1
Community Dr.Suhyla
THE PRE-TRAVEL CONSULTATION
Outline:
Travelers’ Health Epidemiology
Traveler Assessment
Itinerary Review
Sources of Information
Risks to the Traveler
Travel Vaccines
Travel Medications
Counseling
International Travel
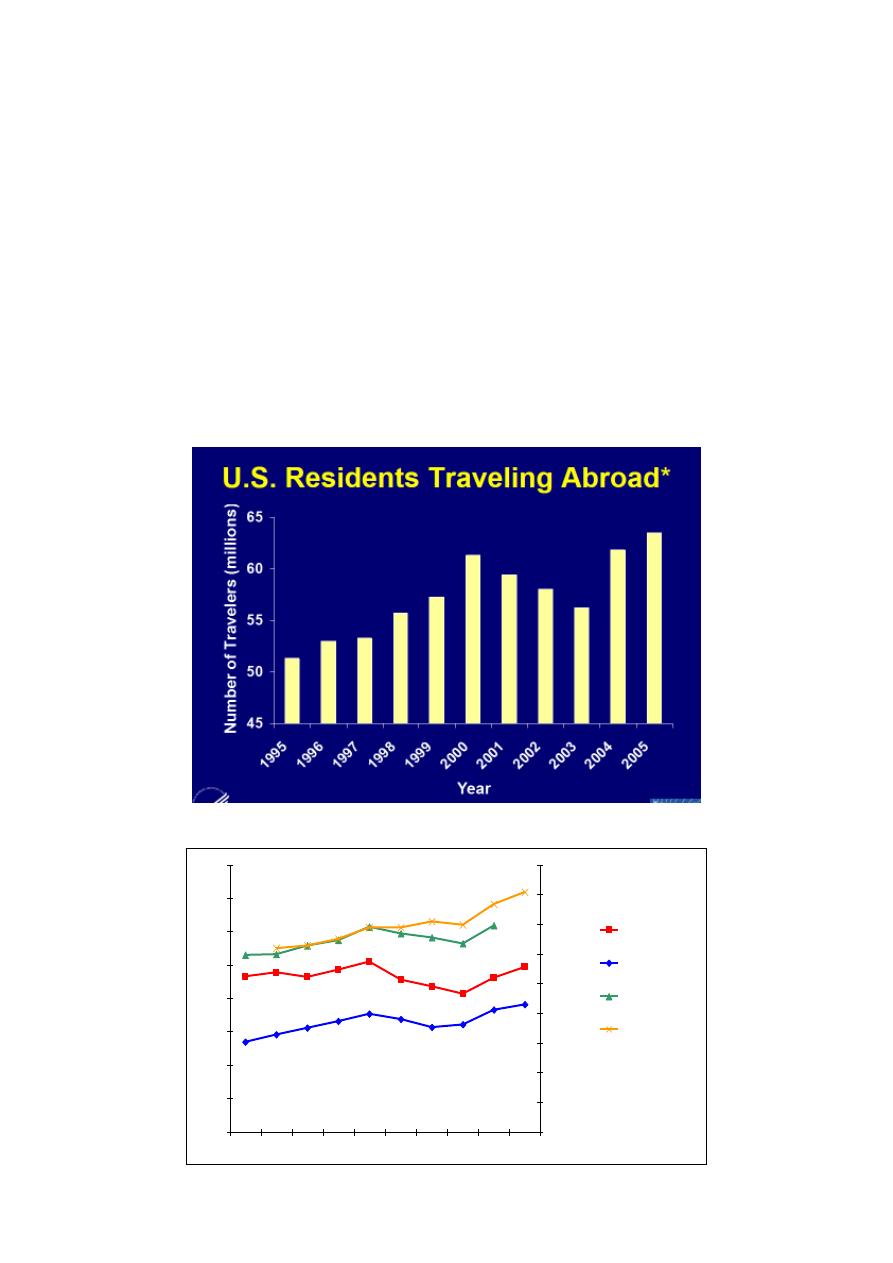
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
1996 1997 1998 1999 2000
2001 2002 2003 2004 2005
U
S
R
e
s
id
e
n
t
tr
a
v
e
l
in
m
il
li
o
n
s
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
W
o
rl
d
w
id
e
a
rr
iv
a
ls
i
n
m
il
li
o
n
s
US nonresident
Inbound (ITA)
US Resident Air
Outbound (ITA)
All US Resident
Outbound (ITA)
Worldwide arrivals
(WTO)
2
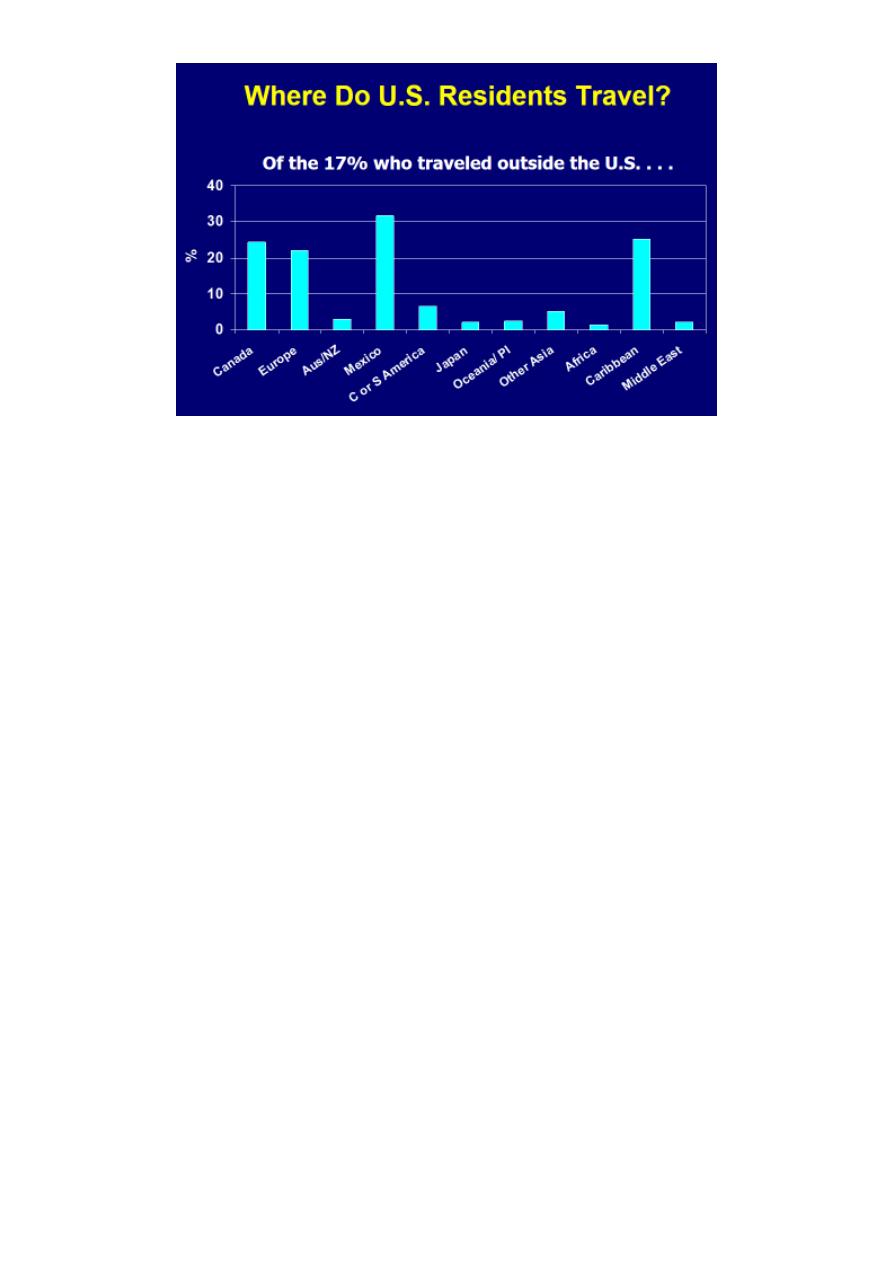
VFRs: Visiting Friends and Relatives:
• Foreign-born increased 57% since 1990 from 19.8 million to 31.1 million
1
• 20% of US population are first- or second-generation immigrants
• VFRs comprised ~46% of US international air travelers in 2004
3
1
US Census Bureau, Census 2000 Brief, The Foreign-Born Population: 2000, issued
Dec 2003 (Previous: US Census Bureau, Profile of the Born Outside the United States
Population 2000, issues Dec 2003???
2
Angell & Cetron, 2005
3
2004 Profile of U. S. Resident Travelers Visiting Overseas Destinations Reported
From: Survey of International Air Travelers, Office of travel and tourism Industries,
USDOC
Travelers’ Health Risks:
Of 100,000 travelers to a developing country for 1 month:
– 50,000 will develop some health problem
– 8,000 will see a physician
– 5,000 will be confined to bed
– 1,100 will be incapacitated in their work
– 300 will be admitted to hospital
– 50 will be air evacuated
– 1 will die

3
The Patient: Medical Issues:
1. Age-specific issues
2. Underlying illness, immunosuppression
3. Systems review
4. Medical history
5. Medication use
6. Vaccination history
7. Allergies
8. Contraindications to vaccines and medications
The Patient: Other Issues:
Reproductive
– Pregnant
– Breastfeeding
– Preconception
Risk-taking behaviors
Travel Itinerary:
Full itinerary
– Dates, duration, stopovers
– Seasonal considerations
Styles of travel
– Rural vs. urban
– Budget vs. luxury
Accommodation: Hotel vs. camping
Activities
– Business vs. tourism
– Adventure, safari
– Missionary/Humanitarian/NGO
Travel Health Resources:
• CDC Travelers’ Health Website
• International Society of Travel Medicine
• Health Information for International Travel CDC “Yellow Book”
• International Travel and Health WHO “Green Book”
4
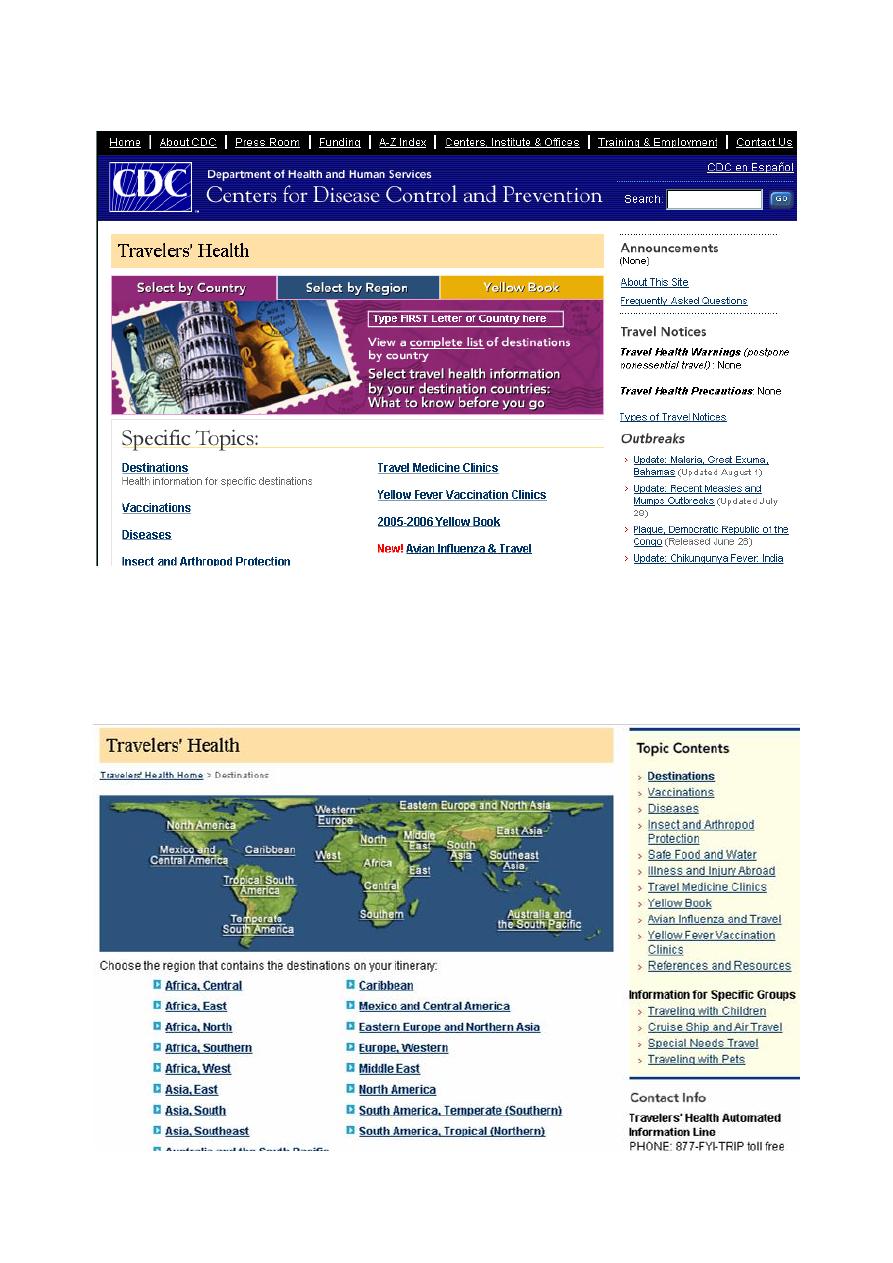
Travelers’ Health Website
www.cdc.gov/travel
Regional Destinations:
• Region-specific pages
• Goal to move to country-specific format

5
Travel Notices & Announcements:
6
Infectious Disease Risks to the Traveler:
1. Malaria
2. Diarrhea
3. Leishmaniasis
4. Rabies
5. Dengue
6. Meningococcal Meningitis
7. Schistosomiasis
8. Tuberculosis
9. Leptospirosis
10. Polio
11. Yellow Fever
12. Measles
13. JEV
Other Risks to the Traveler:
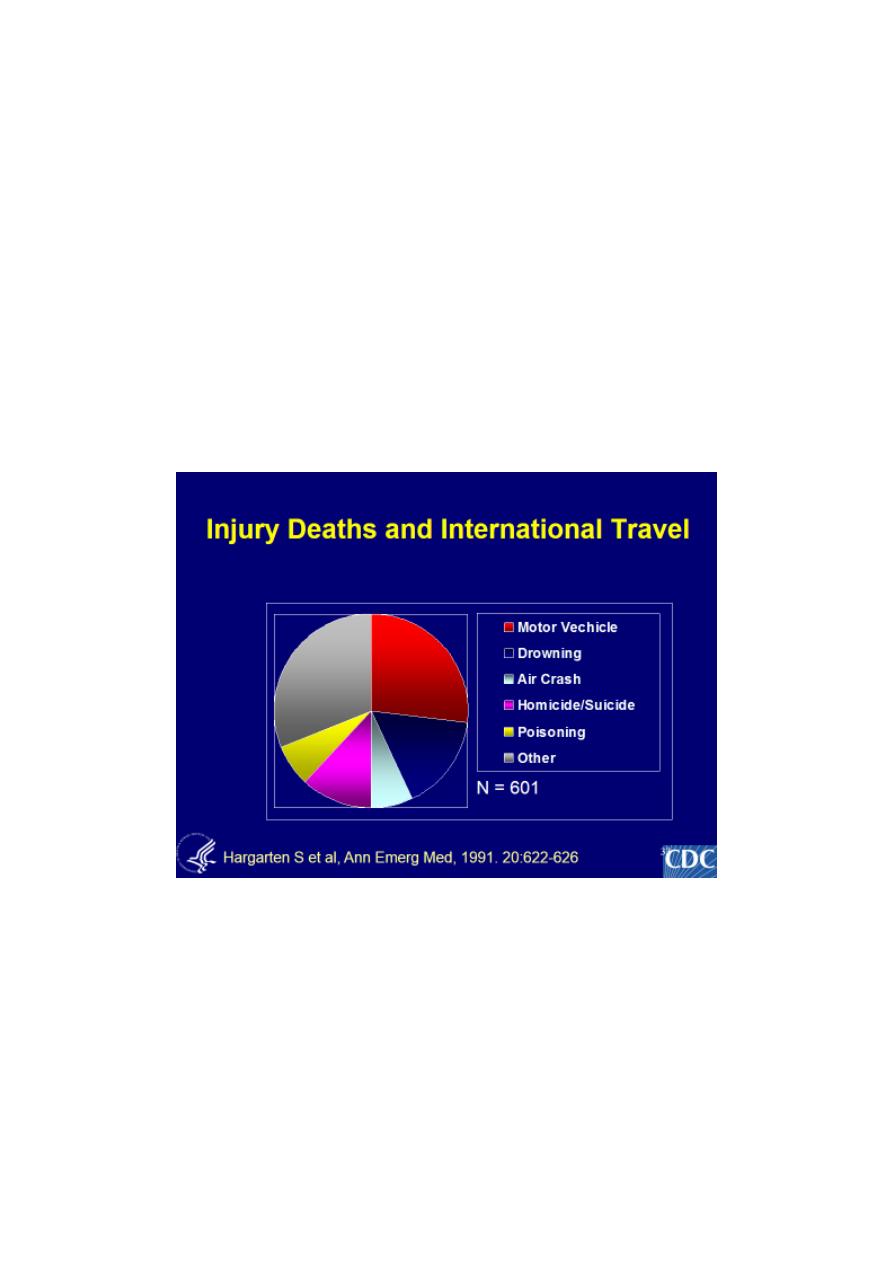
1) Accidental injury
2) Environmental hazards
3) Crime and assault
4) Psychiatric problems
5) Animal bites, stings and envenomations
6) Dermatologic disorders
7) Altitude

7
Immunizations to Consider for Adult Travelers:
Routine
1. Diphtheria*
2. Tetanus*
3. Pertussis*
4. Measles +
5. Mumps+
6. Rubella +
7. Varicella
8. Pneumococcus
9. Influenza
Travel related
1) Hepatitis A
2) Hepatitis B
3) Typhoid
4) Rabies
5) Meningococcal disease
6) Polio
7) Japanese encephalitis
8) Yellow Fever
Travel Medications: Prophylaxis & Self Treatment
Malaria: chloroquine, atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone), doxycycline, mefloquine
(Lariam), primaquine
Diarrhea: quinolone, azithromycin
Altitude: acetazolamide
Motion sickness: scopolamine, dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
Patient Counseling:
Sufficient time for patient education
Tailored to suit traveler
Fitness for travel
– Understanding impact on existing conditions
– Advisability of destinations
*Td or Tdap
+ MMR

8
Travel Preparation:
a. Travel health insurance
- Medical care
- Hospitalization
- Evacuation
b. Obtaining medical care abroad
c. Awareness of travel notices
d. Hand washing and hygiene
Environmental Precautions:
Air Travel
Jet Lag
Sun Protection
Extreme Heat and Cold
– dehydration, heat stroke
– hypothermia, frostbite
Altitude
Water recreation
– Drowning, boating & diving accidents
– Risk of schistosomiasis or leptospirosis
– Biological and chemical contamination
Food and Water Precautions:
Bottled water
Selection of foods: well-cooked and hot
Avoidance of
a. salads, raw vegetables
b. unpasteurized dairy products
c. street vendors
d. ice
Vector Precautions:
1. Covering exposed skin
2. Insect repellent containing DEET 25 – 50%
3. Treatment of outer clothing with permethrin
4. Use of permethrin-impregnated bed net
5. Use of insect screens over open windows
6. Air conditioned rooms

9
7. Use of aerosol insecticide indoors
8. Use of pyrethroid coils outdoors
9. Inspection for ticks
Blood borne and STD Precautions:
Z Prevalence of
– STDs
– Hepatitis B
– Hepatitis C
– HIV
Z Unprotected sexual activity
Z Commercial sex workers
Z Tattooing and body piercing
Z Auto accidents
Z Blood products
Z Dental and surgical procedures
Animal Precautions:
b Animal avoidance
b Rabies
– Specific animal threats
– Medical evaluation of bites/scratches
– Post exposure immunization and immunoglobulin
b Envenomations
– Snakes, scorpions, spiders
– Maritime animals
Injury and Crime:
Vehicles
– Risk of road and pedestrian accidents
– Night travel
– Seat belts and car seats
Use of drugs and alcohol
Understanding local crime risks
– Scam awareness
– Situational awareness
– Location avoidance

11
Travel Emergency Kit:
` Copy of medical records and extra pair of glasses
` Prescription medications
` Over-the counter medicines and supplies
– Analgesics
– Decongestant, cold medicine, cough suppressant
– Antibiotic/antifungal/hydrocortisone creams
– Pepto-Bismol tablets, antacid
– Band-Aids, gauze bandages, tape, Ace wraps
– Insect repellant, sunscreen, lip balm
– Tweezers, scissors, thermometer
Post-Travel Care:
3 Post-travel checkup
o Long term travelers
o Adventure travelers
o Expatriates in developing world
3 Post-travel care
Fever, chills, sweats
Persistent diarrhea
Weight loss
