-
1
-
Antenatal care
dr: ayoub
community
Introduction:
Every year there are an estimated 200 million pregnancies in the world. Each of these
pregnancies is at risk for an adverse outcome for the woman and her infant. While risk can not be
totally eliminated, they can be reduced through effective, affordable, and acceptable maternity
care. To be most effective, health care should begin early in pregnancy and continue at regular
intervals
Outlines
:
•
Goals of antenatal care.
•
Signs of pregnancy.
•
Physical changes during pregnancy.
•
Assessment and physical examination.
☺ history.
☺ Physical assessment.
☺ Laboratory data.
☺ Ultrasound.
•
Managing the minor disorders of pregnancy.
•
Health teaching during pregnancy.
Goals of antenatal care:
•
To reduce maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity rates.
•
To improve the physical and mental health of women and children.
•
To prepare the woman for labor, lactation, and care of her infant.
•
To detect early and treat properly complicated conditions that could endanger the life or
impair the health of the mother or the fetus.
Signs of pregnancy:
•
)signs of pregnancy:
subjective
Presumptive (
These signs are least indicative of pregnancy; they could easily indicate other conditions.
lead a woman to believe that she is pregnant
signs
Amenorrhea.
Breast changes and tangling sensation.
-
2
-
Chlosma and linea nigra.
Abdominal enlargement & striae gravidarum.
Nausea & vomiting.
Frequent urination.
Fatigue
sensations of fetal movement in the abdomen. Firstly felt by the patient at
:
quickening
approximately 16 to 20 weeks
.
Probable signs( objective) of pregnancy:
.
They are more reliable than the presumptive signs, but they still are not positive or true
diagnostic findings.
8 weeks
-
6
(softening of the lower uterine segment).
Hegar’s sign
6 weeks
-
4
(softening of the cervix ,uterus, and vagina during pregnancy.).
Goodell’s sign
dropping and rebounding of the fetus in its surrounding amniotic fluid
Ballottement.
in response to a sudden tap on the uterus
.
Positive pregnancy test
more frequently felt after 28 weeks. They usually disappear
.
hicks contractions
Braxton
with walking or exercise.
•
The uterus changes from a pear shape to a globe shape.
•
Enlargement and softening of the uterus
•
Chadwick’s sign---bluish discoloration of the cervix, vagina and labia during pregnancy as a
result of increased vascular congestion.
•
-Osiander`s sign (pulsation of fornices)
Positive signs of pregnancy:
from the last menstrual period
9 to 10 weeks
Fetal heart tones can be detected as early as
(LMP) by Doppler technology
Fetal movement felt by the examiner. after about 20 weeks' gestation
.
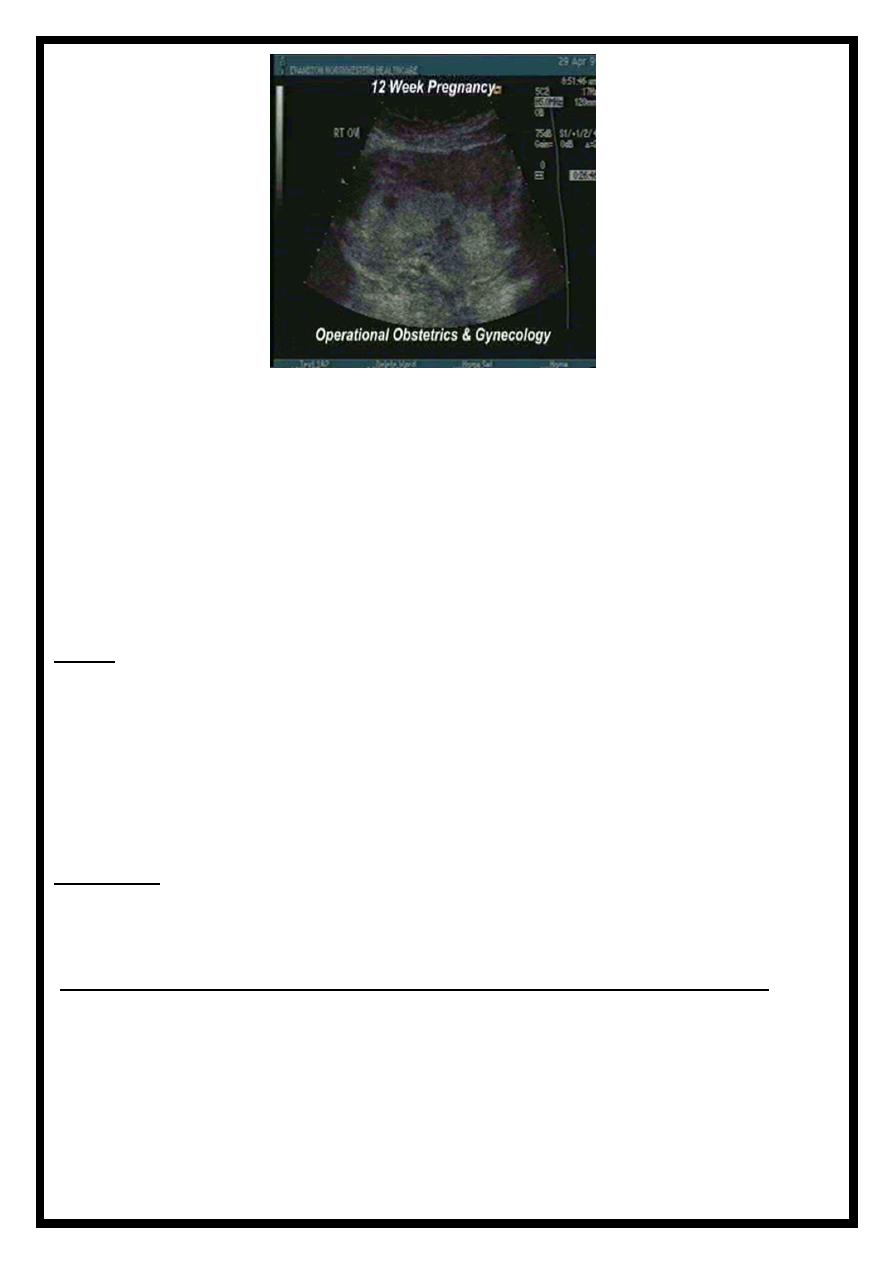
the ultrasound
Visualization of the fetus by
-
3
-
Antenatal Care:
Definitions
•
It is a planed examination and observation for the woman from conception till the birth .Or
Antenatal care refers to the care that is given to an expected mother from time of
conception is confirmed until the beginning of labor
Goals and Objectives of Antenatal Care:
Goals:
*To reduce maternal mortality and morbidity rates.
* To improve the physical and mental health of women and children.
* antenatal care aims to prevent, identify, and ameliorate maternal and fetal abnormality that
can adversely affect pregnancy outcome.
*to decrease financial recourses for care of mothers.
Objectives
•
Antenatal care support and encourage a family’s healthy psychological adjustment
to childbearing
FACTORS AFFECTING MOTHERS UTILIZATION OF ANTENATAL CARE
•
Demographic and Biological Factors
•
Socioeconomic Factors
•
Psychosocial Factors
•
Health Services Factors
-
4
-
•
Environmental Factors
Assessment and physical examination:
Component of antenatal care :
Assessment:
1
.
The initial assessment interview can establish the trusting relationship between the nurse
and the pregnant woman.
2
.
establishing rapport
3
.
getting information about the woman’s physical and psychological health,
4
.
obtaining a basis for anticipatory guidance for pregnancy .
During the firs visit, assessment and physical examination must be completed. Including:
history
.
Physical examination
.
Laboratory data
.
Psychological assessment
.
Nutritional
assessment
History:
•
Welcome the woman, and ensure a quite place where she can express concerns and
anxiety without being overheard by other people.
•
Personal and social history:
This include: woman’s name, age, occupation, address, and phone number. marital status,
duration of marriage, Religion , Nationality and language, Housing and finance
Menstrual history:
A compete menstrual history is important to establish the estimated date of delivery. It includes:
-
Last menstrual period (LMP).
-
Age of menarche.
-
Regularity and frequency of menstrual cycle.
-
Contraception method.
-
5
-
-
Any previous treatment of menstrual
-
Expected date of delivery (EDD) is calculated as followed:
1
st
day of LMP −3 months +7 days, and change the year.
Example: calculate EDD if LMP was august 30, 2007.
= June 6, 2008.
Current problems with pregnancy :
Ask the patient if she has any current problem, such as:
- Nausea & vomiting.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Headache.
-
Urinary complaints.
-
Vaginal bleeding.
-
Edema.
-
Backache.
-
Heartburn.
-
Constipation.
•
Obstetrical history:
This provides essential information about the previous pregnancies that may alert the care
provider to possible problems in the present pregnancy. Which includes:
Gravida, para, abortion, and living children.
Weight of infant at birth & length of gestation.
Labor experience, type of delivery, location of birth, and type of anesthesia.
Maternal or infant complications.
•
Medical and surgical history:
Chronic condition such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and renal disease can affect the
outcome of the pregnancy and must be investigated.
-
6
-
Prior operation, allergies, and medications should be documented.
Previous operations such as cesarean section, genital repair, and cervical cerclagc.
Accidents involving injury of the bony pelvis
•
Family history:
Family history provides valuable information about the general health of the family, and it may
reveal information about patters of genetic or congenital anomalies.
Including:
-
D.M.
-
Hypertension.
-
Heart disease.
-
Cancer.
-
Anemia.
Physical examination:
Physical examination is important to:
detect previously undiagnosed physical problems that may affect the pregnancy outcome.
and to establish baseline levels that will guide the treatment of the expectant mother and
fetus throughout pregnancy
.
General Examination:
It should be started from the moment the pregnant woman walks into the examination room.
Examine general appearance:
•
stature or body build and gait
Observe the woman for
•
as pallor and pigmentation as chloasma.
The face is observed for skin color
•
for edema of the eyelids and color of conjunctiva. Healthy eyes are
Observe the eyes
clear.
bright and
Vital signs:
Blood pressure:
-
7
-
1
.
It is taken to ascertain normality and provide a baseline reading for a comparison
throughout the pregnancy.
2
.
In late pregnancy, raised systolic pressure of 30 mm Hg or raised diastolic pressure of 15
mm Hg above the baseline values on at least two occasions of 6 or more hours apart
indicates toxemia.
Pulse:
The normal pulse rate = 60-90 BPM.
Tachycardia is associated with anxiety, hyperthyrodism, or infection.
Respiratory rate:
The normal is 16-24 BPM.
Tachypnea may indicate respiratory infection, or cardiac disease.
Temperature:
normal temperature during pregnancy is 36.2C to 37.6C.
Increased temperature suggests infection.
Cardiovascular system:
•
Venous congestion:
Which can develop into varicosities, venous congestion most commonly noted in the legs, vulva,
and rectum.
•
Edema:
Edema of the extremities or face necessitates further assessment for signs of
pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Musculoskeletal system :
•
Posture and gait:
Body mechanics and changes in posture and gait should be addressed. Body mechanics during
pregnancy may produce strain on the muscles of the lower back and legs.
•
Height & weight:
An initial weight is needed to establish a baseline for weight gain throughout pregnancy.
Preconception:

-
8
-
Wt. lower than 45kg, or Ht. under 150 cm is associated with preterm labor, and low birth
weight infant.
Wt. higher than 90 kg is associated with increased incidence of gestational diabetes,
pregnancy induced hypertension, cesarean birth, and postpartum infection.
Recommendation for weight gain during pregnancy are often made based on the woman’s body
mass index.
•
Pelvic measurement:
The bony pelvis is evaluated early in the pregnancy to determine whether the diameters are
adequate to permit vaginal delivery.
•
Observe the neck for enlarged thyroid gland and scars of previous operations.
* Observe complexion for presence of blotches.
* Ensure that the general manner of the woman indicates vigor and vitality.
* An anemic, depressed, tired or ill woman is lethargic, not interested in her appearance, and
unenthusiastic about the interview.
* Lack of energy is a temporary state in early pregnancy, a woman often feels exhausted and
debilitated.
* Discuss the woman's sleeping patterns and minor disorders and give advice as necessary.
* Report any signs of ill health.
Abdomen:
The size of the abdomen is inspected for:
- the height of the fundus, which determines the period of the gestation.
- multiple pregnancy.
The shape of the abdomen is inspected for:
-
9
-
- fetal lie & position.
- the abdomen is longer if the fetal lie is longitudinal as occurs in 99.5% of cases.
- the abdomen is lower & broad if the lie is transverse.
- fetal movement is inspected as evidence of fetal life and position.
- fetal heart beat can be heard by stethoscope after the 20
th
week, or Doppler after 8
th
week.
Normal fetal heart rate is 120-160 beats/min.
1-Inspection:
•
The nurse should look at the following:
•
• Skin changes such as linea nigra, striae gravidarum and scars of previous operations.
•
• The size of the abdomen is inspected for:
•
* Height of the fundus, which determines the period of gestation.
•
* Multiple pregnancy and polyhydramnios will enlarge both the length and breadth of the
uterus.
•
* A large fetus increases only the length of the uterus.
Contour of the abdominal wall is observed for pendulous abdomen, lightening protrusion of
umbilicus and full bladder
2-Palpation
12th week of gestation
the
• The uterus will be palpable per abdomen after
Abdominal palpation includes
Estimation of the period of gestation. This is done by determination of fundal height
.
•
The uterus may be higher than expected :
1
.
large fetus, multiple pregnancy
2
.
polyhydrammnios
3
.
mistaken date of last menstrual period
•
:
may be lower than expected
The uterus
1
.
small fetus, intrauterine growth restriction
2
.
oligohydramnios
3
.
mistaken date of last menstrual period.
-
11
-
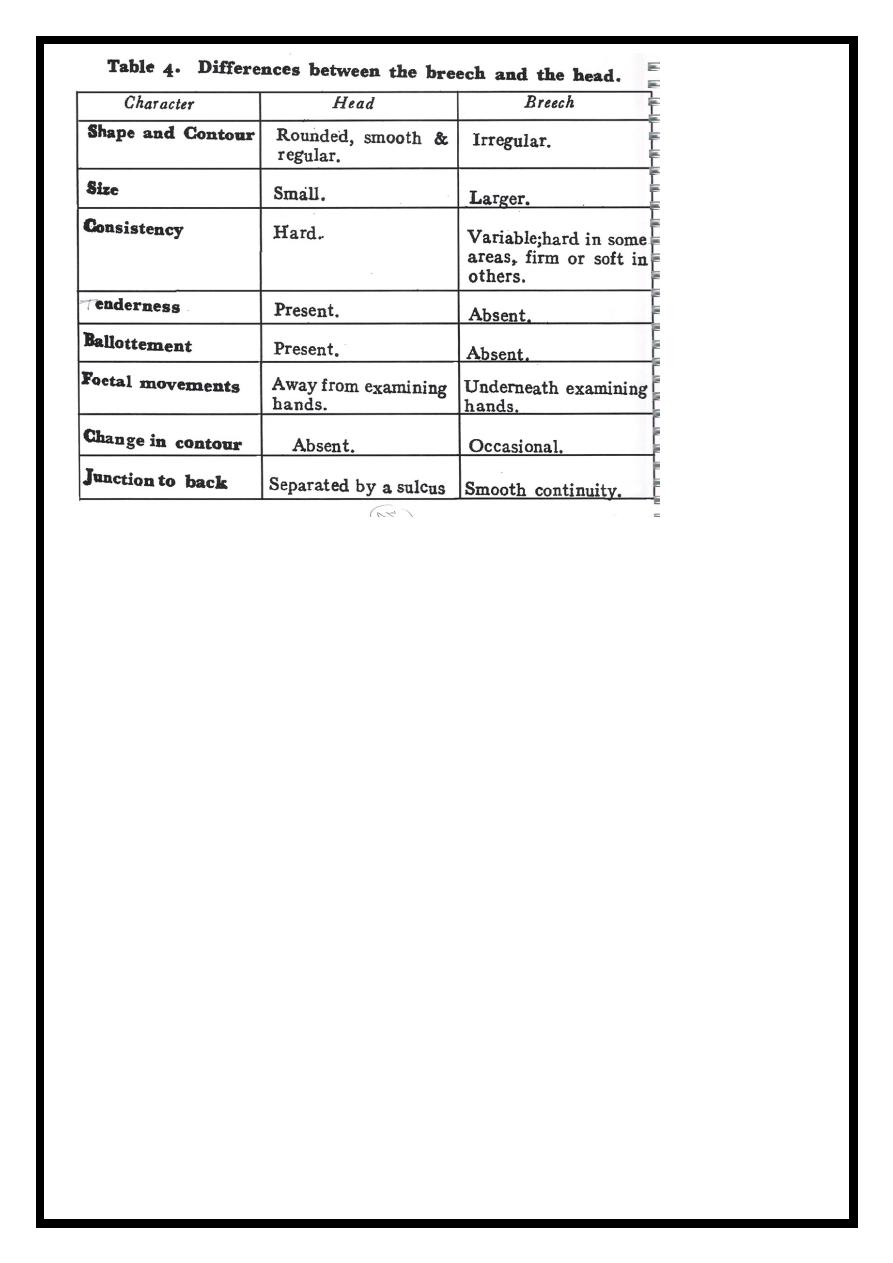
Fundal palpation
is performed to determine whether it contains the breech or the head. This
will help to diagnose the fetal lie and presentation
•
Calculations:
•
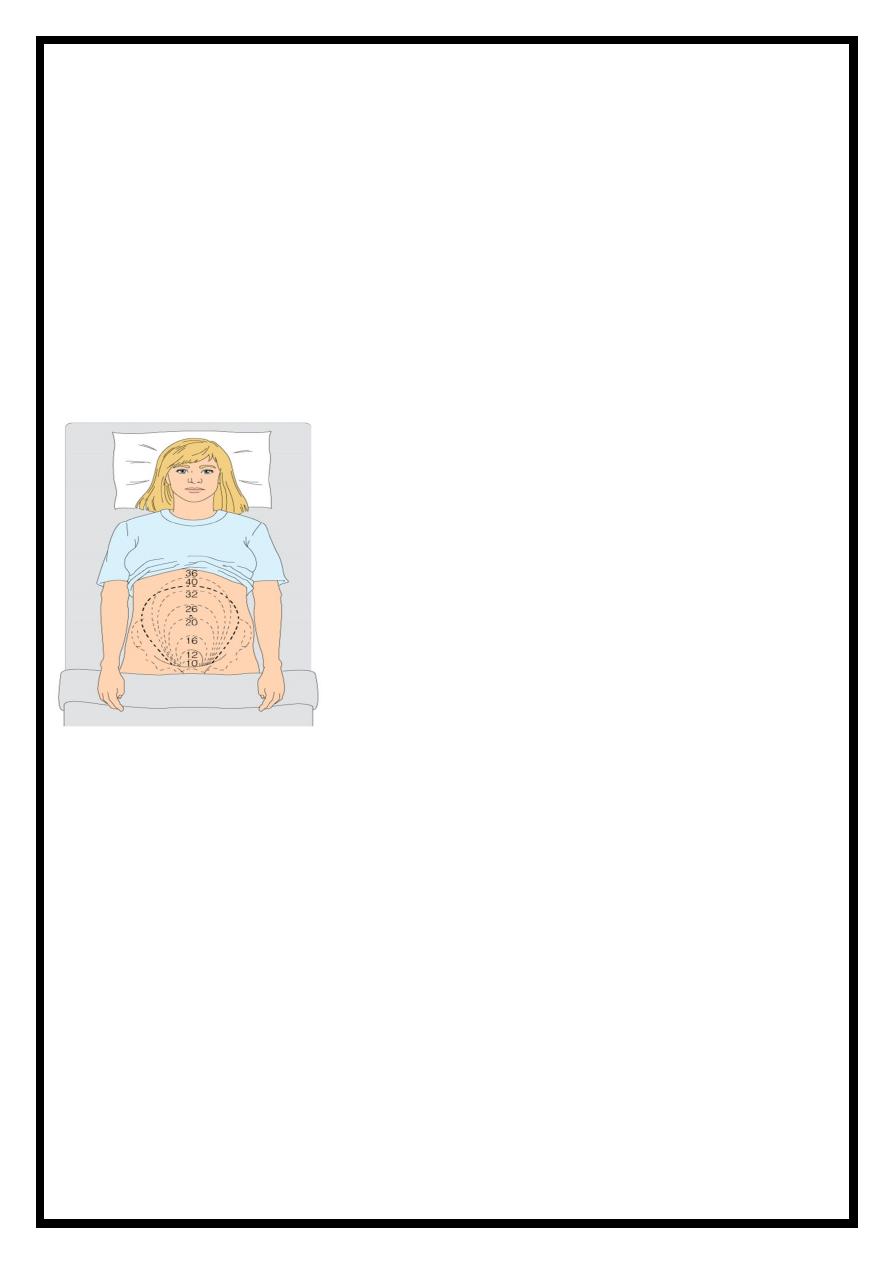
Calculation of gestation using fundal height
–
McDonald’s method: Measure from symphasis pubis to top of fundus in cm.
–
Gestation is measurement + or – 2 weeks
12weeks :the uterus fills the pelvis so that the fundus of the uterus is palpable at the symphysis
pubis
.
16weeks, the uterus is midway between the symphysis pubis and the umbilicus
.
20weeks, it reaches the umbilicus
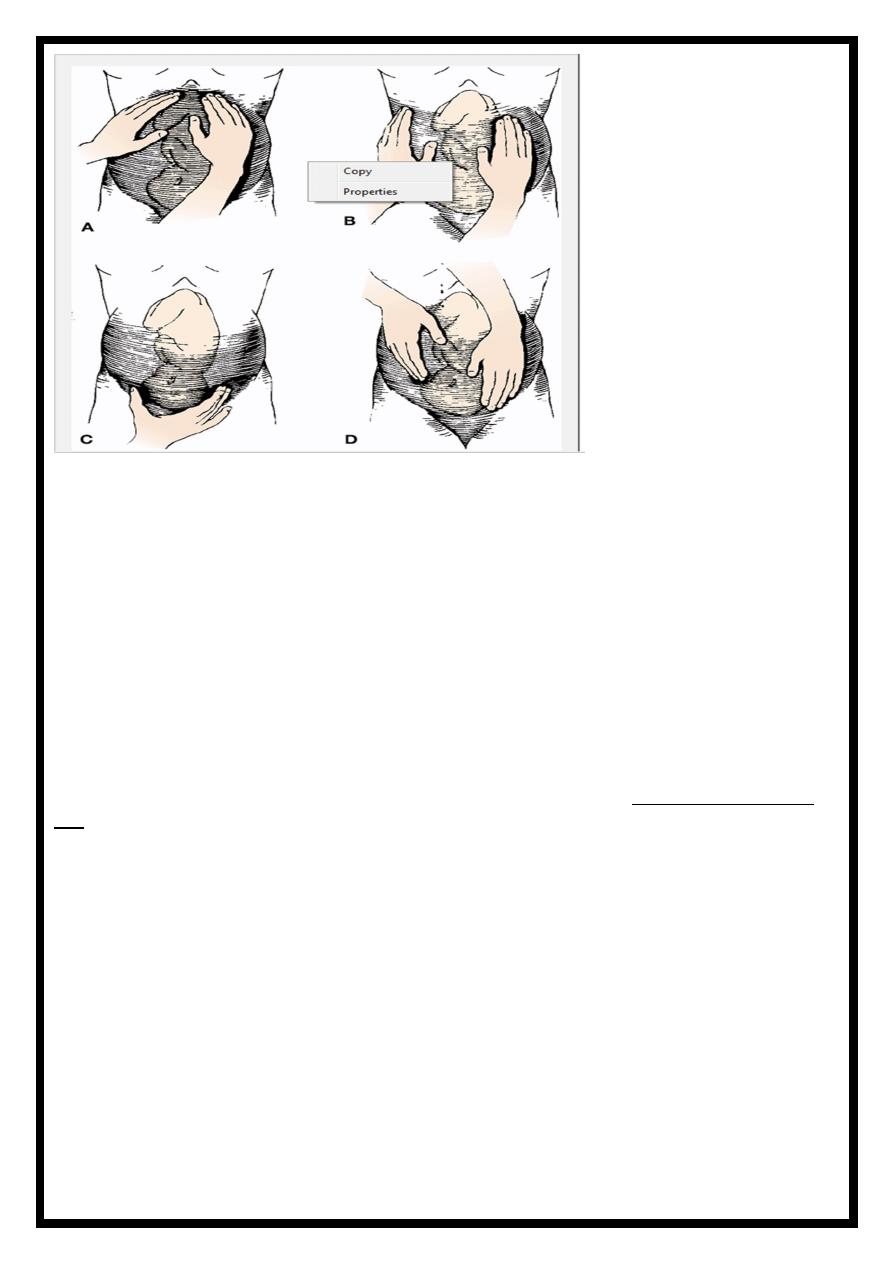
Methods for Determining Fetal Presentation
Leopold's maneuvers
-
11
-
•
First maneuver
:to determine fetal presentation (longitudinal axis) or the part of the fetus
(fetal head or breech) that is in the upper uterine fundus
.
•
:
Second maneuver
:to determine the fetal position or identify the relationship of the fetal
back and the small parts to the front, back, or sides of the maternal pelvis.
*Determine what fetal body part lies on the side of the abdomen. Reverse the hands and repeat
the maneuver. If firm, smooth, and a hard continuous structure, it is likely to be the fetal back; if
smaller, knobby, irregular, protruding, and moving, it is likely to be the small body parts
(extremities).
•
Third maneuver :
to determine the portion of the fetus that is presenting.
The head will feel firm and globular. If not engaged into the pelvis, the presenting part is movable.
Pallach's maneuver or
If immobile, engagement has occurred. This maneuver is also known as
grip
•
Fourth maneuver :
to determine fetal attitude or the greatest prominence of the fetal head
over the pelvic brim
•
If the cephalic prominence is felt on the same side as the small parts, it is usually the
sinciput (fetus' forehead), and the fetus will be in vertex or flexed position. If the cephalic
prominence is felt on the same side as the back, it is the occiput (or crown), and the fetus
will be vertex or slightly extended position.
•
If the cephalic prominence is felt equally on both sides, the fetus' head may be in a military
position (common in posterior position). Then move the hands toward the pelvic brim. If the
hands converge (come together) around the presenting part, it is floating. If the hands
diverge (stay/move apart), the presenting part is either dipping or engaged in the pelvis
.
-
12
-
Neurological system:
•
Deep tendon reflexes should be evaluated because hyperreflexia is associated with
complications of pregnancy.
Skin:
•
Pallor of the skin my indicate anemia.
•
Jaundice may indicate hepatic disease.
•
Chloasma and linea nigra related to pregnancy.
•
Striae graviderum should be noted.
•
Nail beds should be pink with instant capillary return.
Legs:
Legs should be noted for edema.
* They should be observed for varicose veins
* The calf must be observed for reddened areas which may be caused by phlebitis and white
areas which could be caused by deep vein thrombosis.
* Ask the woman to report tenderness during examination.
* The legs should be observed for unequal length or muscle wasting which may be an indication
of pelvic abnormalities.
-
13
-
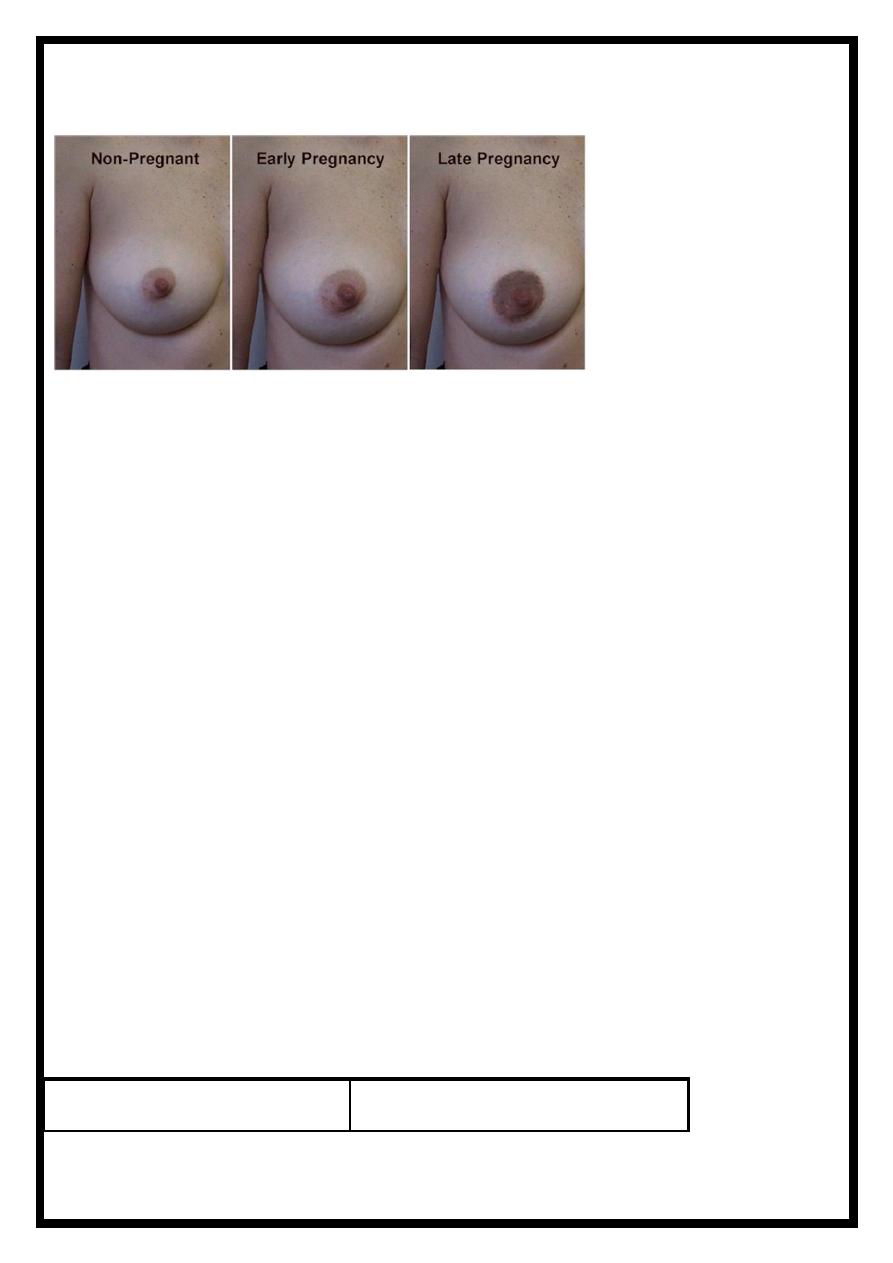
Breast:
•
Assess breast size, symmetry, condition of nipple, and the presence of colostrum.
Gastrointestinal systems:
•
Mouth:
•
The gum may be red, tender, edematous as a result of the effects of increased estrogen.
Observe the mouth for:
•
Dryness or cyanosis of the lips.
•
Gingivitis of the gums.
•
Septic focus or caries of the teeth
•
Intestine:
Assess for the bowel sound.
•
AssesVaginal discharge:
* Ask the woman about any increase or change of vaginal discharge.
•
Report to the obstetrician any mucoid loss before the 37th week of pregnancy.
Vaginal bleeding:
* Vaginal bleeding at any time during pregnancy should be reported to the obstetrician to
investigate its origin.
s for constipation or diarrhea.
1
Laboratory data:
Test
Purpose
-
14
-
Stool analysis
for ova and parasites
* Venereal disease tests should be
performed (VDRL)
To screen for syphilis
Hepitits Bserface antigine
To detect carrier status or active
disease
•
* Hemoglobin will be repeated:
•
- At 36 weeks of gestation.
•
- Every 4 weeks if Hb is<9g/dl.
•
- If there is any other clinical reason.
Ultrasound:
Is performed to:
•
estimate the gestational age.
•
Check amniotic fluid volume.
•
Check the position of the placenta.
•
Detect the multifetal pregnancy.
Blood group
To determine blood type.
Hgb & Hct
To detect anemia.
(RPR) rapid plasma reagin
To screen for syphilis
Rubella
To determine immunity
Urine analysis
To detect infection or renal disease.
protein, glucose, and ketones
Papanicolaou (pap) test
To screen for cervical cancer
Chlamydia
To detect sexual transmitted
disease.
Glucose
To screen for gestational diabetes.
-
15
-
•
The position of the baby.
•
Fetal kick count:
•
The pregnant woman reports at least 10 movements in 12 hours.
* Absence of fetal movements precedes intrauterine fetal death by 48 hours.
Schedual of antenatal care:
•
a medical check up every four weeks up to 28 weeks gestation,
•
every 2 weeks until 36 weeks of gestation
•
visit each week until delivery
•
More frequent visits may be required if there are abnormalities or complications or if danger
signs arise during pregnancy
Services at subsequent visits:
•
the nurse inquires about physical changes that are related directly to the pregnancy, such
as the woman’s perception of fetal movement, any exposure to contagious illness, medical
treatment and therapy prescribed for non-pregnancy problems since the last visit,
•
prescribed medications that were not prescribed as a part of the women’s prenatal care.
:
health education
•
Follow up:
•
Advice the mother to follow up according to the schedule of antenatal care that mentioned
before, advise the mother to follow up immediately if any danger sings appears, describe
the important of follow up to the mother.
Health teaching during pregnancy
Health promotion during pregnancy begins with reviewing health hare.
Hygiene:
•
Daily all over wash is necessary because it is stimulating, refreshing, and relaxing.
•
Warm shower or sponge baths is better than tub bath.
•
Hot bath should be avoided because they may cause fatigue. &fainting
•
Regular washing for genital area, axilla, and breast due to increased discharge and
sweating.
•
Vaginal douches should avoided except in case of excessive secretion or infection.

-
16
-
Danger signs of pregnancy:
Vaginal bleeding including spotting
.
Persistent abdominal pain
.
Sever & persistent vomiting
.
Sudden gush of fluid from vagina
.
Absence or decrease fetal movement
.
Sever headache
.
Edema of hands, face, legs & feet
.
.)
Dizziness, blurred vision, double vision & spots before eyes
.
Painful urination
Breast care:
•
Wear firm, supportive bra with wide straps to spread weight across the shoulder.
•
Wash breasts with clean tap water (no soap, because that could be drying). Daily to remove
the colostrum & reduce the risk of infection.
•
It is not recommended to massage the breast, this may stimulate oxytocin hormone
secretion and possibly lead to contraction.
•
advise the mother to be mentally prepared for breast feeding
•
advise the pregnant woman to expresses colostrums during the last trimester of pregnancy
to prevent congestion.
Dental care:
•
The teeth should be brushed carefully in the morning and after every meal.
•
Encourage the woman the to see her dentist regularly for routine examination & cleaning.
•
Encourage the woman to snack on nutritious foods, such as fresh fruit & vegetables to
avoid sugar coming in contact with the teeth.
•
A tooth can be extracted during pregnancy, but local anesthesia is recommended.
Dressing:
Woman should avoid wearing tight cloths such as belt or constricting bans on the legs, because
these could impede lower extremity circulation
.
-
17
-
Suggest wearing shoes with a moderate to low heel to minimize pelvic tilt & possible backache
.
Loose, and light clothes are the most comfortable
Travel:
Many women have questions about travel during pregnancy.
•
Early in normal pregnancy, there are no restrictions.
•
Late in pregnancy, travel plans should take into consideration the possibility of early labor.
Sexual activity:
Sexual intercourse is allowed with moderation, is absolutely safe and normal unless specific
problem exist such as: vaginal bleeding or ruptured membrane
.
If a woman has a history of abortion, she should avoid sexual intercourse in the early months of
pregnancy
Exercises:
•
Exercise should be simple. Walking is ideal, but long period of walking should be avoided.
•
The pregnant woman should avoid lifting heavy weights such as: mattresses furniture, as it
may lead to abortion.
•
She should avoid long period of standing because it predisposes her to varicose vein.
•
She should avoid setting with legs crossed because it will impede circulation.
Purpose
:
1
.
To develop a good posture
.
2
.
To reduce constipation & insomnia
.
3
.
To alleviate discomvortable, postural back ache& fatigue
.
4
.
To ensure good muscles tone& strength pelvic supports
.
5
To develop good breathing habits, ensure good oxygen supply to the fetus
.
6
-
to prevent circulatory stasis in lower extremities, promote circulation, lessen the possibility of
venous thrombosis
•
Guide lines for exercises during pregnancy:
•
-Maintain adequate fluid intake.
•
-Warm up slowly, use stretching exercises but avoid over stretching to prevent injury to
ligaments.
•
-Avoid jerking or bouncing exercises.

-
18
-
•
Be careful of loose throw rugs that could slip& cause injury.
•
Exercises on regular basis (three times per week).
•
After first trimester, avoid exercises that require supine position.
:
-
Vaginal bleeding
.
-
Sever anemia
.
-
History of preterm labor
,
-
Extreme over or under weight
.
-
Hypertension, heart, lung, thyroid diseases
Sleep:
•
The pregnant woman should lie down to relax or sleep for 1 or 2 hours during the afternoon.
•
At least 8 hours sleep should be obtained every night & increased towards term, because
the highest level of growth hormone secretion occurs at sleep.
•
Advise woman to use natural sedatives such as: warm bath & glass of worm milk.
A good sleeping position is sims’ position, with the top leg forward. This puts the weight of the
fetus on the bed, not on the woman, and allows good circulation in the lower extremities
.
avoid resting in supine position, as supine hypotension syndrome can develop
.
•
Hazards
•
Occupational hazards: lead, mercury, X ray s& ethylene oxide.
•
Infection: rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis.......................
•
Smoking & alcohol: increase risk for pregnancy, prematurity, fetal death, mental
retardation & congenital anomalies.
•
Drugs: as sedative & analysis, anticoagulant, antithyrodism, hormones& antibiotics.
Immunization
:
the nurse instructs the woman to receive immunization against -tetanus to prevent the risk for her
and her fetus
.
Also, it is important that every pregnant mother should receive a tetanus vaccination card with her
first tetanus dose and keep it to record subsequent doses
•
Diet:
•
-Daily requirement in pregnancy about 2500 calories.
-
19
-
•
- Women should be advised to eat more vegetables, fruits, proteins, and vitamins and to
minimize their intake of fats.
•
Purpose:
–
*Growing fetus.
–
*Maintain mother health.
–
*Physical strength & vitality in labor.
–
*Successful lactation.
Managing the minor disorders of pregnancy:
Nausea and vomiting :
•
-
occur between 4-6 weeks gestation
•
Causes:
- hormonal influences: hcg, progesterone, estrogen.
- emotional factors like tension.
•
Management:
- adequate rest and relaxation.
- eating small six meals a day rather than three large meals.
- solid food tolerated better than liquid food like: crackers or piece of dry toast.
- carbohydrate snacks at bedtime can prevent hypoglycemia which cause nausea & vomiting.
- Food should not have a strong odor, should not be either very hot or very cold, and fried or
greasy foods should be avoided.
Heartburn :
•
Causes:
- progesterone hormone relaxes the cardiac sphincter of the stomach and allows reflex or
bubbling back of gastric contents into the esophagus.
- the pressure of the growing uterus on the stomach from about 30-40 weeks.
•
Management:
- avoid lying flat.
-
21
-
- sleeping with more pillows and lying on the right side.
- small frequent meals.
- take antacids.
- taking baking soda in a glass of water is contraindicated because of the possibility of retention
of sodium and subsequent edema
Avoid fried ,spicy, and fatty food
Avoid citrus juices
Backache :
•
Cause:
Backache may be due to muscular fatigue and strain that accompany poor body balance.
•
It may be due to increased lordosis during pregnancy in an effort to balance the body.
•
•The pregnancy hormones sometimes soften the ligaments to such a degree that some
support is needed.
•
Management:
- exercise.
- sit with knee slightly higher than the hips.
-The pregnant woman is reassured that once birth has occurred, the ligaments will return to their
pre-pregnant strength.
Urinary frequency:
•
Cause:
Occur due to the pressure of the growing uterus on the bladder.
•
Management:
The problem will resolved when the uterus rises into the abdomen after the 12
th
week.
Kegel exercises are some times recommended to help maintain the bladder.
Varicosities:
•
Causes:
-
21
-
- progesterone relaxes the smooth muscles of the veins and result in sluggish circulation. The
valves of the dilated veins become inefficient & varicose veins result.
- weight of the uterus partially compressed the veins returning blood from the legs.
•
Management:
- lying flat on the bed with the feet elevated.
- moving the legs about is better than standing still.
Constipation:
•
Causes:
- intestinal motility decreased during pregnancy as a result of progesterone.
- iron supplementation.
•
Management:
- the food should have amount of fruit & green vegetables which contain fibers.
- drinking a lot of water.
- exercise & walking.
- laxatives could prescribed by physician.
Edit by : ali anas
