DR.SABAH
الصفحة
1
ElectroCardioGraphy
Definition and types
Indications
Leads
ECG grid
Normal configurations( waves and intervals)& axis
Analysis of ECG
ECG in special disease states
Myocardial ischemia and infarction
Hypertrophy-(ventricles) and BBB
Arrhythmias-
Electrolyte
definition
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) =
Graphic recording of electric potentials generated by heart.
signals detected by means of metal electrodes attached to the extremities and chest wall
amplified and recorded by electrocardiograph.(displayed on moniter)
ECG leads display =
instantaneous differences in potential between these electrodes
indication and abnormalties
ECG --used to determine
1- cardiac rhythm and condition of conducting tissues. (arrhythmias, conduction disturbances )
2- chamber size
3- myocardial ischaemia and infarction
4- effects of some drugs and electrolytes on the heart
Major ECG Abnormalities
Cardiac Enlargement and Hypertrophy
Bundle Branch Blocks
DR.SABAH
الصفحة
2
Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction
Metabolic Factors and Drug Effects
Electrophysiology
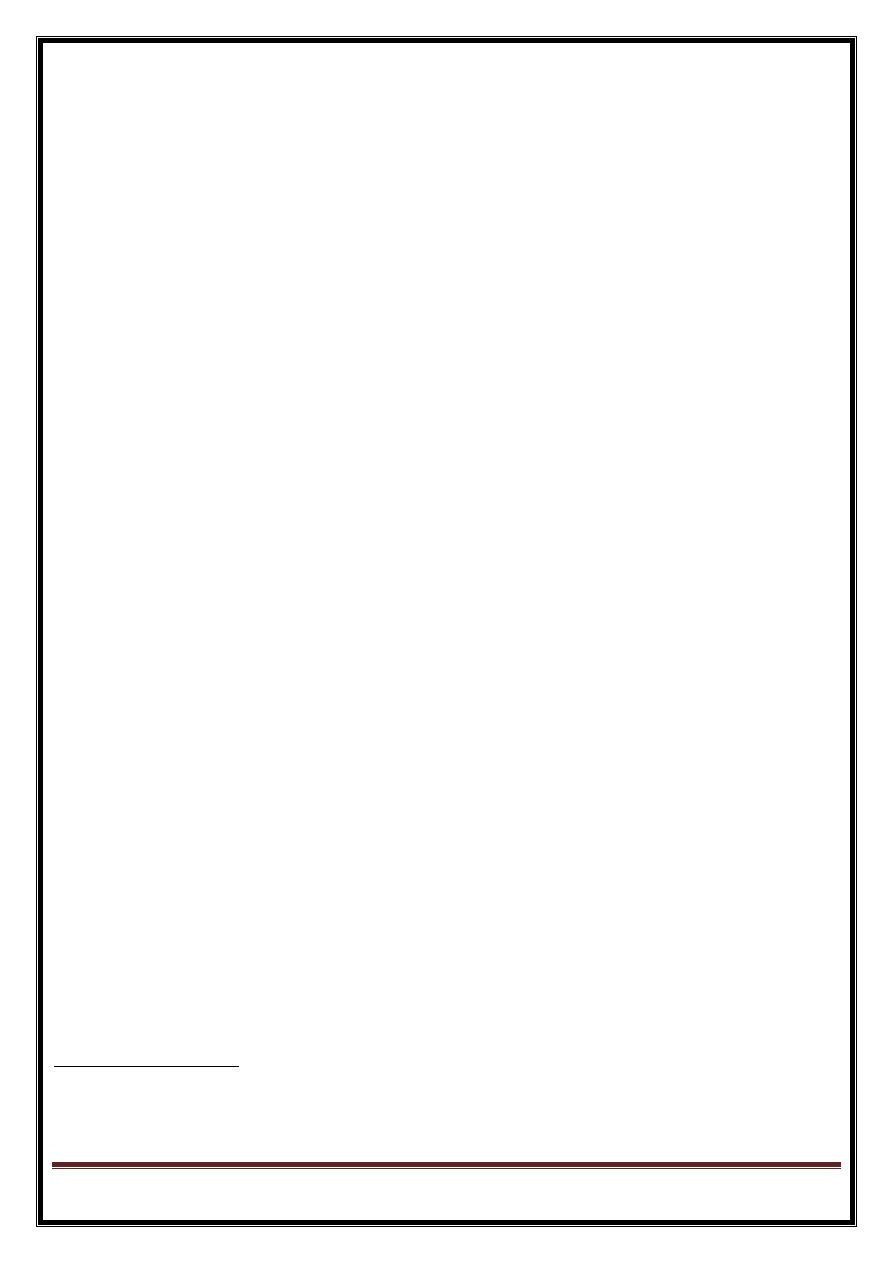
Electrical activation of heart muscle cell => membrane depolarization==>propagated along length cell or fibre
=moving of wave front of depolarization – passes through heart = electrical currents detected by electrode pairs
on body surface
Electrical current produced by :
1 cardiac pacemaker cells
2 specialized conduction tissue
3 heart muscle itself
Depolarization stimulus for the normal heartbeat
originates in sinoatrial (SA) node or sinus node, (pacemaker cells). cells fire spontaneously= automaticity.
= spread of depolarization wave through right and left atria== atrial contraction.
==>impulse stimulates pacemaker and specialized conduction tissues in atrioventricular (AV) nodal and His-
bundle areas( AV junction).
bundle of His bifurcates into two main branches, right and left bundles,- rapidly transmit depolarization
wavefronts to right and left ventricular myocardium by way of Purkinje fibers. (
depolarization wavefronts spread through ventricular wall, from endocardium to epicardium, triggering
ventricular contraction
DR.SABAH
الصفحة
3
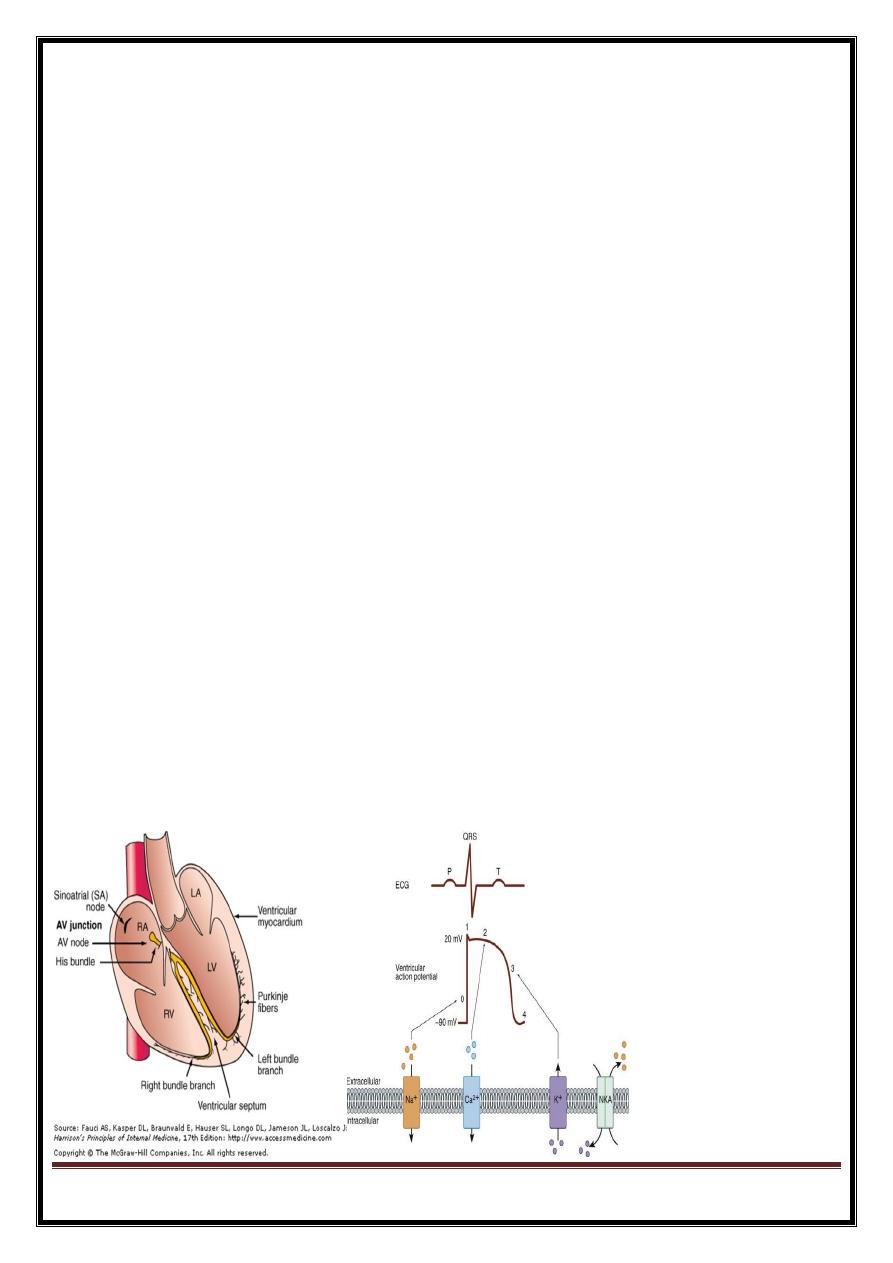
Important principles
electrically (cf.mechanically) heart acts -two chambers (two atria and two ventricles contract together)
Dominat ventricle = left -(LV has greater muscle mass == contributes major component of the QRS complex)
Direction=
When depolarisation moves towards positive electrode= positive deflection in ECG;
depolarisation in opposite direction negative deflection.
DR.SABAH
الصفحة
4
types
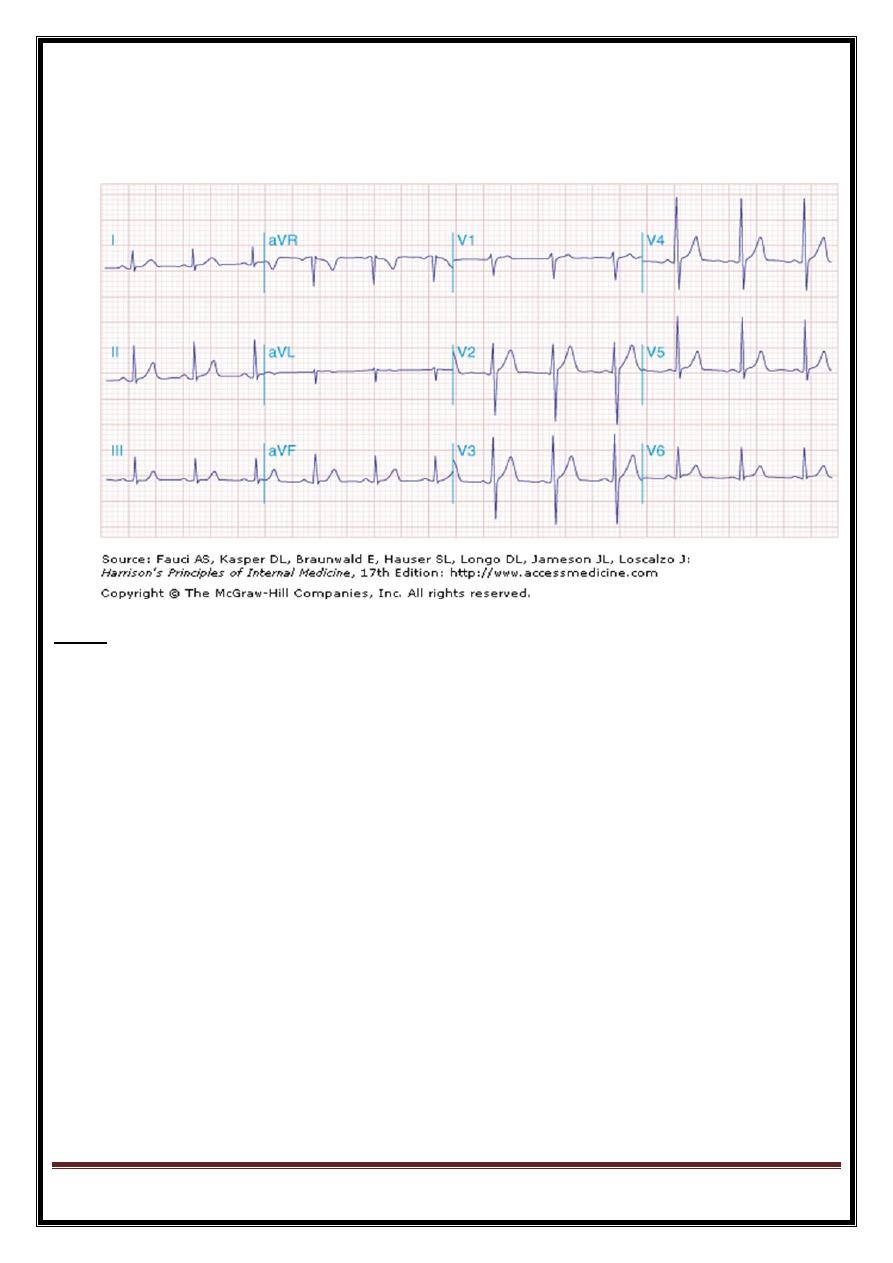
standard 12-lead ECG
Exercise (stress) ECG
Ambulatory ECG
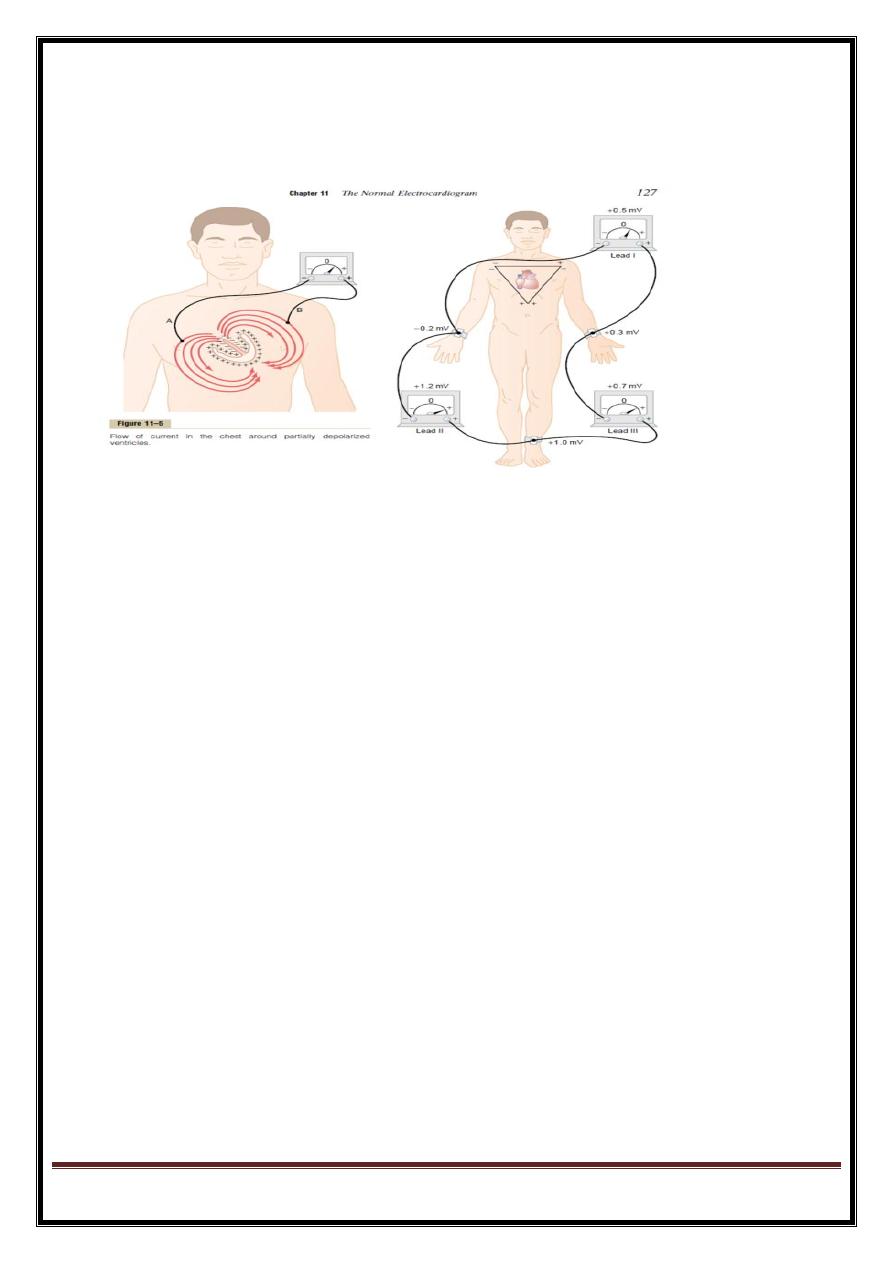
Limb leads
Four limb electrodes: one on each wrist and one on each ankle, connected to a central terminal which is
electrically neutral.
electrode on left arm - augmented relative to central terminal = lead aVL .
augmented signals -right arm (aVR)
augmented signals- left leg (aVF).
leads I, II and III (bipolar leads) =
difference 2 adjacent electrodes.
Lead I =left arm and right arm,
lead II =left leg and right arm,
DR.SABAH
الصفحة
5
lead III =left leg and left arm.
six chest leads, V1-V6-electrodes placed on anterior and lateral left side of chest, over heart.
Each lead records signal between corresponding chest electrode (+ve) and central terminal (-ve).
Leads V1 and V2 lie approximately over RV,
V3 and V4 over interventricular septum, and
V5 and V6 over the LV .
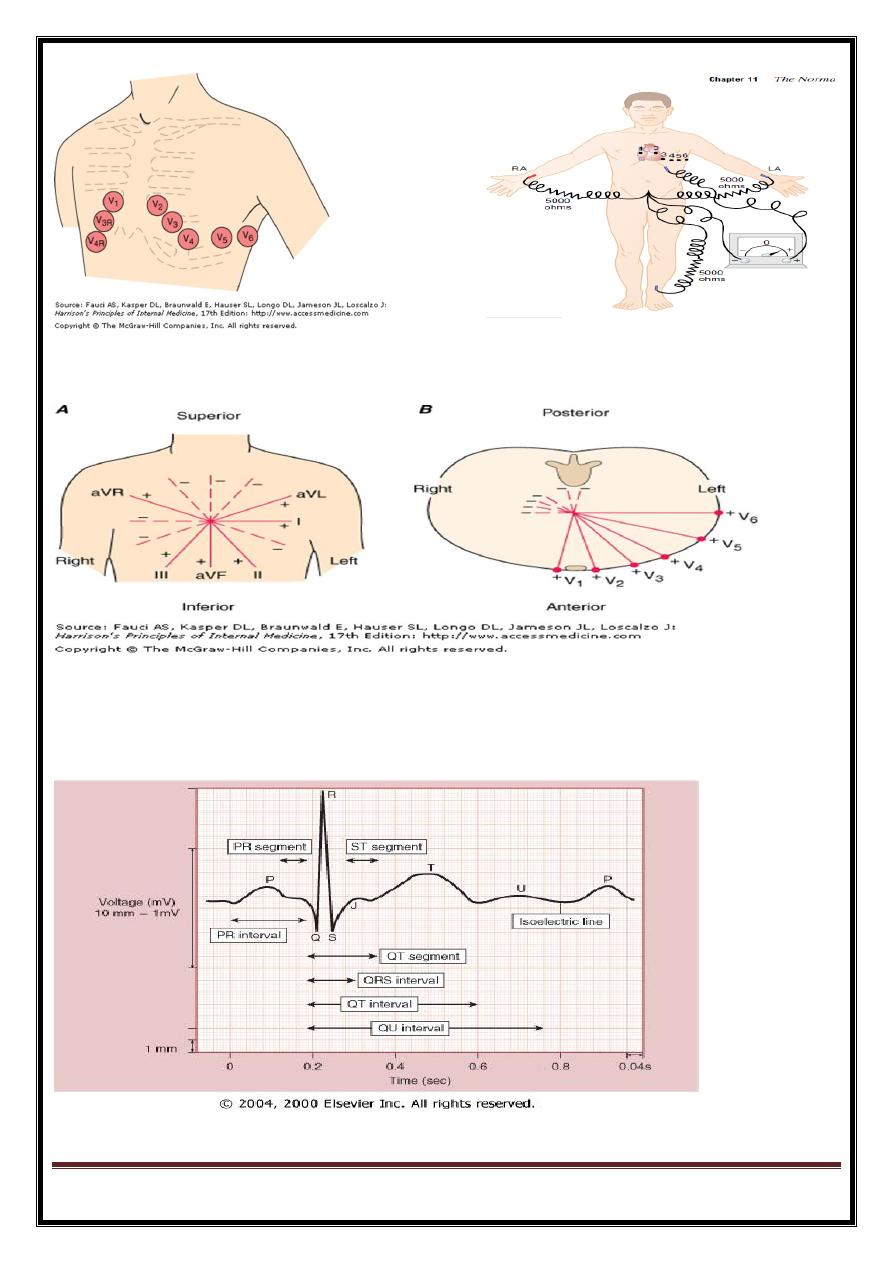
LEFT VENT. CONE=
LAT(1+AVL),
SEPTAL(V1-V3),
APICAL(V5-V6),
INF(11,111,AVF).
POST.WALL
DR.SABAH
الصفحة
6
