Relative and Attributable Risks
Absolute RiskInvolves people who contract disease due to an exposure
Doesn’t consider those who are sick but haven’t been exposed
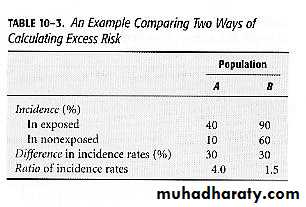
Calculating Excess Risk
Relative Risk
Definition:A measure of the strength of association based on prospective studies (cohort studies).
Determining Relative Risk
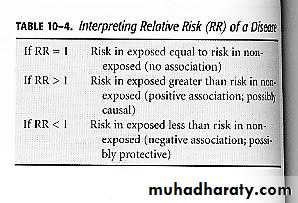
Interpreting Relative Risk
Relative Risk Calculations
Relative Risk Calculations (cont.)Relative Risk in Case-Control Studies
Can’t derive incidence from case-control studiesBegin with diseased people (cases) and non-diseased people (controls)
Therefore, can’t calculate relative risk directly
But, we can use another method called an odds ratio
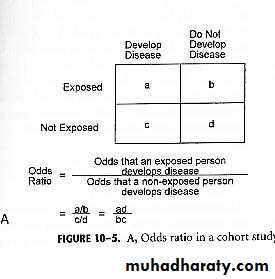
Odds Ratio in Prospective (Cohort) Studies
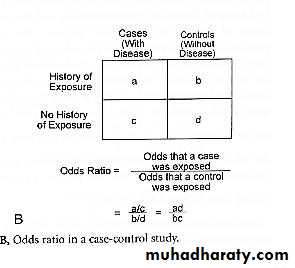
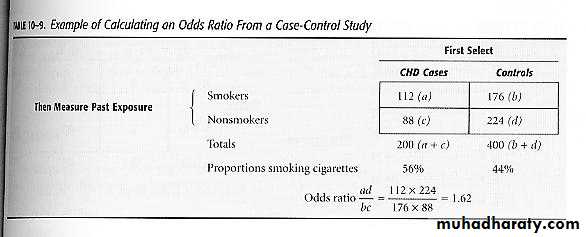
Odds Ratio in Case-Control Studies
Odds Ratio in Case-Control Studies (cont.)
When is the Odds Ratio a Good Estimate of Relative Risk?When cases are representative of diseased population
When controls are representative of population without disease
When the disease being studied occurs at low frequency
REMEMBER !!!
An odds ratio is a useful measure of associationIn a cohort study, the relative risk can be calculated directly
In a case-control study the relative risk cannot be calculated directly, so an odds ratio is used instead
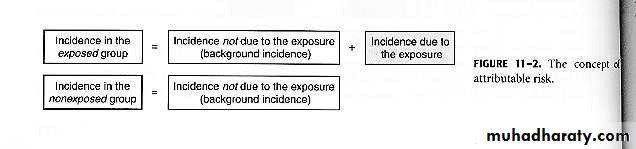
Attributable Risk
Definition:The amount of disease that can be attributed to a certain exposure.
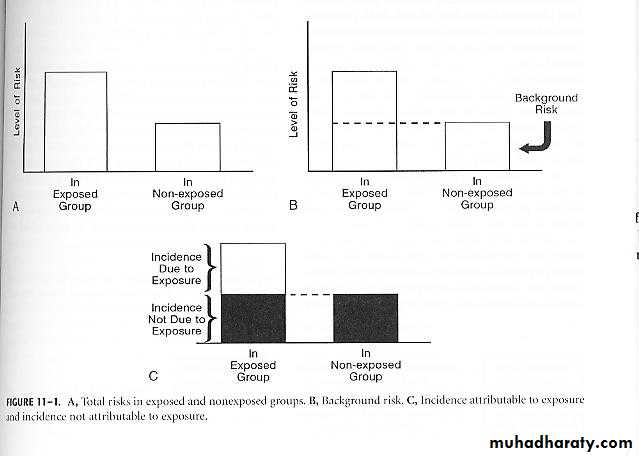
Concept of Attributable Risk
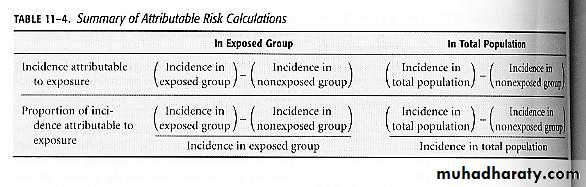
Attributable Risk for an Exposed Group
OR, expressed as a proportion:
Attributable Risk for an Exposed Group (cont.)From previous relative risk example:
Calculation for Proportional Incidence in Total Population
First calculate A-R for group from
Formulas 11.1 & 11.2 (previous slide),
then use Formula 11.3
For proportion of the incidence in the
total population, use Formula 11.4
Calculations for Attributable Risks (cont.)
Summary
Relative risk and odds ratio are important as measures of the strength of associationImportant for deriving causal inference
Attributable risk is a measure of how much disease risk is attributed to a certain exposure
Useful in determining how much disease can be prevented
Therefore:
Relative risk is valuable in etiologic studies of disease
Attributable risk is useful for Public Health guidelines and planning