Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Sorting Algorithms
Common problem: sort a list of values, starting from lowest to highest. List of exam scores,
Words of dictionary in alphabetical order, Students names listed alphabetically, Student
records sorted by ID#.
Main types of sorting algorithms: Selection sort, Insertion sort, Bubble sort.
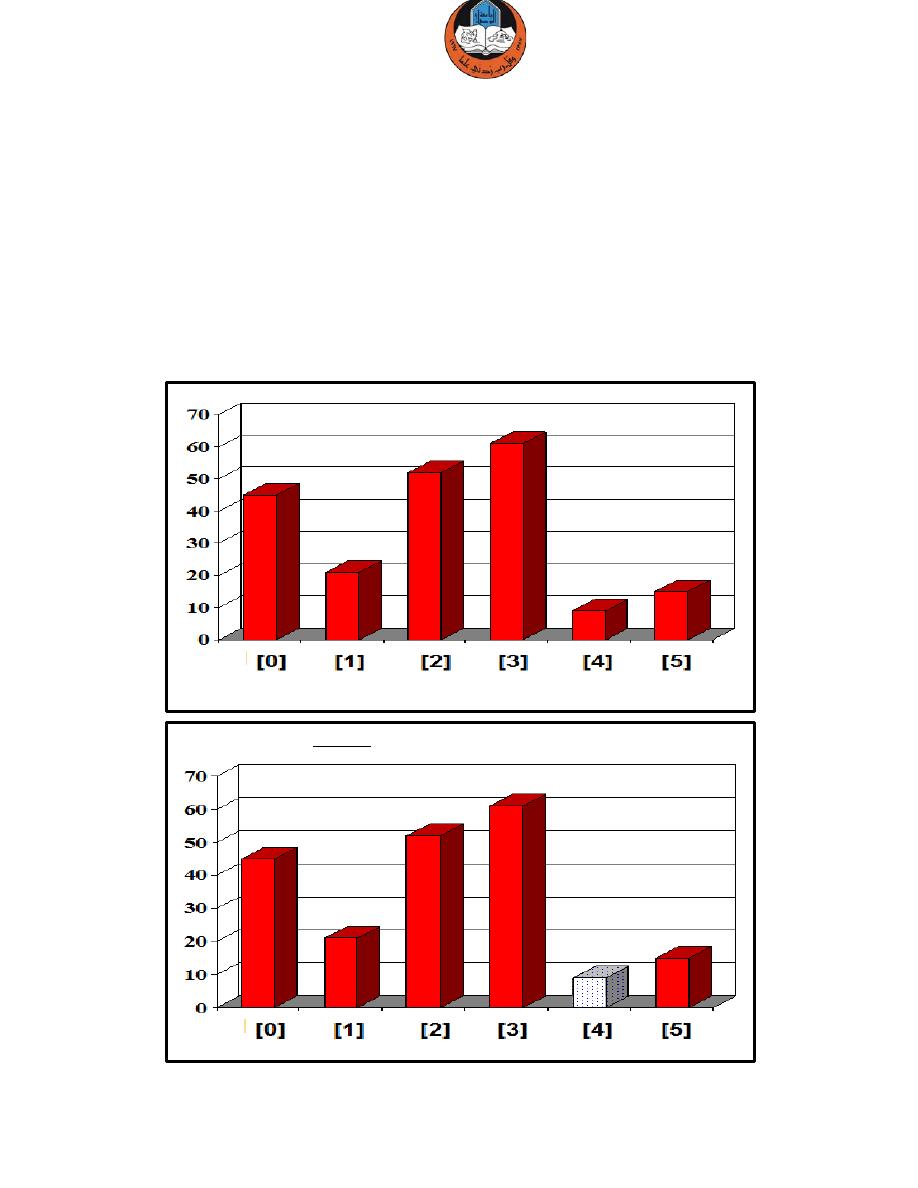
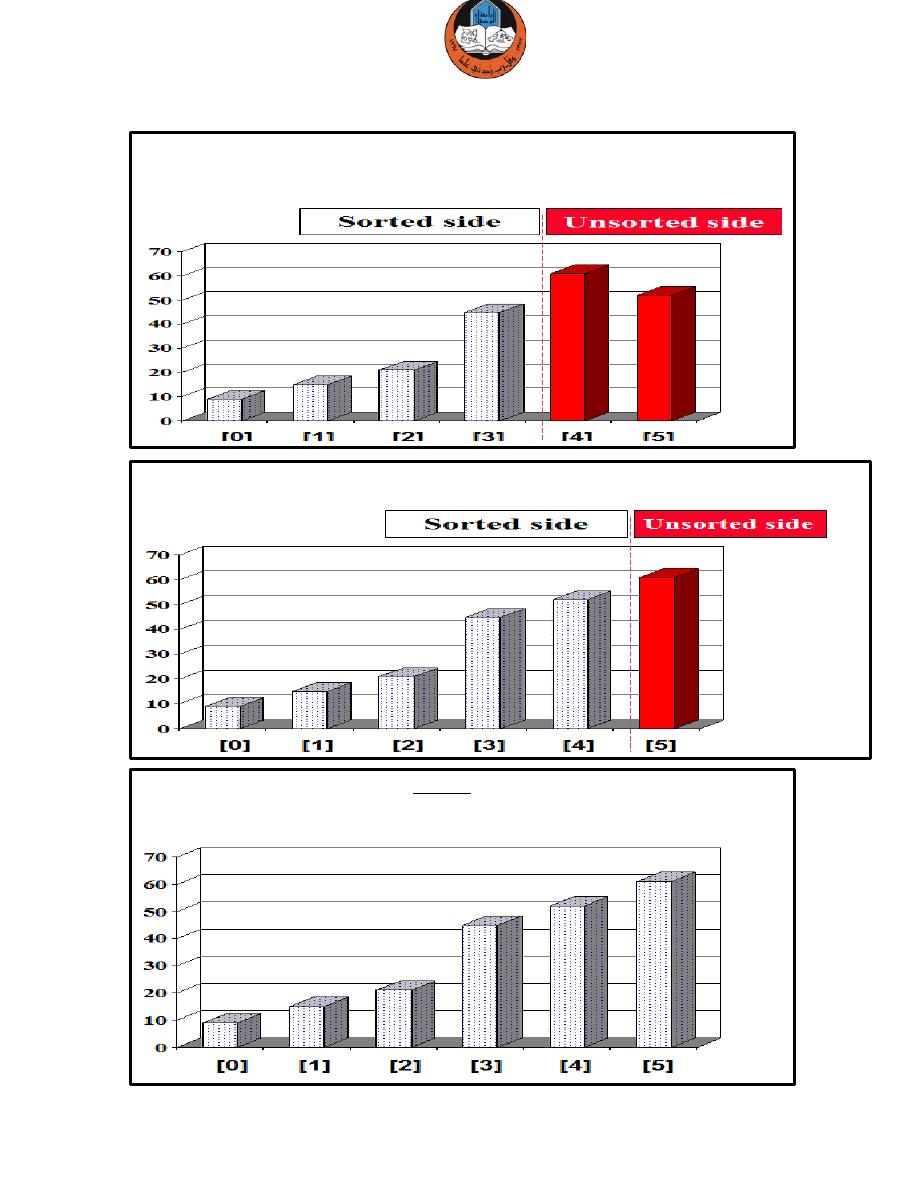
Selection Sort Algorithm
Depends on finding the smallest item and swap it with the first item of the unsorted side.
Example: we are given an array of six integers that we want to sort from smallest to largest.
Start by finding the smallest entry.
1
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
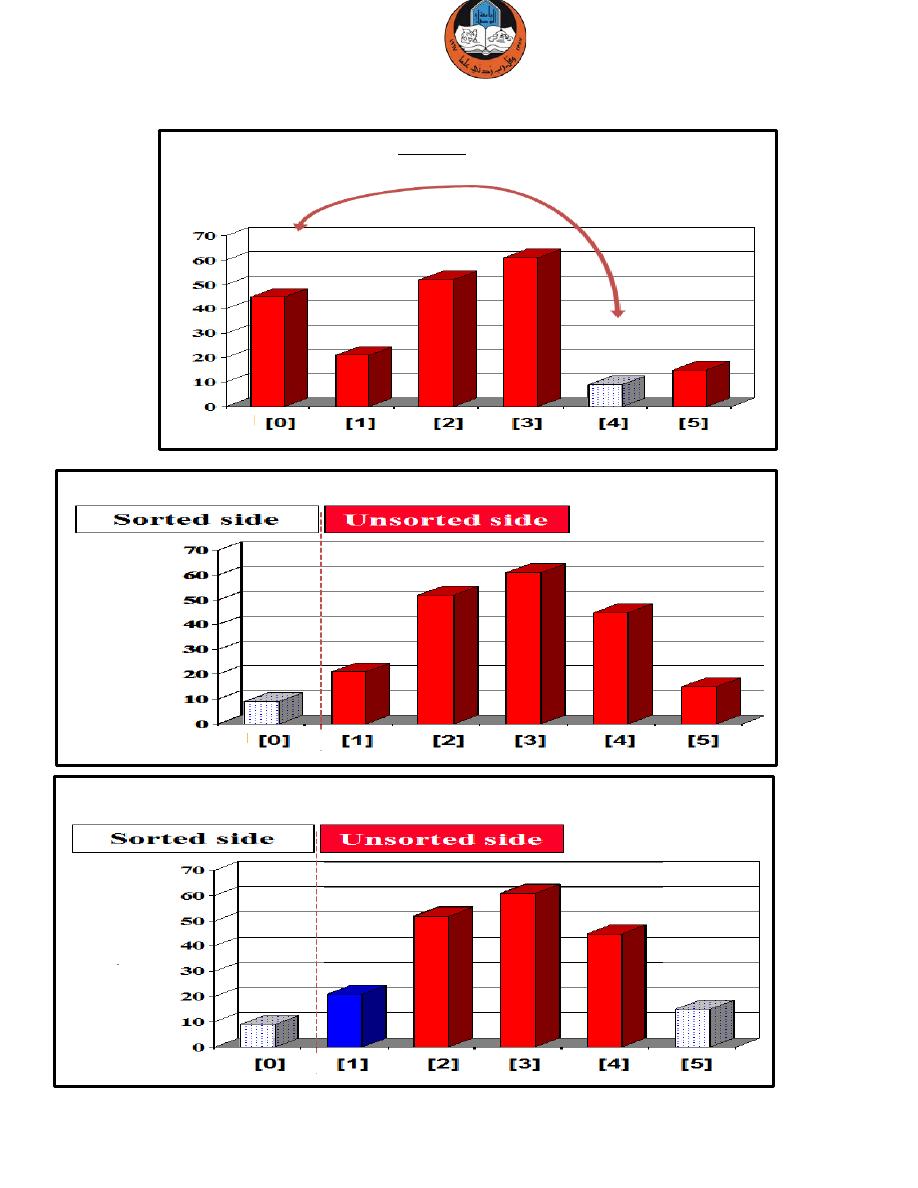
Swap the smallest entry with the first entry.
Part of the array is now sorted.
Find the smallest element in the unsorted side.
2
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
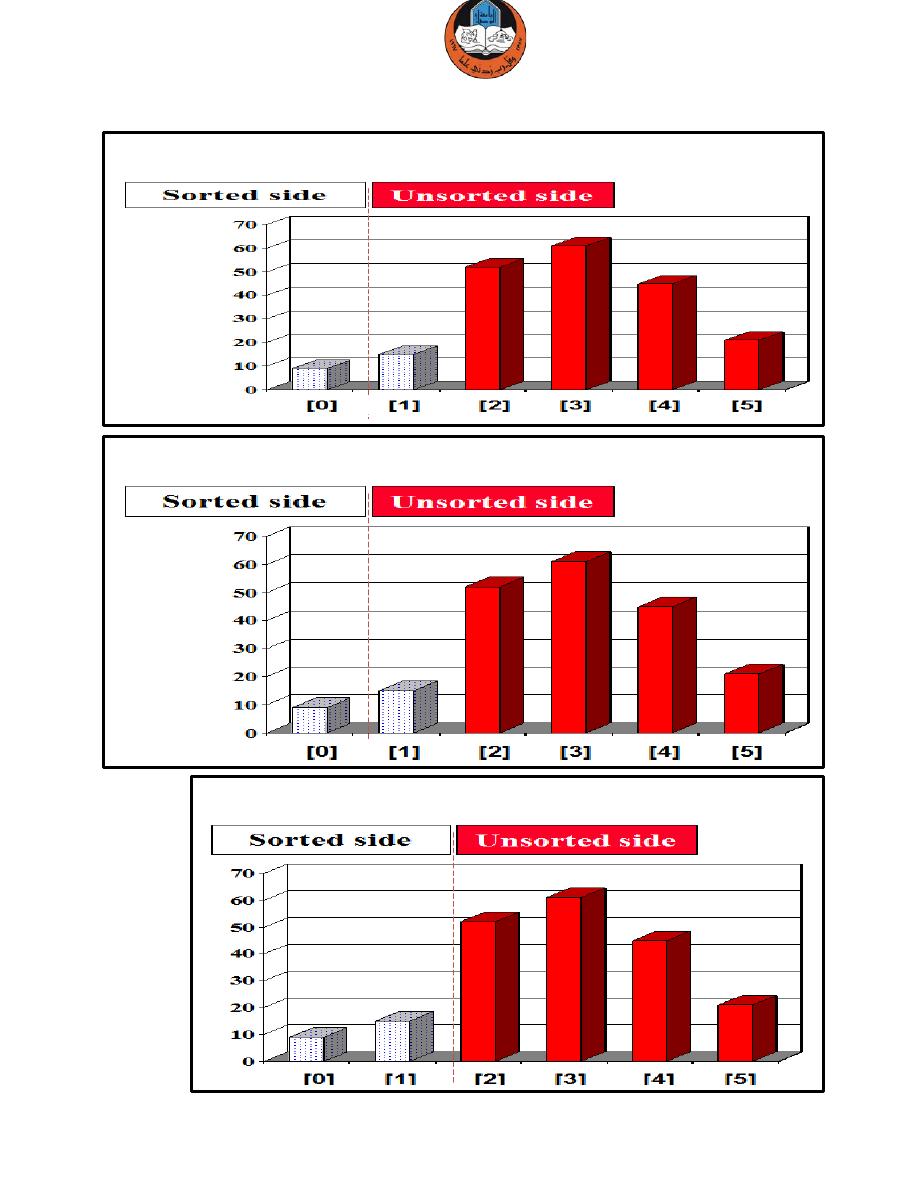
Swap with the front of the unsorted side.
Swap with the front of the unsorted side.
We have increased the size of the sorted side by one element.
3
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
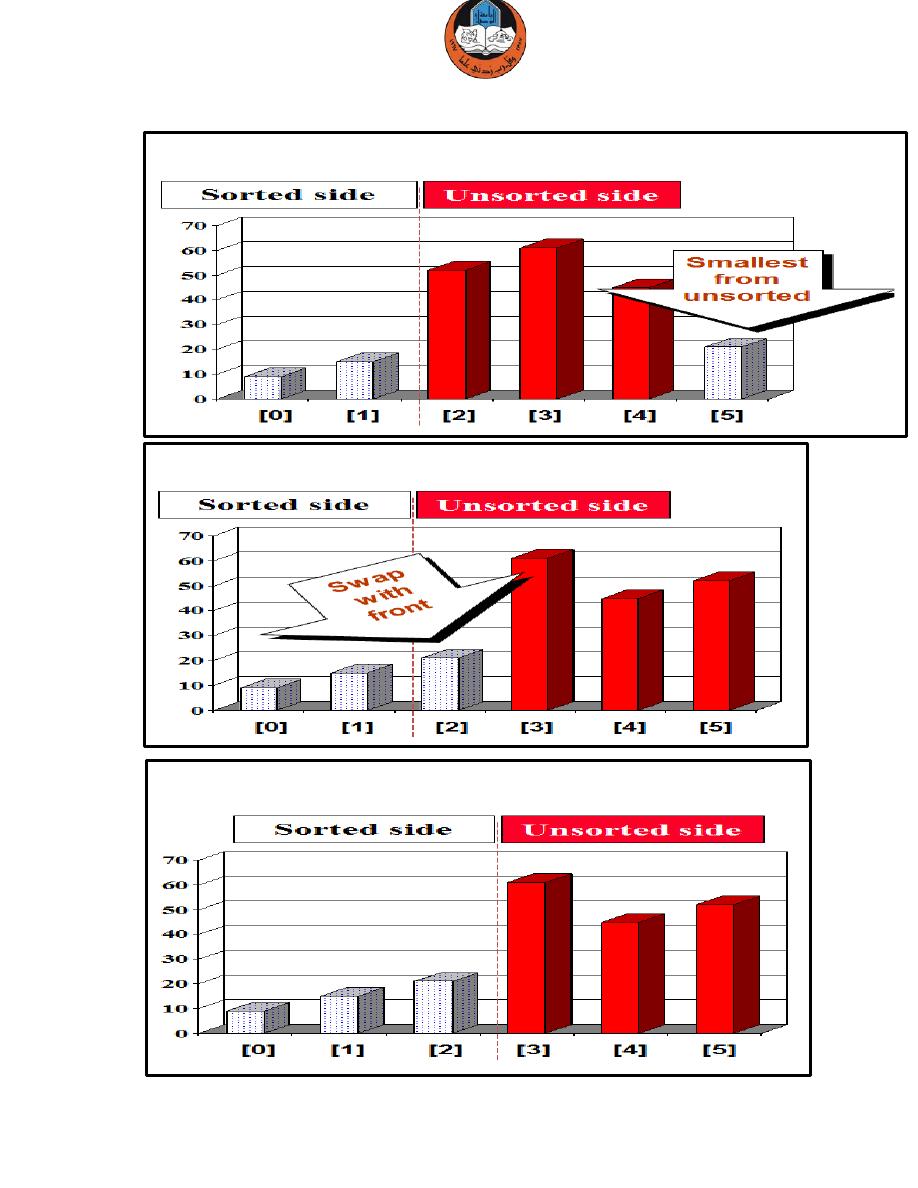
The process continues...
The process continues...
The process continues...
4
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
The process keeps adding one more number to the sorted side, which has the smallest
numbers, arranged from small to large.
We can stop when the unsorted side has just one number, since that number must be the largest number.
The array is now sorted, We repeatedly selected the smallest element, and moved this
element to the front of the unsorted side.
5

Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Example 1: Write a C++ program to apply the selection sorting algorithm on a
10-element 1D array.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define size 10
int i,j,temp,smallest;
void selection_sort(int array[size])
{
for(i=0;i<size-1;i++)
{
smallest=i;
for(j=i+1;j<size;j++)
if(array[smallest]>array[j])
smallest=j;
if(smallest!=i)
{
temp=array[i];
array[i]=array[smallest];
array[smallest]=temp;
}}}
void main()
{
int a[size];
cout<<"Enter elements of array[10]"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //reading array
{
cout<<"Enter element NO."<<i+1<<": ";
cin>>a[i];
}
cout<<"\nThe array before sorting:\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //printing array
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
selection_sort(a);
cout<<"\n\nThe array after sorting:\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
getch();
}
6
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
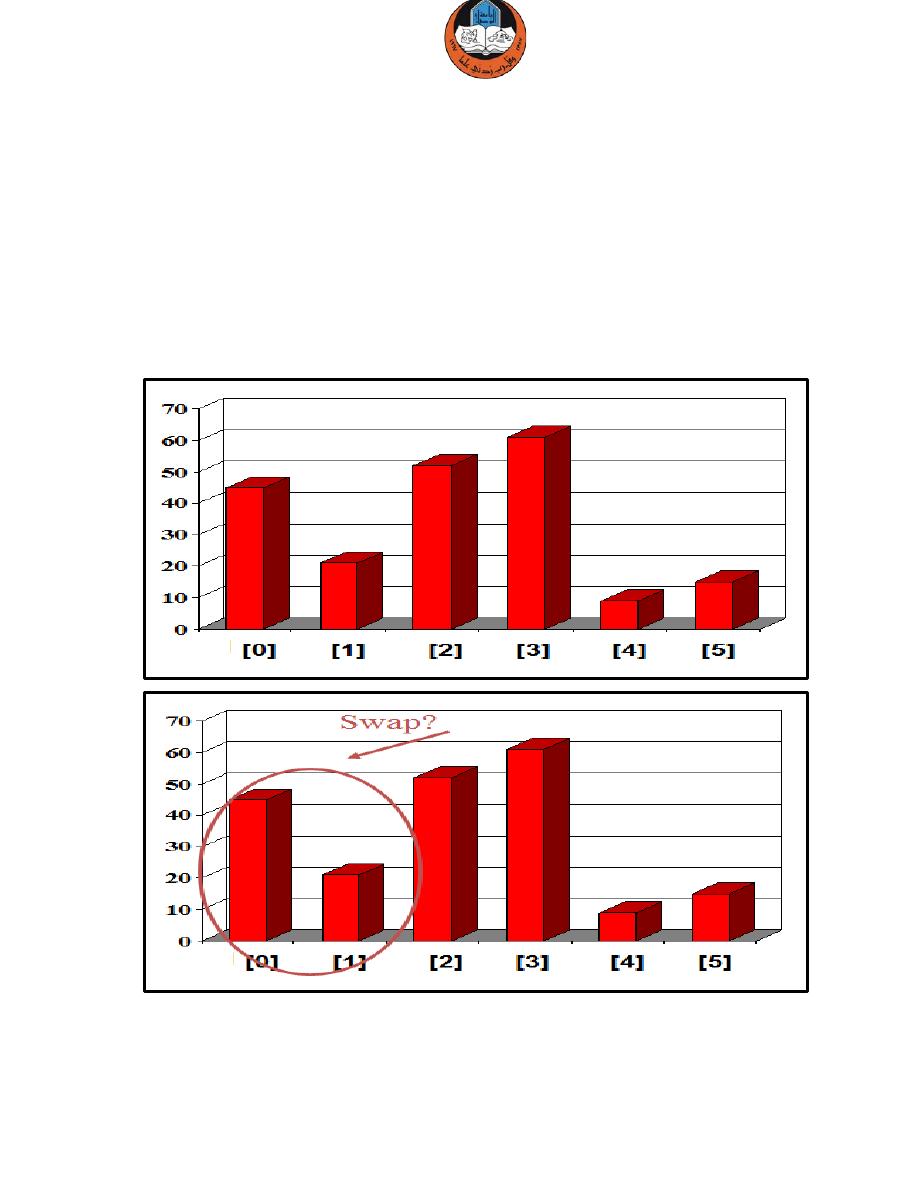
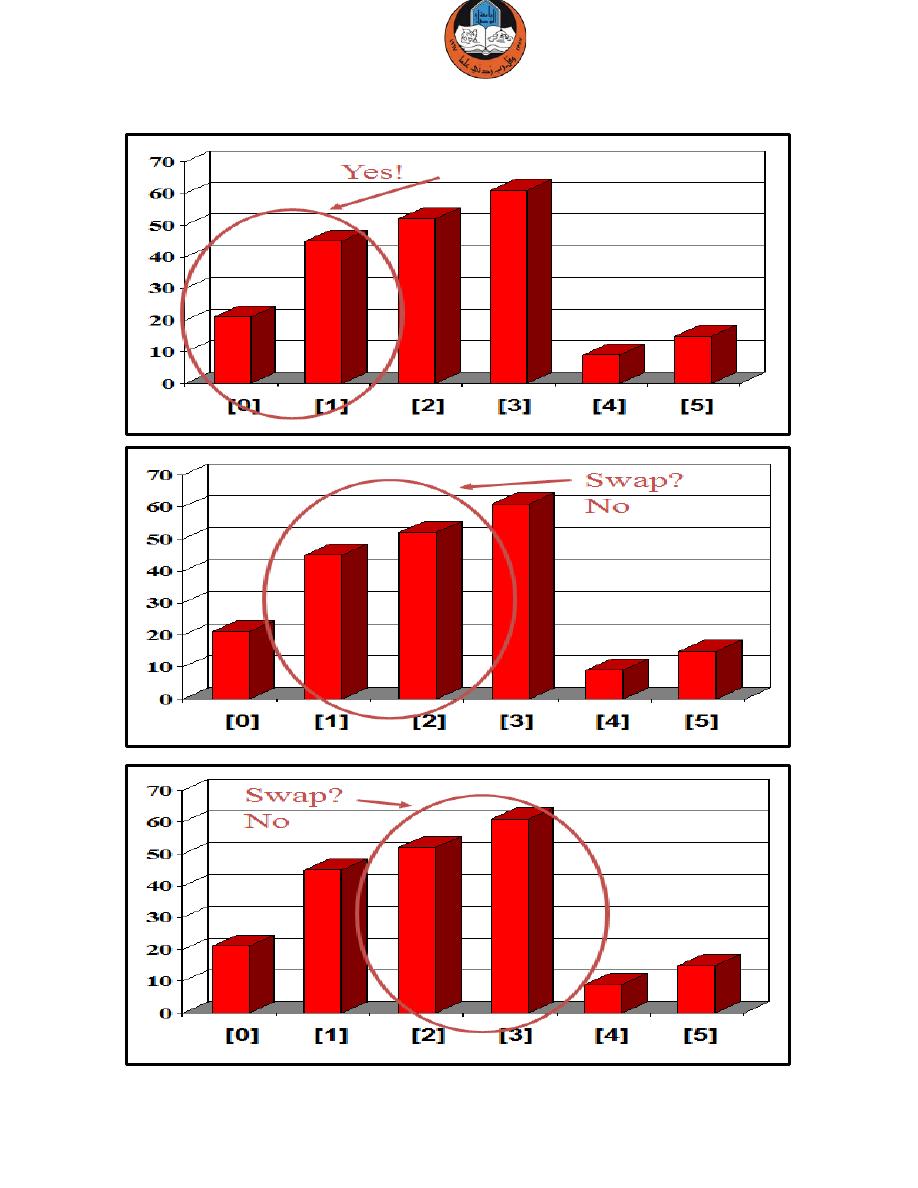
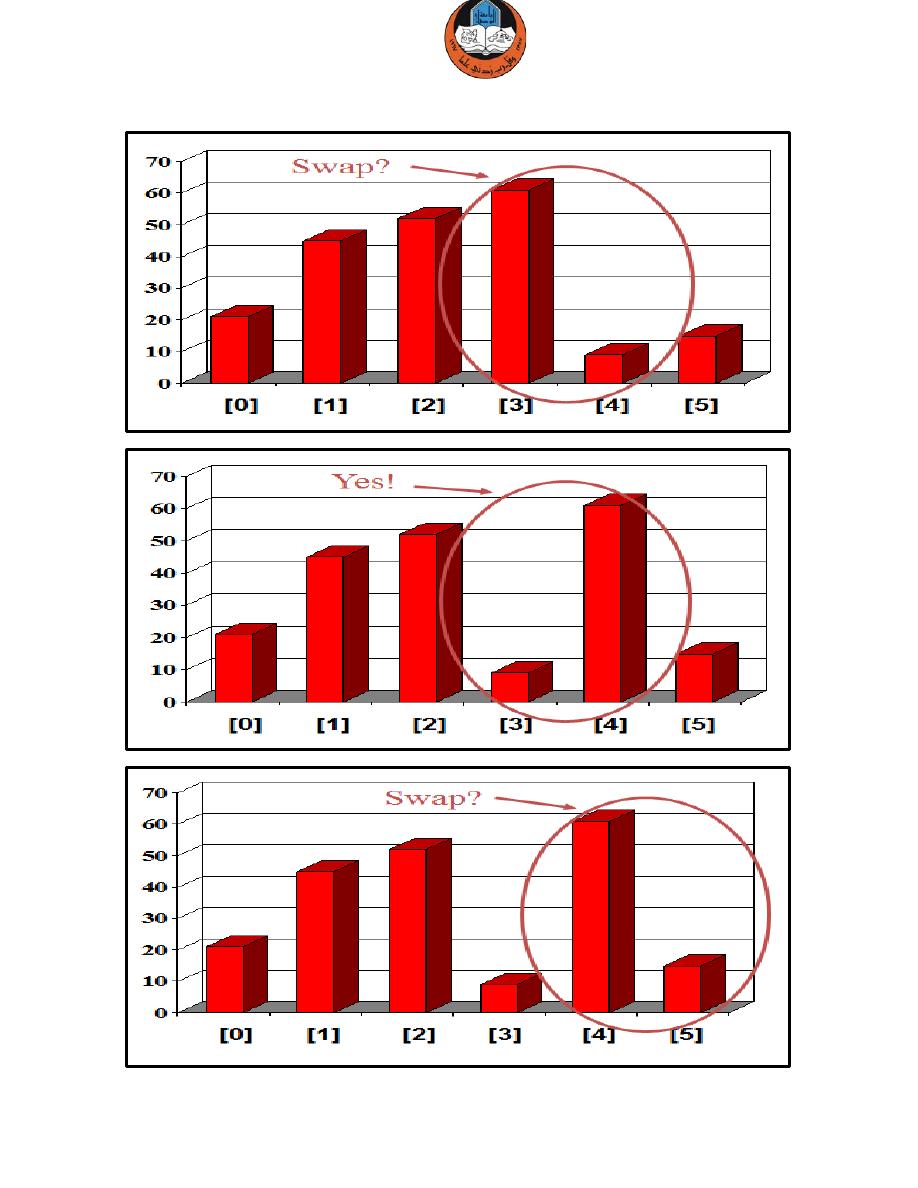
Bubble Sort Algorithm
The Bubble Sort algorithm looks at pairs of entries in the array, and swaps
their order if needed.
The same process is repeated till the loop ends and the array is sorted
completely.
Example: we are given an array of six integers that we want to sort from
smallest to largest.
7
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
8
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
9
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Repeat till the end…
10

Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Example 2: Write a C++ program to apply the bubble sorting algorithm on a
10-element 1D array.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define size 10
int i,j,k,temp;
void bubble_sort(int array[size])
{
for(k=0;k<size-1;k++)
for(i=0;i<size-1;i++)
for(j=i+1;j<size;j++)
if(array[i]>array[j])
{
temp=array[i];
array[i]=array[j];
array[j]=temp;
}
}
void main()
{
int a[size];
cout<<"Enter elements of array[10]"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //reading array
{
cout<<"Enter element NO."<<i+1<<": ";
cin>>a[i];
}
cout<<"\nThe array before sorting:\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //printing array
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
bubble_sort(a);
cout<<"\n\nThe array after sorting:\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
getch();
}
11

Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Searching Algorithms
A search algorithm is a method of locating a specific item of information in a
larger collection of data. We are going to discuss two algorithms for searching
the contents of an array.
Linear Search
This is a very simple algorithm. It uses a loop to sequentially step through an
array, starting with the first element. It compares each element with the value
being searched for and stops when that value is found or the end of the array
is reached.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
The advantage is its simplicity.
– It is easy to understand
– Easy to implement
– Does not require the array to be in order
The disadvantage is its inefficiency
– If there are 20,000 items in the array and what you are looking for
is in the 19,999
th
element, you need to search through the entire
list.
12

Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Example 3: write a C++ program to search an item in a 10-element 1D array
using linear search algorithm.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define size 10
int i;
void linear_search(int array[size],int item)
{
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
if(array[i]==item)
{
cout<<"\nData found, location = "<<i;
i=size+1;
}
if(i==size)
cout<<"\nData not found!";
}
void main()
{
int a[size],x;
cout<<"Enter elements of array[10]"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //reading array
{
cout<<"Enter element NO."<<i+1<<": ";
cin>>a[i];
}
cout<<"\nThe array is\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //printing array
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
cout<<"\n\nEnter that value you want to search for: ";
cin>>x;
linear_search(a,x);
getch();
}
Homework 4:
Re-write the linear search function using (while) instead of (for).
13

Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Binary Search
The binary search is much more efficient than the linear search.
It requires the list to be in order.
The algorithm starts searching with the middle element.
– If the item is less than the middle element, it starts over searching
the first half of the list.
– If the item is greater than the middle element, the search starts
over starting with the middle element in the second half of the list.
– It then continues halving the list until the item is found.
Example 4: write a C++ program to search an item in a 10-element 1D array
using binary search algorithm.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define size 10
int i,j,k,temp;
void bubble_sort(int array[size])
{
for(k=0;k<size-1;k++)
for(i=0;i<size-1;i++)
for(j=i+1;j<size;j++)
if(array[i]>array[j])
{
temp=array[i];
array[i]=array[j];
array[j]=temp;
}
}
void binary_search(int array[size],int item)
{
int first=0,last=size-1,middle,location=-1;
bool found=false;
while(!found && first<=last)
14

Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
{
middle=(first+last)/2; //calculate middle point
if(array[middle]==item)
{
found=true;
location=middle;
}
else if(item<array[middle])
last=middle-1;
else
first=middle+1;
}
if(location==-1)
cout<<"\nData not found!";
else
cout<<"Data found, location = "<<location;
}
void main()
{
int a[size],x;
cout<<"Enter elements of array[10]"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //reading array
{
cout<<"Enter element NO."<<i+1<<": ";
cin>>a[i];
}
cout<<"\nThe array before sorting:\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++) //printing array
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
bubble_sort(a);
cout<<"\n\nThe array after sorting:\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
cout<<"\n\nEnter that value you want to search for: ";
cin>>x;
binary_search(a,x);
getch();
}
15
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
Simulink in MATLAB
Used to model, analyze and simulate dynamic systems using block diagrams.
Provides a graphical user interface for constructing block diagram of a system,
therefore is easy to use.
However modeling a system is not necessarily easy!
Model – simplified representation of a system – e.g. using mathematical
equation
We simulate a model to study the behavior of a system – need to verify that
our model is correct – expect results.
Hint: Knowing how to use Simulink or MATLAB does not mean that you
know how to model a system
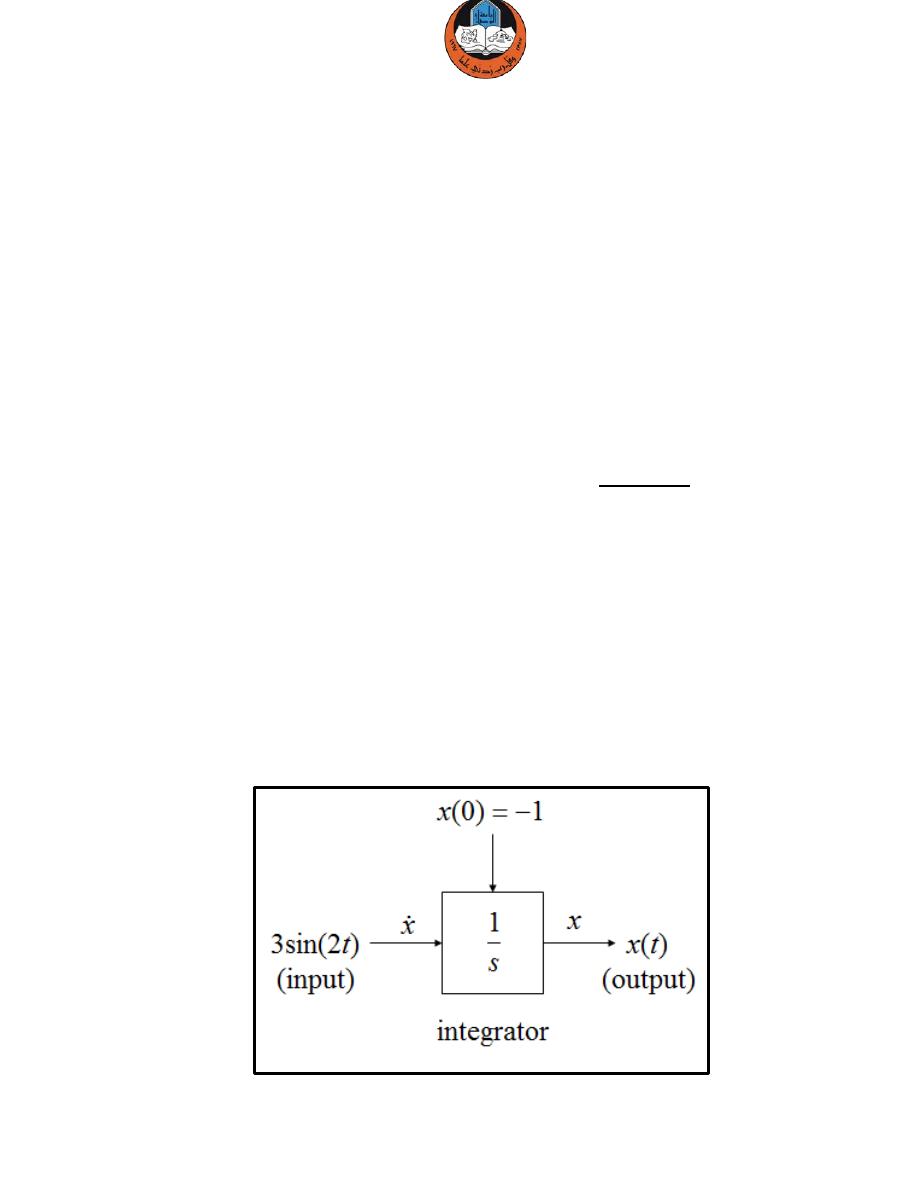
Example 5:
Build a Simulink model that solves the differential equation
Initial condition
First, sketch a simulation diagram of this mathematical model (equation).
Solution:
Input is the forcing function 3sin(2t).
Output is the solution of the differential equation x(t).
( )
t
x
2
sin
3
=
.
1
)
0
(
−
=
x
16
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
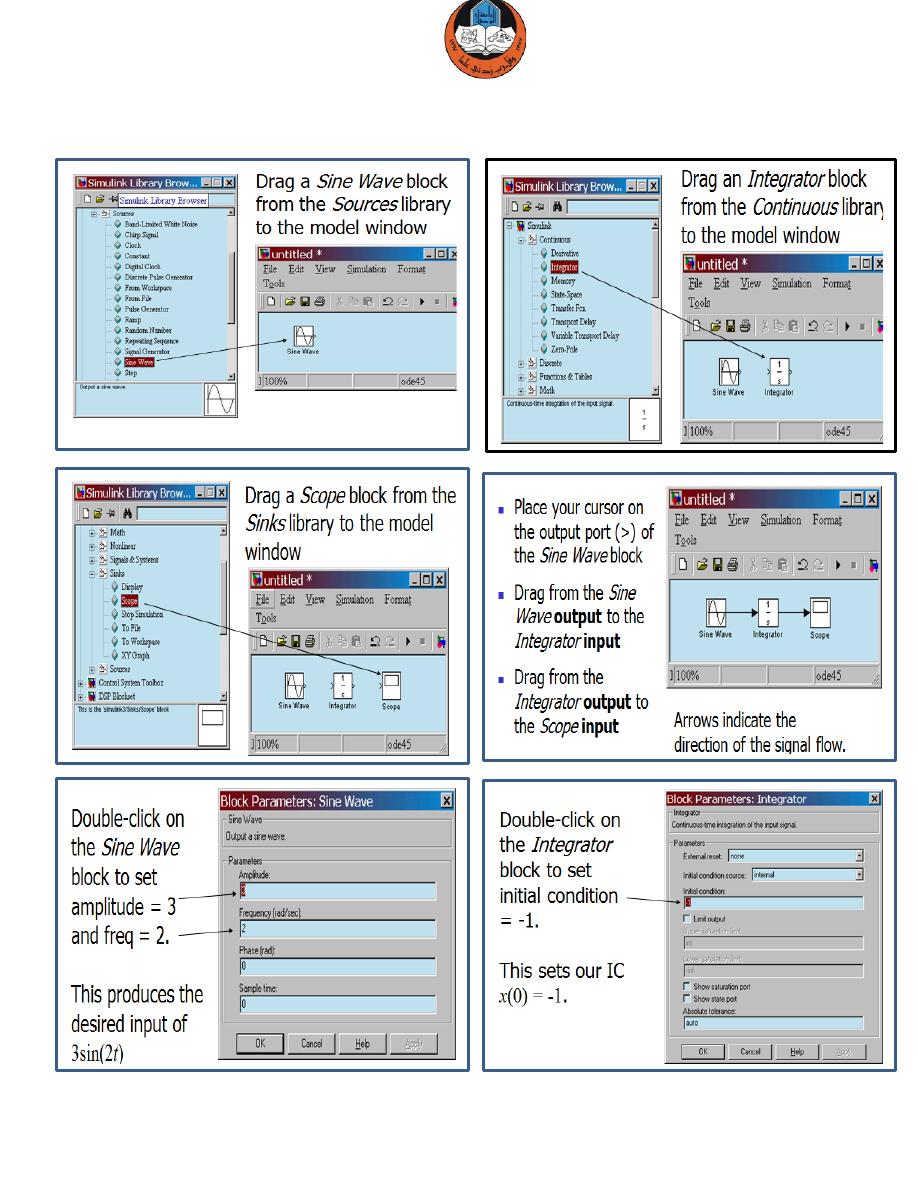
Now build this model in Simulink
17
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
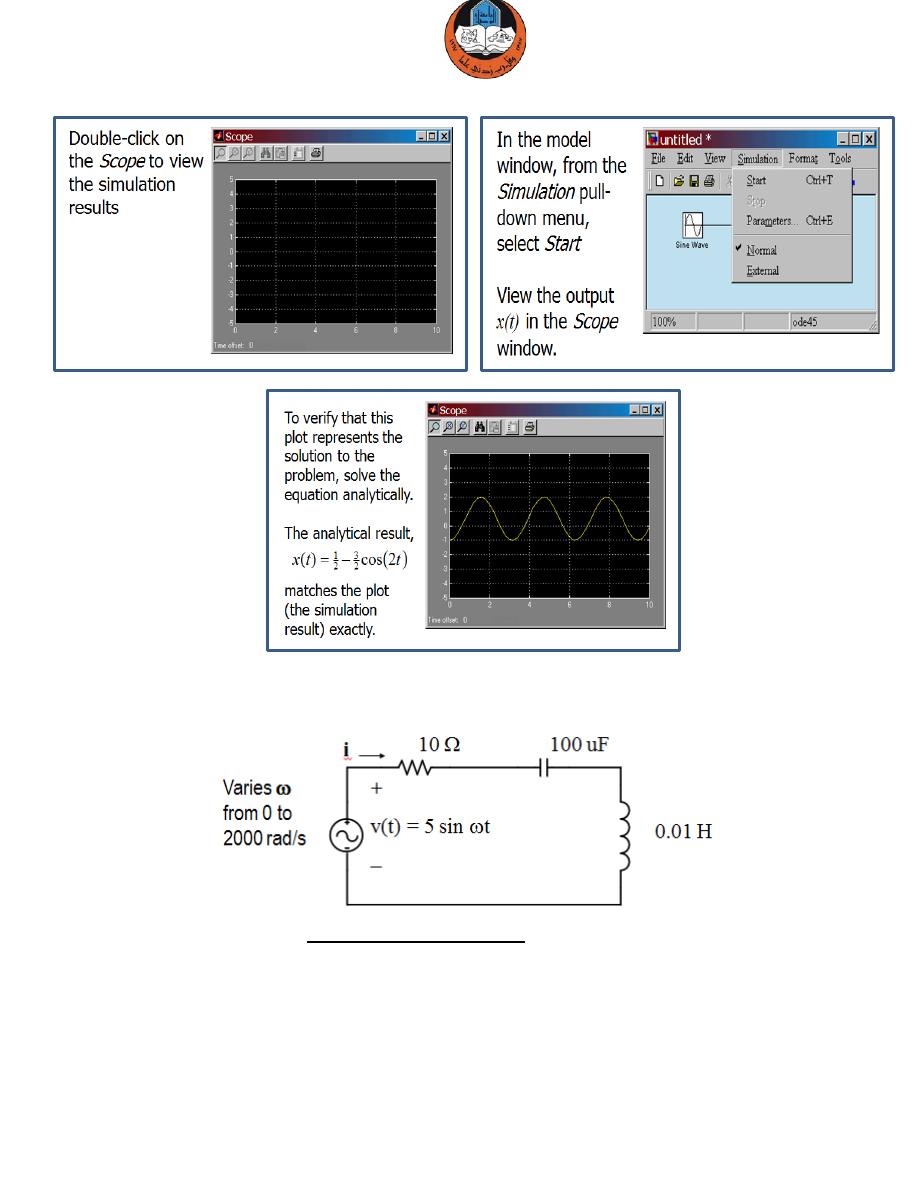
Example 6:
Simulate the resonant circuit and display the current waveform as we change
the frequency dynamically.
Observe the current. What do you expect?
The amplitude of the current waveform will become maximum at resonant
frequency, i.e. at
ω = 1000 rad/s.
How to model our resonant circuit?
18
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
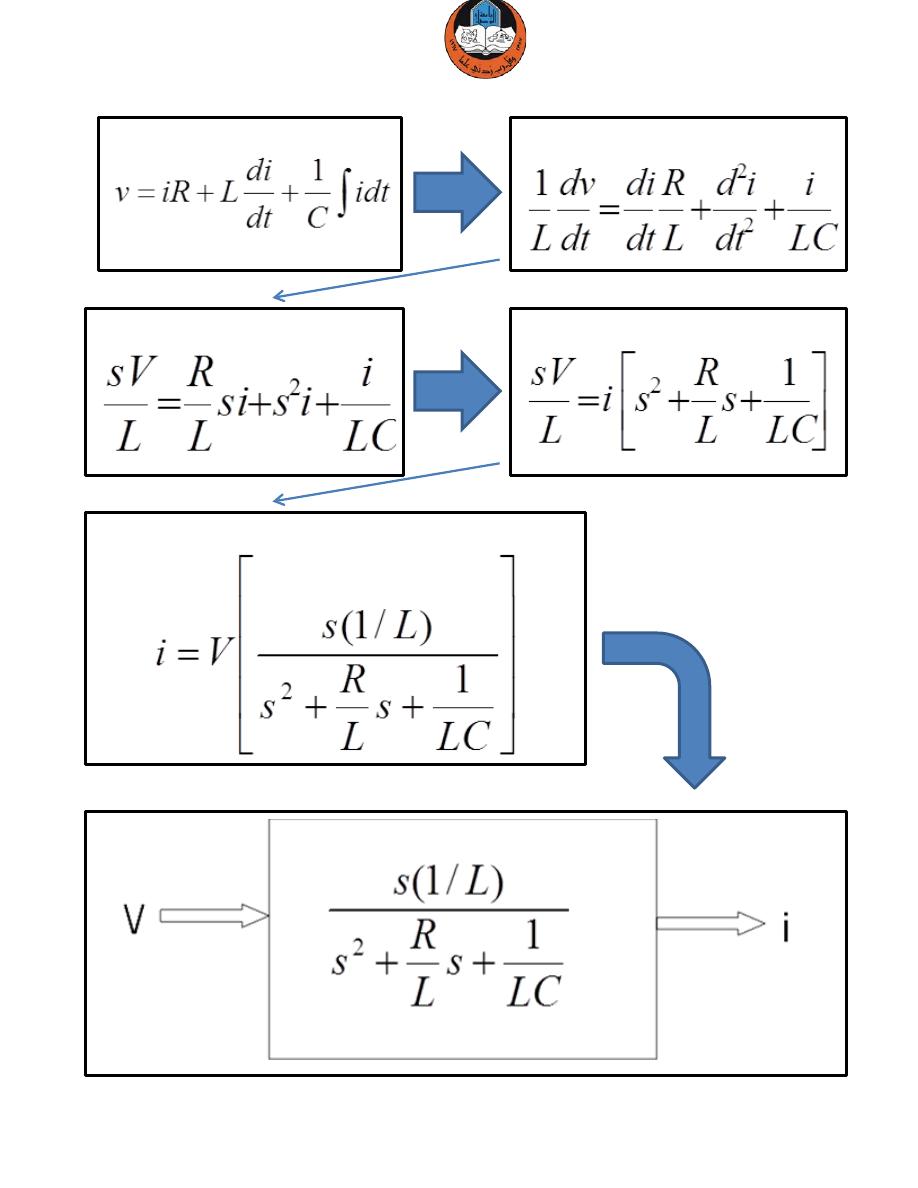
Writing KVL around the loop:
Differentiate time and re-arrange:
Taking Laplace transform:
Simplify the equation:
Thus the current can be obtained from the voltage:
19
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
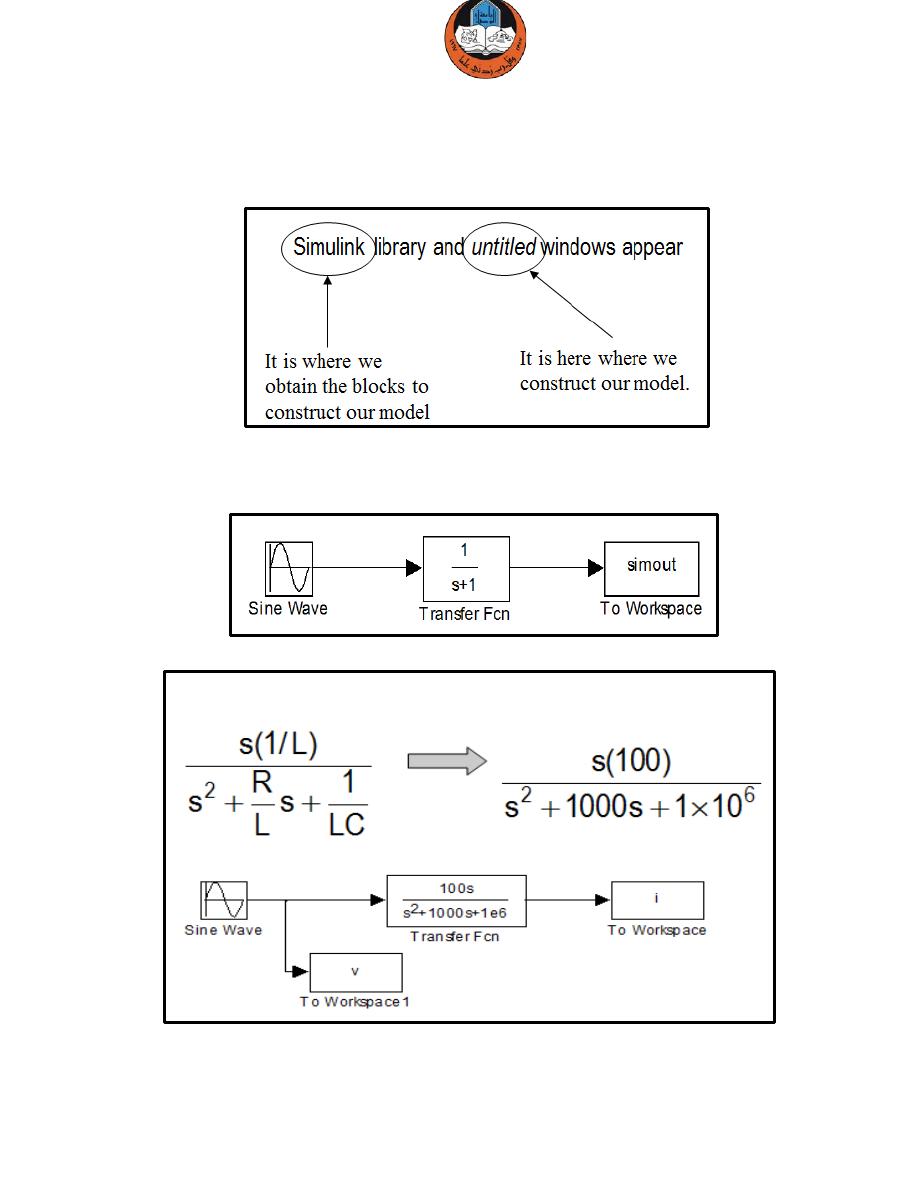
Moving to Simulink to create the simulation circuit.
Start Simulink by typing simulink at Matlab prompt.
Constructing the model using Simulink:
‘Drag and drop’ block from the Simulink library window to the untitled window
Substitution of values:
20
Lecture4 – C++: Sorting & Searching Algorithms. MATLAB: Simulink in MATLAB
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2015-2016 Kirkuk
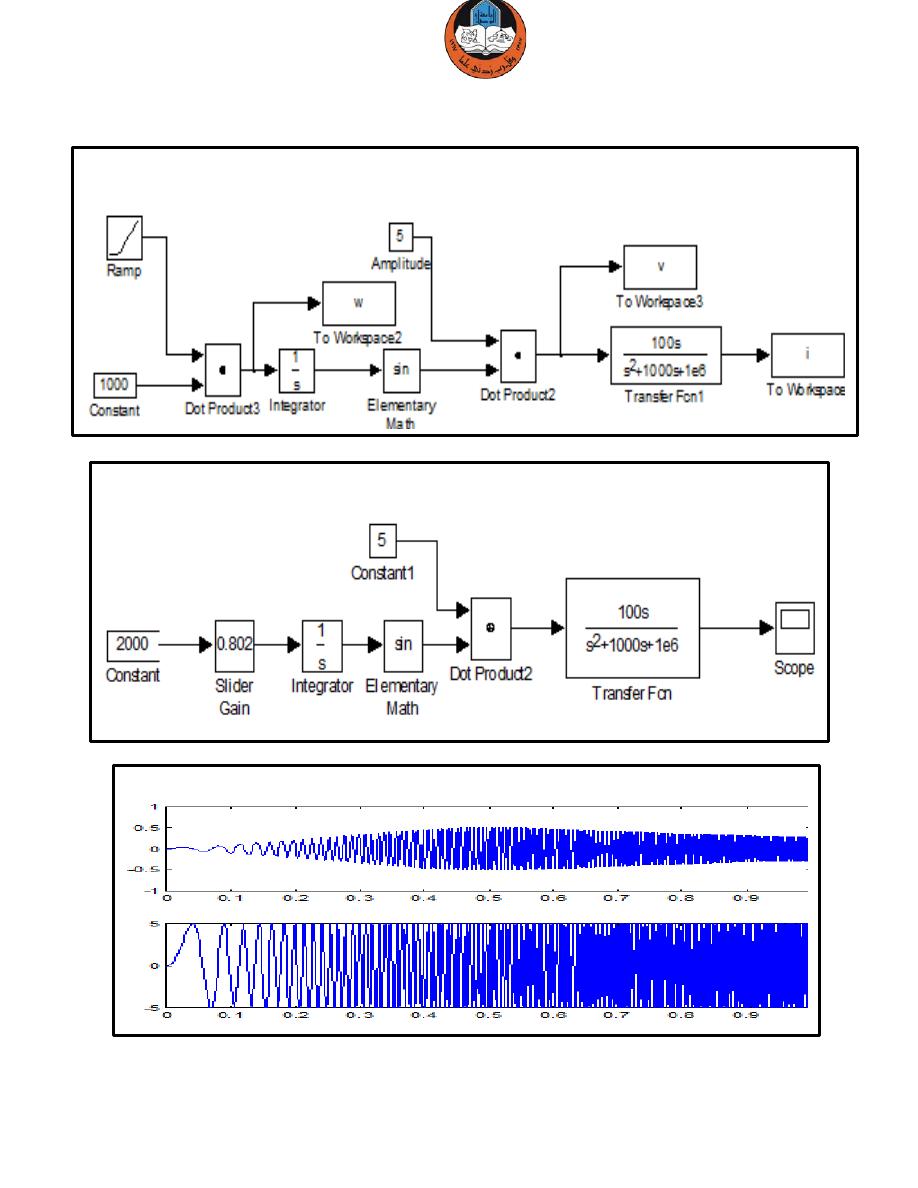
We need to vary the frequency and observe the current:
Output waveform:
The waveform can be displayed using scope – similar to the scope in the lab
21
