
Dr.Mohammed Jasim
1
Dr.Mohammed Jasim
2
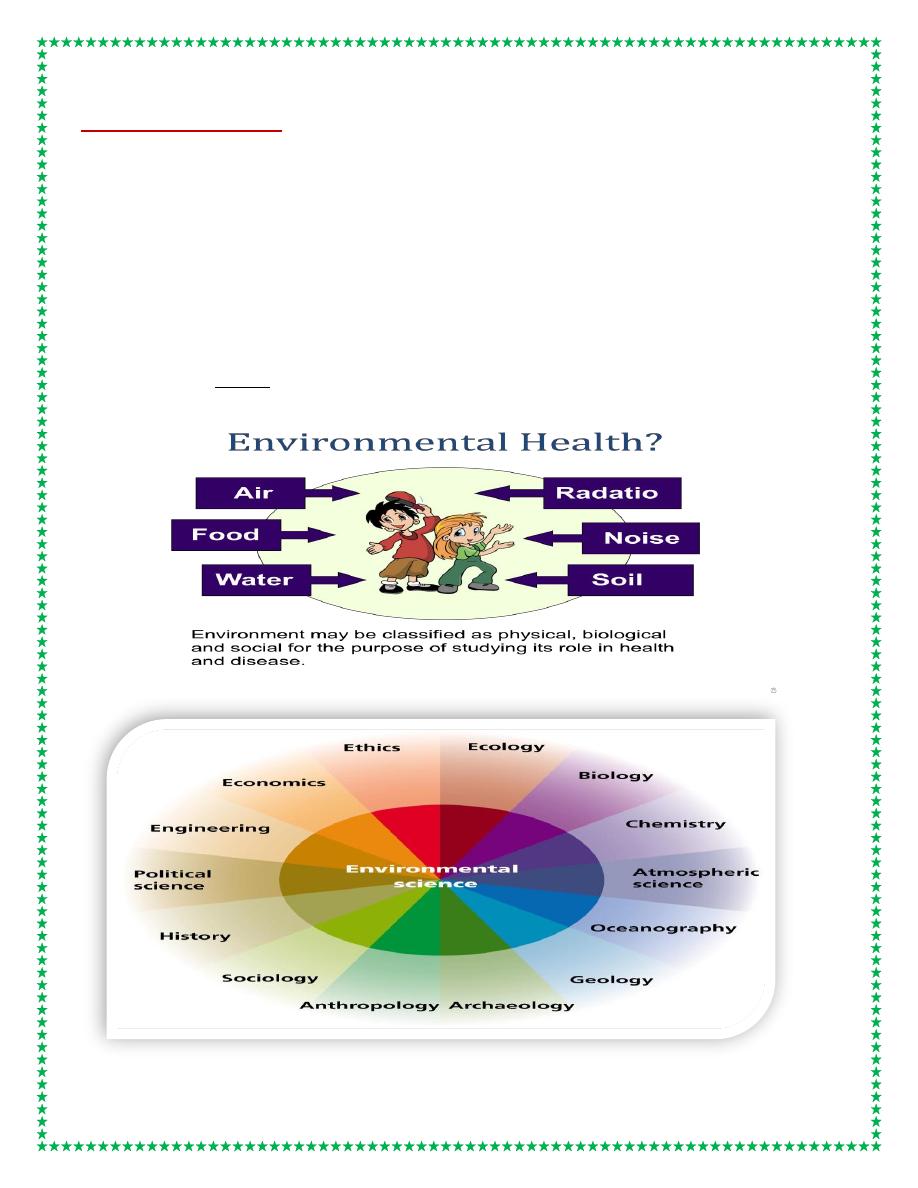
Environmental Health?
The word ‘environment’ is derived from an French word
‘environ’
meaning ‘encircle’.
According to WHO,
Environmental sanitation means
“The control of all those factors in man’s environment which exercise or may exercise
a deleterious effect on his physical development, health and survival”.
• Environmental health is the study of how the environment affects human health
An environmental scientist might study how water pollution is hurting fish. An
environmental health scientist would study what happens to the health of people
when they catch and eat those fish.
Dr.Mohammed Jasim
3
Physical environment
• Air
• Water
• Soil and housing
• Place of work, (occupational health)
• Wastes such as refuse and human excreta
• Food
Air
1. PHYSICAL AGENTS
• Temperature
• Humidity
• Wind velocity
• Pressure of atmospheric air.
2. CHEMICAL AGENTS
Dust, soot, smoke, other organic and inorganic particles
emanating from houses, factories and vehicles, etc.
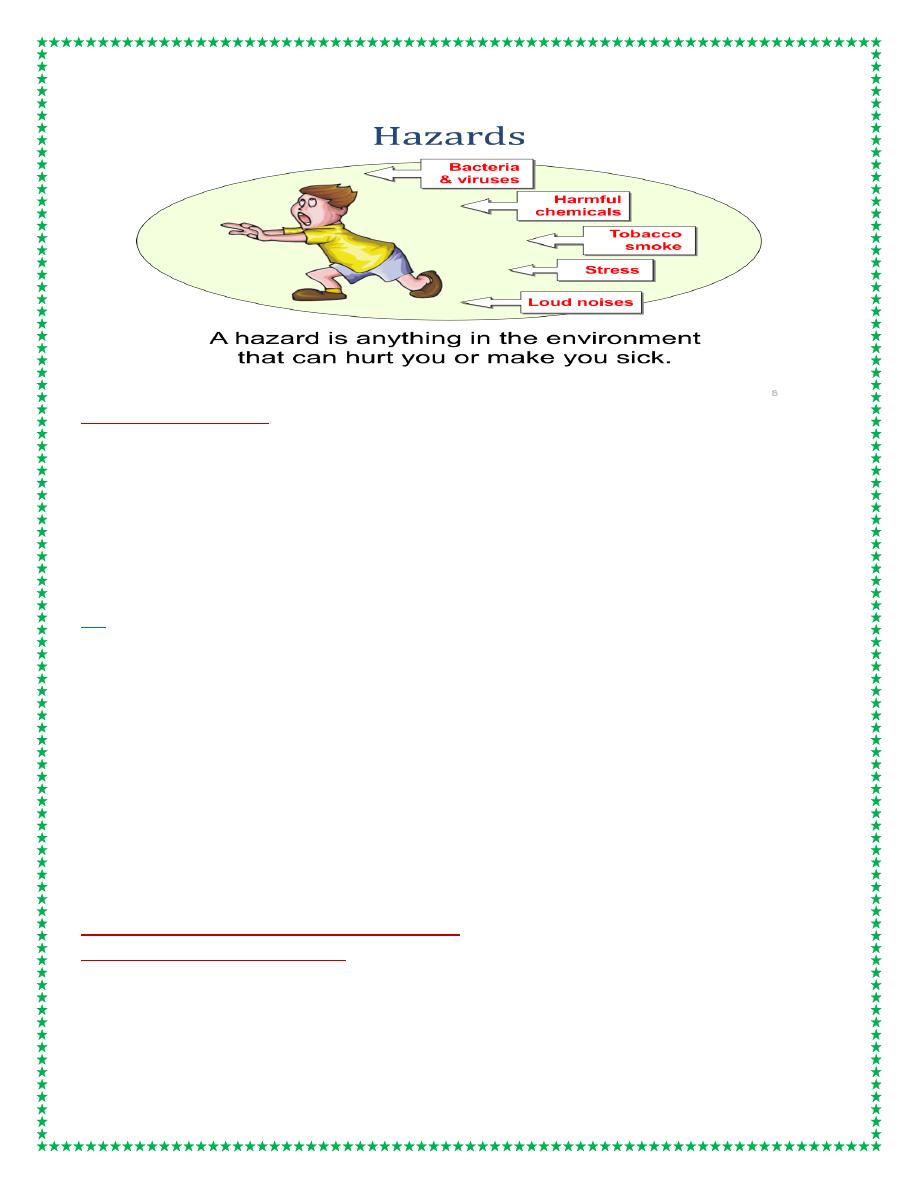
3. BIOLOGICAL AGENTS
Bacteria and viruses, etc
Factors Affecting Atmospheric Environment
METEOROLOGICAL VARIABLES
• Degree of sunshine
• Atmospheric pressure
• Humidity
• Rainfall

Dr.Mohammed Jasim
4
• Velocity and direction of wind
• Air temperature.
Effects of Air Pollution on Health
• Conjunctivitis, dermatitis, chronic bronchitis and lung
cancer are due to irritants and carcinogens due to smoke
• Smoke cuts off ultraviolet light, (sterilization of air by killing microorganisms).
• Dusts cause pneumoconiosis.
• Pollutants, particularly smoke, adversely affect plant
and animal life and damage property.
Effect on human health مهم
1. Local effect
2. General effect
Local Effects
• These include darkening of skin.
• prickly heat.
• sunburn.
• dermatitis.
General Effects
1. Heatstroke
2. Heat exhaustion
3. Heat cramps
4. Cold weather
5. High humidity
Heatstroke:
It is characterized by hyperpyrexia
(42–44) along with giddiness, anorexia and frequency of micturition followed by
unconsciousness.
There is sudden cessation of sweating, this leads to failure of heat regulating
mechanism.
Mortality is more in young children and old people, especially if they are ill-nourished.

Dr.Mohammed Jasim
5
Heat exhaustion:
It is due to profuse sweating chloride
The fluid loss may be as high as 1 liter per hour, especially if there is muscular
exercise. Body temperature, may be subnormal. Blood pressure is low and pulse is
fast. The patient feels faint, weak and, dizzy and lethargic
Heatcramps:
• Due to excessive loss of salts in the sweat,
• there is increased muscular irritability. Painful spasms of skeletal and abdominal
muscles may develop.
•
LOW TEMPERATURE OR COLD CLIMATE
Frostbite occurs when the tissues are actually frozen on exposure to temperature
below 0°C. Immersion foot
or trench foot occurs when feet are immersed in cold water or snow.
High humidity and wind velocity,
Fatigue and anoxia at high altitude worsen the situation.
HUMIDITY مهم
It makes the warm climate warmer and cold climate colder.
In warm climate, heat loss from the skin is prevented because humid air cannot dry off
much sweat or moisture from the skin.
In cold climate the moist air, being a better conductor than dry air (water is 23 times
better conductor of heat than air), causes more heat loss from the body.
Assessment of Air Pollution
Common indices in use are:
• DUSTFALL
• SUSPENDED PARTICLES
• SMOKE INDEX
• SULFUR DIOXIDE
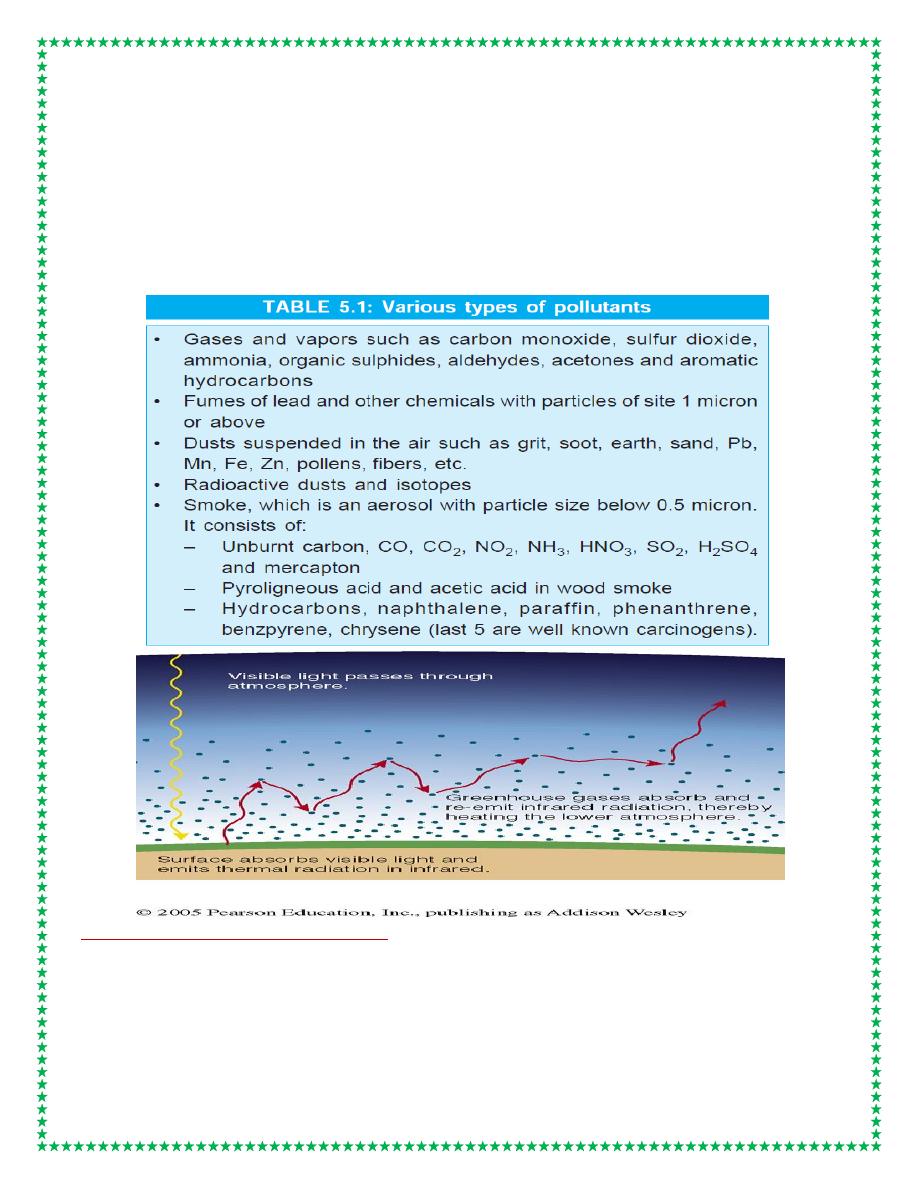
Global Warming
• Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of near surface of
Earth
Dr.Mohammed Jasim
6
DIFFERENT GREEN HOUSE GASES
1. Water vapor
2. Carbon dioxide (CO2)
3. Methane (CH4)
4. Nitrous oxide (N2O)
5. Ozone (O3)
6. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Prevention and Control of Pollution
The WHO9 has listed the following five general principles
to control of pollution:
1.
Containment
: Preventing the pollutants from escaping into air from the source of
production.

Dr.Mohammed Jasim
7
2.
Replacement
: Changing the existing techniques to those producing less amount of
pollutants.
3.
Dilution
: Diluting the concentration of pollutants in the air to such a level that they
can be removed by natural means, such as foliage.
4.
Legislation
: Enacting suitable laws aimed at prevention of pollution.
5.
International action
: The WHO has established two international pollution
monitoring centers at Washington and London, three regional centers at Tokyo,
Moscow and Nagpur and 20 laborat
