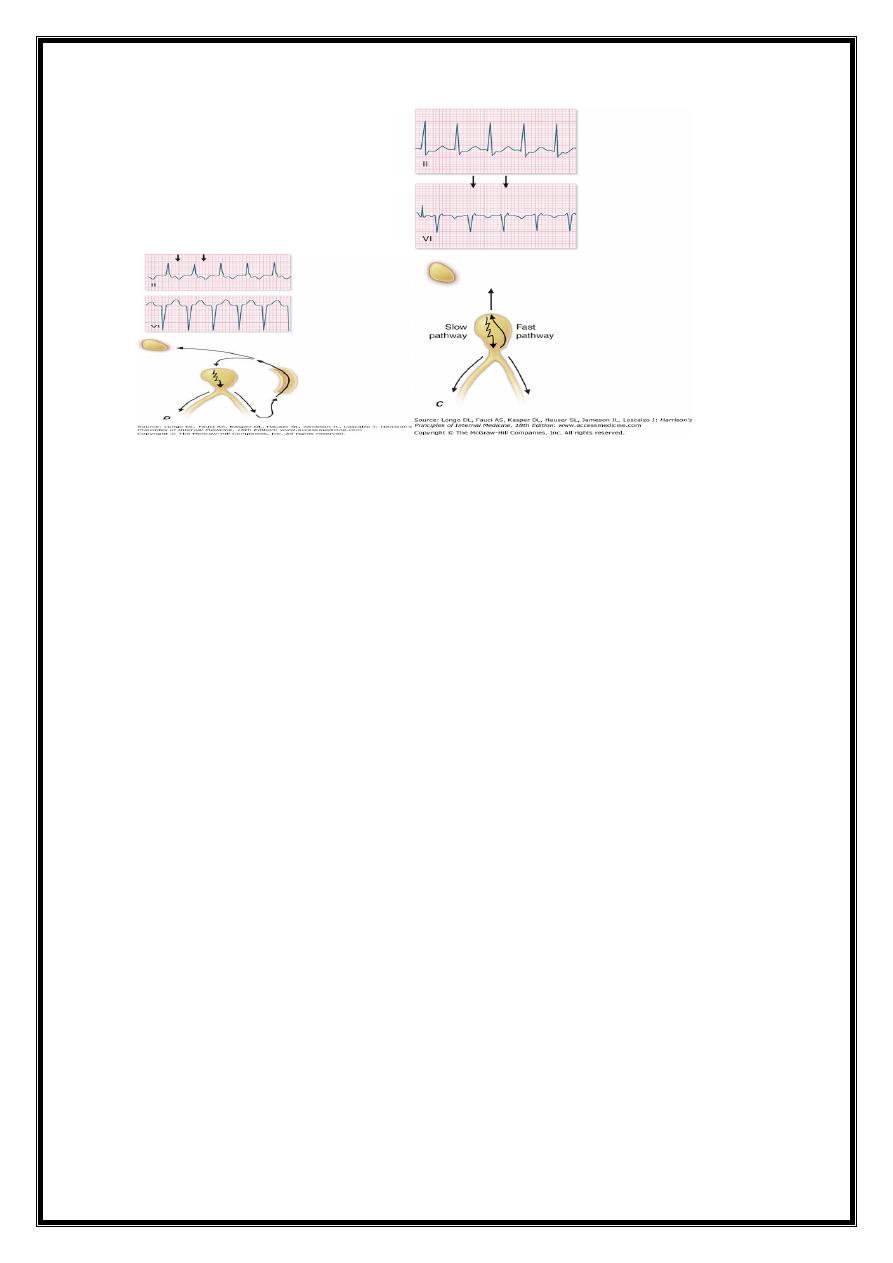
SUPRA-VENTRICULR TACHYCARDIA
{ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODAL REENTRANT TACHYCARDIA (AVNRT)}
Mechanism= re-entry in circuit involving AV node and its two right atrial input
pathways (superior fast pathway and inferior slow pathway )
regular tachycardia with a rate of 140-220/min.
Aetiology=tends to occur in normal hearts
ECG = tachycardia with normal QRS complexes
occasionally there may be rate-dependent bundle branch block
SUPRA-VENTRICULARTACHYARRHYTHMIAS
1-ATRIAL=AT.AF.AF
2-JUNCTIONAL(AV-NODAL)=
AV NODAL DUAL REENTRY
TYPICAL-ant. Slow &retro. fast
ATYPICAL-
A-V ACCESSORY REENTRANT(BYPASS)
CONCEALED-ORTHO (in AV node)
MANIFEST-ANTI
13
