
1
|
P a g e
#Mohdz
DONE BY:-
Epidemiology of Rotavirus infection
Dr .Zahraa.A.Hasan
M.B.ch.B/MSc./F.I.B.M.S./CM
Clinical Features
Rotavirus disease is characterized by vomiting and watery diarrhea for 3 to 8 days.
Fever and abdominal pain also frequently occur. Additional symptoms include loss of
appetite and dehydration .
The incubation period for rotavirus disease is approximately 2 days.
Vaccinated and unvaccinated children may develop rotavirus disease more than once
because neither vaccine nor natural infection provide full immunity (protection) from
future infections. A child’s first infection with rotavirus tends to cause the most
severe symptoms.
• Rotavirus disease is most common in infants and young children. However, older
children and adults can also become infected with rotavirus. Once a person has been
exposed to rotavirus, it takes 2 days for the symptoms to appear.
• Adults who get rotavirus disease tend to have milder symptoms.
2
|
P a g e
#Mohdz
DONE BY:-
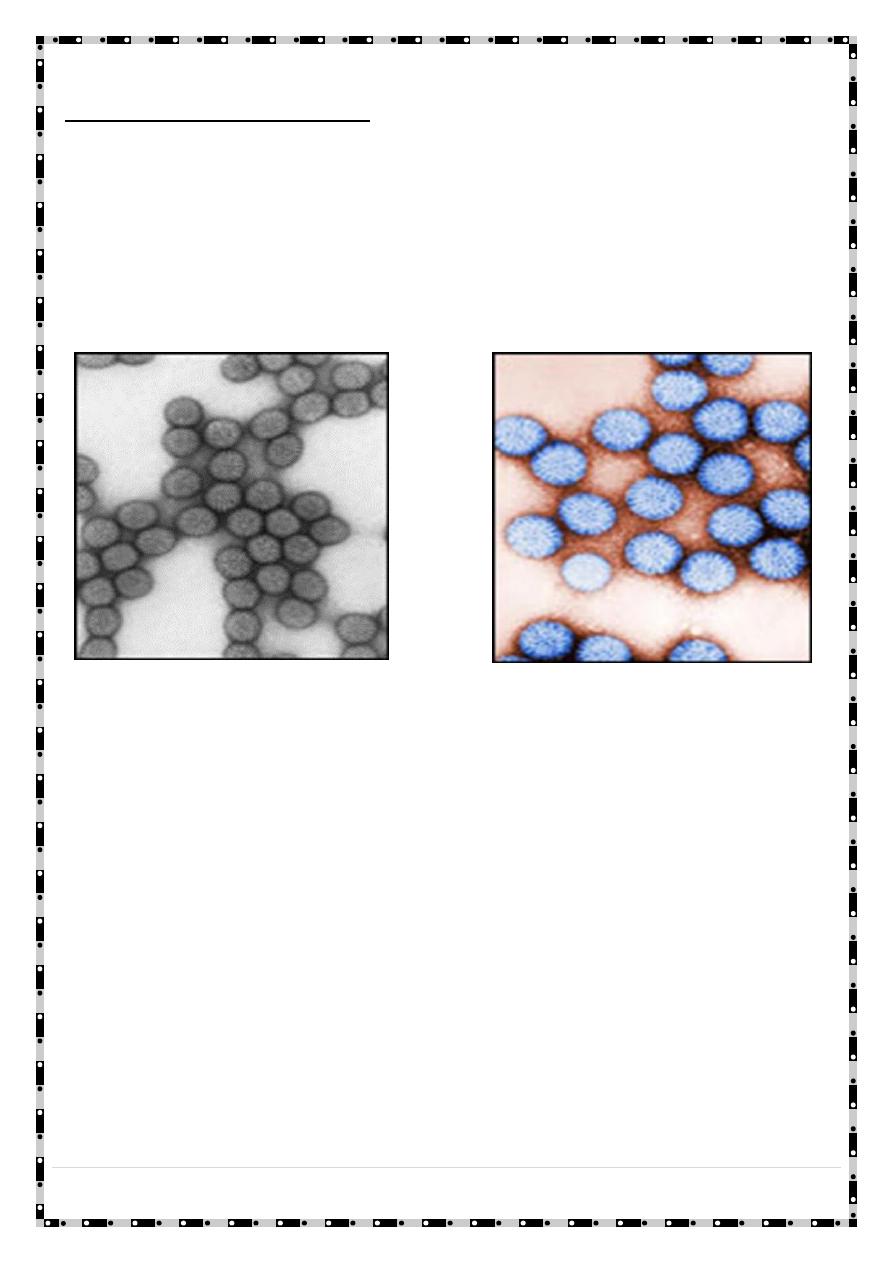
The Virus characteristics:
Rotavirus has a characteristic wheel-like appearance when viewed by an electron
microscopy. The name rotavirus is derived from the Latin Rota, meaning "wheel".
Rotaviruses are no enveloped, double-shelled viruses. The genome is composed of 11
segments of double-stranded RNA, which code for six structural and five nonstructural
proteins. The virus is stable in the environment .
Children, even those that are vaccinated, may develop rotavirus disease more than
once, because neither natural infection with rotavirus nor rotavirus vaccination
provides full immunity from future infections .
Usually a person’s first infection with rotavirus causes the most severe symptoms
.
3
|
P a g e
#Mohdz
DONE BY:-
Transmission of the disease:
o Rotavirus spreads easily among infants and young children. Children can spread the
virus both before and after they become sick with diarrhea and during the first 3 days
after they recover from rotavirus disease.
o They can also pass rotavirus to family members and other people with close contact.
o People who are infected with rotavirus shed rotavirus in their feces .They shed the
virus most when they are sick
The virus spreads by the fecal-oral route; Rotavirus can be spread by contaminated
Hands
Objects (toys, surfaces)
Food
Water
Children are most likely to get rotavirus in the winter and spring (December through
June).
Epidemiologic Features
The primary mode of transmission is the fecal-oral route. Because the virus is stable
in the environment, transmission can occur through ingestion of contaminated water
or food and contact with contaminated surfaces or objects .
The disease has a winter seasonal pattern, with annual epidemics occurring from
December through June.
The highest rates of illness occur among infants and young children, and most
children are infected by 5 years of age .
Diagnosis
Diagnosis may be made by rapid detection of rotavirus antigen in stool specimens.
Strains may be further characterized by enzyme immunoassay or reverse transcriptase
polymerase chain reaction, but such testing is not commonly done.
4
|
P a g e
#Mohdz
DONE BY:-
Treatment
For people with healthy immune systems, rotavirus disease is self-limited, lasting for only
a few days. Treatment is nonspecific and consists primarily of oral rehydration therapy to
prevent dehydration .
About 1 out of 70 children with rotavirus disease will require hospitalization for
intravenous fluids.
Burden
Rotavirus was the leading cause of severe diarrhea among infants and young children
before rotavirus vaccine was introduced in 2006, rotavirus led to
More than 400,000 doctor visits,
More than 200,000 emergency room visits, 55,000 to 70,000 hospitalizations, and 20
to 60 deaths.
Globally, rotavirus is still the leading cause of severe diarrhea in infants and young
children .
In 2008, rotavirus caused an estimated 453,000 deaths worldwide in children
younger than 5 years of age.
People Most at Risk for Rotavirus Disease
• Children are most at risk for getting rotavirus disease (child care centers or other
settings with many young children).The most severe rotavirus disease occurs
primarily among unvaccinated children aged 3 to 35 months old.
• Older adults have a higher risk of getting rotavirus disease, and also adults who:
• Care for children with rotavirus disease,
• Compromised immune systems (human immunodeficiency virus (HIV )
• Traveling.
5
|
P a g e
#Mohdz
DONE BY:-
Prevention and Control
• Good hygiene (handwashing) are important but are not enough to control the spread
of the disease.
• Rotavirus vaccines are very effective in preventing rotavirus gastroenteritis and the
accompanying diarrhea and other symptoms. CDC recommends routine vaccination
of infants with either of the two available vaccines:
• RotaTeq which is given in 3 doses at ages 2 months, 4 months, and 6 months; or
• Rotarix which is given in 2 doses at ages 2 months and 4 months.
• Both rotavirus vaccines are given orally. The vaccines are very effective (85% to 98%)
in preventing severe rotavirus disease in infants and young children, including
rotavirus infection that requires hospitalization.
Rotavirus vaccines will not prevent diarrhea or vomiting caused by other viruses or
pathogens.
There is no antiviral drug to treat rotavirus infection .
• Rotavirus infection can cause severe vomiting and diarrhea. This can lead to
dehydration (loss of body fluids). During rotavirus infection, infants and young
children, older adults, and people with other illnesses are most at risk becoming
dehydrated.
• The best way to protect against dehydration is Oral rehydration solutions for mild
dehydration. Severe dehydration may require hospitalization for treatment with
intravenous (IV) fluids .
• This first dose of either vaccine is most effective if it is given before a child is 15
weeks of age. Also, children should receive all doses of rotavirus vaccine before 8
months old.
The vaccines differ in how they are made and the number of doses, but both are
given orally.
6
|
P a g e
#Mohdz
DONE BY:-
