1
U
NIVERSITY OF
T
ECHNOLOGY
Electromechanical Department
2009‐2010
Fourier series
Dr.Eng Muhammad.A.R.Yass
Sultan
M O H D
_
Y A S S
9 7 @
Y A H O O
.
C O M

2
Advance Mathematics
Fourier series
3
rd
Class
Electromechanical Eng.
Dr. Eng
Muhammad. A. R. Yass

3
Fourier series
Definition
The
series
1
2
cos
∞
sin
Si the Fourier series of
f
on ( -L , L ) when the constant are chosen to be the
Fourier coefficient of “
f
“on (-L , L)
Where
1
cos
–
0 , 1 , 2
And
1
sin
–
1 , 2 , 3
And
1
Example
Let f(x) = x for –π ≤ x ≤ π . we will write the Fourier series of “f” on [ -π , π]
. the coefficient are
1
0
1
cos
1
cos
sin
0
4
1
sin
1
sin
cos
0
2
cos
2
1
Since cos ( n ) = (-1)
n
if n is an integer . the fourier series of “x” on [ - , ] is
2
∞
1
sin
2 sin
sin 2
2
3
sin 3
1
2
sin 4
2
5
sin 5 …
Example
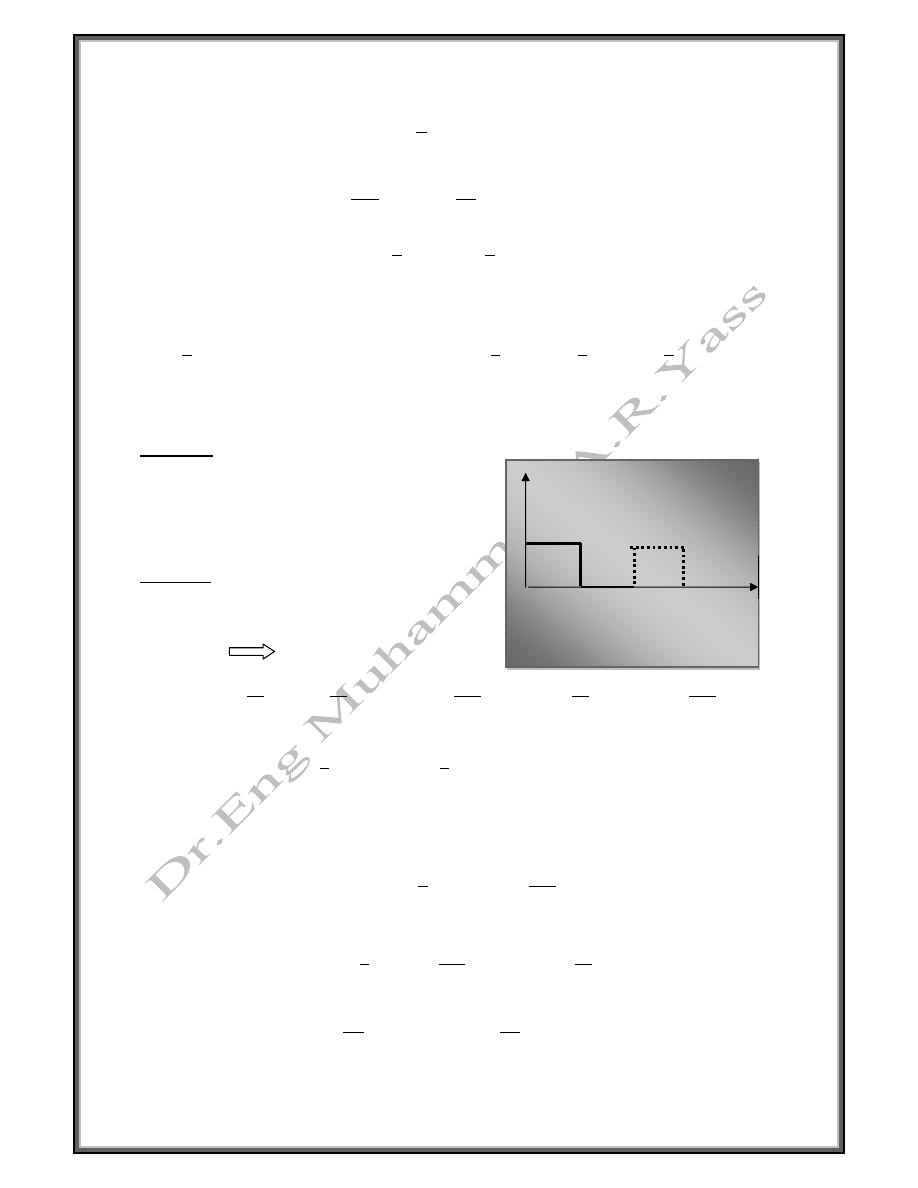
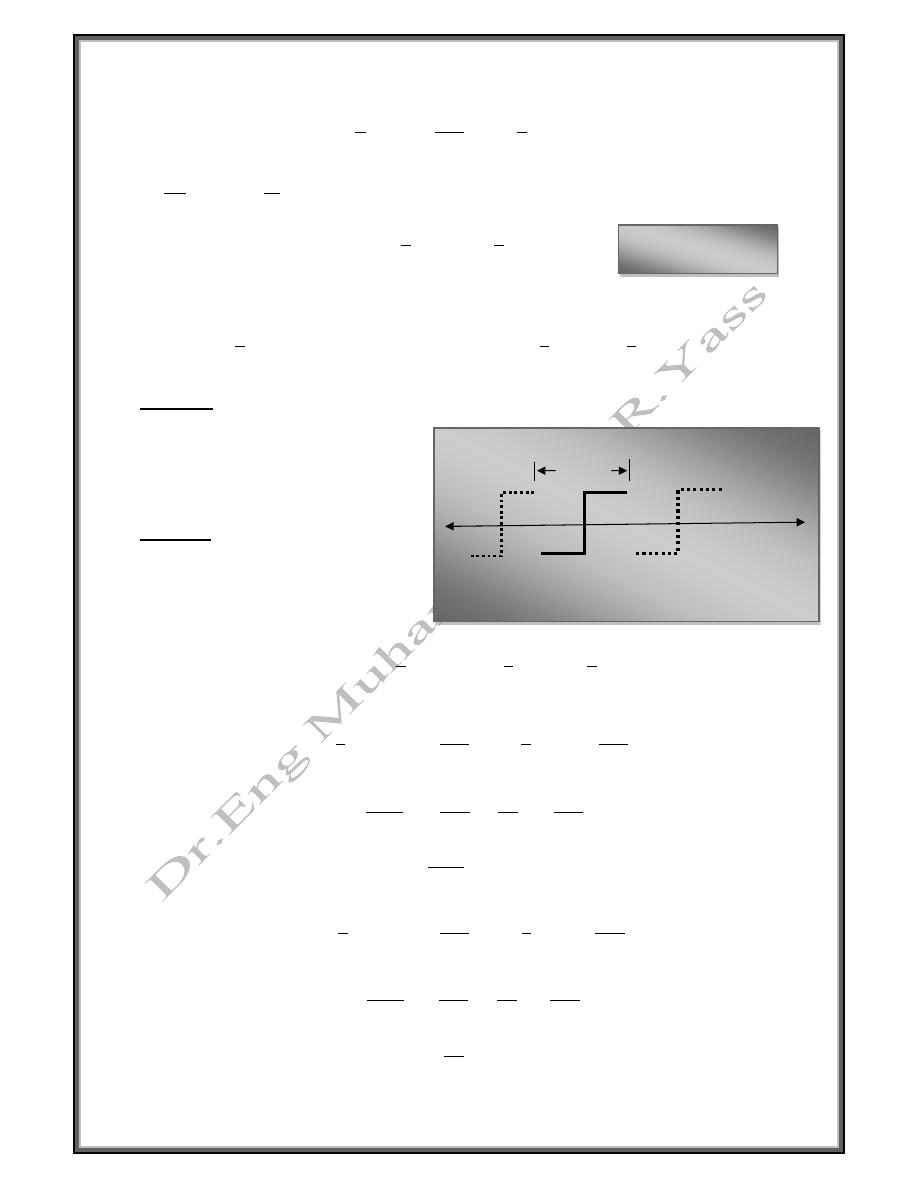
Find the fourier series of the periodic function
1 0
1
0 1
2
Solution
d = 0
2 p = 2 p = 1
2
cos
… …
cos
… … sin
… …
sin
1
1
1
1
0
| 1
1
1
cos
1
1
1 cos
0 cos
1
sin
| 0
1
sin
0
0
f(t)
1 2
1
t
5
0
1
sin
1
1 sin
0 sin
1
cos
|
1
cos
1
cos 0
1
1
cos
1
1
cos
2/
1
2
1
cos
0
1
3
1
2
2
3
1
4
1
4
0
The fourier series become
1
2
2
sin
0
2
3
sin 3
0
3
5
sin 5
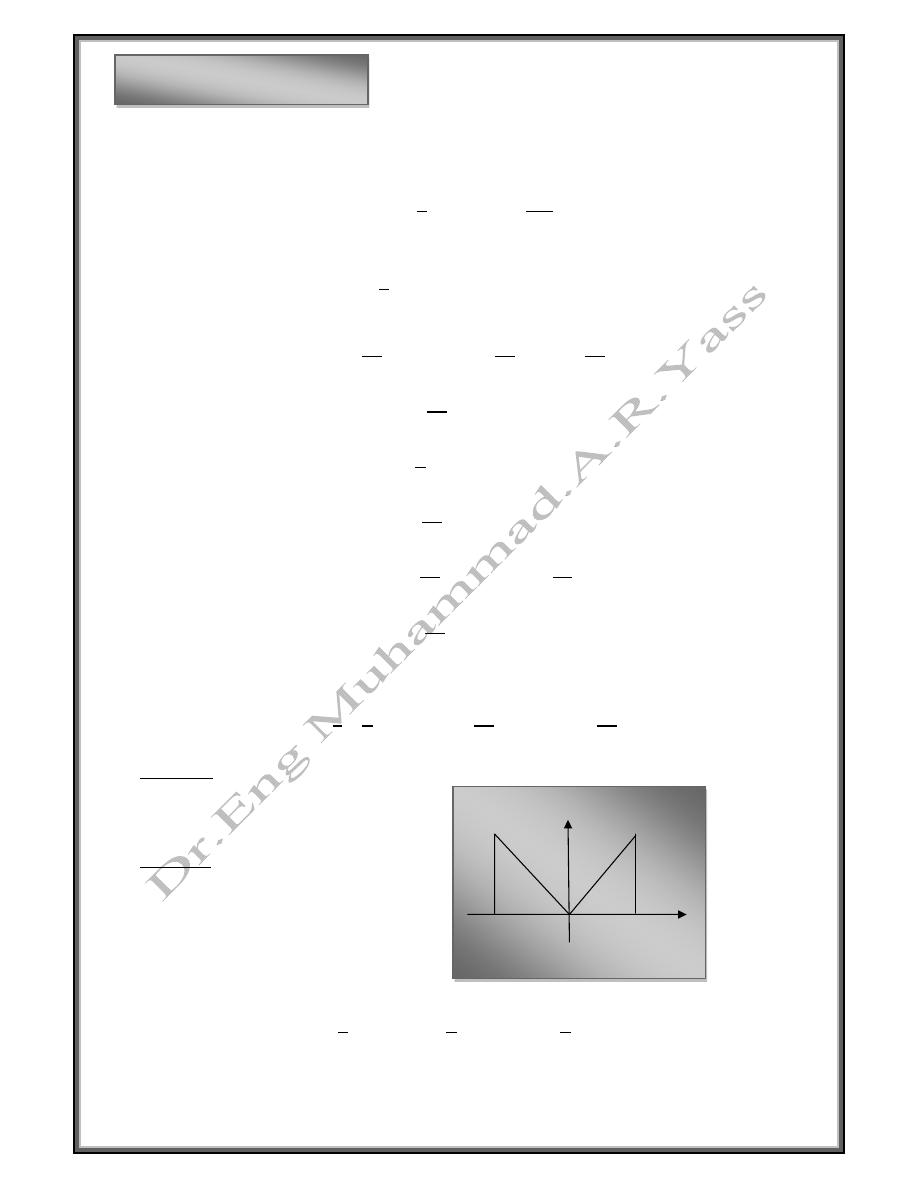
Example
0
0
Solution
d = -
d + 2p =
p =
1
1
1
Always sin (n ) = 0
f(t)
t
-
6
1
cos
–
1
–
cos
cos
Integral by partial we get
0 if n = even and
if n = odd
1
sin
1
sin
0
Fourier series will be
1
2
∞
cos
2
2
2
Example
Let f (x) = x for - ≤ x ≤
1
1
2
0
1
cos
1
cos
1
cos
sin
0
1
cos
1
cos
period
-
3
-3
7
1
sin
1
sin
sin
cos
2
cos
2
1
Fourier series will be
2
1
sin
∞
2 sin
sin 2
2
3
sin 3
1
2
sin 4
… …
Example
Let
0
3
0
0
3
Solution
L = 3
1
3
1
3
3
2
1
3
cos
3
1
3
3
3
cos
3
sin
3
3
1
1
1
3
sin
3
1
3
sin
3
3
sin
3
cos
3
3
1
cos
1
period
3
-3
6
-6
8
The Fourier series
3
4
3
∞
1
1 cos
3
3
1
sin
3
Example
Let
2
2 find fourier series
1
2
dx
1
8
1
2
cos
nπx
2
dx
8 1
64
1
2
sin
2
3
sin
3
cos
3
3
1
The Fourier series will be
3
4
3
1
1
∞
cos
3
3
1
sin
3
9
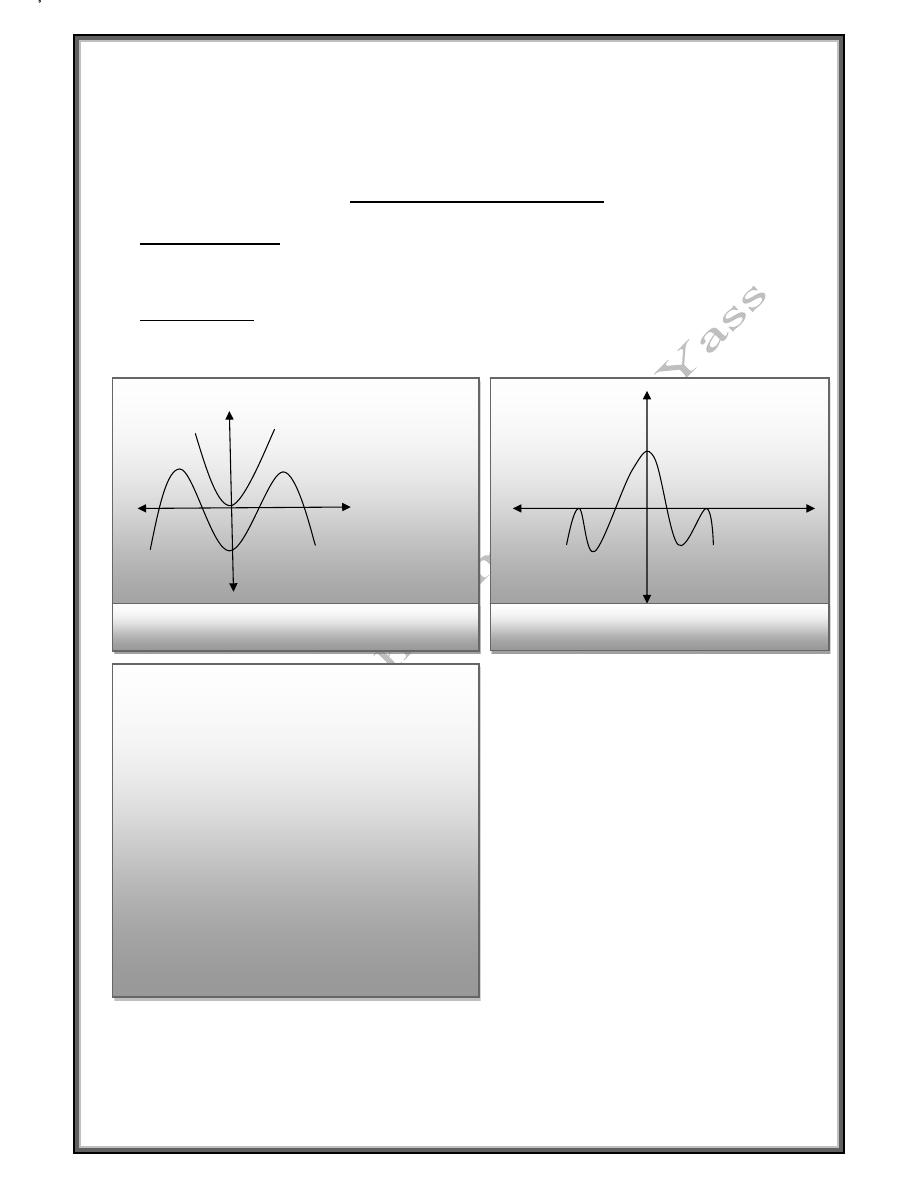
Even and odd function
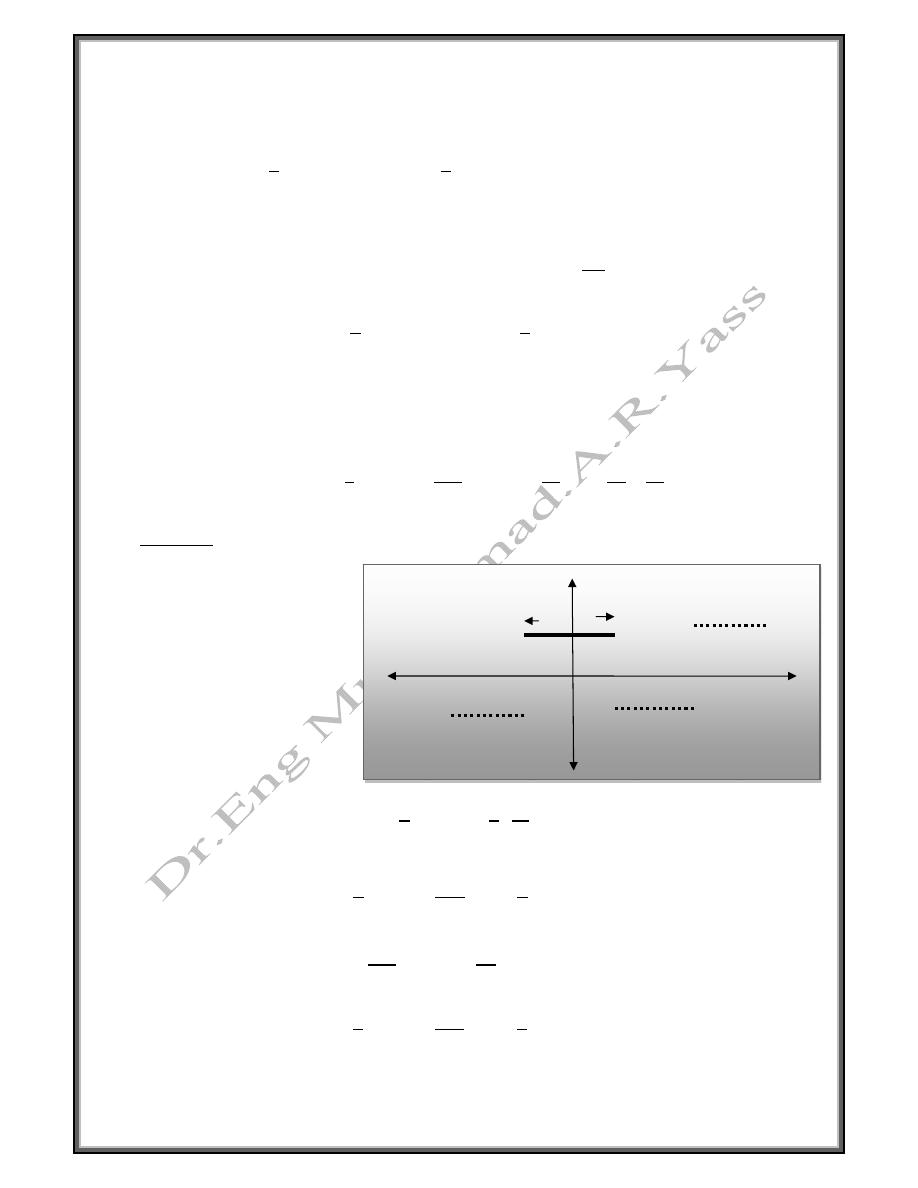
Even Function
f
is an even function on [-L , L ] if f(-x) = f(x) for -L ≤ x ≤ L
Odd Function
f
is an odd function on [-L , L] if f(-x) = - f (x) -L≤ x ≤ L
Fig(1) Even function
,
cos
-3
+3
-1
Fig (2) Even function symmetrical a bout y-axis
Fig (3) Odd function
,
sin
Fig (4) Odd function symmetric through
the origin
+2
-2
+4
-4
+3
-3 -1
+1
-2
+2
+4
-1

10
If the function is even then
/
/
2
/
While if is odd then
/
/
0
Also even function
2
2
cos
0
Then the function will be
2
cos
0
0
2
sin
sin
∞
Symmetric a bout the origin
11
Example
Find the fourier series of the function of the
2
1
0
1 0
2
Solution
Its an odd-function
0
0
2
sin
2
1 sin
2 sin
2
1
cos
2
cos
2
4
cos
2
cos
2
2
1
2 1
2
cos
2
2
∞
1
2 1
cos
2
sin
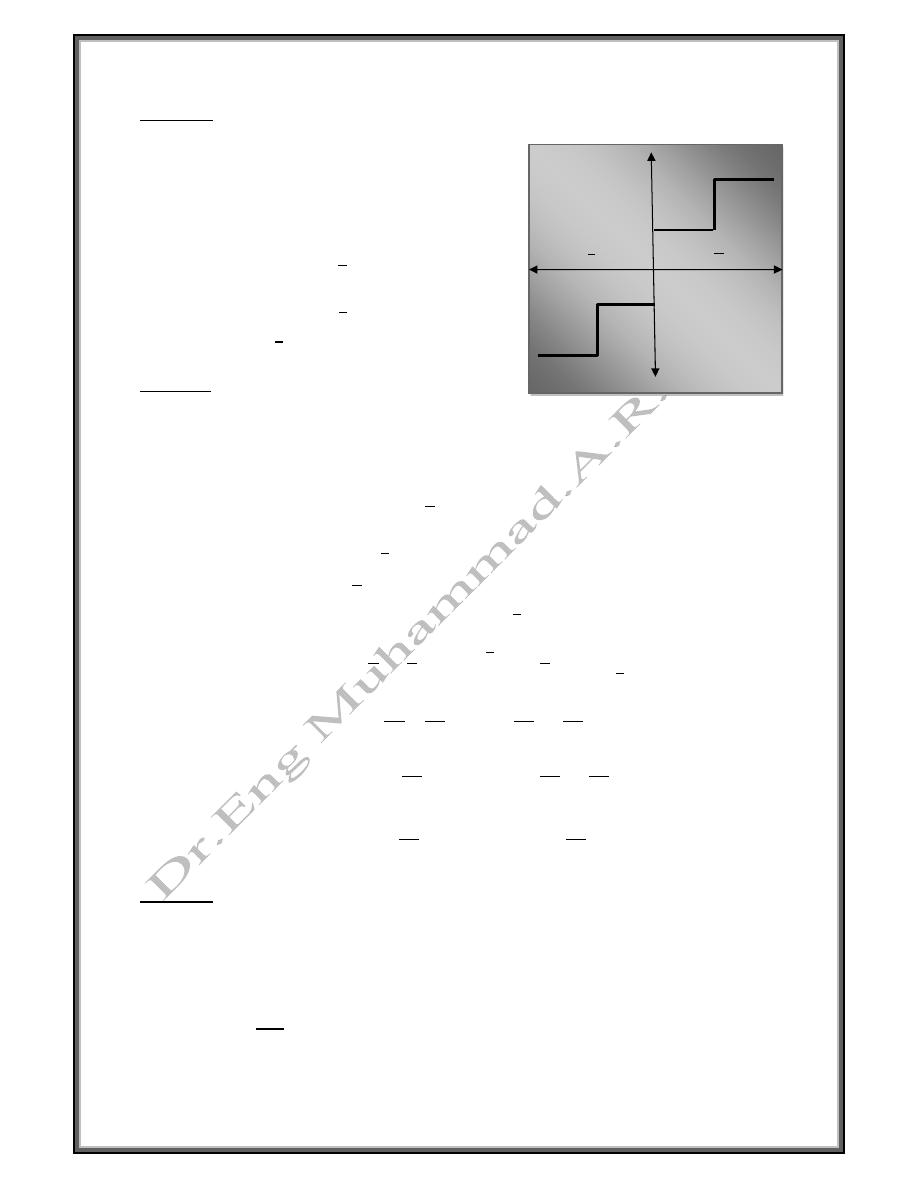
Example
Find fourier series of the function
0
0
The function is odd then
0 ;
0
-
-2
+2
2
-
+1
-1

12
sin
cos
1 1
0
∑
sin
∞
Example
Let
1,1 find Fourier series
Solution
is an even function because f(-x) = f (x) (
i.e.
example
f(-3) = f (3) on so on ) then
0
2
cos
2
cos
8
6
1
the Fourier series
1
5
8
∞
6
1 cos
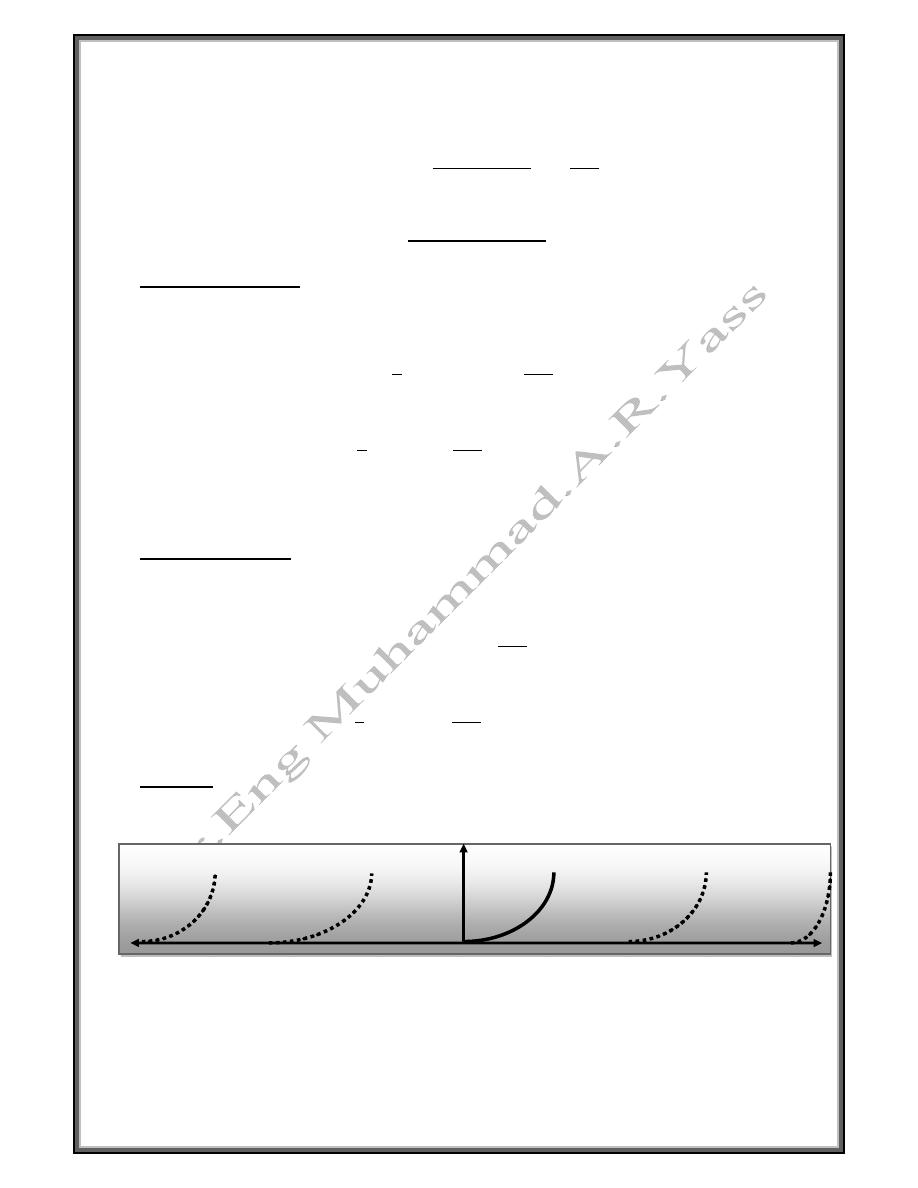
Example
4
4
Solution
0
1
4
sin
4
1
2
sin
4
1
128
6/
-
h
-h
0
13
The Fourier series will be
1
∞
128
6
sin
4
Conclusion
Even Function
Fourier series will be
1
2
∞
cos
2
cos
0 , 1 , 2
Odd Function
Fourier series will be
∞
sin
2
sin
1 , 2
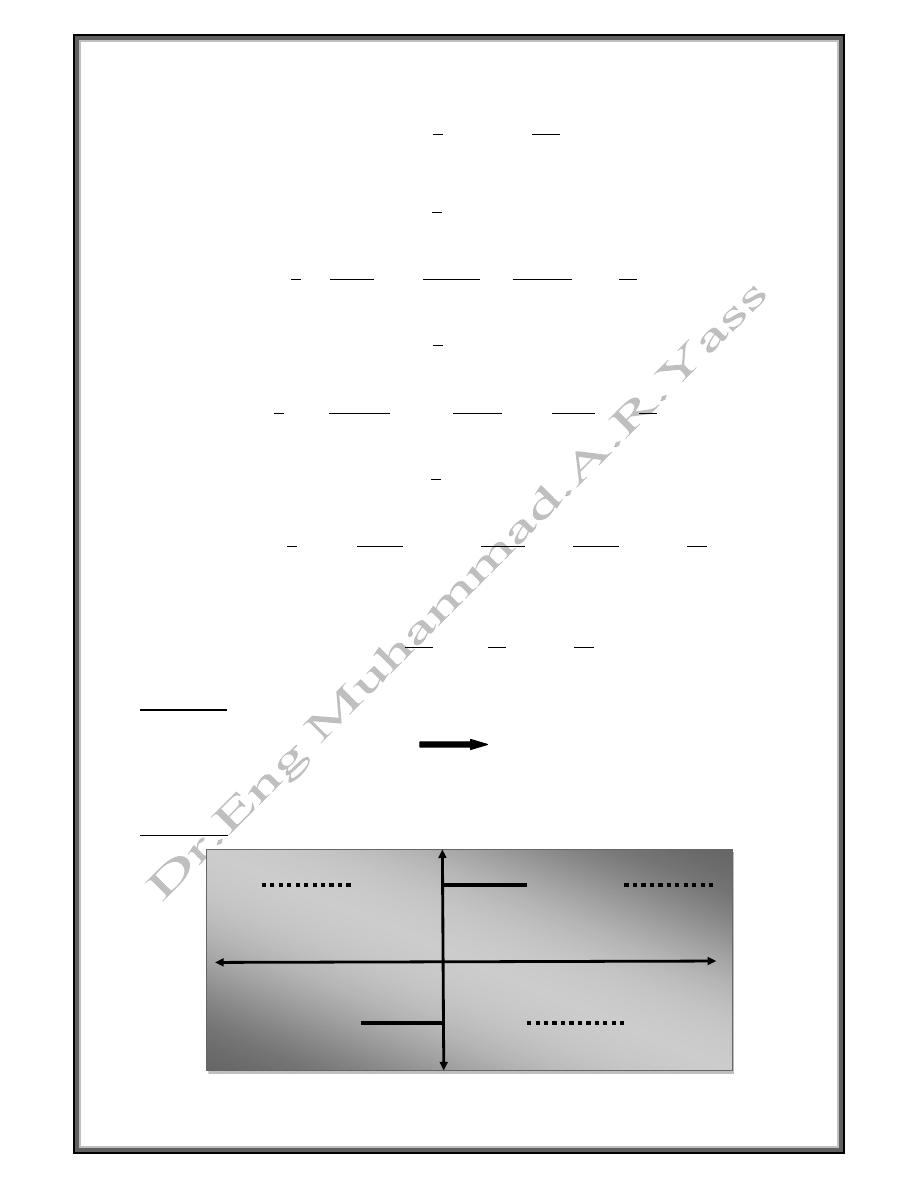
Example
Find the Fourier series if f(x) = x
2
0 < x < 2
Neither even nor odd
Period = 2L = 2 L =
0
2
-2
f(t)
4
4
14
1
8
3
1
cos
1
sin
2
– cos
2
sin
4
0
1
sin
1
cos
2
cos
2
sin
4
0
1
sin
1
cos
2
sin
2
cos
4
The Fourier series will be
4
3
4
∞
cos 4
4
sin
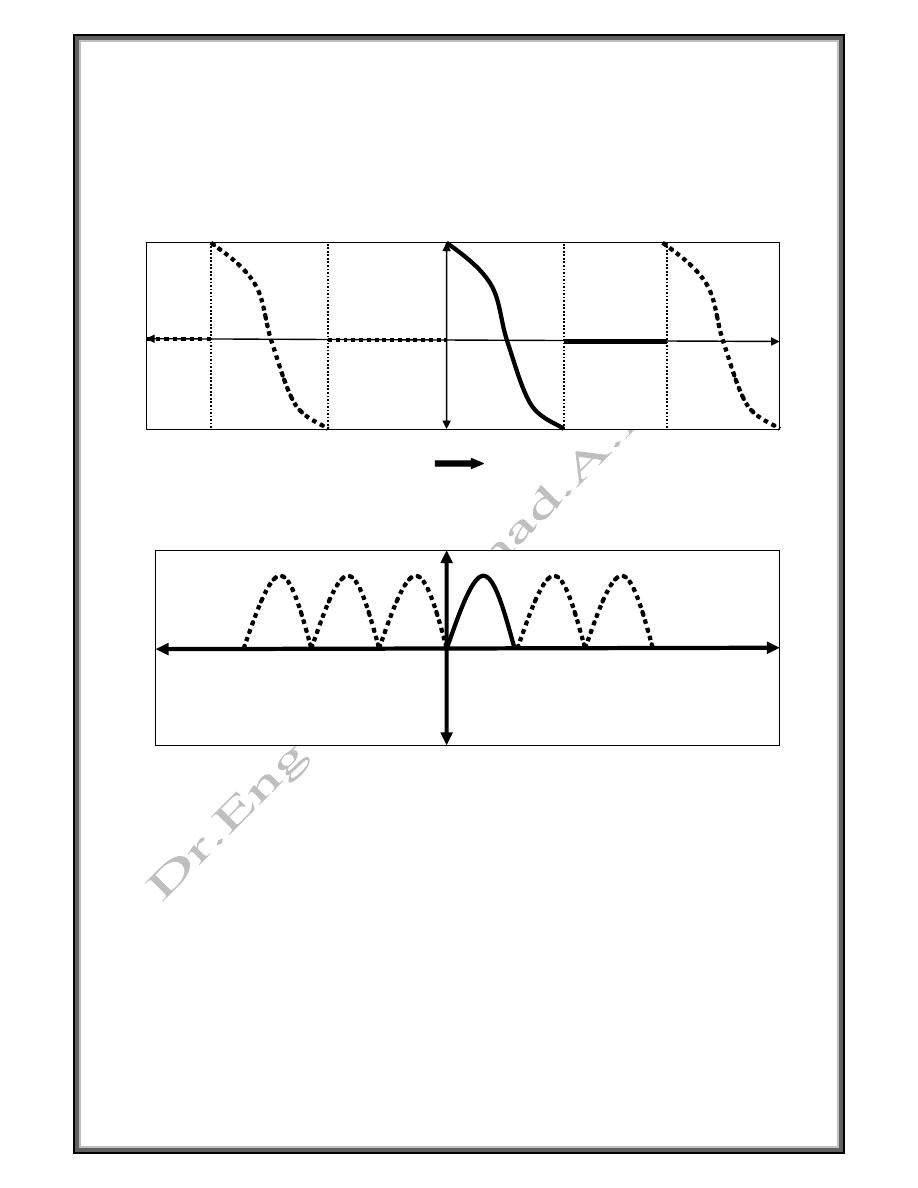
#Example
“a” odd f (-x) = - f (x)
2 0
3
2
3
0
-2
2
3 6
-3
-6
15
“b” Neither EVEN nor odd
0
0
2
2
“C” EVEN f (-x) = f (x)
10
0
10
10
0
1
-1
2
-
-2
0 5 10
-10
2.5

16
Half Range Expansions
Half range fourier series if function f (x) is defined only in the half fourier interval
(0 ) the equation of such function can be problem into other half of period (- 0)
infinite way .
a) An odd
b) An even
c) Neither odd nor even
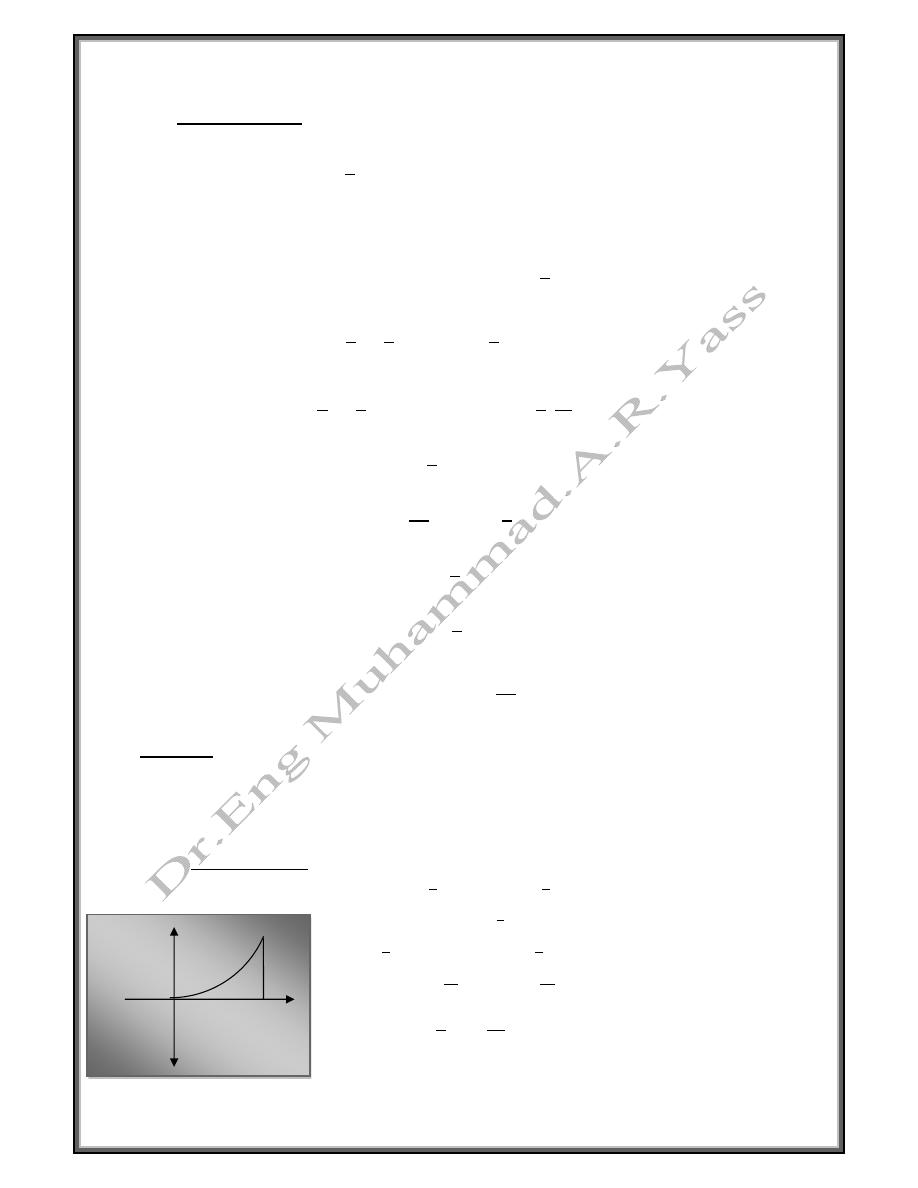
Example
Give f(x) = x in the interval 0
0 < x <
a) Find the Fourier series an a even function ( cos function)
b) Find the Fourier series an odd function (sin function)
a- Even function b
n
= 0
2
2
cos
U = x du = dx
dv = cos (nx) dx v = sin (nx)
2
sin
1
sin
2
sin
sin 0
1
cos
2
1
cos
cos 0
2
1
1
4
2
4
cos
∞
, ,
17
b – odd function
0
0
2
sin
sin
1
cos
2
cos
1
cos
0
2
cos
0 cos 0
2 1
2
cos
2
1
2
2
2
cos
2
cos
∞
sin
Example
Find the sine and the cosine half range series of the function series
0
a. Even function
cos
cos
cos
1
2
3
4
1
∞
cos
0
f(x)

18
b. Odd function
Solved Examples
The formula for a Fourier series on an interval [c,c+T] is:
Example (1)
Find the Fourier series for
,
.
Following the rules from the link above,
.

19
.
So,
Example (2)
Find the Fourier series for .
FOURIER SERIES BOOKS

20
Example (3)
Find the Fourier series for
on
The general Fourier series on
is:
The
n
= 0 case is not needed since the integrand in the formula for is
.
In the present problem,
But since the right hand side is not defined if
n
= 0, the 0 index for
a
will have to be
calculated seperately.
So the Fourier series is
for
21
Example (4) Find the Fourier series for
on
The general Fourier series on
is:
In the present problem,

22
So the Fourier series is:
Setting
x
= 0 gives
Example (5) Find the Fourier series for
on
So the Fourier series is:

23
Example (6) Find the Fourier series for
on
The general Fourier series on
is:
In the present problem,
So the Fourier series is:
on
Example (7) Find the Fourier series for a function
on .
Make the change of variables
.
Now, look for the Fourier series of the function
on

24
Since ,
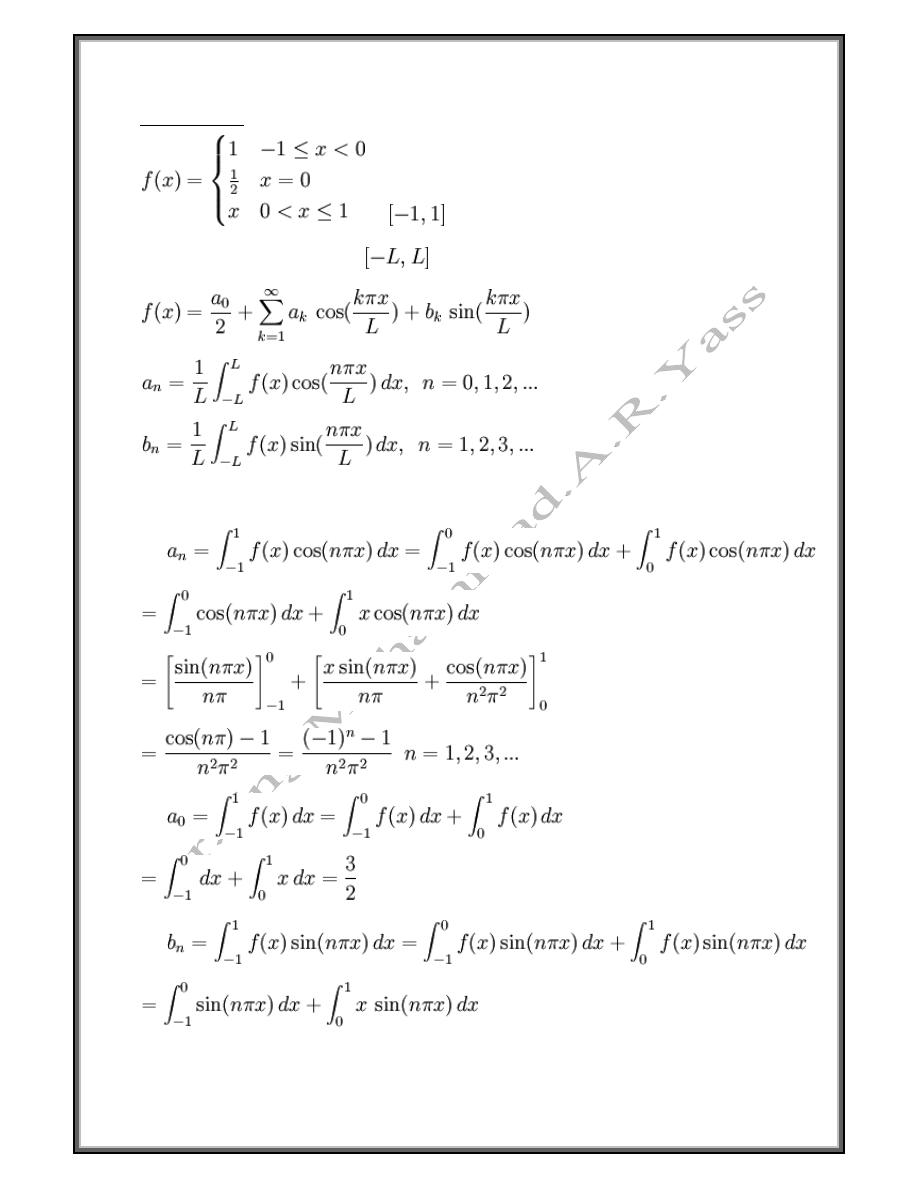
Example (8)
Find the Fourier series for
on
.
A general formula for the Fourier series of a function on an interval
is:
In the current problem,
and
.
The function
is odd, so the cosine coefficients will all equal zero.
Nevertheless,
should still be calculated separately.

25
So the Fourier series for
is
Example (9) Find the Fourier series for
This is the general Fourier Series:
So the given function can be replaced by its Fourier expansion:

26
So the solution is

27
Home Work
Problem (1) Find the Fourier series of the function
Answer.
Problem (2) . Find the Fourier series of the function
Answer. We have
Therefore, the Fourier series of f(x) is
Problem
(3
) Find the Fourier series of
Answer.
