
HELICOBACTER
HELICOBACTER
PYLORI
PYLORI
DR
DR
Luay
Luay
·
·
-ability
-ability
to
to
hydrolyse
hydrolyse
urea,
urea,
resulting
resulting
in
in
the
the
production
production
of
of
ammonia,
ammonia,
a
a
strong
strong
alkali.
alkali.
The
The
effect
effect
of
of
ammonia
ammonia
on
on
the
the
antral
antral
G
G
cells
cells
is
is
to
to
cause
cause
the
the
release
release
of
of
gastrin,
gastrin,
result
result
in
in
gastric
gastric
acid
acid
hypersecretion
hypersecretion
·
·
-enzymes
-enzymes
produced
produced
by
by
the
the
organism
organism
disrupt
disrupt
the
the
gastric
gastric
mucous
mucous
barrier
barrier
·
·
-inflammation
-inflammation
induced
induced
in
in
the
the
gastric
gastric
epithelium
epithelium
·
·
-duodenal
-duodenal
gastric
gastric
metaplasia
metaplasia
normal
normal
response
response
of
of
the
the
duodenal
duodenal
mucosa
mucosa
to
to
excess
excess
acidity
acidity
·
·
-increases
-increases
with
with
age
age
·
·
-inversely
-inversely
related
related
to
to
socio-economic
socio-economic
group
group
·
·
-classed
-classed
by
by
the
the
World
World
Health
Health
Organization
Organization
as
as
a
a
class
class
1
1
carcinogen
carcinogen
·
·
-The
-The
spiral
spiral
bacterium
bacterium
H.
H.
pylori
pylori
is
is
critical
critical
in
in
the
the
development
development
of
of
type
type
B
B
gastritis,
gastritis,
peptic
peptic
ulceration
ulceration
and
and
gastric
gastric
cancer
cancer
·
·
1.Serologic
1.Serologic
test
test
:
:
·
·
Test
Test
of
of
choice
choice
when
when
endoscopy
endoscopy
is
is
not
not
indicated
indicated
and
and
is
is
not
not
an
an
option,
option,
no
no
anti
anti
helicobacter
helicobacter
use
use
.Noninvasive;
.Noninvasive;
sensitivity
sensitivity
of
of
>
>
80%,specificity
80%,specificity
of
of
about
about
90%.
90%.
Does
Does
not
not
confirm
confirm
eradication
eradication
·
·
2.Urea
2.Urea
breath
breath
test
test
:
:
·
·
Preferred
Preferred
for
for
confirming
confirming
cure
cure
of
of
H.
H.
pylori
pylori
infection,
infection,
but
but
no
no
sooner
sooner
than4
than4
wk
wk
after
after
completion
completion
of
of
therapy.
therapy.
Simple;
Simple;
sensitivity
sensitivity
and
and
specificity
specificity
of
of
90
90
to
to
99%.
99%.
False-negatives
False-negatives
possible,
possible,
expensive
expensive
·
·
3.Histologic
3.Histologic
test
test
:
:
·
·
To
To
directly
directly
ascertain
ascertain
presence
presence
of
of
H.
H.
pylori,
pylori,
Sensitivity
Sensitivity
of
of
80
80
–
–
100%,Requires
100%,Requires
laboratory
laboratory
facilities
facilities
and
and
experience;
experience;
·
·
4.Rapid
4.Rapid
urease
urease
test
test
:
:
·
·
Simplest
Simplest
method,
method,
rapid,
rapid,
sensitivity
sensitivity
of
of
80
80
to
to
95%,
95%,
Invasive;
Invasive;
false-
false-
negatives
negatives
possible.
possible.
·
·
5.Culture:
5.Culture:
·
·
antimicrobial
antimicrobial
resistance
resistance
is
is
suspected
suspected
or
or
high
high
level
level
of
of
resistance
resistance
exists,
exists,
Time-consuming;
Time-consuming;
expensive.
expensive.

GASTRITIS
GASTRITIS
··
··
Type
Type
A
A
gastritis:
gastritis:
·
·
An
An
autoimmune
autoimmune
condition
condition
·
·
Circulating
Circulating
antibodies
antibodies
to
to
the
the
parietal
parietal
cell
cell
·
·
Atrophy
Atrophy
of
of
the
the
parietal
parietal
cell
cell
mass,
mass,
resulting
resulting
in
in
hypochlorhydria
hypochlorhydria
·
·
As
As
intrinsic
intrinsic
factor
factor
is
is
also
also
produced
produced
by
by
the
the
parietal
parietal
cell
cell
·
·
Malabsorption
Malabsorption
of
of
vitamin
vitamin
B12,
B12,
pernicious
pernicious
anaemia
anaemia
·
·
Antrum
Antrum
is
is
not
not
affected
affected
·
·
Hypergastrinaemia
Hypergastrinaemia
··
··
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy
of
of
the
the
enterochromaffin-like
enterochromaffin-like
ECL
ECL
cells
cells
in
in
the
the
body
body
of
of
the
the
stomach=microadenomas=Very
stomach=microadenomas=Very
rarely,these
rarely,these
tumours
tumours
can
can
become
become
malignant
malignant
··
··
2.Type
2.Type
B
B
gastritis
gastritis
·
·
Association
Association
of
of
this
this
type
type
of
of
gastritis
gastritis
with
with
H.
H.
pylori
pylori
infection
infection
·
·
Most
Most
commonly
commonly
affects
affects
the
the
antrum
antrum
·
·
Patients
Patients
with
with
pangastritis
pangastritis
seem
seem
to
to
be
be
most
most
prone
prone
to
to
the
the
development
development
of
of
gastric
gastric
cancer
cancer
··
··
3.Reflux
3.Reflux
gastritis
gastritis
·
·
caused
caused
by
by
enterogastric
enterogastric
reflux
reflux
and
and
is
is
particularly
particularly
common
common
after
after
gastric
gastric
surgery
surgery
·
·
found
found
in
in
patients
patients
with
with
no
no
previous
previous
surgical
surgical
intervention
intervention
or
or
who
who
have
have
had
had
a
a
cholecystectomy
cholecystectomy
··
··
4.
4.
Erosive
Erosive
gastritis
gastritis
:
:
caused
caused
by
by
agents
agents
that
that
disturb
disturb
the
the
gastric
gastric
mucosal
mucosal
barrier;NSAIDs
barrier;NSAIDs
and
and
alcohol
alcohol
are
are
common
common
causes,
causes,
inhibition
inhibition
of
of
the
the
cyclo-oxygenase
cyclo-oxygenase
type
type
1
1
(COX-1)
(COX-1)
enzyme,
enzyme,
hence
hence
reducing
reducing
the
the
production
production
of
of
cytoprotective
cytoprotective
prostaglandins
prostaglandins
in
in
the
the
stomach
stomach
··
··
5.Stress
5.Stress
gastritis
gastritis
·
·
common
common
sequel
sequel
of
of
serious
serious
illness
illness
or
or
injury
injury
·
·
a
a
reduction
reduction
in
in
the
the
blood
blood
supply
supply
to
to
superficial
superficial
mucosa
mucosa
of
of
the
the
stomach
stomach
·
·
Prevention
Prevention
of
of
the
the
stress
stress
bleeding
bleeding
from
from
the
the
stomach
stomach
is
is
much
much
easier
easier
than
than
·
·

·
·
treating
treating
it,
it,
hence
hence
the
the
routine
routine
use
use
of
of
H2-receptor
H2-receptor
antagonists.
antagonists.
·
·
6
6
.
.
M
M
é
é
n
n
é
é
trier
trier
’
’
s
s
disease
disease
:
:
gross
gross
hypertrophy
hypertrophy
·
·
of
of
the
the
gastric
gastric
mucosal
mucosal
folds,
folds,
mucus
mucus
production
production
and
and
hypochlorhydria
hypochlorhydria
,pre-malignant
,pre-malignant
caused
caused
by
by
over
over
expressionof
expressionof
transforming
transforming
growth
growth
factor
factor
alpha
alpha
(TGF
(TGF
α
α
).
).
·
·
7
7
.
.
Lymphocytic
Lymphocytic
gastritis
gastritis
:
:
infiltration
infiltration
of
of
the
the
gastric
gastric
mucosa
mucosa
by
by
T
T
cells
cells
and
and
is
is
probably
probably
associated
associated
with
with
H.
H.
pylori
pylori
infection
infection
··
··
8
8
.
.
Other
Other
forms
forms
of
of
gastritis:
gastritis:
·
·
Eosinophilic
Eosinophilic
gastritis
gastritis
·
·
Granulomatous
Granulomatous
gastritisis
gastritisis
seen
seen
rarely
rarely
in
in
Crohn
Crohn
’
’
s
s
disease
disease
·
·
(AIDS)
(AIDS)
gastritisis
gastritisis
secondary
secondary
to
to
infection
infection
with
with
Cryptosporidium
Cryptosporidium
·
·
Phlegmonous
Phlegmonous
gastritis
gastritis
PEPTIC
PEPTIC
ULCER
ULCER
·
·
Common
Common
sites
sites
for
for
peptic
peptic
ulcers
ulcers
are
are
the
the
·
·
first
first
part
part
of
of
the
the
duodenum
duodenum
·
·
the
the
lesser
lesser
curve
curve
of
of
the
the
stomach
stomach
·
·
the
the
stoma
stoma
following
following
gastric
gastric
surgery,
surgery,
·
·
the
the
oesophagus
oesophagus
·
·
a
a
Meckel
Meckel
’
’
s
s
diverticulum,
diverticulum,
which
which
contains
contains
ectopic
ectopic
gastric
gastric
epithelium.
epithelium.
aetiology
aetiology
·
·
High
High
acid
acid
out
out
put
put
(Zollinger
(Zollinger
–
–
Ellison
Ellison
syndrome)
syndrome)
·
·
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
·
·
H.
H.
pylori
pylori
·
·
NSAIDs
NSAIDs
·
·
Cigarette
Cigarette
smoking
smoking
predisposes
predisposes
to
to
·
·
peptic
peptic
ulceration
ulceration
and
and
increases
increases
the
the
relapse
relapse
rate
rate
after
after
treatment
treatment
Duodenal
Duodenal
ulceration
ulceration
·
·
the
the
incidence
incidence
of
of
duodenal
duodenal
ulceration
ulceration
and
and
the
the
frequency
frequency
of
of
elective
elective
surgery
surgery
for
for
the
the
condition
condition
were
were
falling.
falling.
·
·
dyspeptic
dyspeptic
patients
patients
presenting
presenting
with
with
a
a
duodenal
duodenal
ulcer
ulcer
at
at
gastroscopy
gastroscopy
are
are
uncommon
uncommon
relate
relate
to
to
the
the
widespread
widespread
use
use
of
of
gastric
gastric
antisecretory
antisecretory
agents
agents
and
and
H.
H.
pylori
pylori
eradication
eradication
therapy
therapy
for
for
patients
patients
with
with
dyspepsia
dyspepsia
·
·
the
the
peak
peak
incidence
incidence
is
is
now
now
in
in
a
a
much
much
older
older
age
age
group
group
than
than
previously
previously

·
·
common
common
in
in
men
men
Pathology
Pathology
·
·
Most
Most
occur
occur
in
in
the
the
first
first
part
part
of
of
the
the
duodenum
duodenum
·
·
chronic
chronic
ulcer
ulcer
penetrates
penetrates
the
the
mucosa
mucosa
and
and
into
into
the
the
muscle
muscle
coat,
coat,
leading
leading
to
to
fibrosis.
fibrosis.
·
·
fibrosis
fibrosis
causes
causes
deformities
deformities
such
such
as
as
pyloric
pyloric
stenosis
stenosis
·
·
Anteriorly
Anteriorly
placed
placed
ulcers
ulcers
tend
tend
to
to
perforate
perforate
·
·
posterior
posterior
duodenal
duodenal
ulcers
ulcers
tend
tend
to
to
bleed
bleed
·
·
malignancy
malignancy
in
in
this
this
region
region
is
is
so
so
uncommon
uncommon
Gastric
Gastric
ulcers
ulcers
·
·
H.
H.
pylori
pylori
and
and
NSAIDs
NSAIDs
are
are
the
the
important
important
aetiological
aetiological
factors
factors
·
·
Associated
Associated
with
with
smoking.
smoking.
·
·
substantially
substantially
less
less
common
common
than
than
duodenal
duodenal
ulceration.
ulceration.
·
·
sex
sex
incidence
incidence
is
is
equal
equal
·
·
tends
tends
to
to
be
be
older
older
·
·
prevalent
prevalent
in
in
low
low
socioeconomic
socioeconomic
groups
groups
Pathology
Pathology
·
·
similar
similar
to
to
that
that
of
of
a
a
duodenal
duodenal
ulcer,
ulcer,
except
except
that
that
gastric
gastric
ulcers
ulcers
tend
tend
to
to
be
be
larger.
larger.
·
·
Fibrosis,
Fibrosis,
when
when
it
it
occurs
occurs
hourglass
hourglass
contraction
contraction
·
·
may
may
erode
erode
·
·
posteriorly
posteriorly
into
into
the
the
pancreas
pancreas
·
·
into
into
major
major
vessels
vessels
such
such
as
as
the
the
splenic
splenic
artery
artery
·
·
into
into
other
other
organs
organs
such
such
as
as
the
the
transverse
transverse
colon.
colon.
·
·
Much
Much
more
more
common
common
on
on
the
the
lesser
lesser
curve
curve
·
·
any
any
gastric
gastric
ulcer
ulcer
should
should
be
be
regarded
regarded
as
as
being
being
malignant,
malignant,
no
no
matter
matter
how
how
classic
classic
the
the
features
features
of
of
a
a
benign
benign
·
·
gastric
gastric
ulcer
ulcer
·
·
Multiple
Multiple
biopsies
biopsies
should
should
always
always
be
be
taken
taken
·
·
Modern
Modern
antisecretory
antisecretory
agents
agents
can
can
frequently
frequently
heal
heal
the
the
ulceration
ulceration
associated
associated
with
with
gastric
gastric
cancer
cancer
·
·
·
·
Modified
Modified
Johnson
Johnson
Classification
Classification
·
·
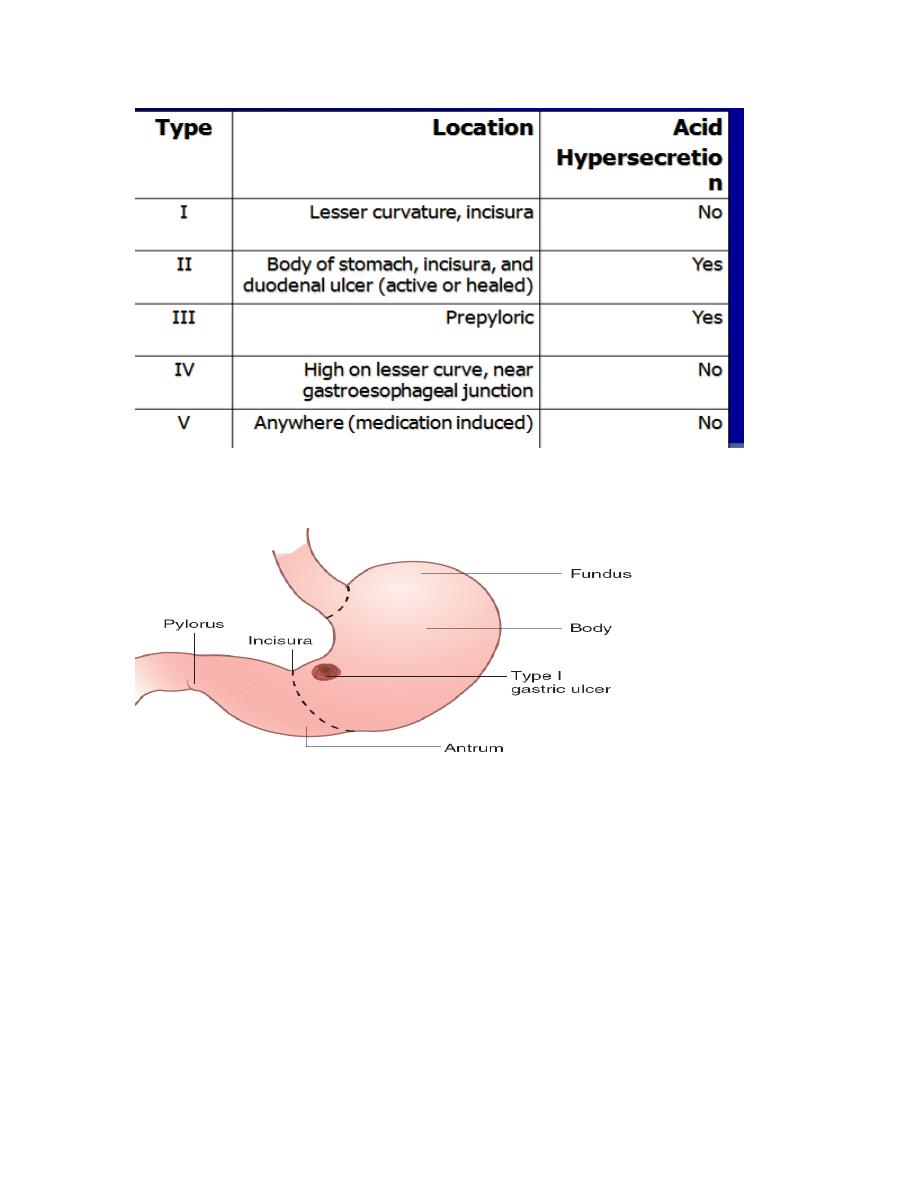
Type
Type
I
I
·
·
·
·
Lesser
Lesser
curvature;
curvature;
incisura
incisura
·
·
MOST
MOST
COMMON
COMMON
·
·
Decreased
Decreased
mucosal
mucosal
protection
protection
(no
(no
vagotomy)
vagotomy)
·
·
Distal
Distal
gastrectomy
gastrectomy
(INCLUDING
(INCLUDING
UCLER)
UCLER)
with
with
BI
BI
·
·
·
·
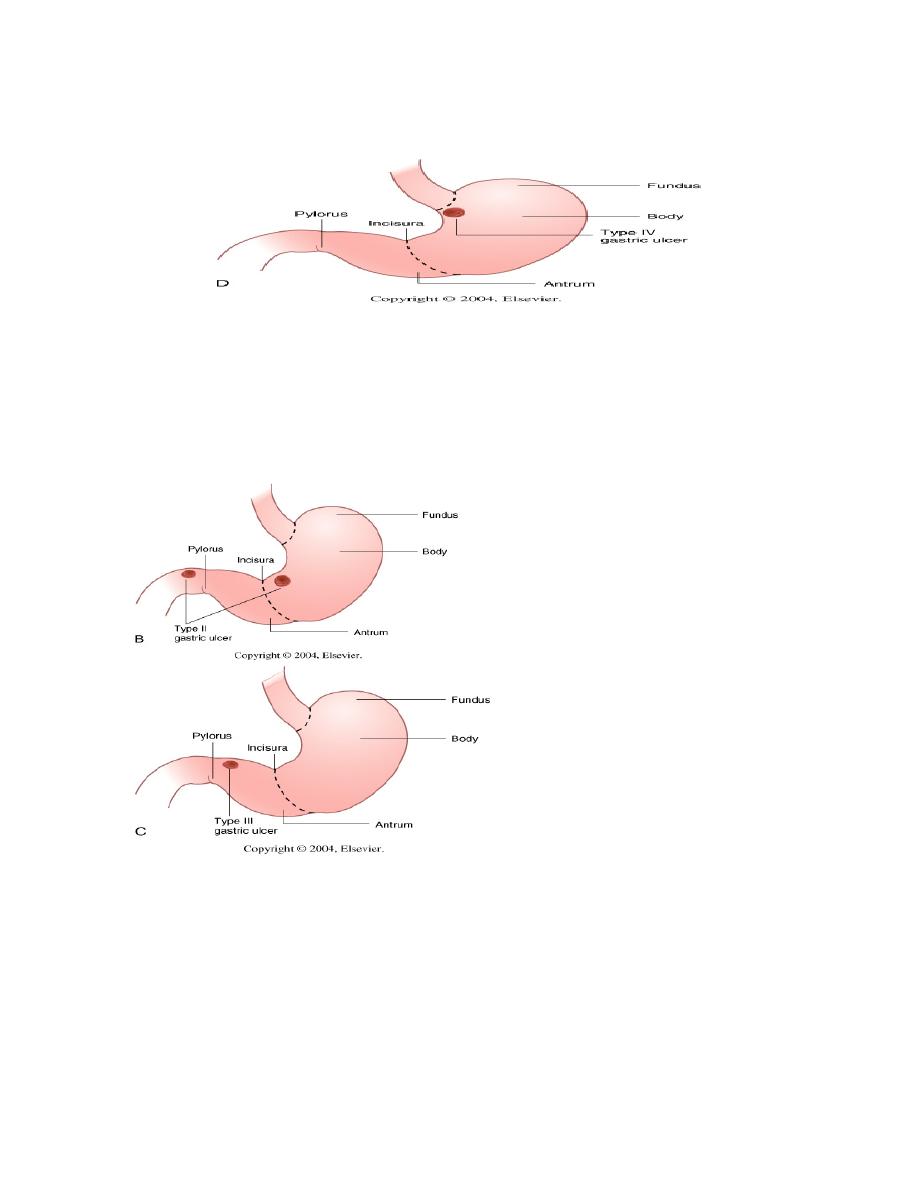
Type
Type
4
4
Ulcers
Ulcers
·
·
·
·
·
·
Least
Least
common
common
(5%
(5%
of
of
all
all
gastric
gastric
ulcers)
ulcers)
·
·
Ulcers
Ulcers
2-5cm
2-5cm
from
from
cardia
cardia
can
can
be
be
treated
treated
with
with
distal
distal
gastrectomy,
gastrectomy,
extending
extending
resection
resection
along
along
the
the
lesser
lesser
curvature
curvature
and
and
BI
BI
(Pauchet/Shoemaker
(Pauchet/Shoemaker
procedure)
procedure)
·
·
Ulcers
Ulcers
closer
closer
to
to
GEJ,
GEJ,
tongue-shaped
tongue-shaped
resection
resection
high
high
onto
onto
lesser
lesser
curve
curve
(Csendes
(Csendes
’
’
procedure
procedure
with
with
Roux-en-Y
Roux-en-Y
reconstruction)
reconstruction)
·
·
Type
Type
2/3
2/3
Ulcers
Ulcers
·
·
·
·
Acid
Acid
hypersecretion
hypersecretion
·
·
Antrectomy
Antrectomy
with
with
ulcer
ulcer
and
and
bilateral
bilateral
truncal
truncal
vagotomy
vagotomy
·
·
Billroth
Billroth
II
II
or
or
Billroth
Billroth
I
I
depending
depending
on
on
technical
technical
difficulty
difficulty
·
·
Parietal
Parietal
cell
cell
vagotomy
vagotomy
option
option
but
but
higher
higher
recurrence
recurrence
·
·
Clinical
Clinical
features
features
of
of
peptic
peptic
ulcers
ulcers
·
·
cannot
cannot
be
be
differentiated
differentiated
on
on
the
the
basis
basis
of
of
symptoms.
symptoms.
·
·
Pain
Pain
epigastric
epigastric
gnawing
gnawing
and
and
may
may
radiate
radiate
to
to
the
the
back.
back.
·
·
Eating
Eating
may
may
sometimes
sometimes
relieve
relieve
the
the
discomfort
discomfort

·
·
The
The
pain
pain
is
is
normally
normally
intermittent
intermittent
·
·
2
2
-
-
Periodicity
Periodicity
Symptoms
Symptoms
may
may
disappear
disappear
for
for
weeks
weeks
or
or
months
months
to
to
return
return
again
again
·
·
3-Vomiting
3-Vomiting
·
·
4-Alteration
4-Alteration
in
in
weight
weight
·
·
5-Bleeding
5-Bleeding
All
All
peptic
peptic
ulcers
ulcers
may
may
bleed.
bleed.
The
The
bleeding
bleeding
may
may
be
be
·
·
chronic
chronic
and
and
presentation
presentation
with
with
microcytic
microcytic
anaemia
anaemia
is
is
not
not
uncommon
uncommon
,
,
·
·
Acute
Acute
presentation
presentation
with
with
haematemesis
haematemesis
and
and
melaena
melaena
·
·
Clinical
Clinical
examination
examination
of
of
the
the
patient
patient
may
may
reveal
reveal
epigastric
epigastric
tenderness
tenderness
