
Prof Dr Amira Shubbar
MRCP, FRCP
A.F.A.

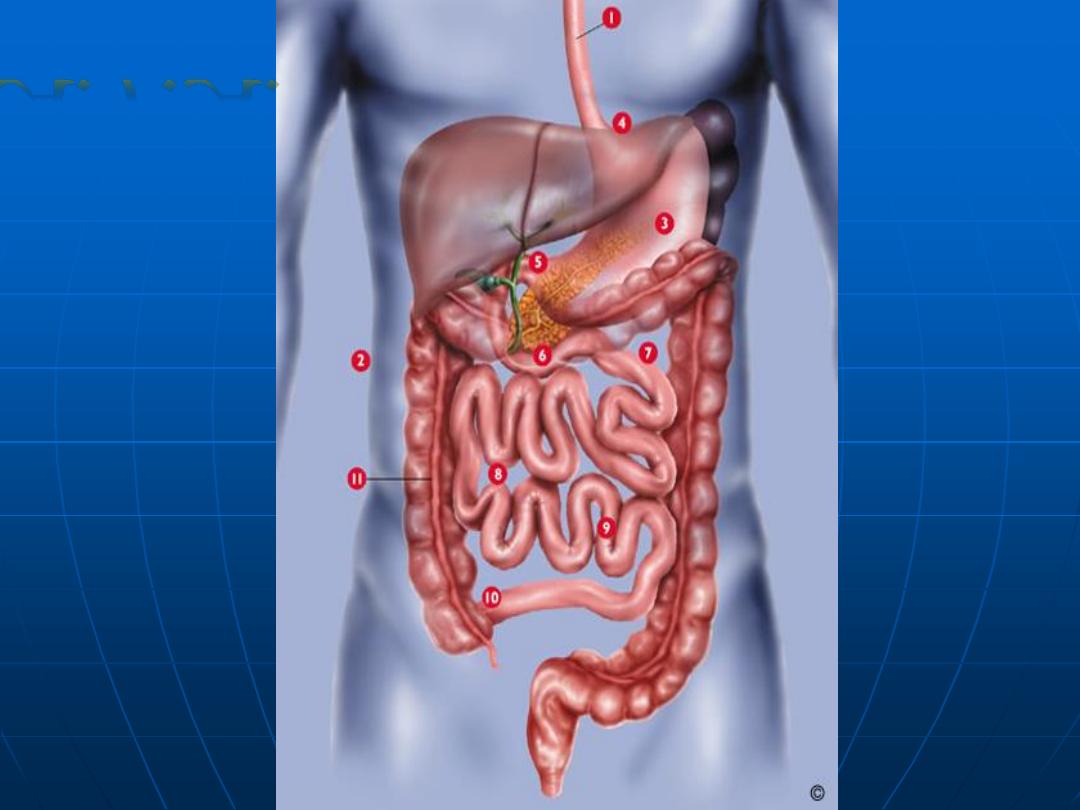
Upper esoph.
sphincter
Lower esop.
Sphincter
Pylorus
Ileocecal
Valve
Anal
sphincter
Receptive relaxation
Regulated emptying
Migrating
motor
complex
Segmenatation
Propulsive
peristaltic
contraction
A.F.A.
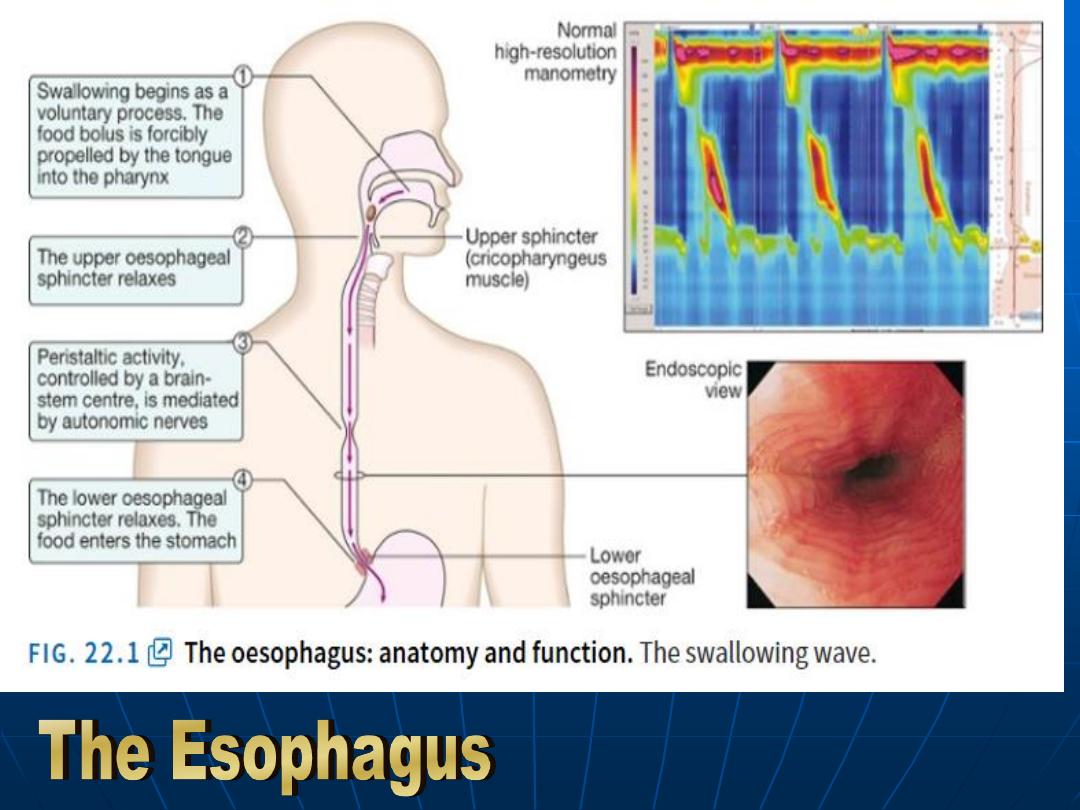
Anatomy & Function
(The swallowing wave)
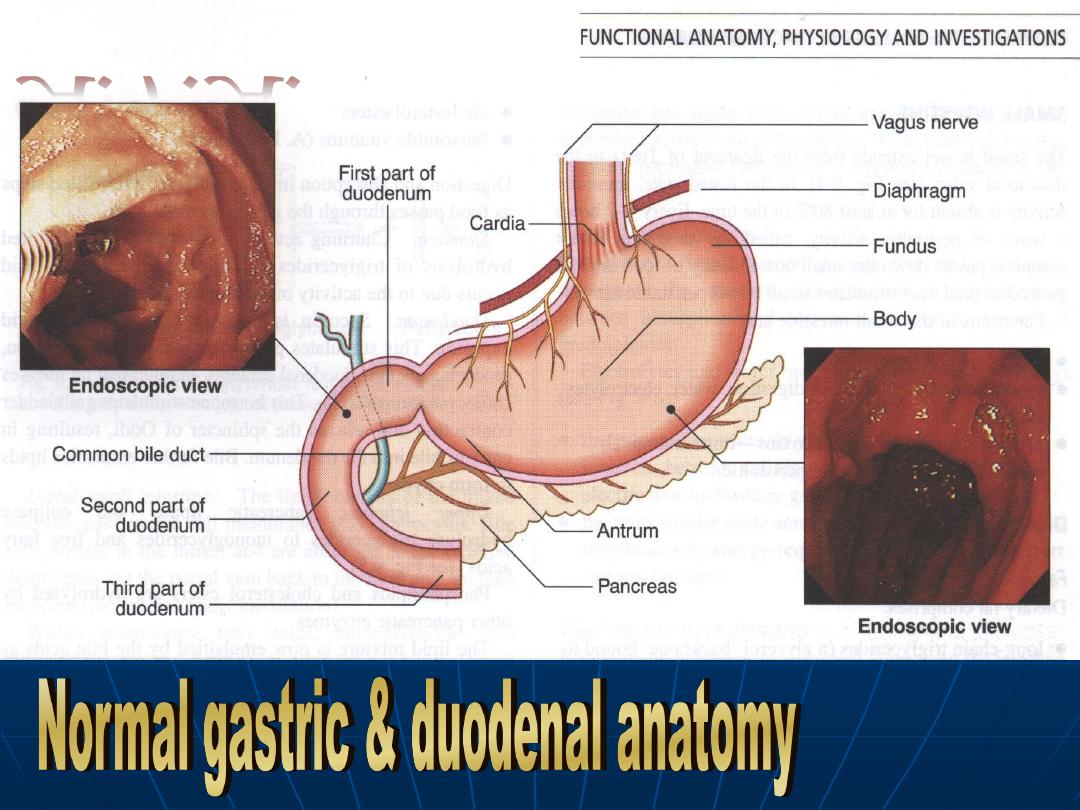
A.F.A.
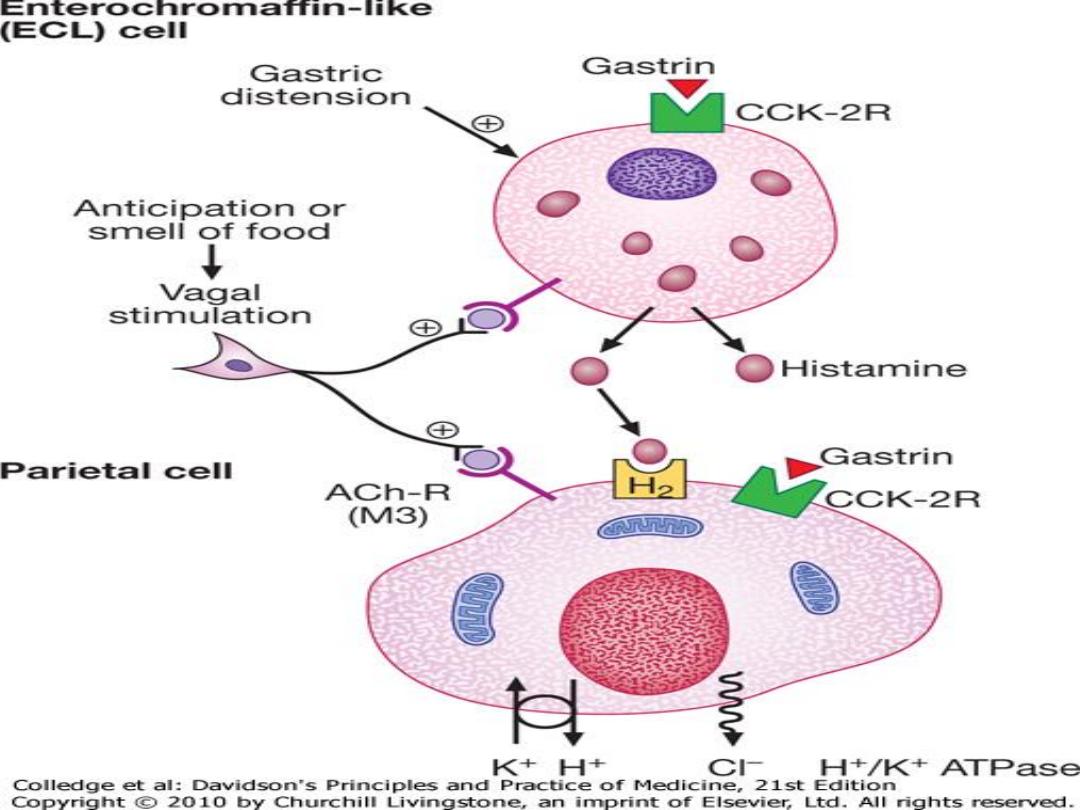

Gastric secretion
Parietal cells :HCL + Intrinsic factor.
Chief cells :Pepsinogen +mucus.
G cells :Gastrin.
D cells : Somatostatin.
Protective factors: Mucus +
Bicarbonate
Oxyntic gland: ghrelin
A.F.A.

Gastric distension & food stimulate the release
of Gastrin from G cells which will act on CCk-
2R on ECL cells releasing Histamine which will
act on H2 receptors in the Parietal cells.
Gastrin act direct on the Parietal cells too.
Vagal stimulation through anticipation or smell
of food act on the Ach-R M3 receptors on the
parietal cells
Hydrogen + Chloride are secreted in response
to H/K ATPase (Proton pump ) from the apical
membrane of the Parietal cell.
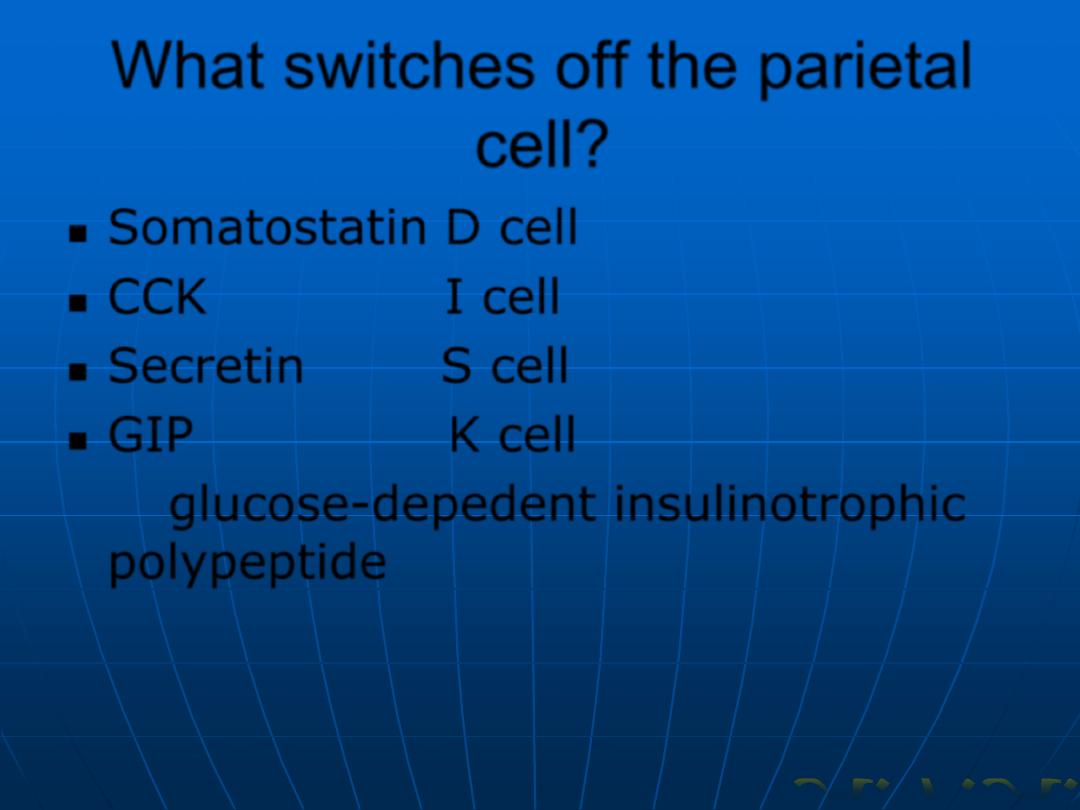
What switches off the parietal
cell?
Somatostatin D cell
CCK I cell
Secretin
S cell
GIP K cell
glucose-depedent insulinotrophic
polypeptide
A.F.A.
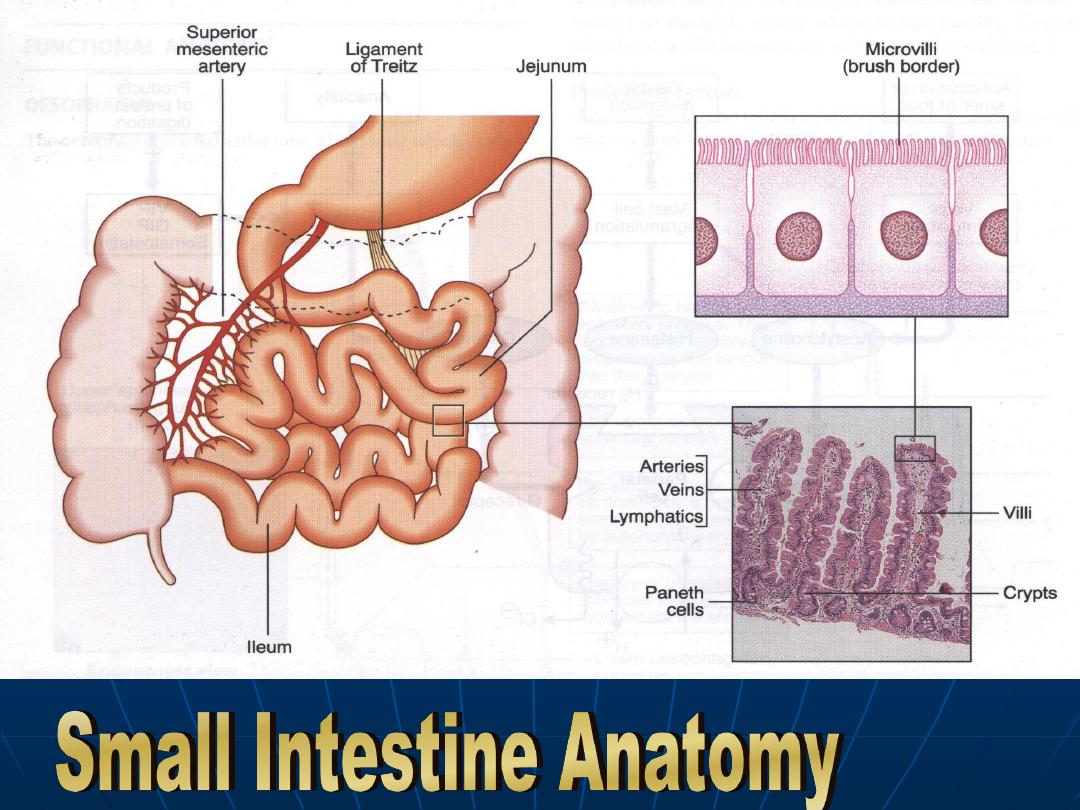

Functions of the small intestine
Digestion
Absorption
Protection against ingested toxins &
immune regulation.
A.F.A.
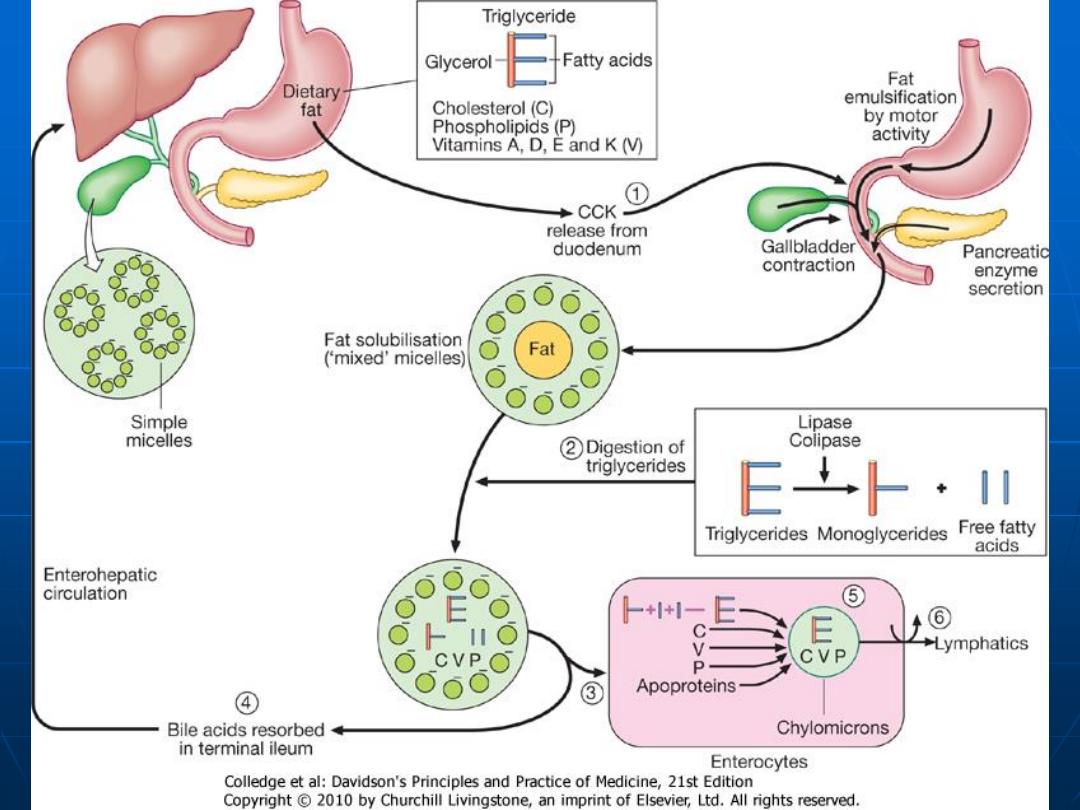

Carbohydrates
Starch Alpha-limit dextrins
containing 4-8 glucose molecules.
Disaccharide Maltose
Trisaccharide
Maltotriose
Disaccharides are digested by enz. in
microvilli to monosaccharides glucose ,
fructose & galactose which diffuse through
enterocytes
A.F.A.

Protein
Protein in the stomach converted by pepsin to
A.A & polypeptide which stimulate secretion of
pancreatic proenzymes trypsinogen ,
chymotrypsinogen , proelastases &
procarboxypeptidase.
Trypsinogen converted to trypsin on enterocyte
brush border .
Protein digested by trypsin to oligopeptides &
A.A.
Oligopeptides hydrolyzed to dipeptides ,
tripeptide & A.A then actively transported into
the enterocytes & then to the portal circulation.
A.F.A.
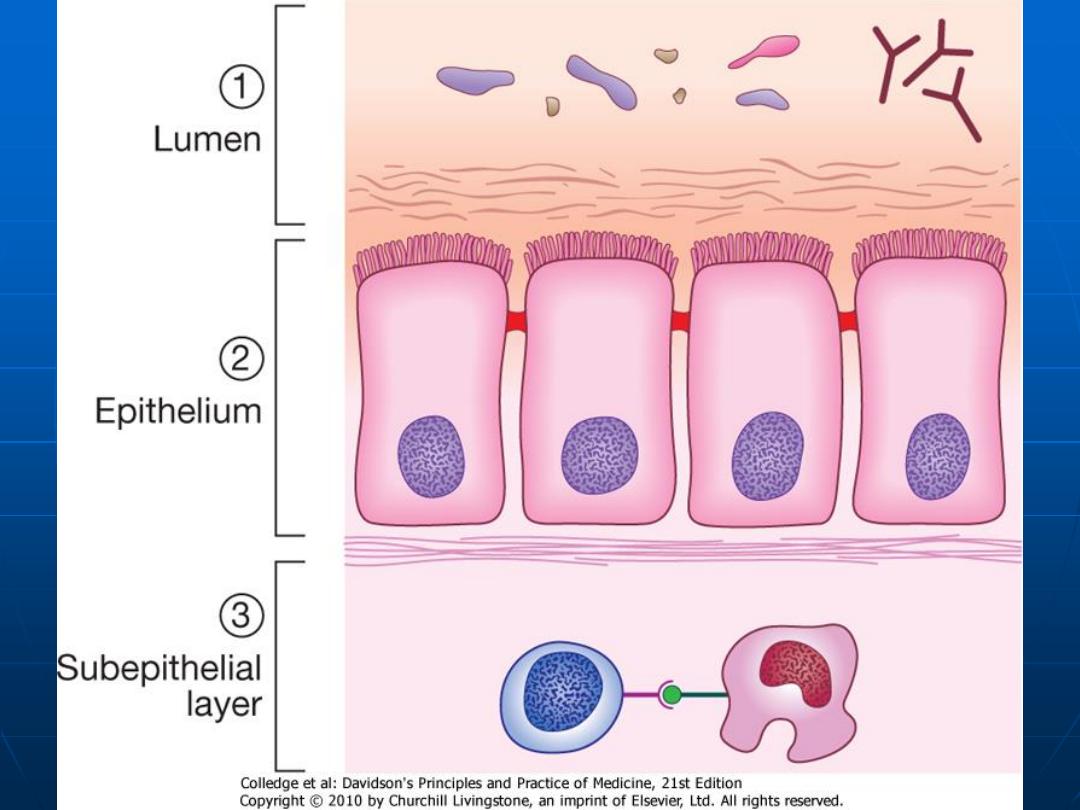

Protective Function of the small
intestine
Immunology
& T Lymphocytes , Macrophages &
Mast cells are found through out GIT.
MALT :constitute 25% of total lymphatic tissue of
the body.
Luminal Ag stimulate B cells to Plasma cell in
peyers patches to mesenteric LN then thoracic
duct & blood stream & lamina propria & secret
IgA.
T lymphocyte localize the plasma cell at the site
of Ag.
Macrophages: Phagocyte foreign material &
secret cytokines.
A.F.A.

Mucosal Barrier
Mucus.
Enterocytes membranes & tight
junctions between them.
Renewal of the intestinal cells every
48 hours.
A.F.A.

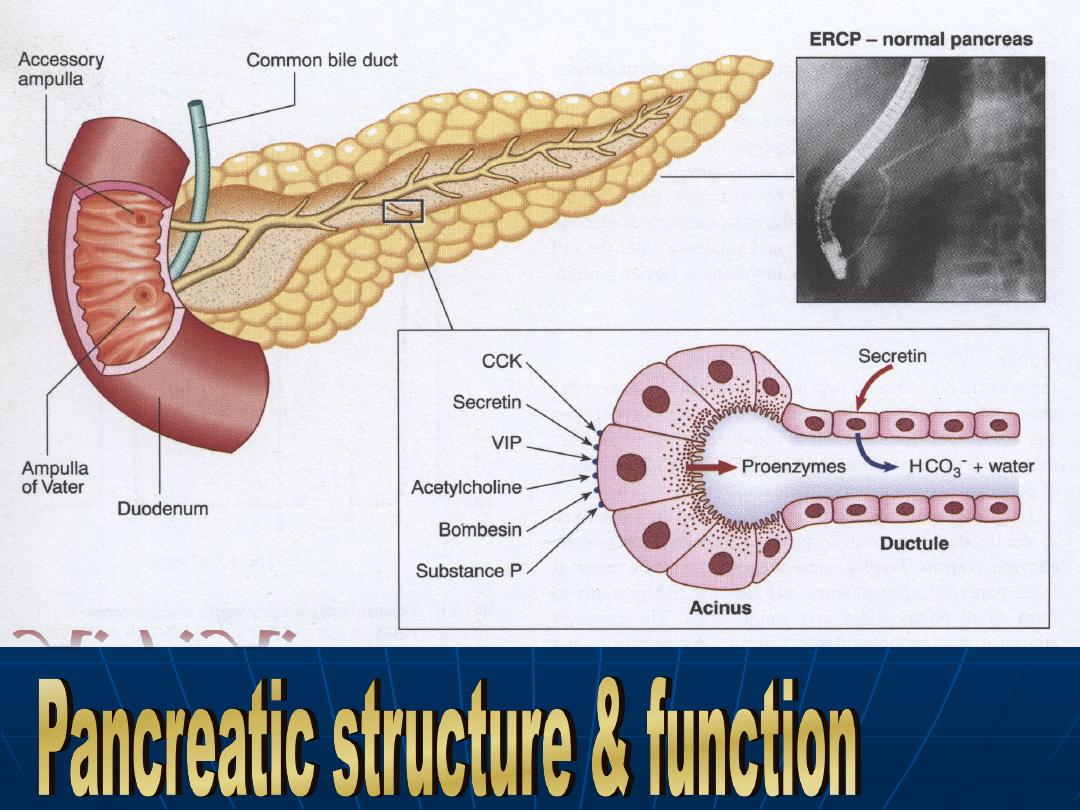
Pancreas
Exocrine pancreas is necessary for
the digestion of
protein , fat &
carbohydrate.
Pancreatic enzymes:
Amylase: Starch & glycogen
Lipase: TG
Colipase: TG
Proteolytic enzymes: Protein &
polypeptide.
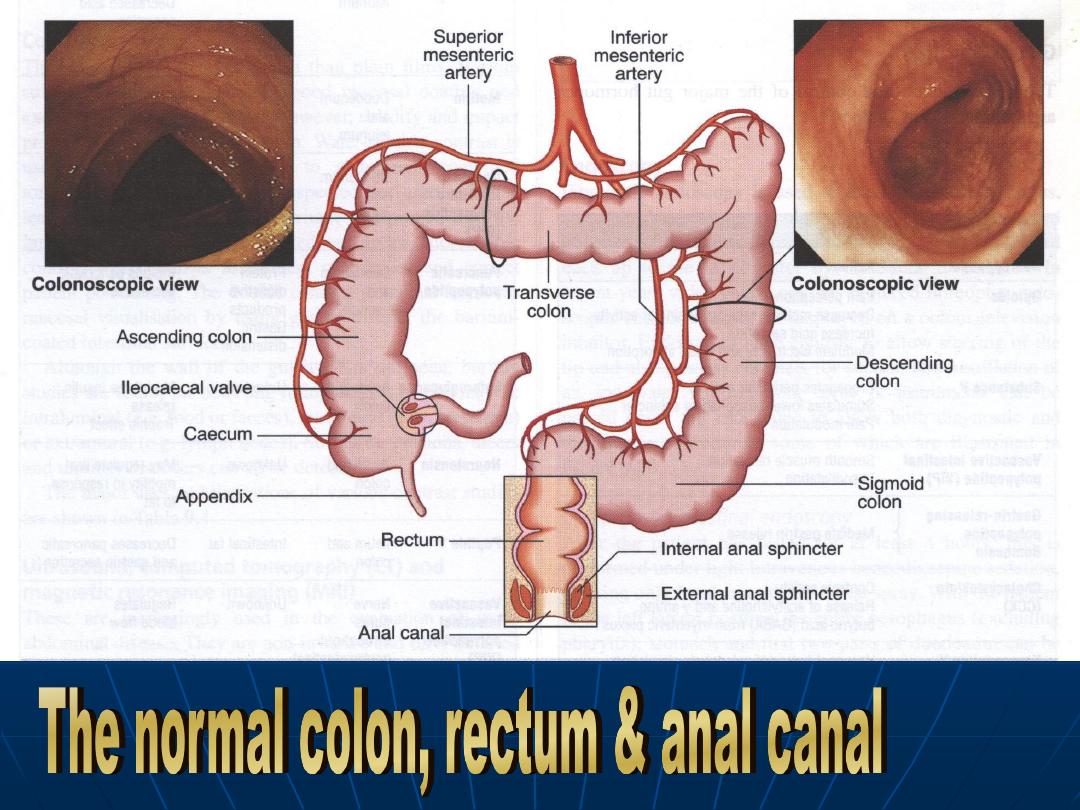

Colon
For absorption of water &
electrolytes & storage organ.
Contractile activity :
Segmentation.
Peristaltic contraction
A.F.A.
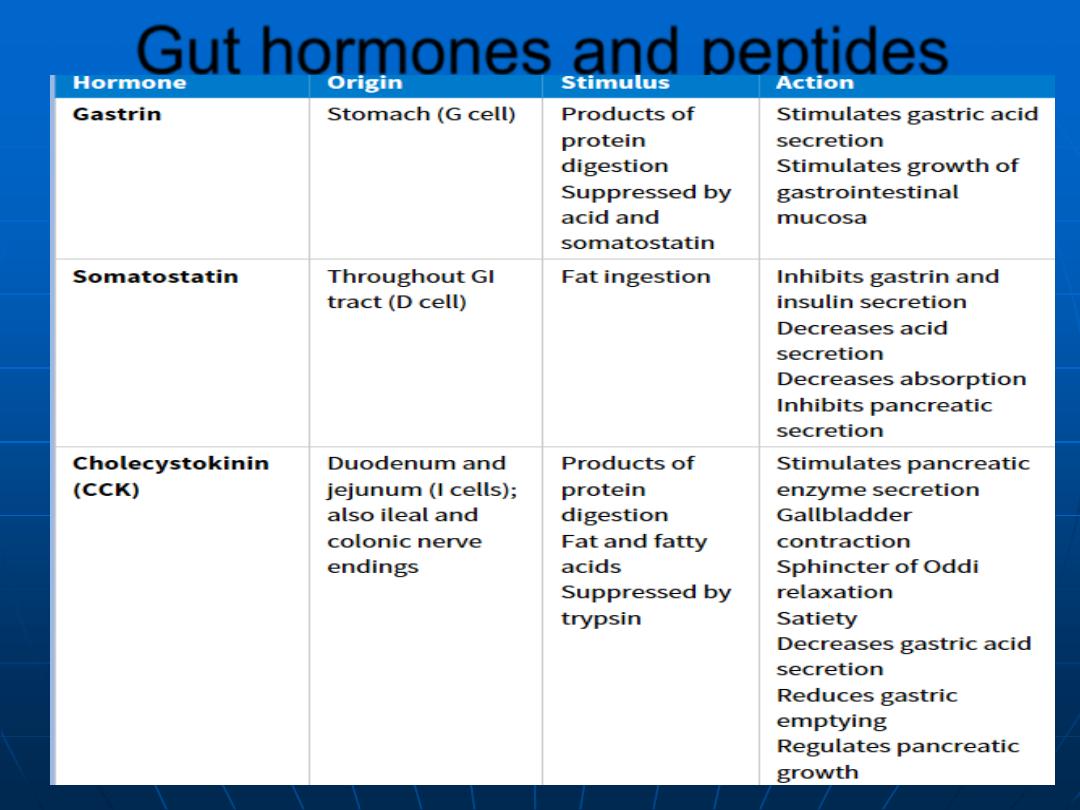
Gut hormones and peptides
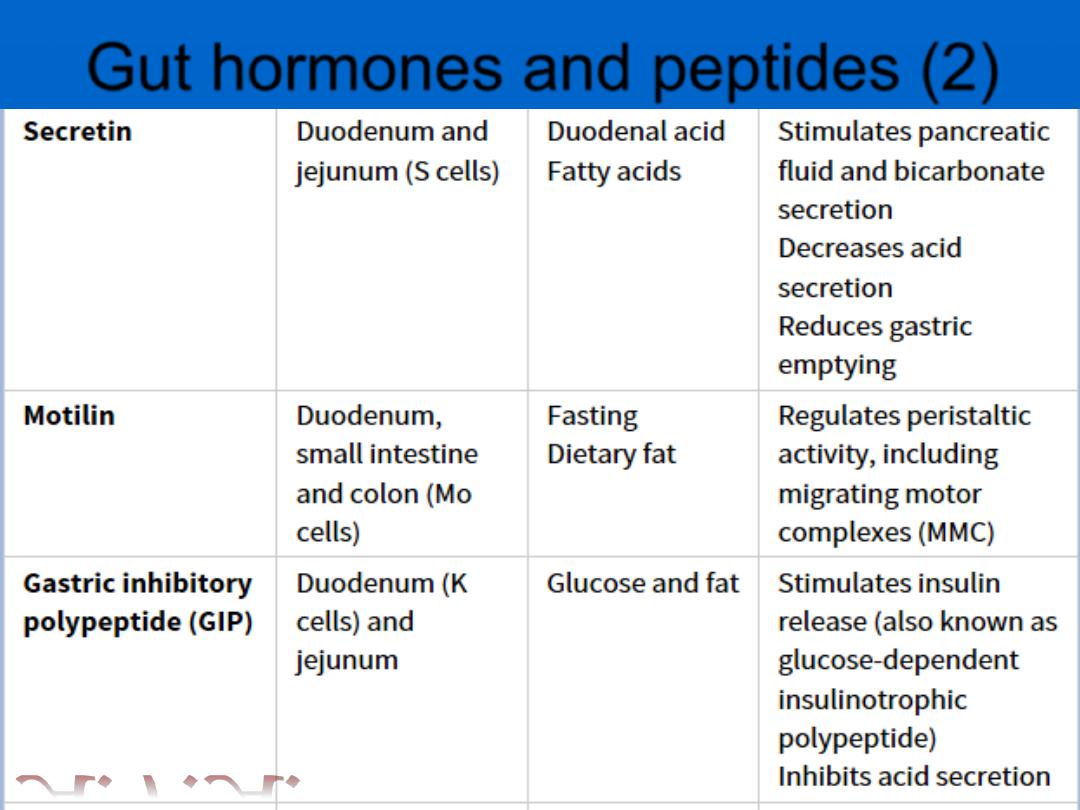
Gut hormones and peptides (2)
A.F.A.
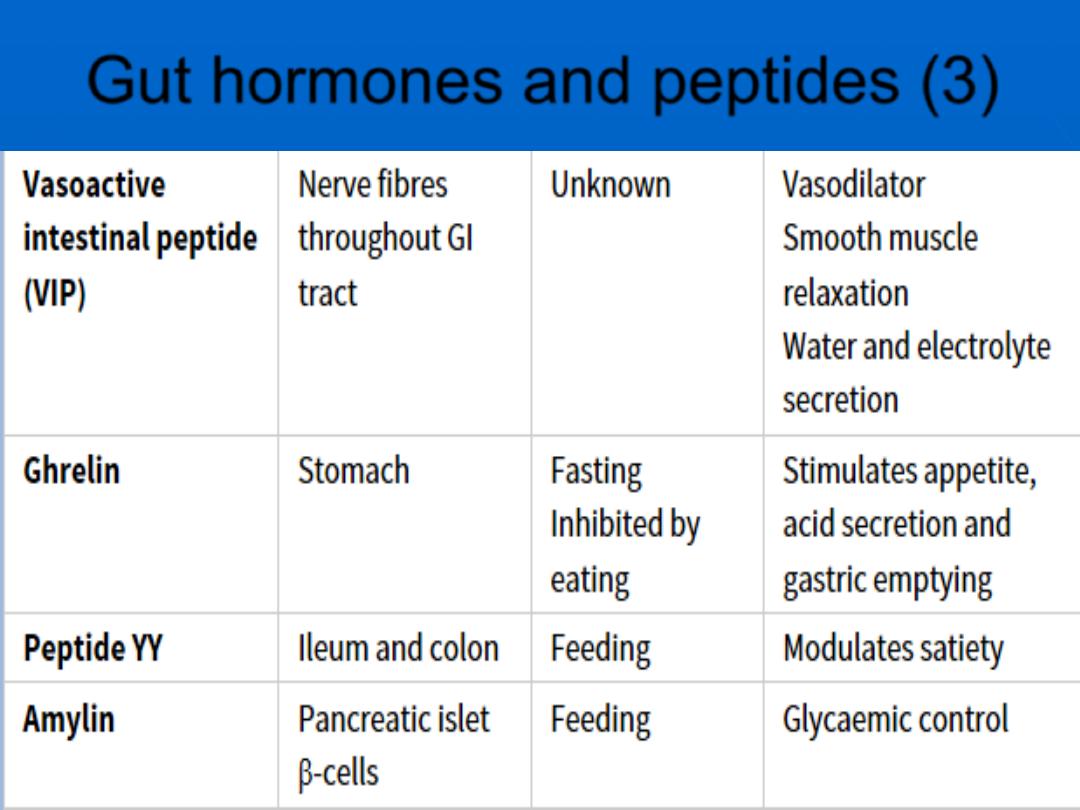
Gut hormones and peptides (3)

A.F.A.
Investigations
of GIT diseases
Tests of structures
Tests of infection
Tests of function
Imaging
Histology
US, CT
MRI
Endoscopy
Contrast
studies
Plain
Radiograph
Bacterial
culture
Serology
Breath
Tests
Pancreatic
Exocrine
function
Mucosal
Inflammation/
permeability
Absorption
GIT
Motility
Radioisotope
Tests

A.F.A.

It is useful in diagnosis of intestinal
obstruction or paralytic ileus
The outlines of soft tissues e.g. liver,
spleen kidneys may be visible
Calcification in the abdominal structures
as well as calculi can be detected
Abdominal radiographs are not useful in
GIT bleeding
CXR shows the diaphragm and erect films
may detect sub-diaphragmatic free air in
cases of perforation
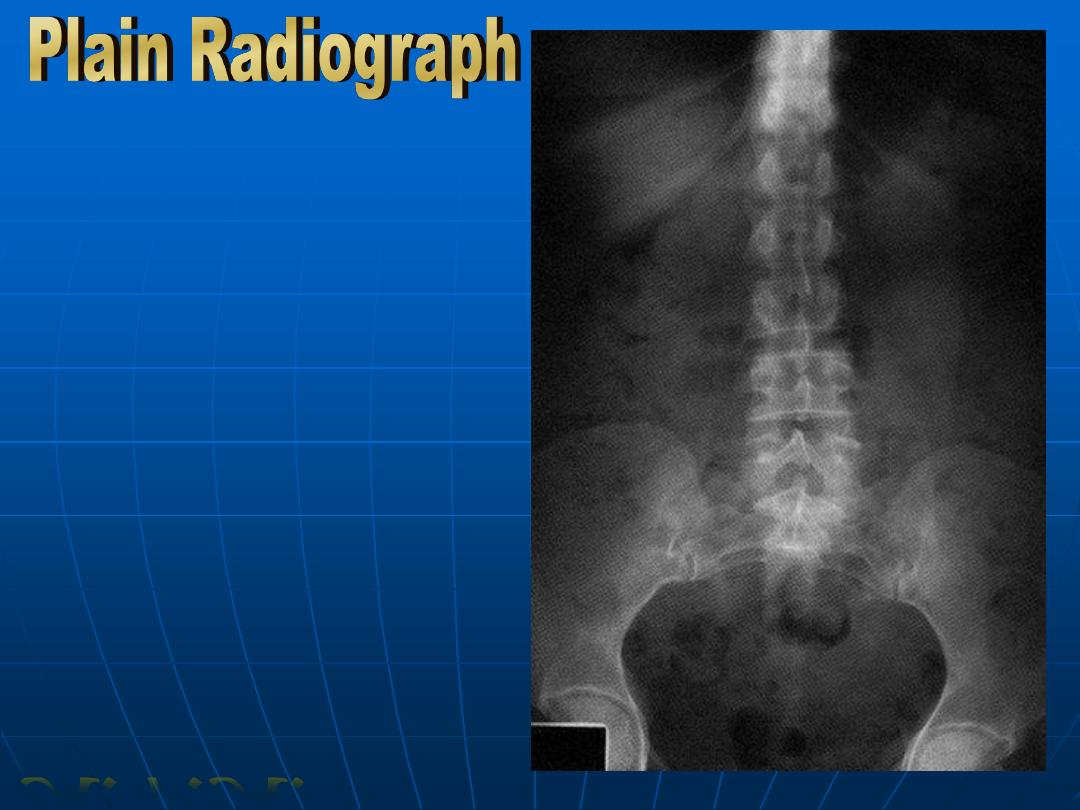
Normal Plain
Abdominal
Radiograph
A.F.A.
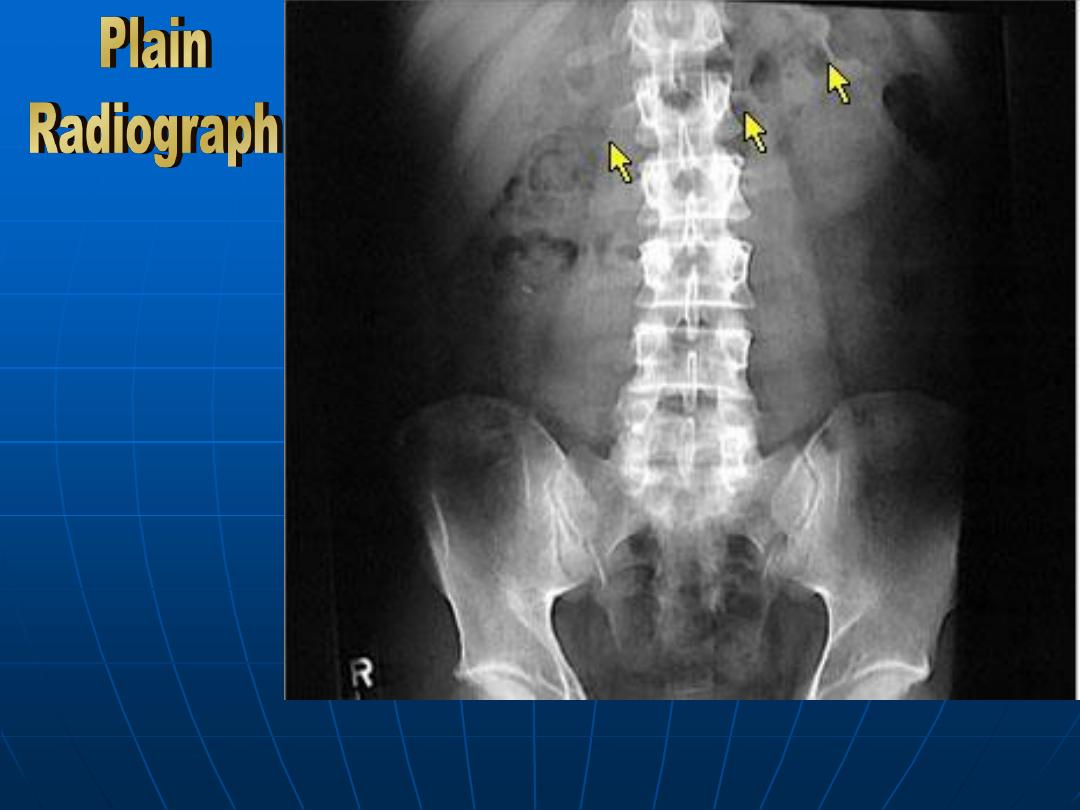
Normal Plain
Abdominal
Radiograph
showing the
identification
of transverse
colon
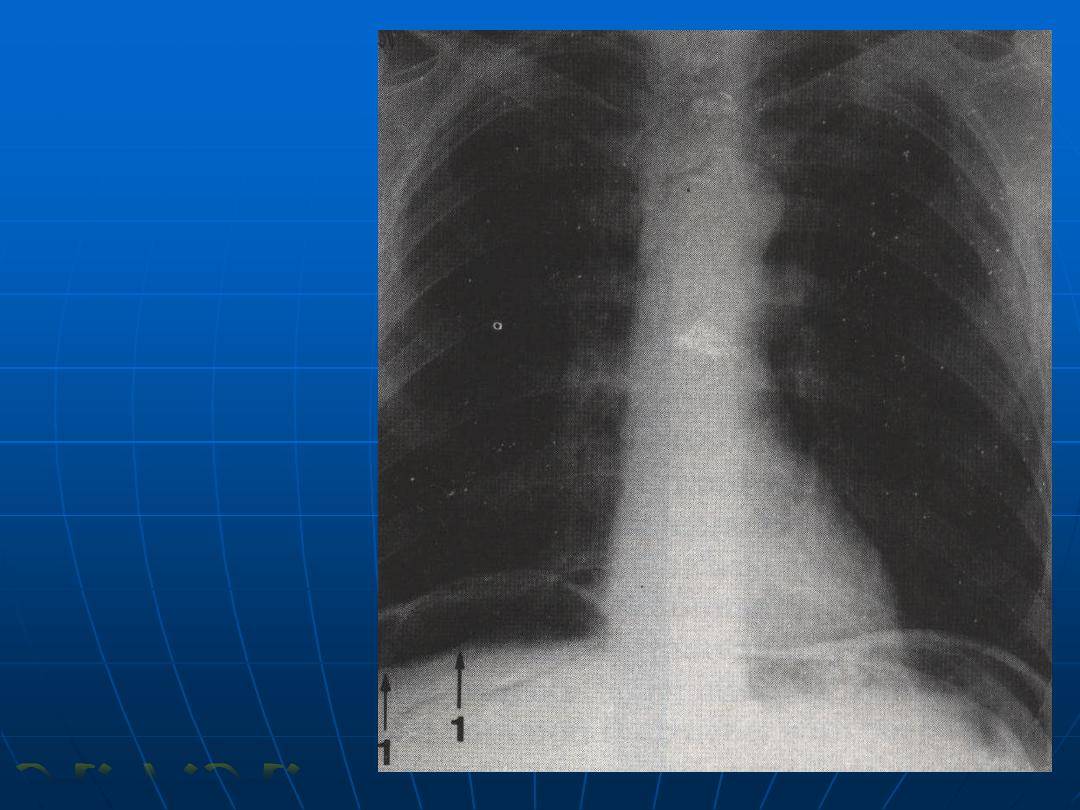
Air under the
diaphragm
(perforated DU)
A.F.A.
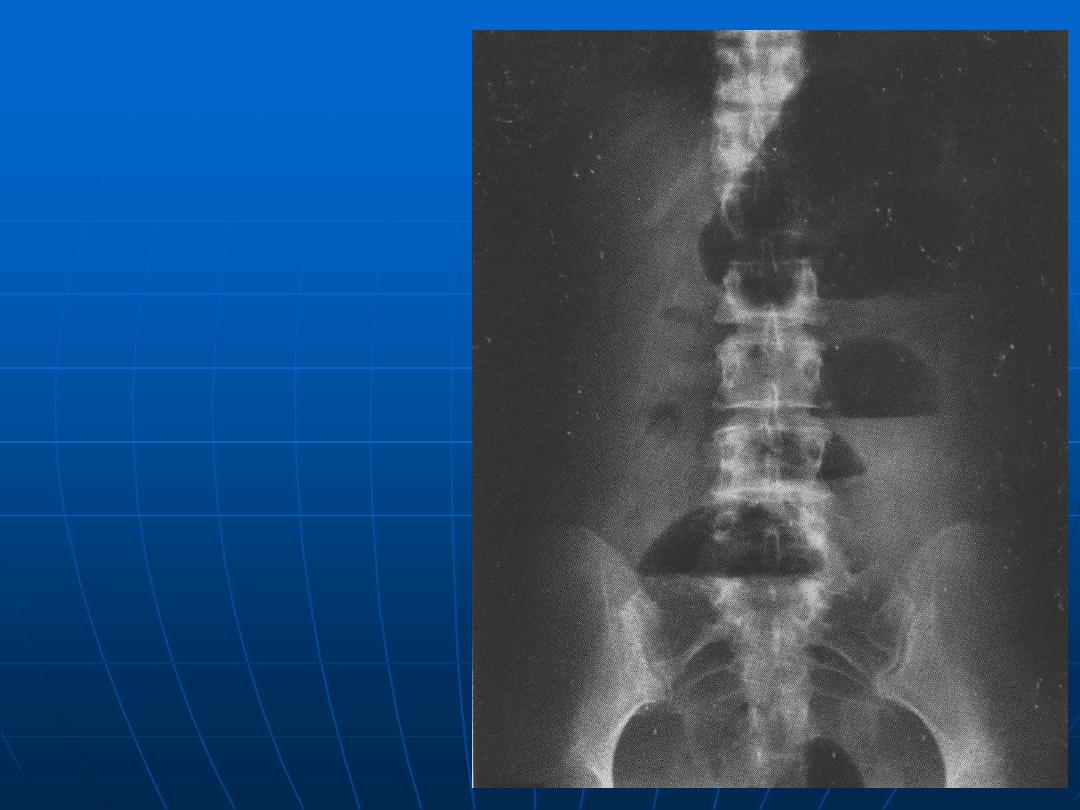
Small Intestinal
obstruction
(multiple fluid levels)
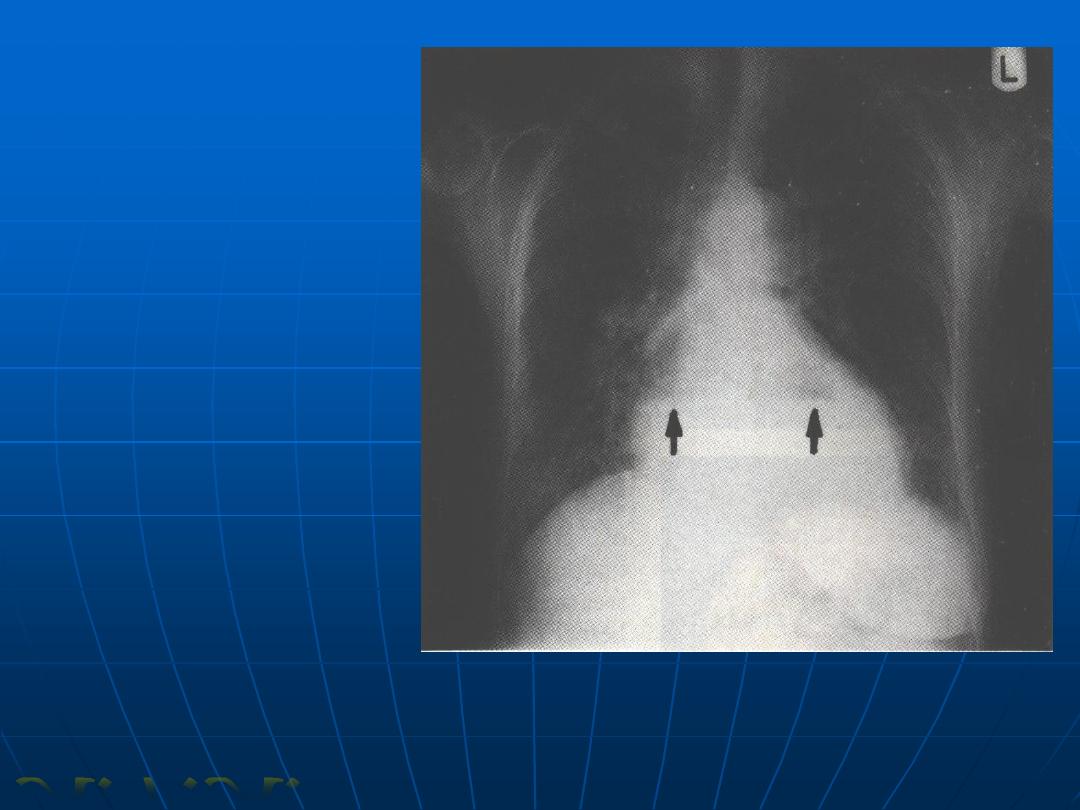
Hiatus hernia
(fluid levels behind
the heart)
A.F.A.
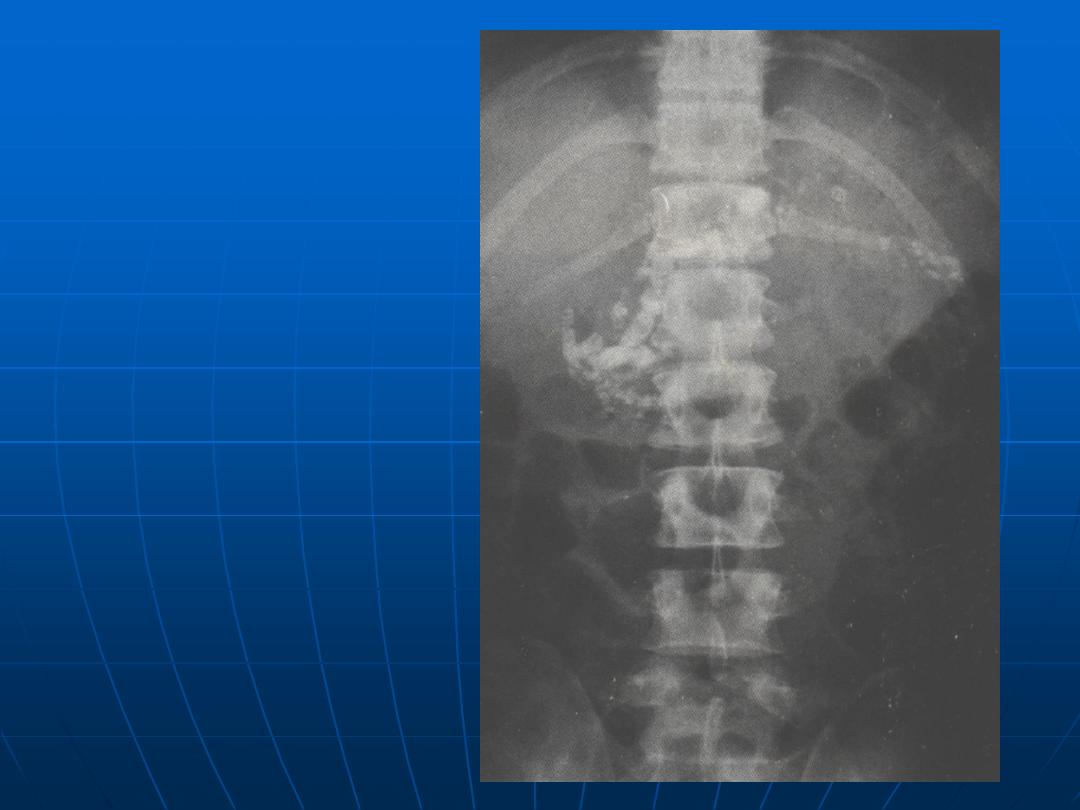
Calcification of the
pancreas
(chronic pancreatitis)
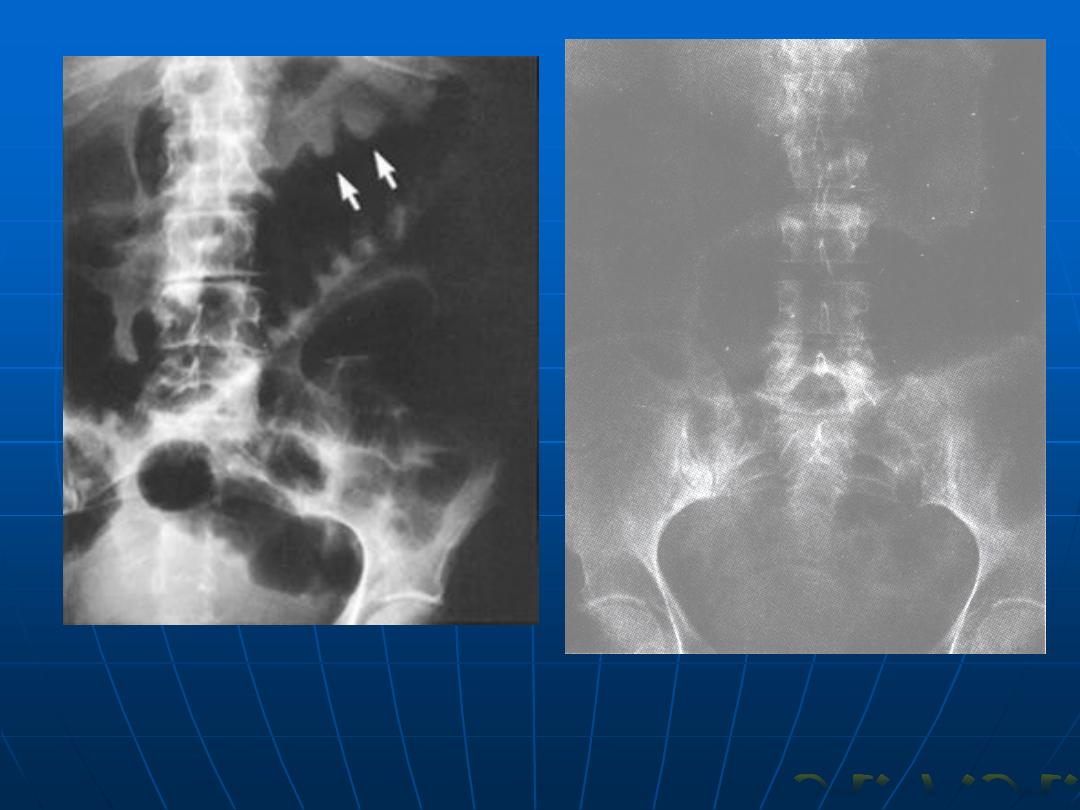
Toxic megacolon
A.F.A.
Investigations
of GIT diseases
Tests of structures
Tests of infection
Tests of function
Imaging
Histology
US, CT
MRI
Endoscopy
Contrast
studies
Plain
Radiograph
Bacterial
culture
Serology
Breath
Tests
Pancreatic
Exocrine
function
Mucosal
Inflammation/
permeability
Absorption
GIT
Motility
Radioisotope
Tests

A.F.A.
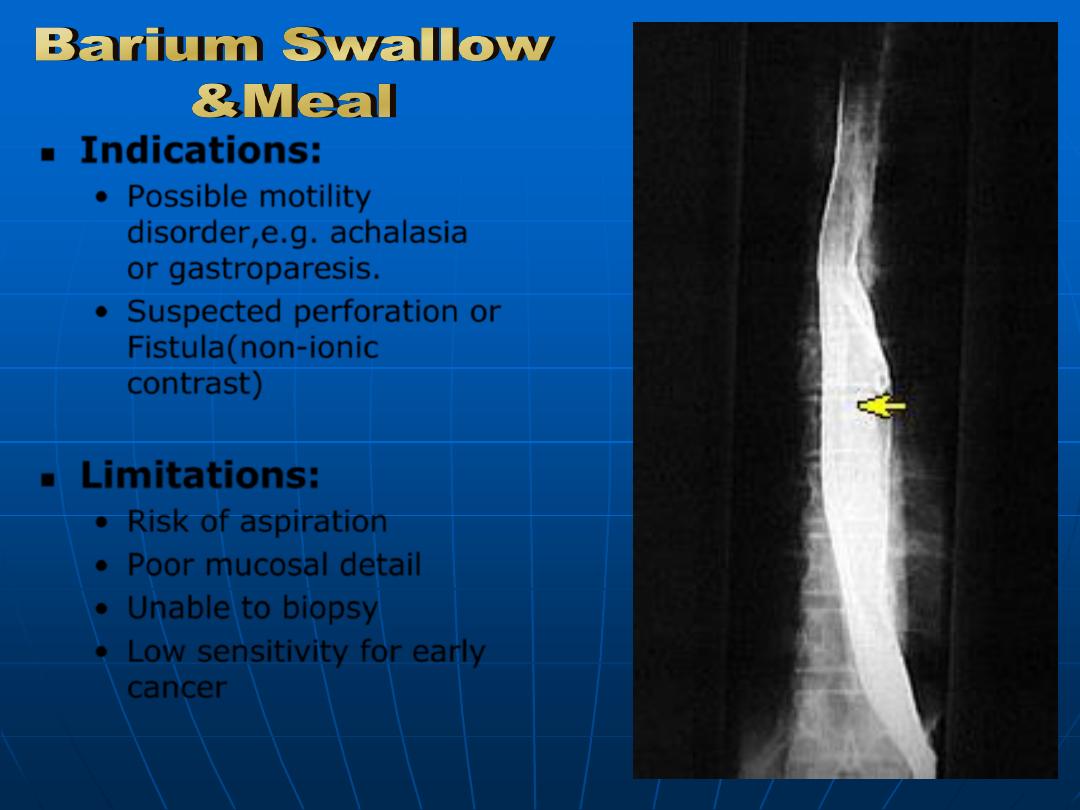
Indications:
•
Possible motility
disorder,e.g. achalasia
or gastroparesis.
•
Suspected perforation or
Fistula(non-ionic
contrast)
Limitations:
•
Risk of aspiration
•
Poor mucosal detail
•
Unable to biopsy
•
Low sensitivity for early
cancer
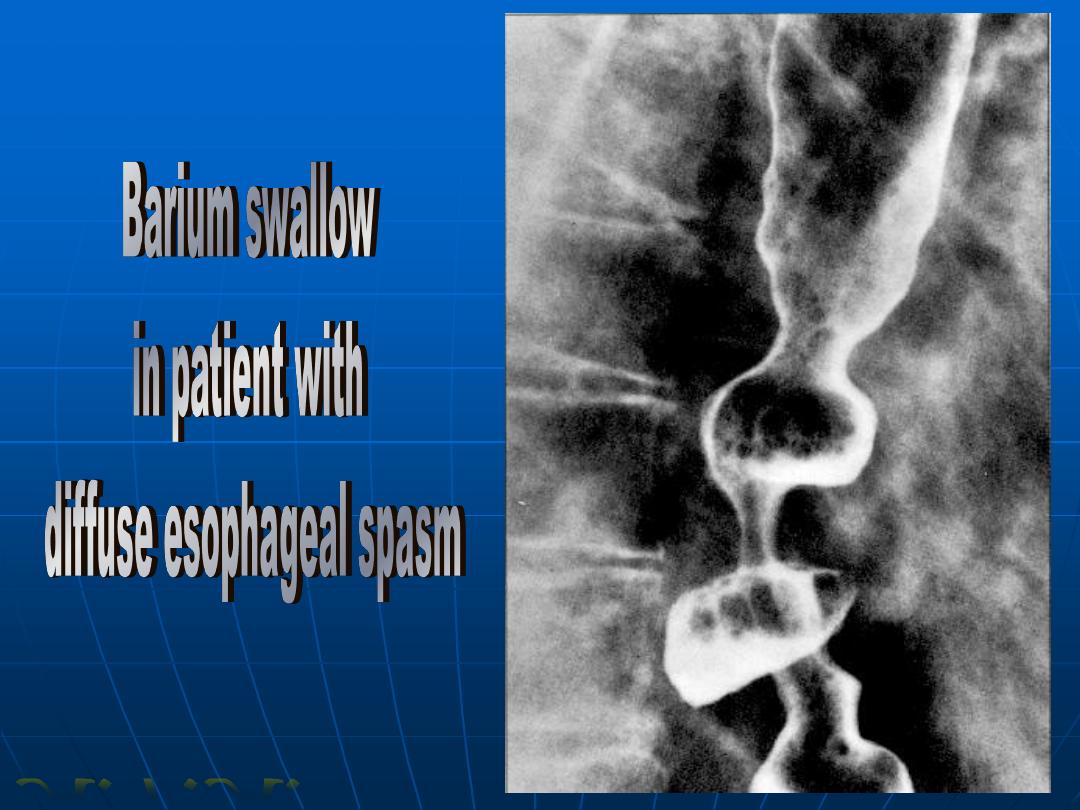
A.F.A.
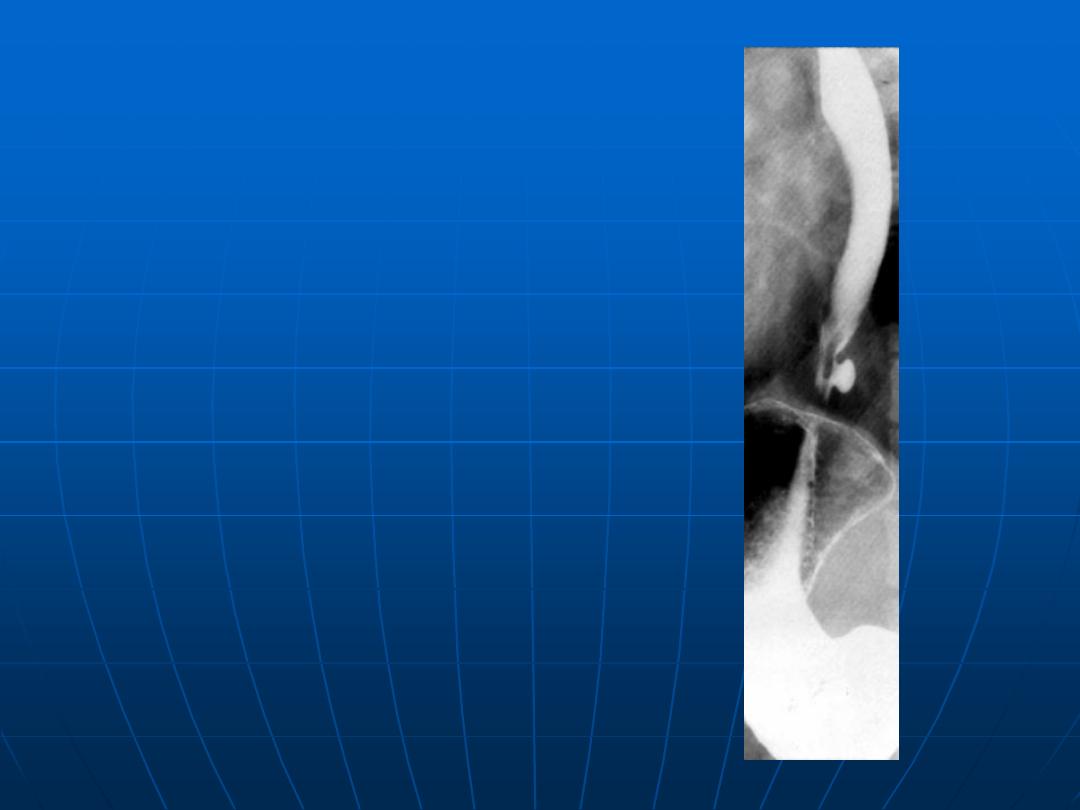
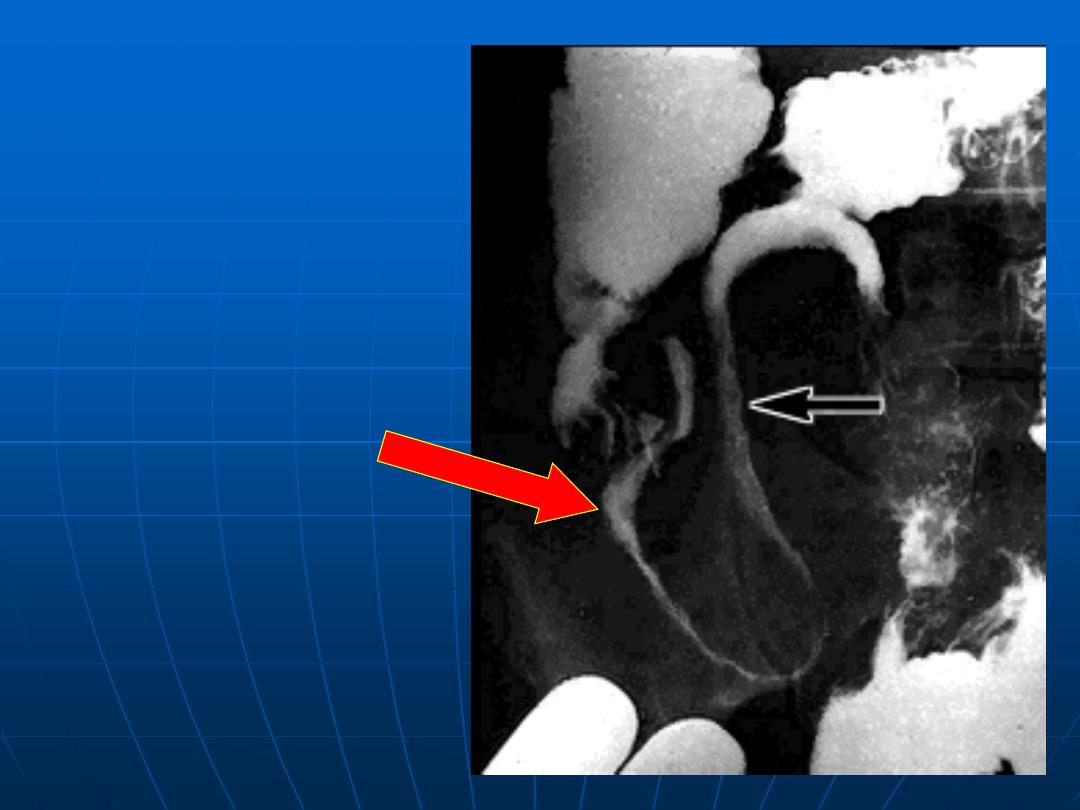
Epiphrenic
diverticulum as
shown by
barium swallow
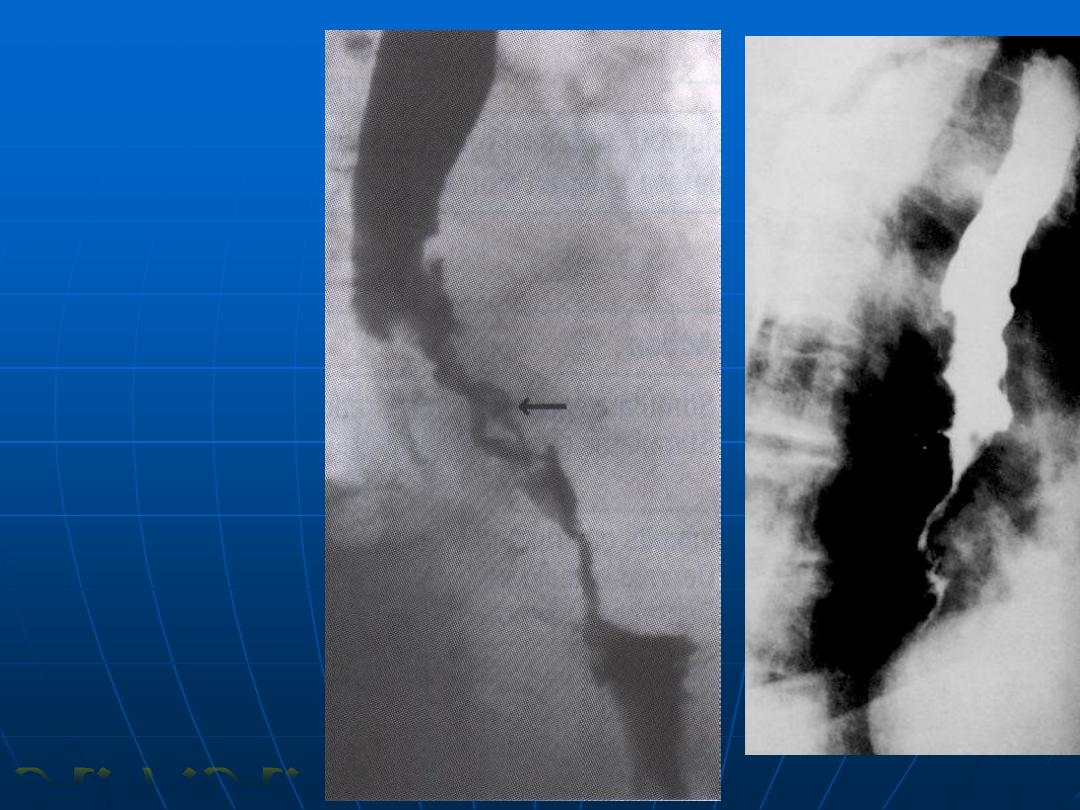
Esophageal
carcinoma
A.F.A.
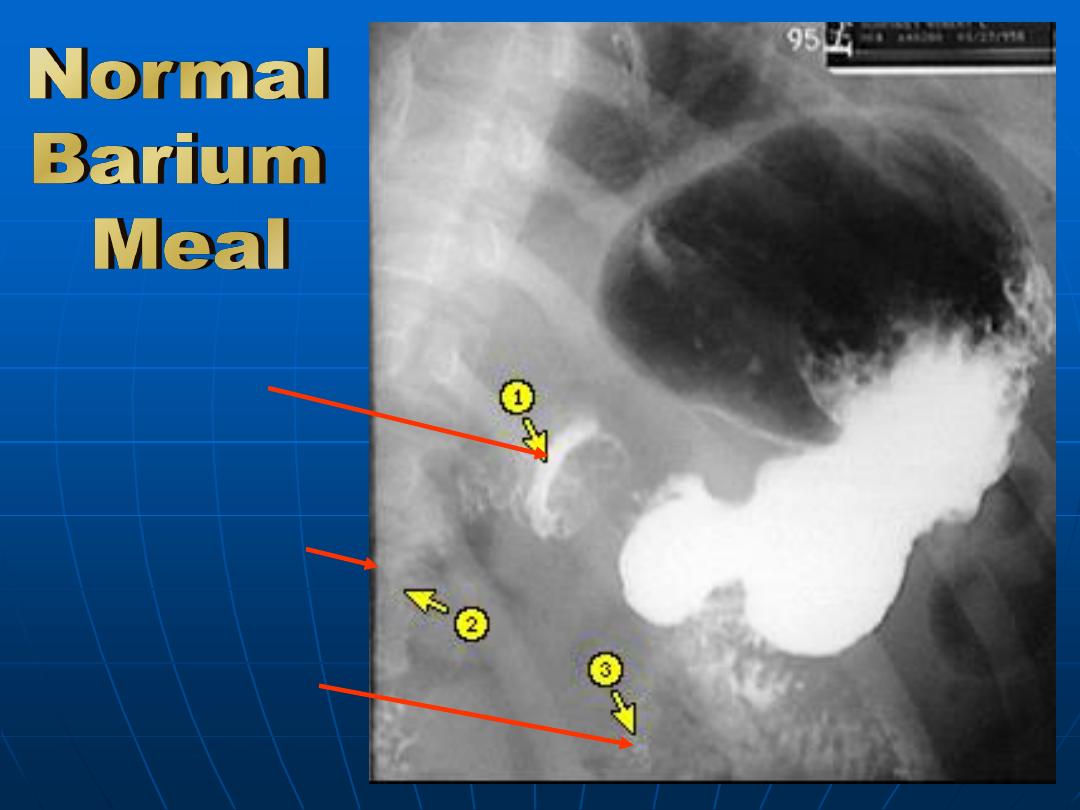
Duodenal
bulb
Descending
duodenum
Ascending
duodenum
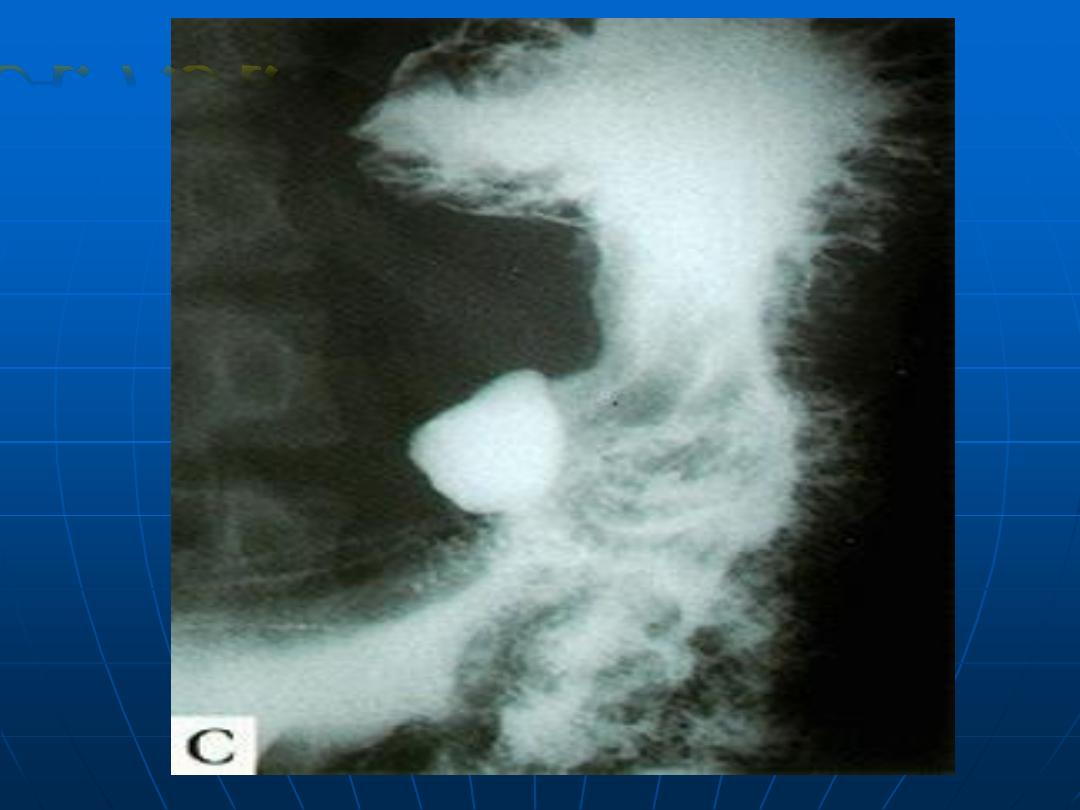
Gastric ulcer
A.F.A.
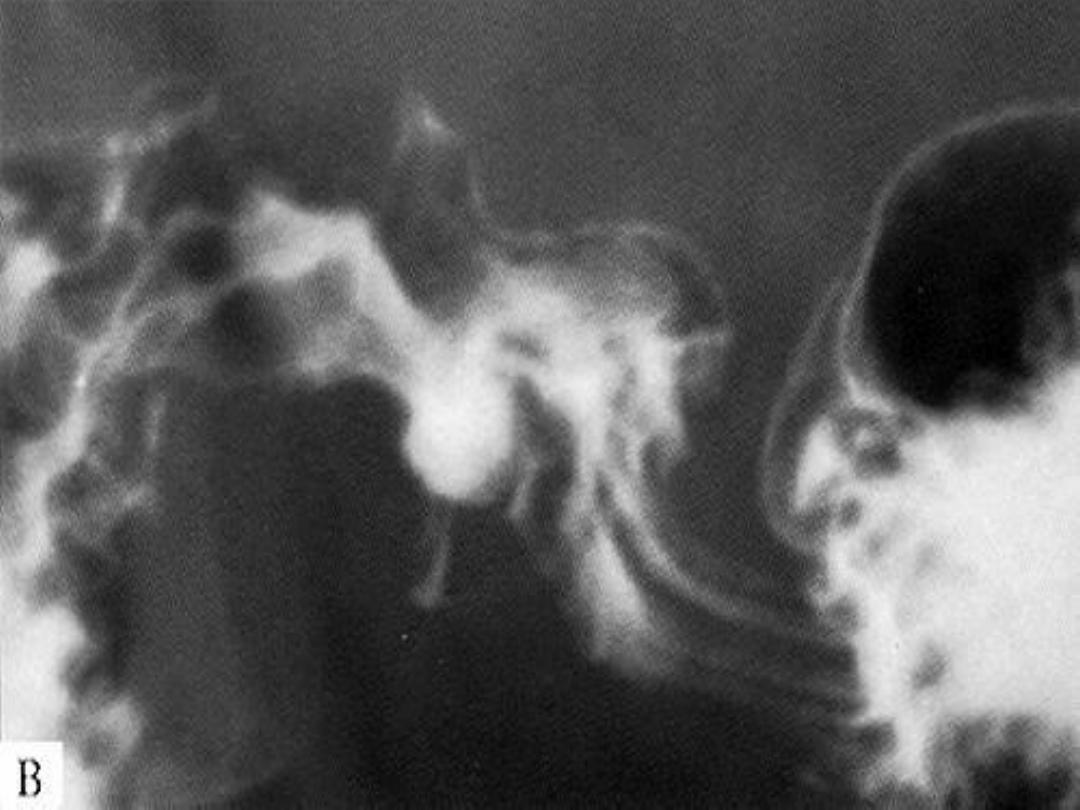
Duodenal ulcer
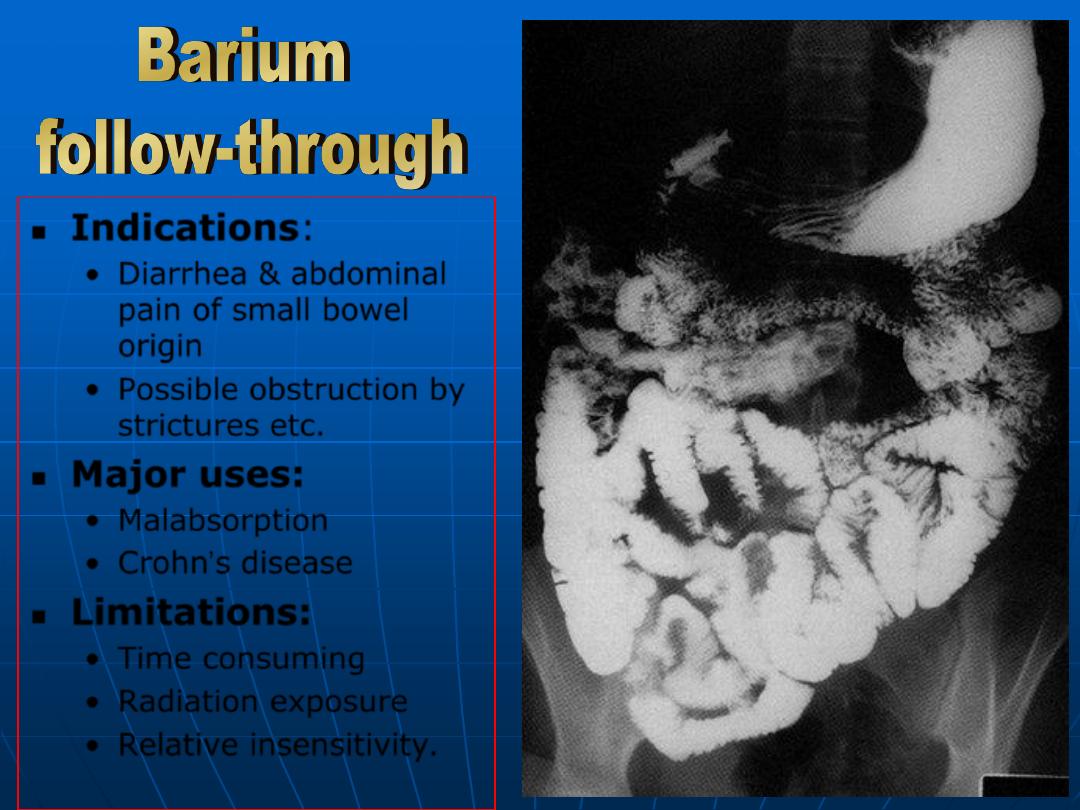
Indications
:
•
Diarrhea & abdominal
pain of small bowel
origin
•
Possible obstruction by
strictures etc
.
Major uses:
•
Malabsorption
•
Crohn’s disease
Limitations:
•
Time consuming
•
Radiation exposure
•
Relative insensitivity
.
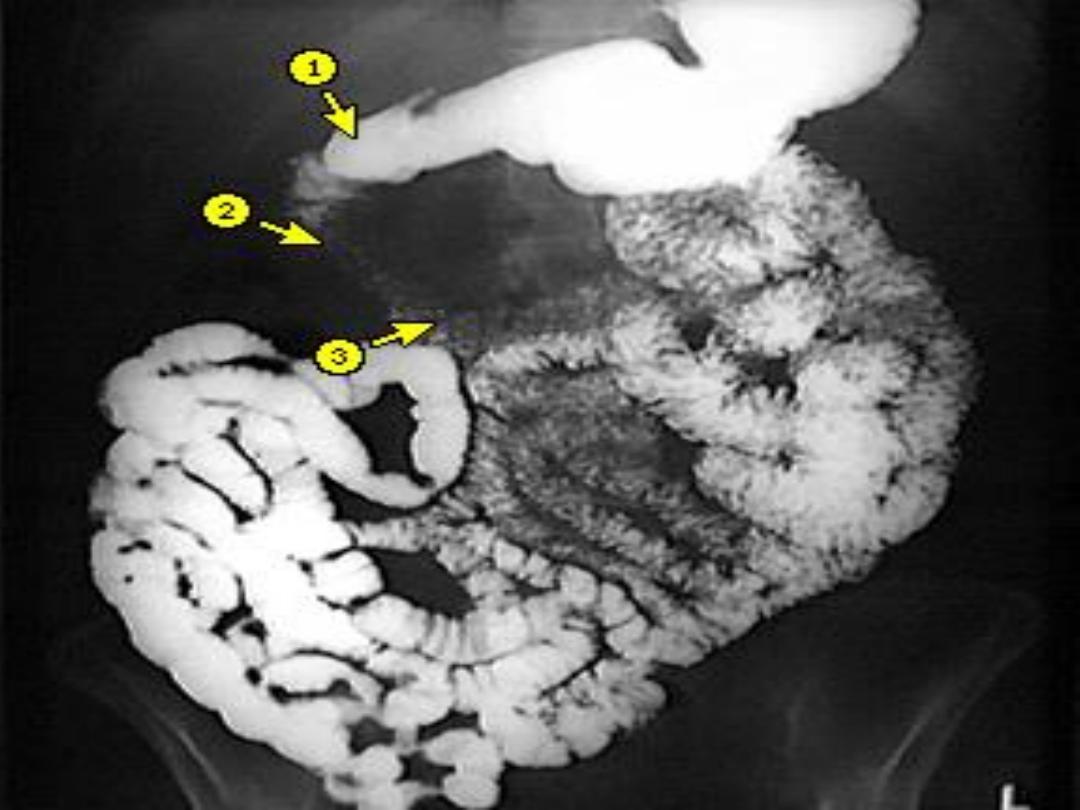
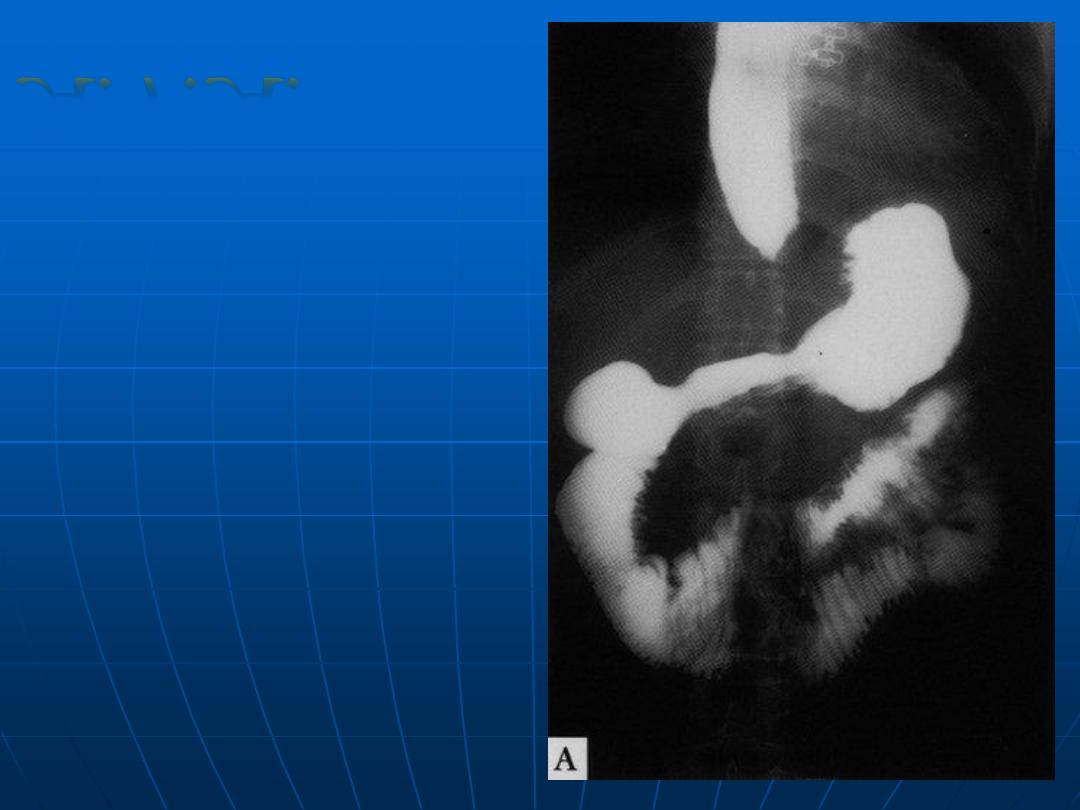
Chronic intestinal
psuedoobstruction
A.F.A.
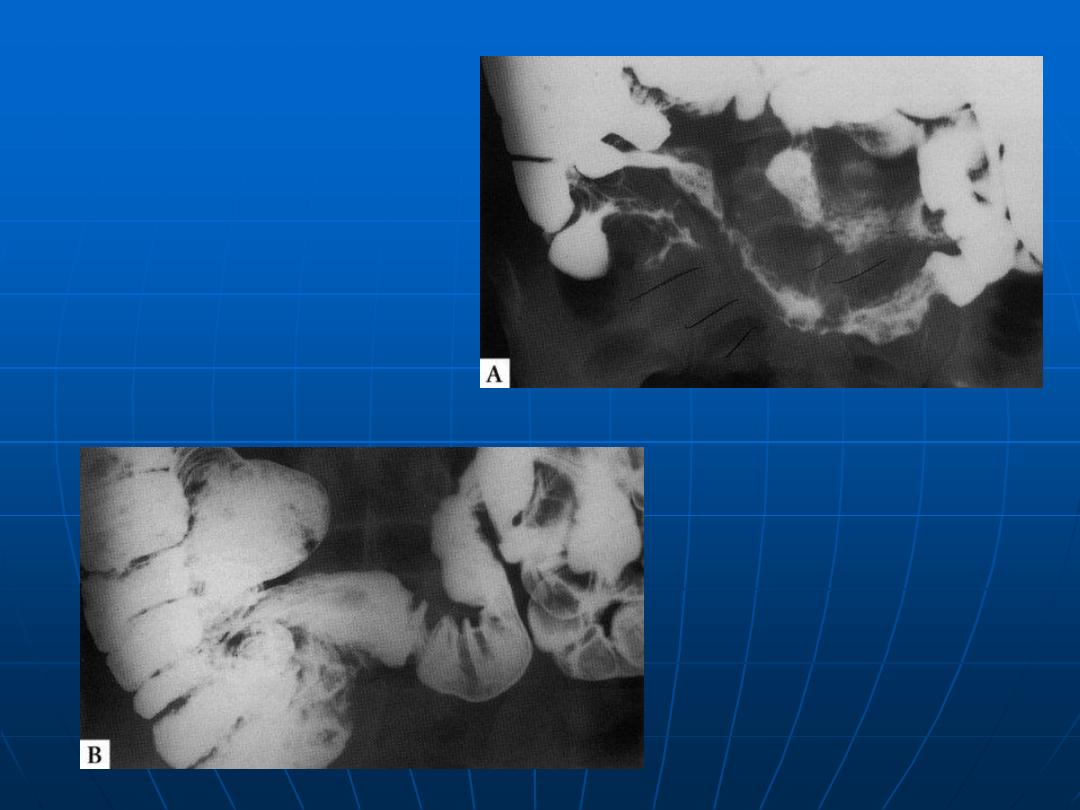
Intestinal
Tuberculosis
At diagnosis
Intestinal
Tuberculosis
(after 5
months of
therapy)
Early
stenosing
Crohn’s
disease
A.F.A.
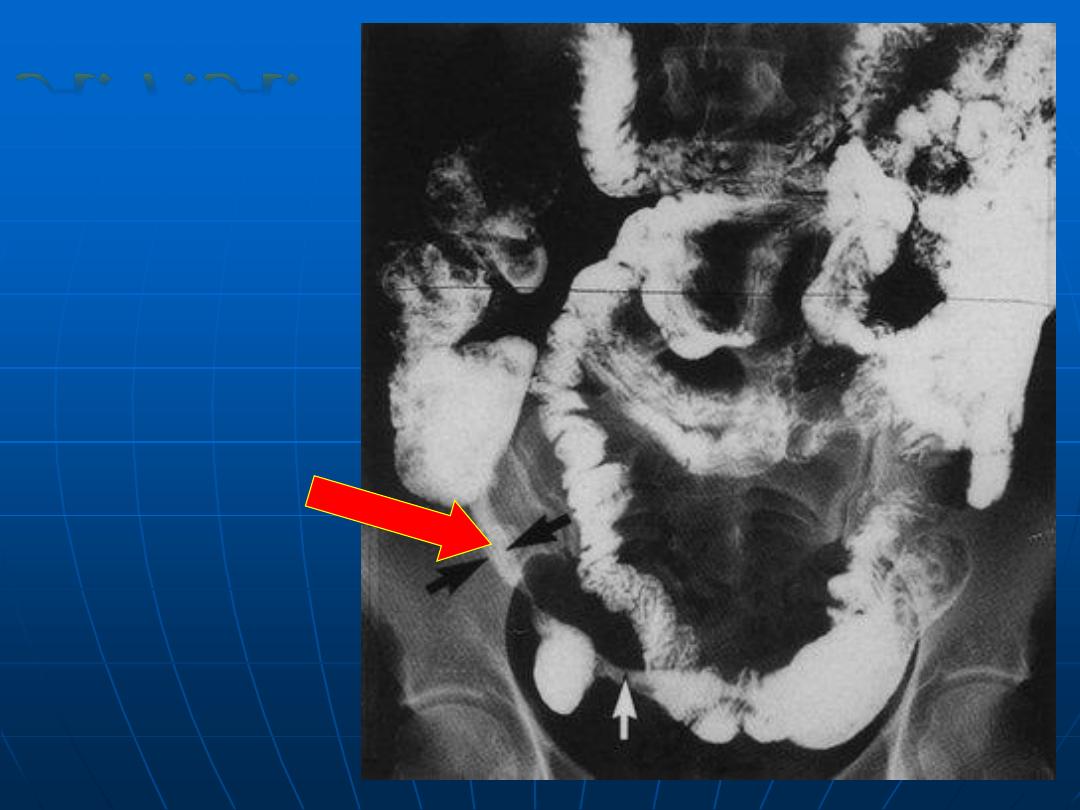
Crohn’s
disease
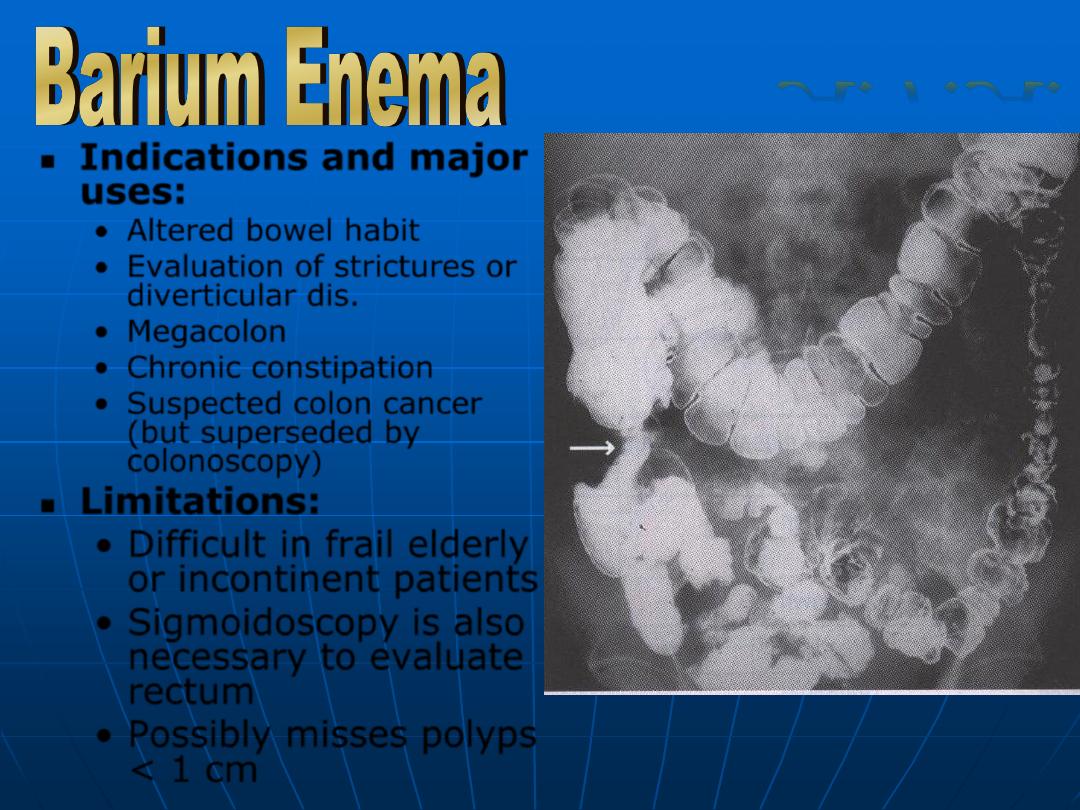
Indications and major
uses:
•
Altered bowel habit
•
Evaluation of strictures or
diverticular dis.
•
Megacolon
•
Chronic constipation
•
Suspected colon cancer
(but superseded by
colonoscopy
)
Limitations:
•
Difficult in frail elderly
or incontinent patients
•
Sigmoidoscopy is also
necessary to evaluate
rectum
•
Possibly misses polyps
< 1 cm
A.F.A.
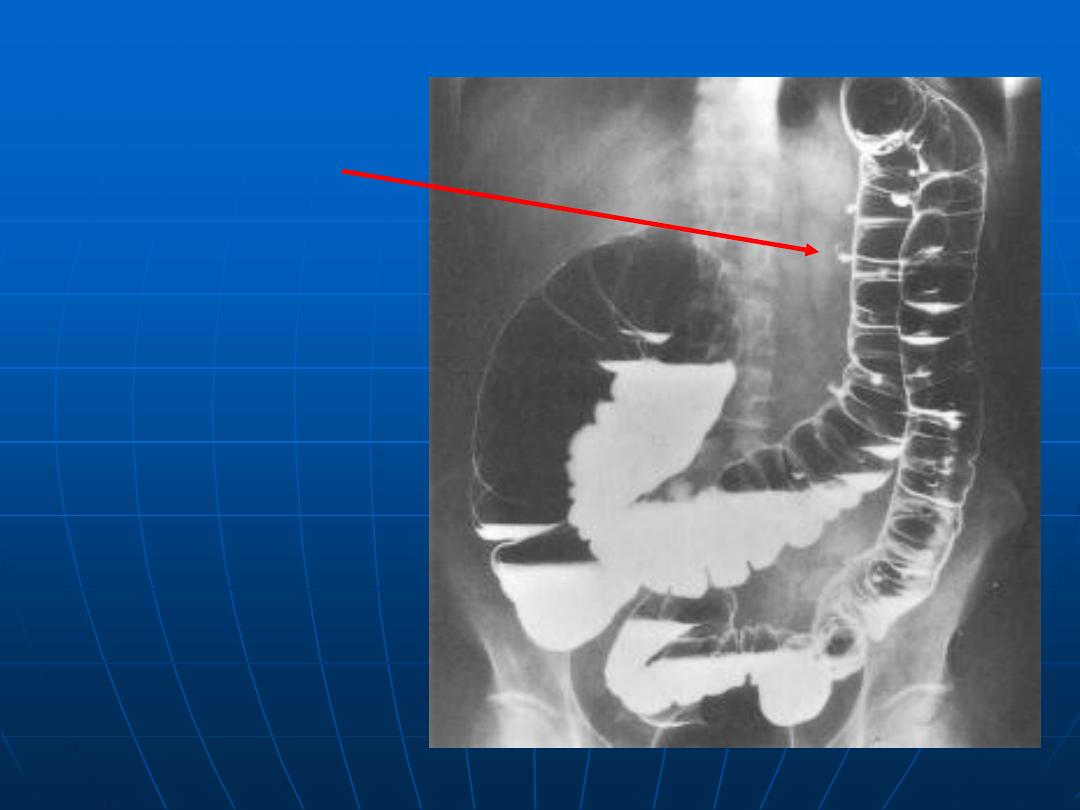
Scattered
diverticulosis
of the left
colon
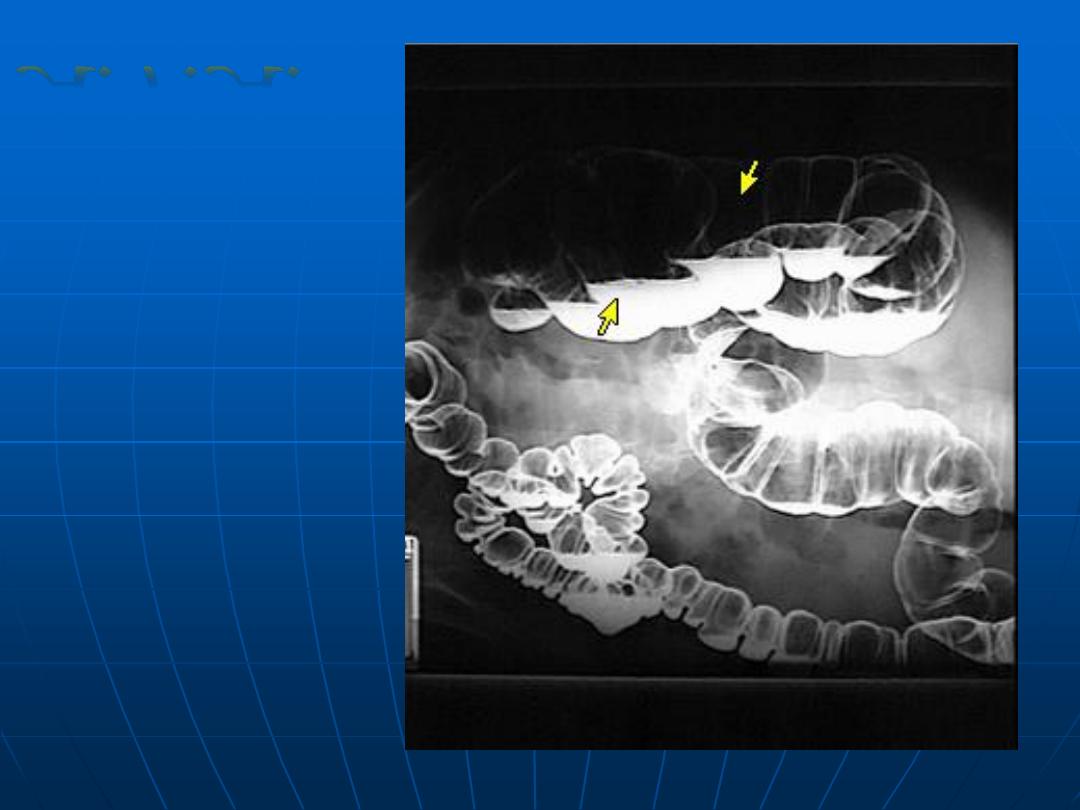
Double
contrast
barium
enema
(normal)
A.F.A.
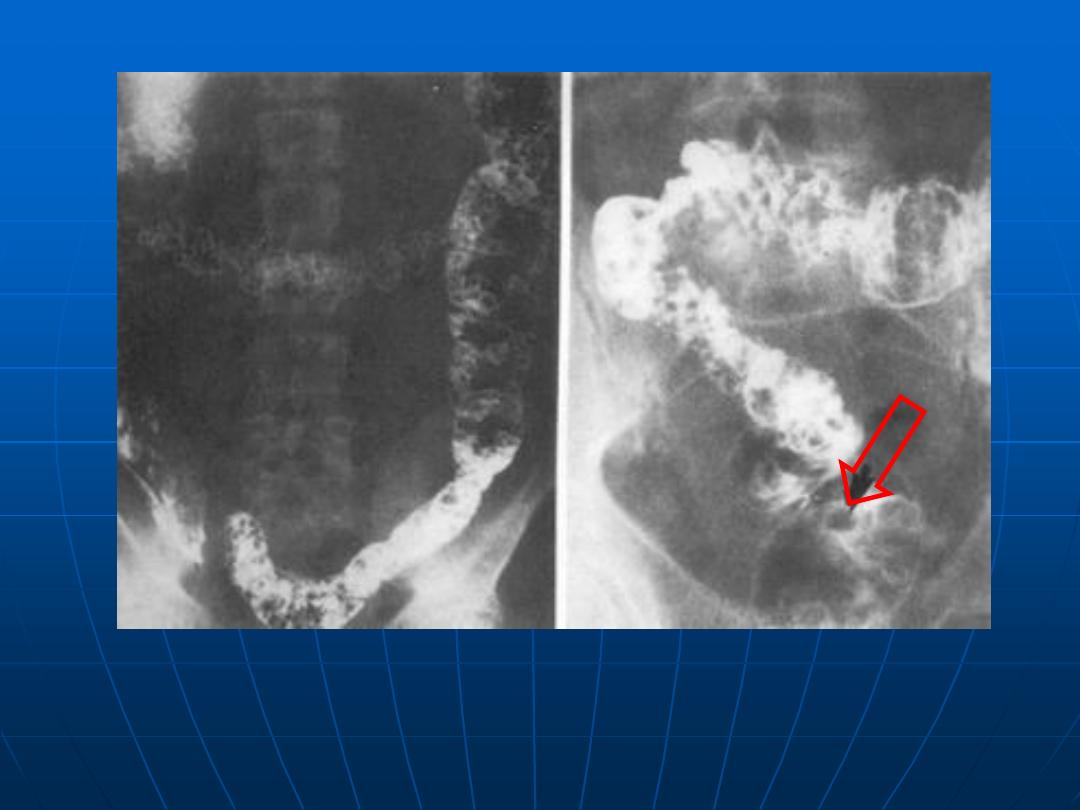
Barium enema showing familial adenomatosis coli
Arrow point to cancer arise in this setting
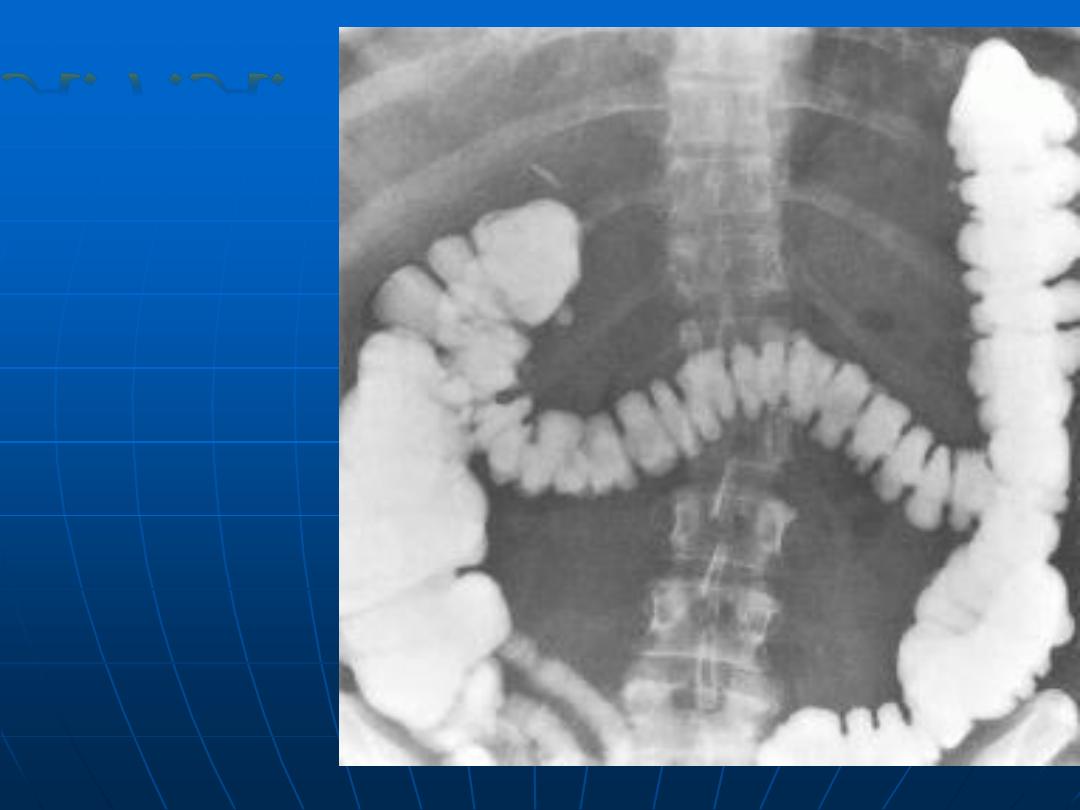
Pancolonic
diverticulosis
A.F.A.
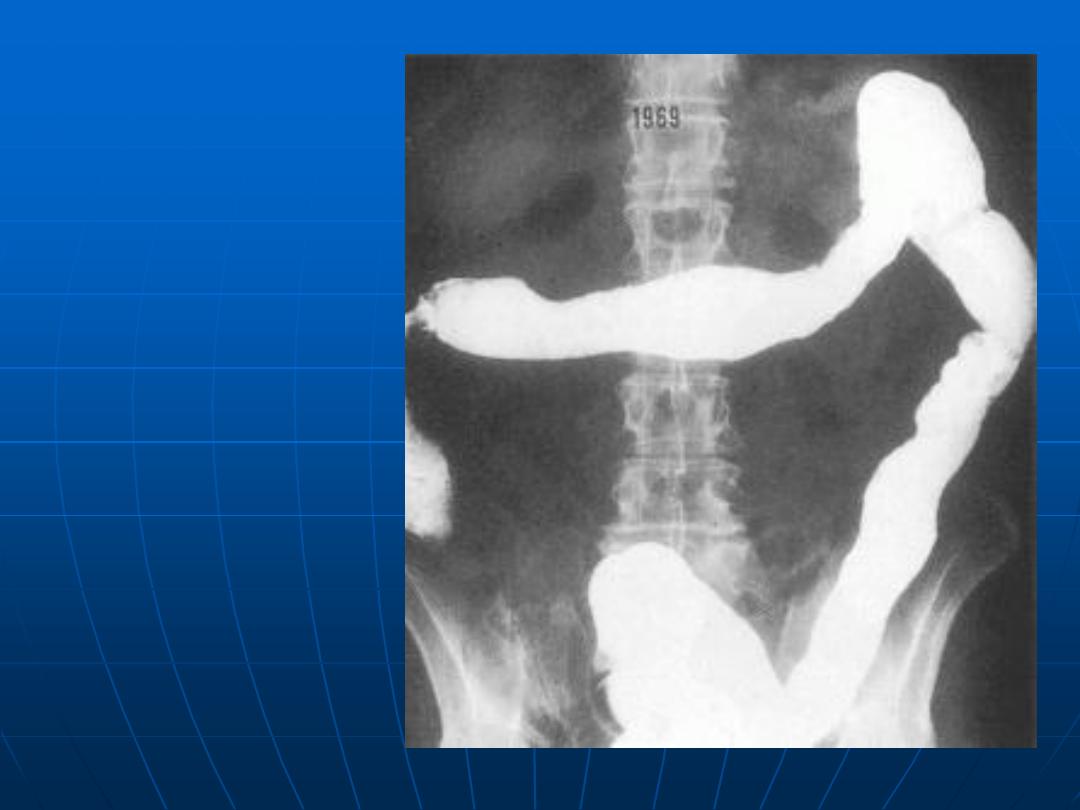
Chronic
Ulcerative
Colitis
A.F.A.
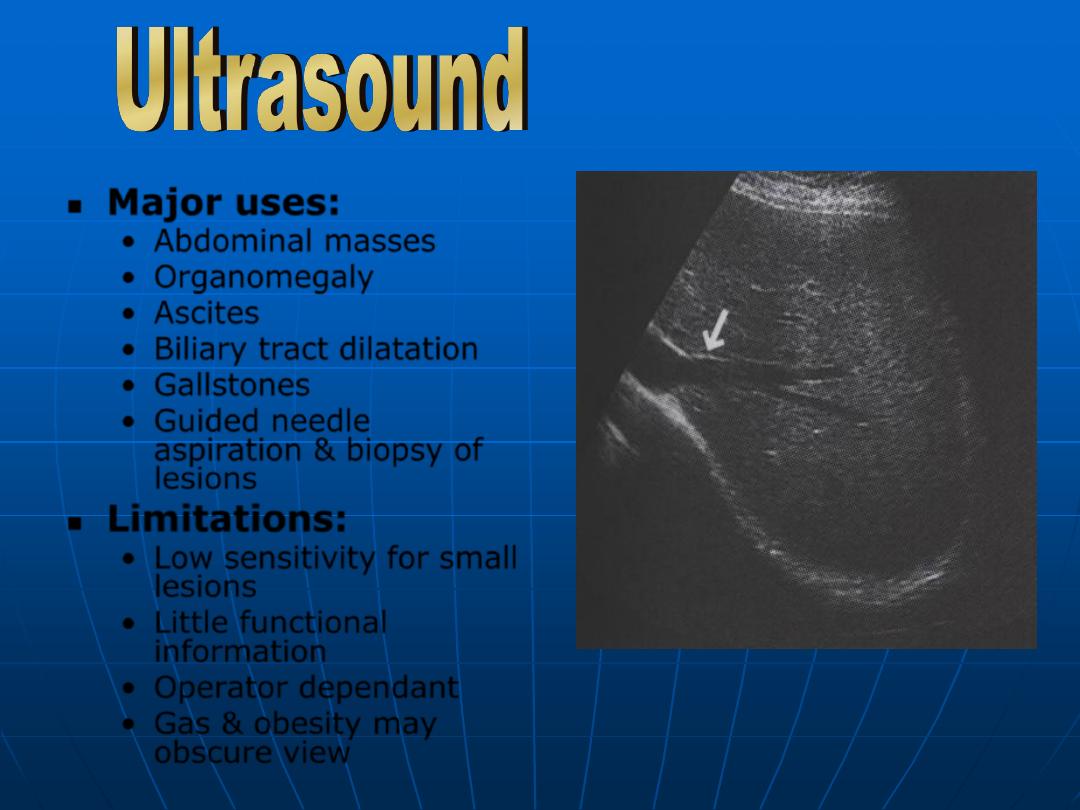
Major uses:
•
Abdominal masses
•
Organomegaly
•
Ascites
•
Biliary tract dilatation
•
Gallstones
•
Guided needle
aspiration & biopsy of
lesions
Limitations:
•
Low sensitivity for small
lesions
•
Little functional
information
•
Operator dependant
•
Gas & obesity may
obscure view
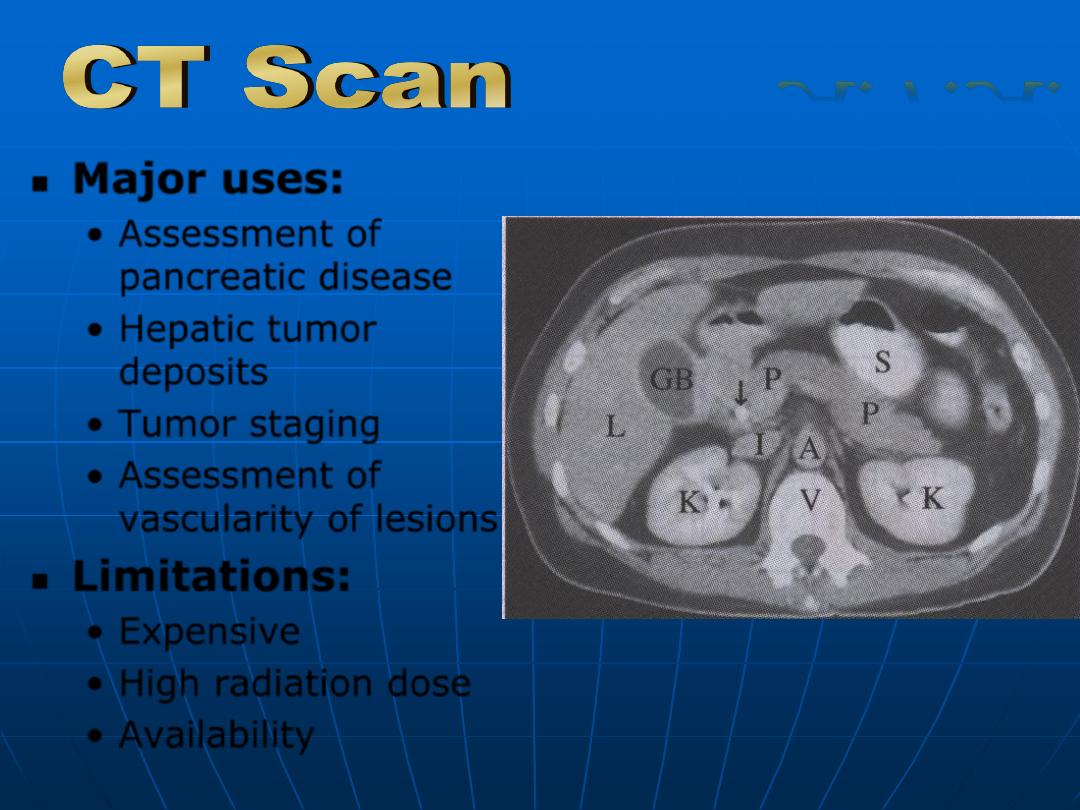
Major uses:
•
Assessment of
pancreatic disease
•
Hepatic tumor
deposits
•
Tumor staging
•
Assessment of
vascularity of lesions.
Limitations:
•
Expensive
•
High radiation dose
•
Availability
A.F.A.
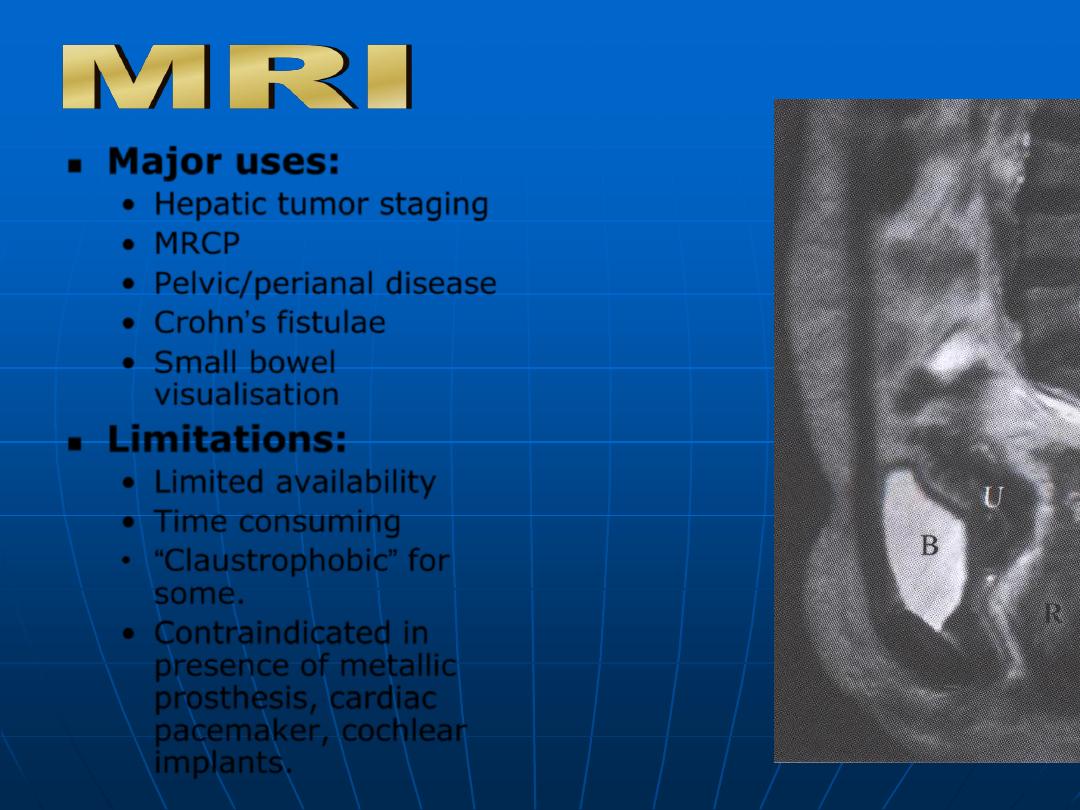
Major uses:
•
Hepatic tumor staging
•
MRCP
•
Pelvic/perianal disease
•
Crohn’s fistulae
•
Small bowel
visualisation
Limitations:
•
Limited availability
•
Time consuming
•
“Claustrophobic” for
some.
•
Contraindicated in
presence of metallic
prosthesis, cardiac
pacemaker, cochlear
implants.
A.F.A.
Investigations
of GIT diseases
Tests of structures
Tests of infection
Tests of function
Imaging
Histology
US, CT
MRI
Endoscopy
Contrast
studies
Plain
Radiograph
Bacterial
culture
Serology
Breath
Tests
Pancreatic
Exocrine
function
Mucosal
Inflammation/
permeability
Absorption
GIT
Motility
Radioisotope
Tests

A.F.A.

INDICATIONS.
Dyspepsia over 55 yr or with alarm symptom
Atypical chest pain
Dysphagia ,Vomiting ,Loss of weight
Acute or chronic gastrointestinal bleeding
suspicious barium meal ,C T .SCREENING for esophareal
varices
Therapeutic.
Duodenal biopsies
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Severe shock ,Recent MI ,Unstable angina , Arrhythmia
Severe respiratory dis., Atlantoaxial subluxation
Possible visceral perforation
COMPLICATION
Cardiorespiratory depression due to sedation
Aspiration pneumonia
Perforation
Video endoscopy
unit
A.F.A.
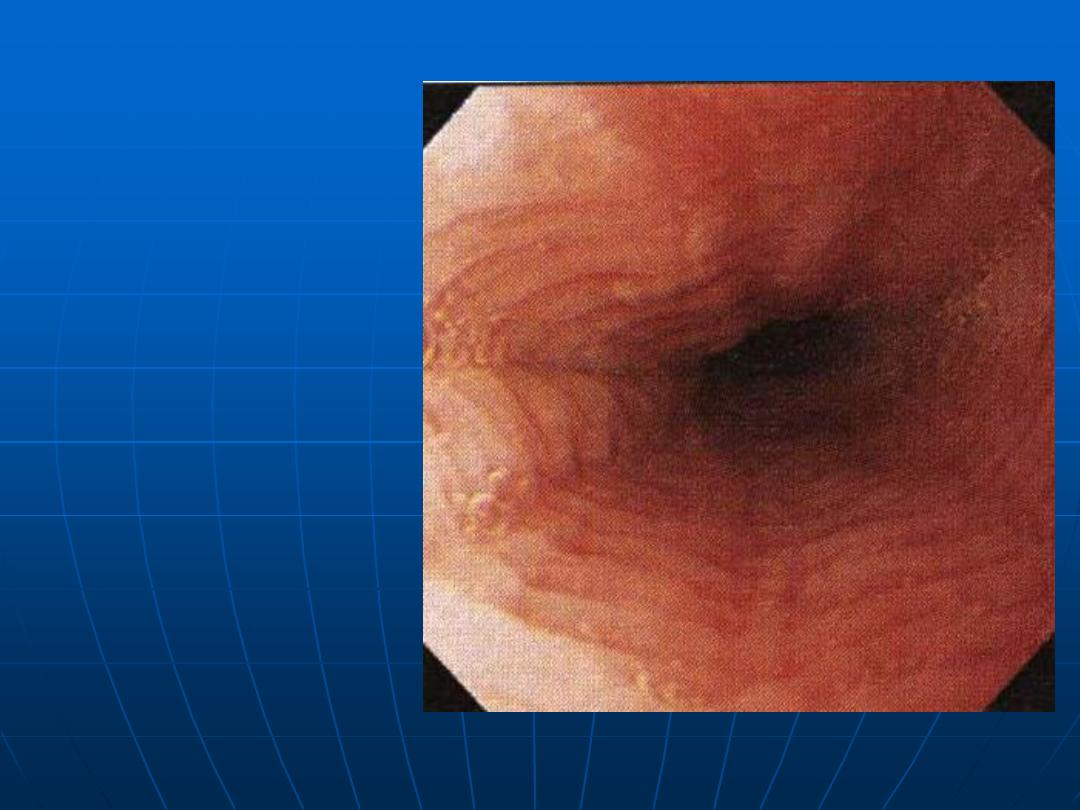
Normal
esophagus
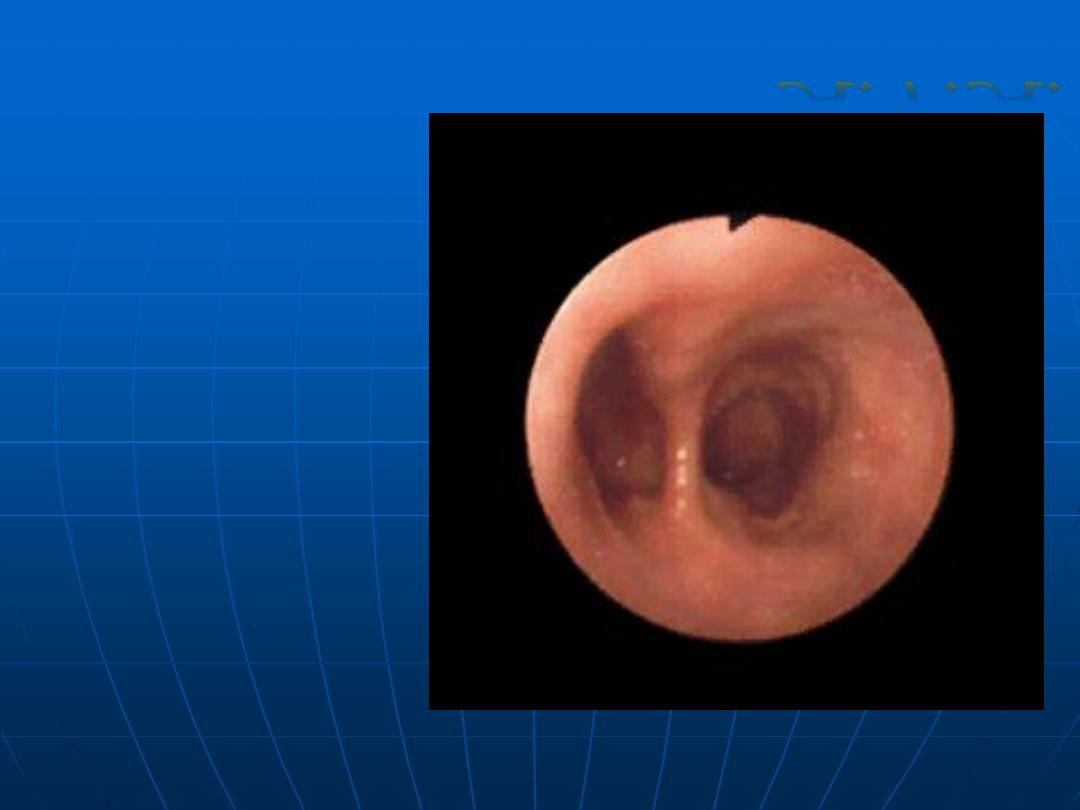
Esophageal
Diverticulum
A.F.A.
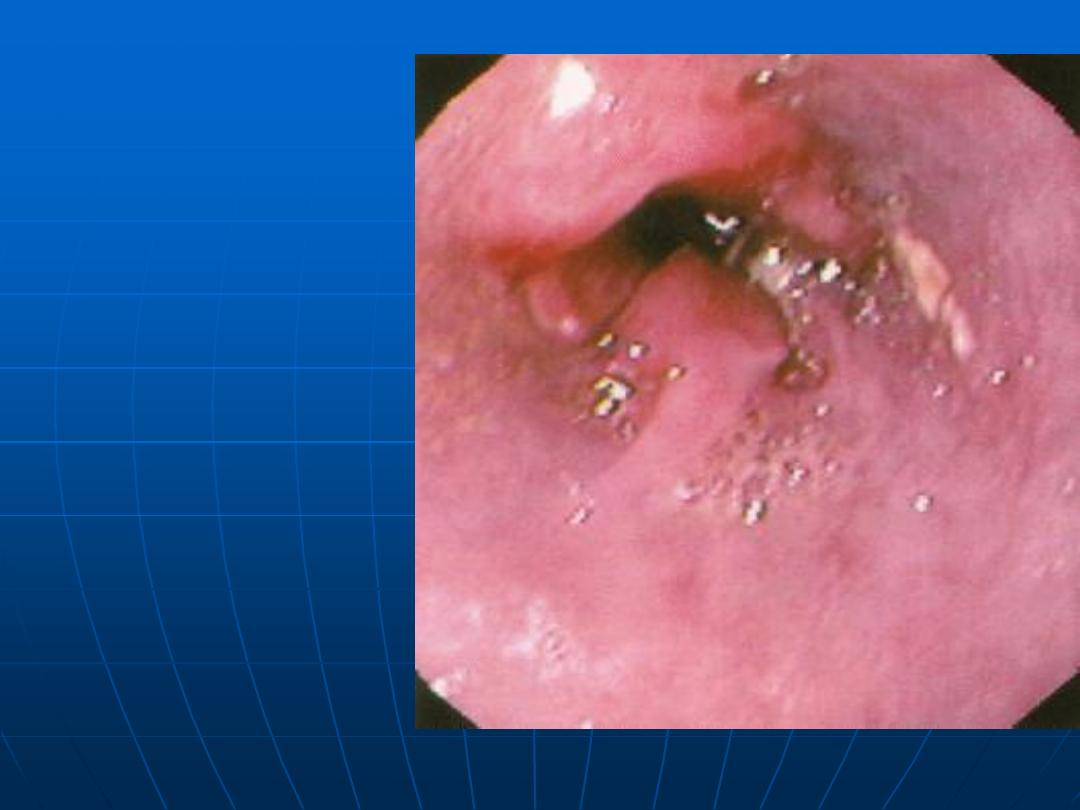
Malignant
esophageal
lesion
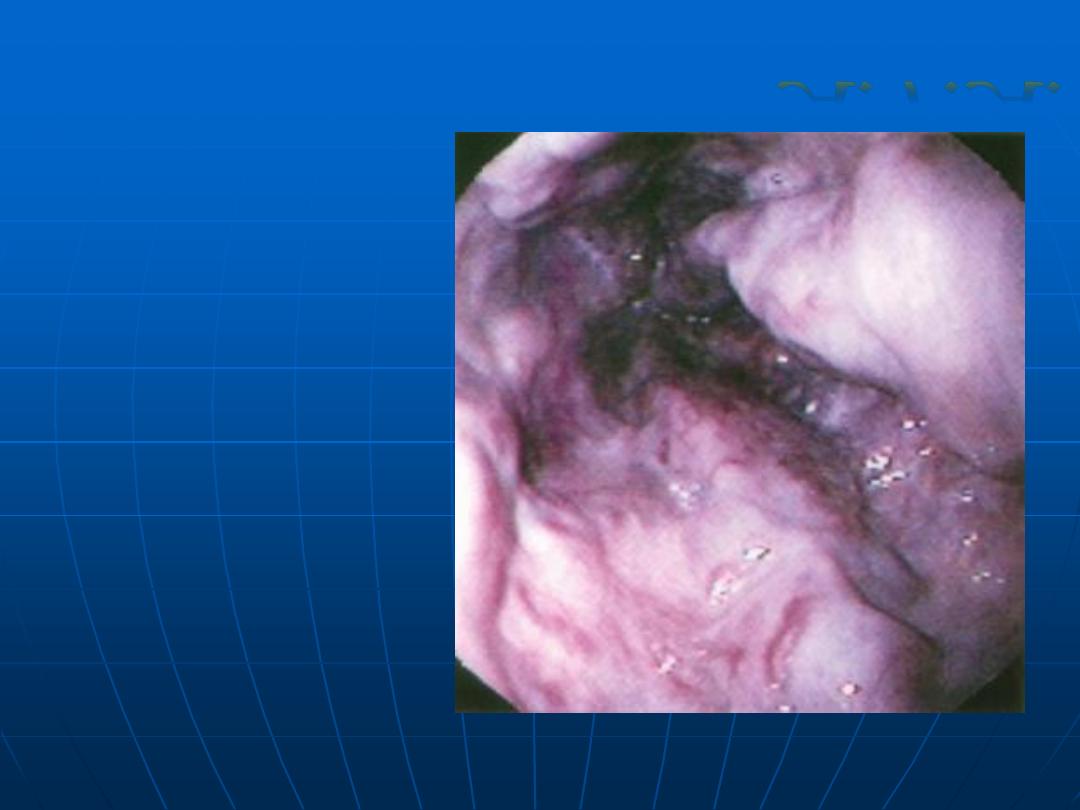
Esophageal
varices
A.F.A.
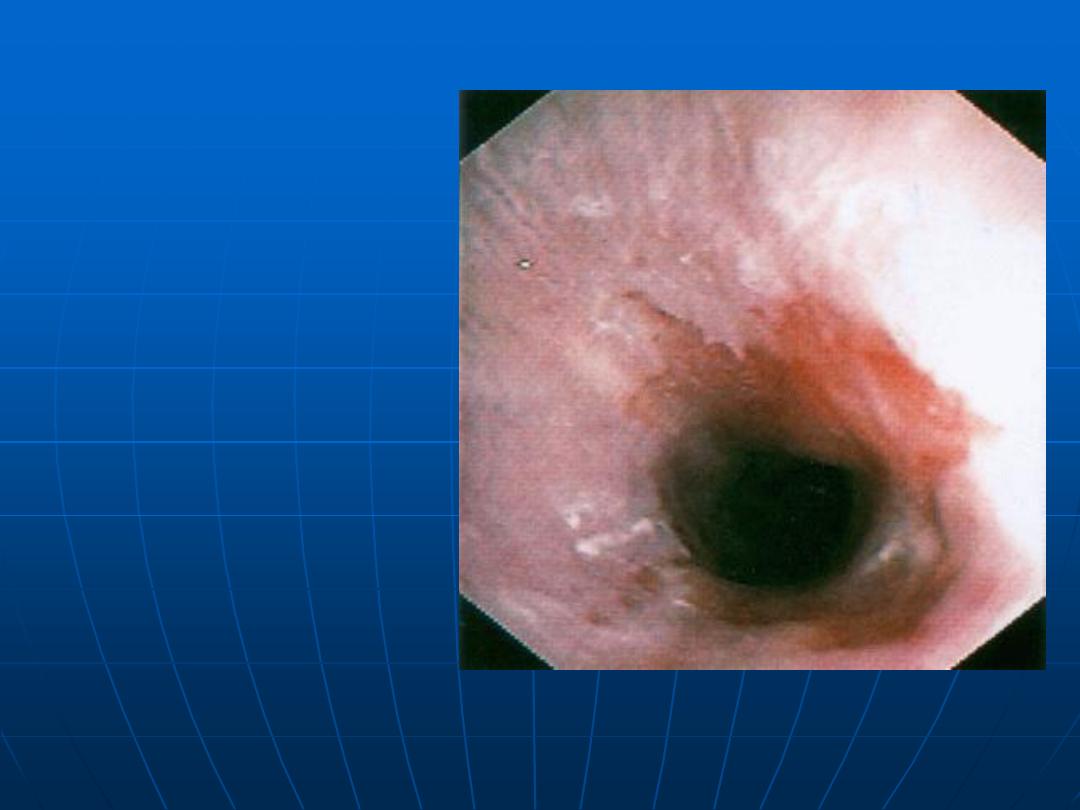
Barrett’s
Esophagus
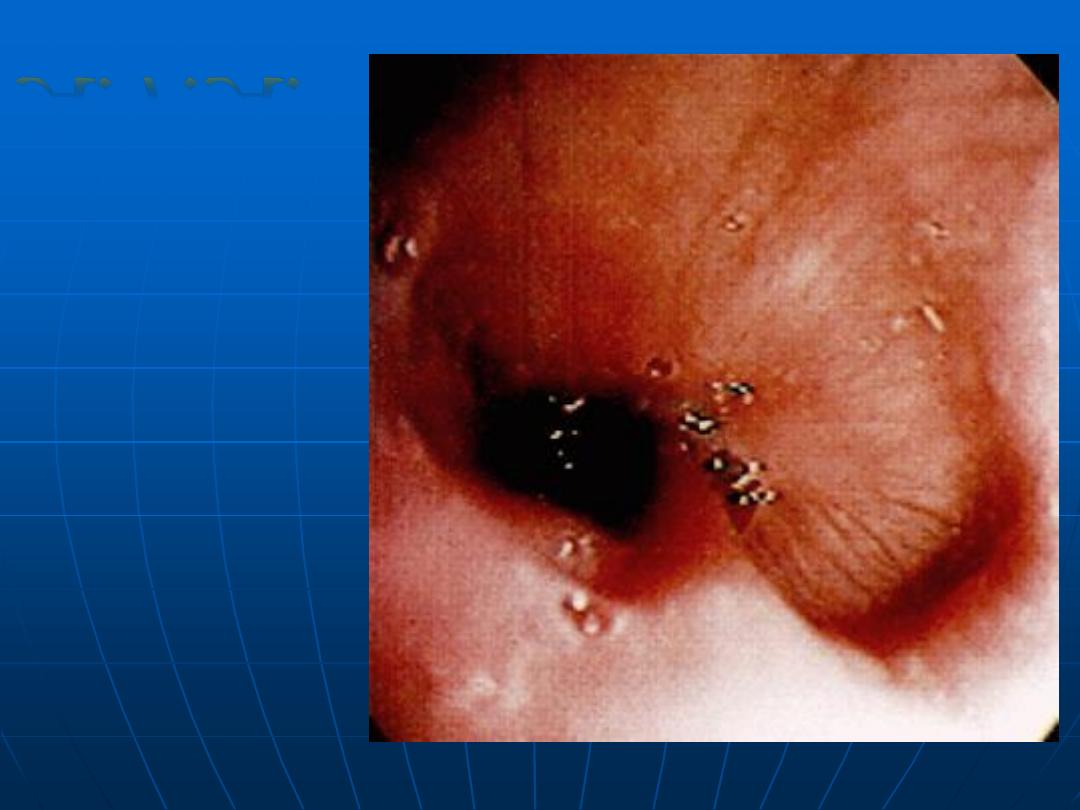
Achalasia
A.F.A.
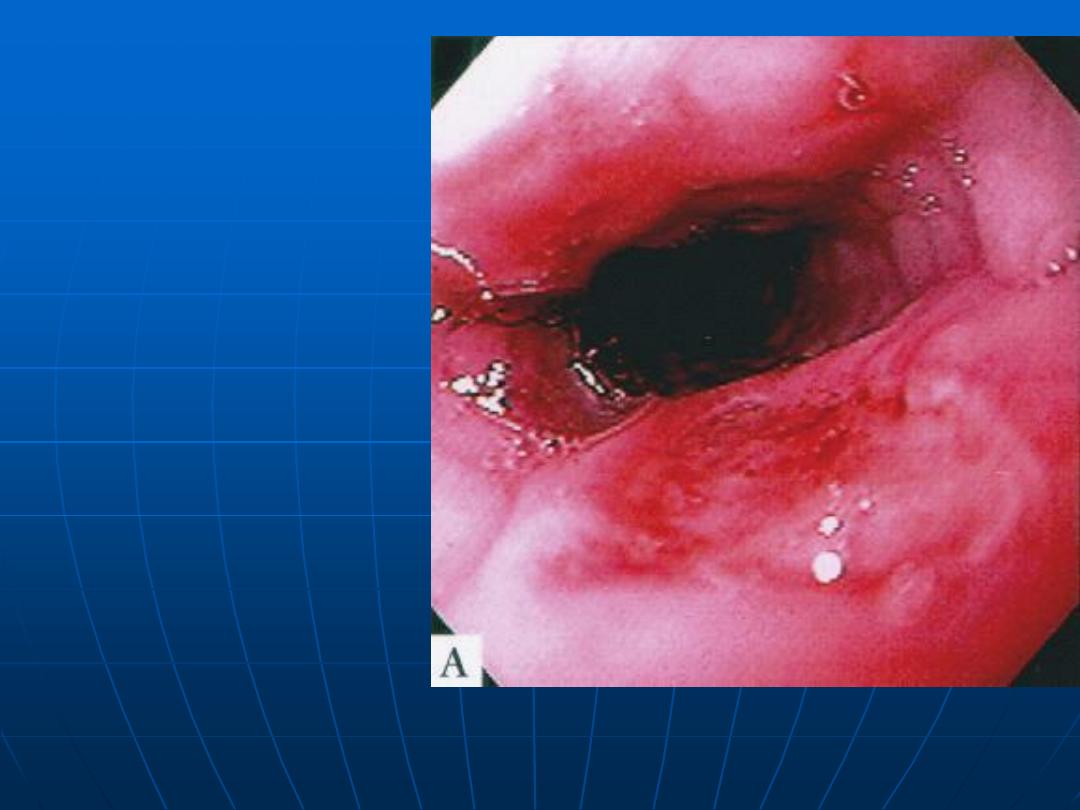
Esophageal Ulcer
HIV patient
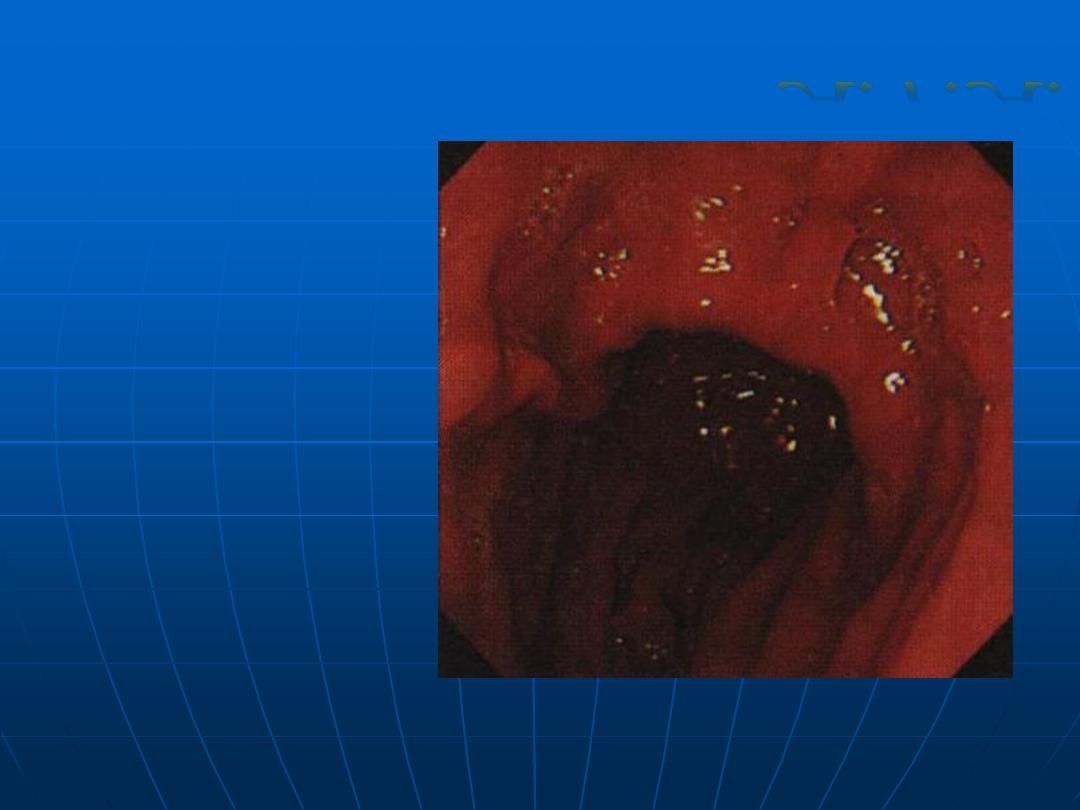
Normal Stomach
Body
A.F.A.
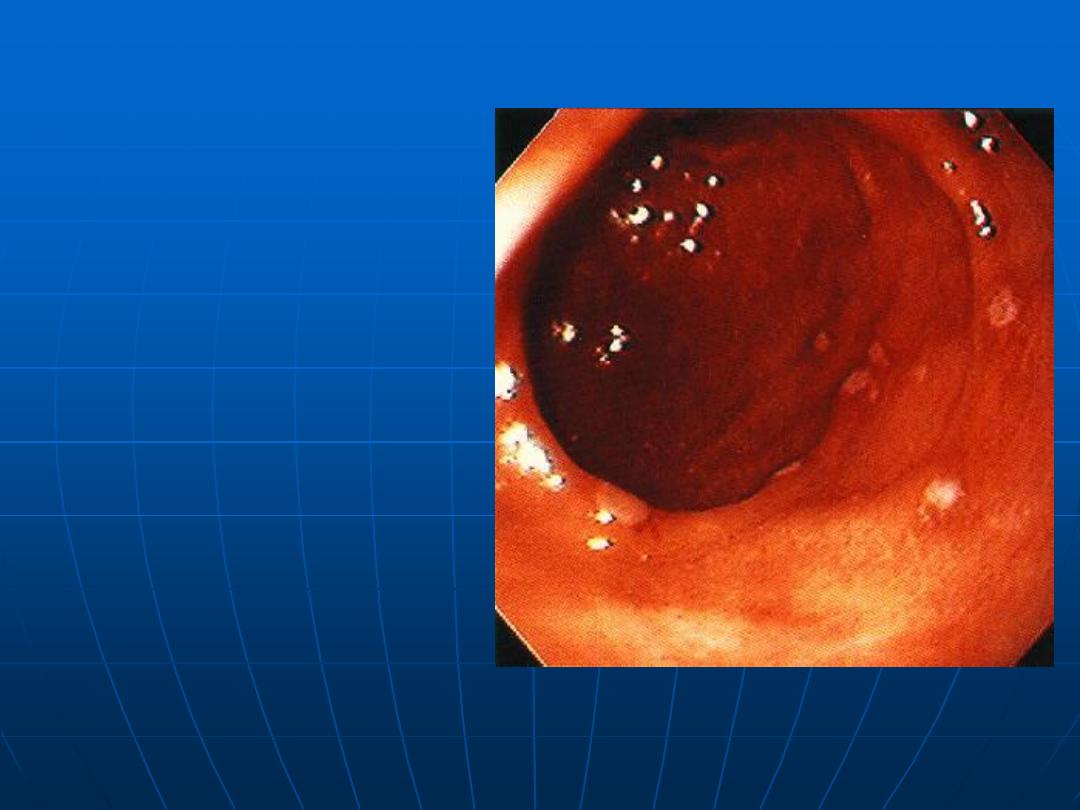
Erosive
Gastritis

Capsule Endoscopy
Indication
Obscure GI bleeding
Small bowel Crohn’s dis ,Coeliac dis,
Familial polyposis syndrome
Contraindication
Small bowel stricture ,pacemaker
A.F.A.
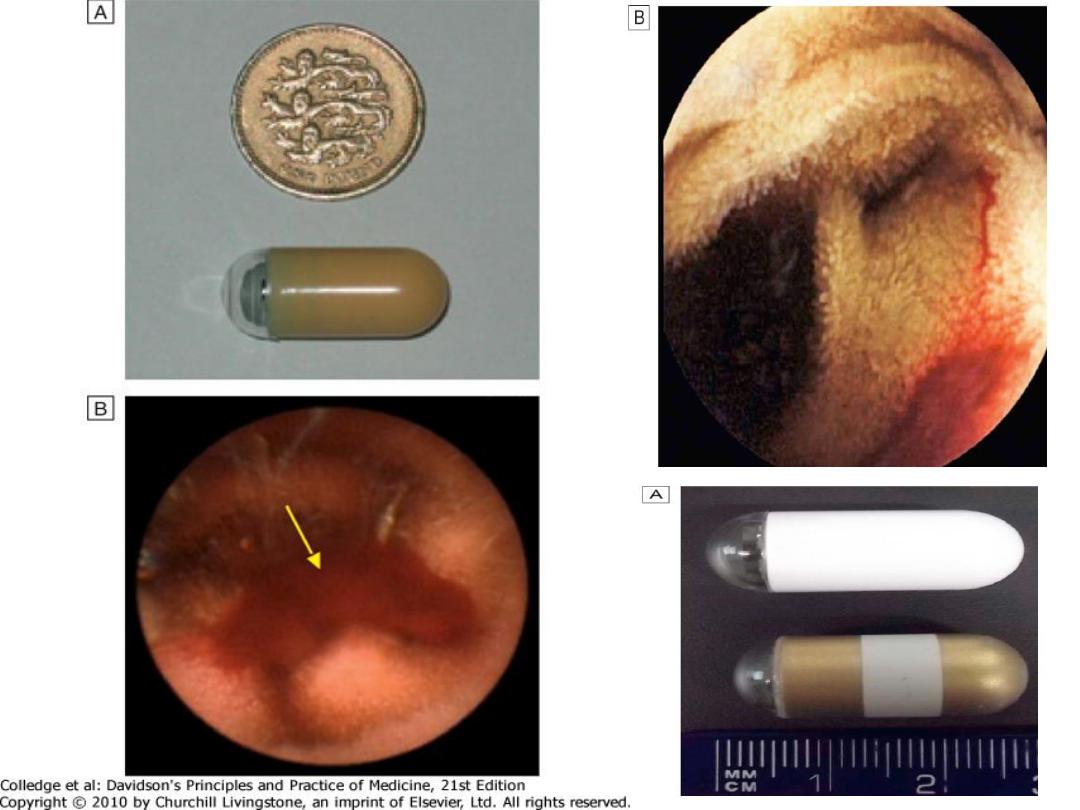

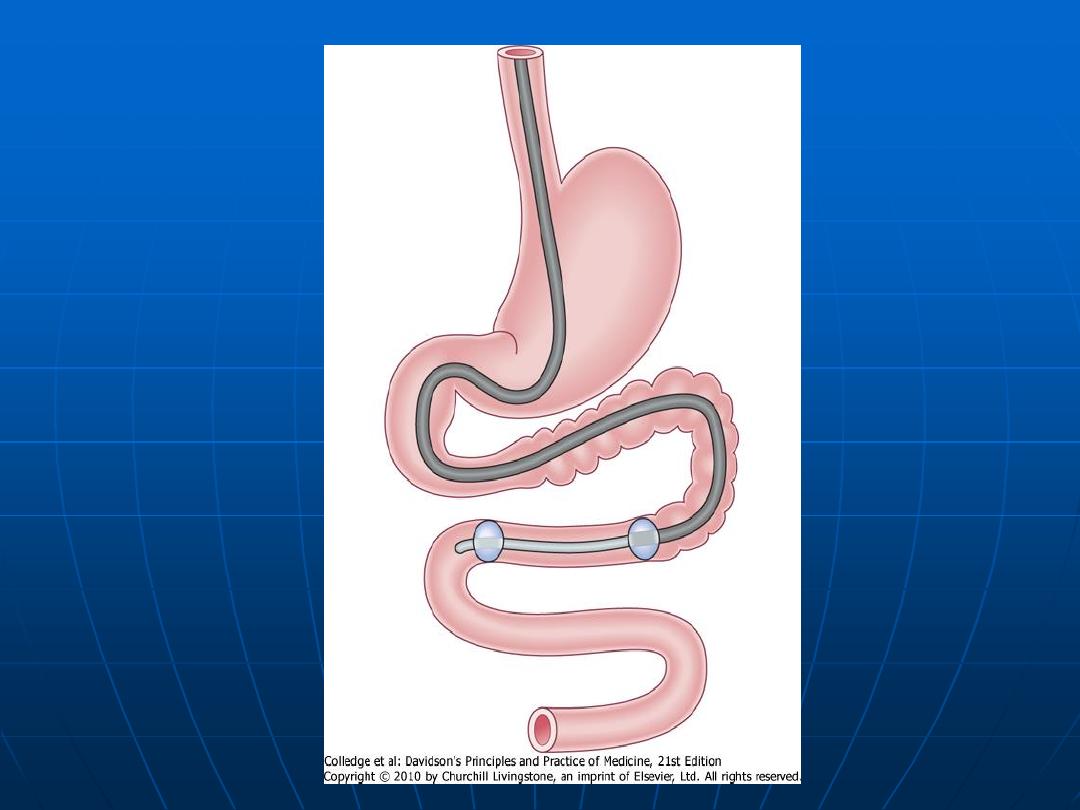
Double Balloon enteroscopy
Indication Diagnostic Therapeutics
Contraindication
Complications: abdominal pain 20%
pancreatitis perforation
A.F.A.

A.F.A.

colonoscopy
Indications
Suspected infl.bowl dis. ,
ch.Diarrhoea
Altered bowl habit
Rectal bleeding or anemia
Assessment of abnormal barium
enema
Colorectal cancer screening
Colorectal adenoma follow-up
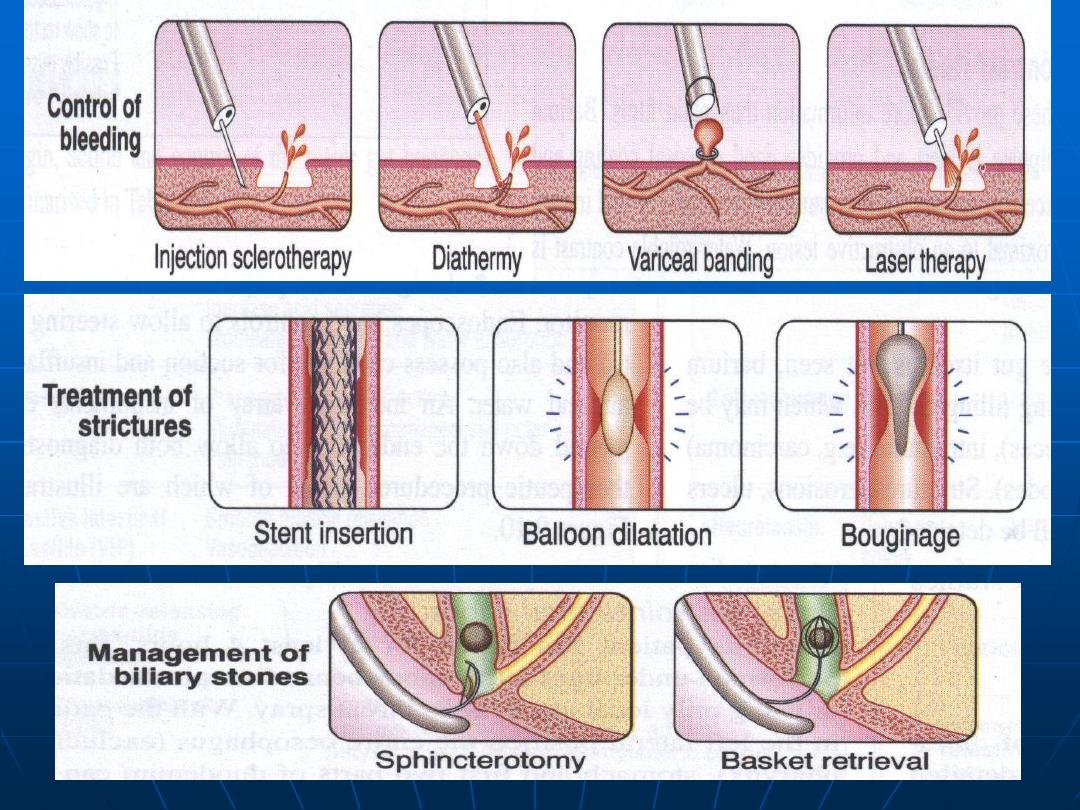
Therapeutic procedures

Contraindications
Severe , active ulcerative colitis
Recent MI,unstable angina
arrhythmia ,severe resp. dis.
Atlantoaxial sublax. ,?Visceral perfor.
Complication
C
ardioresp. Dep. Due to sedation
Perforation
Bleeding
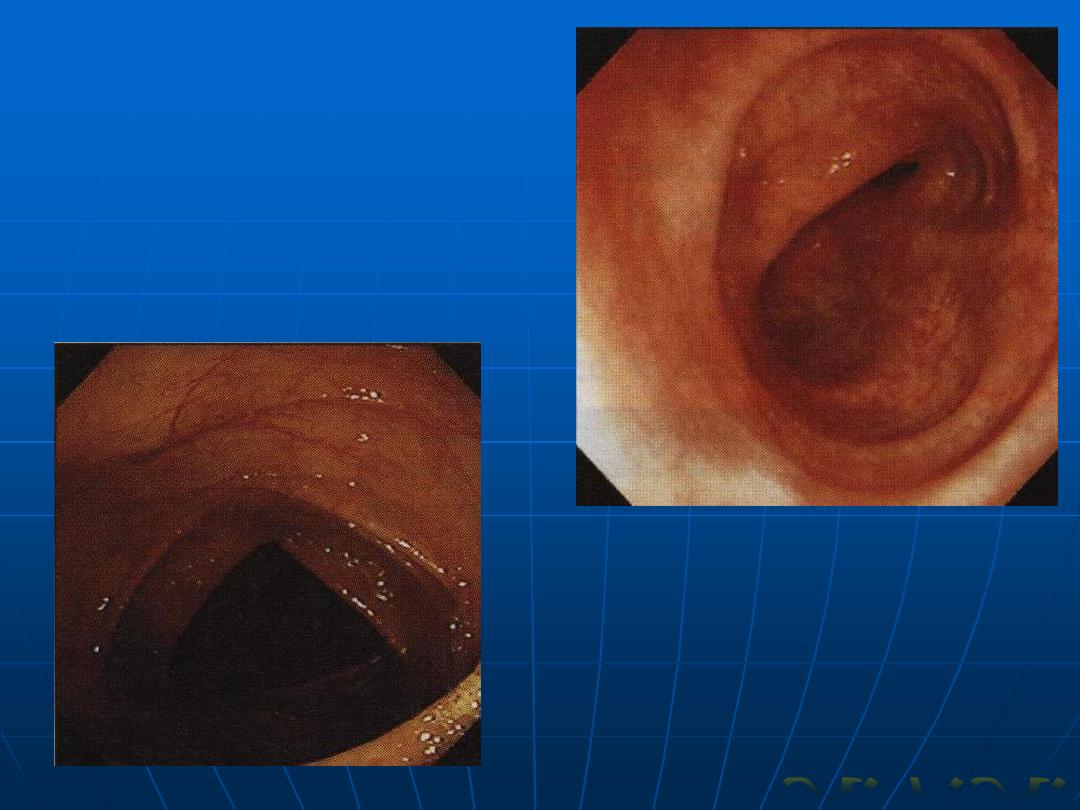
Normal
Colonscopy
A.F.A.

A.F.A.

Stool cultures are essential in the
investigation of diarrhea, especially
when it is acute or bloody, to identify
pathogenic organism.
Detection of antibodies plays a
limited role in the diagnosis of GIT
infection caused by organism like H
Pylori, Salmonella species, and E.
histolytica.

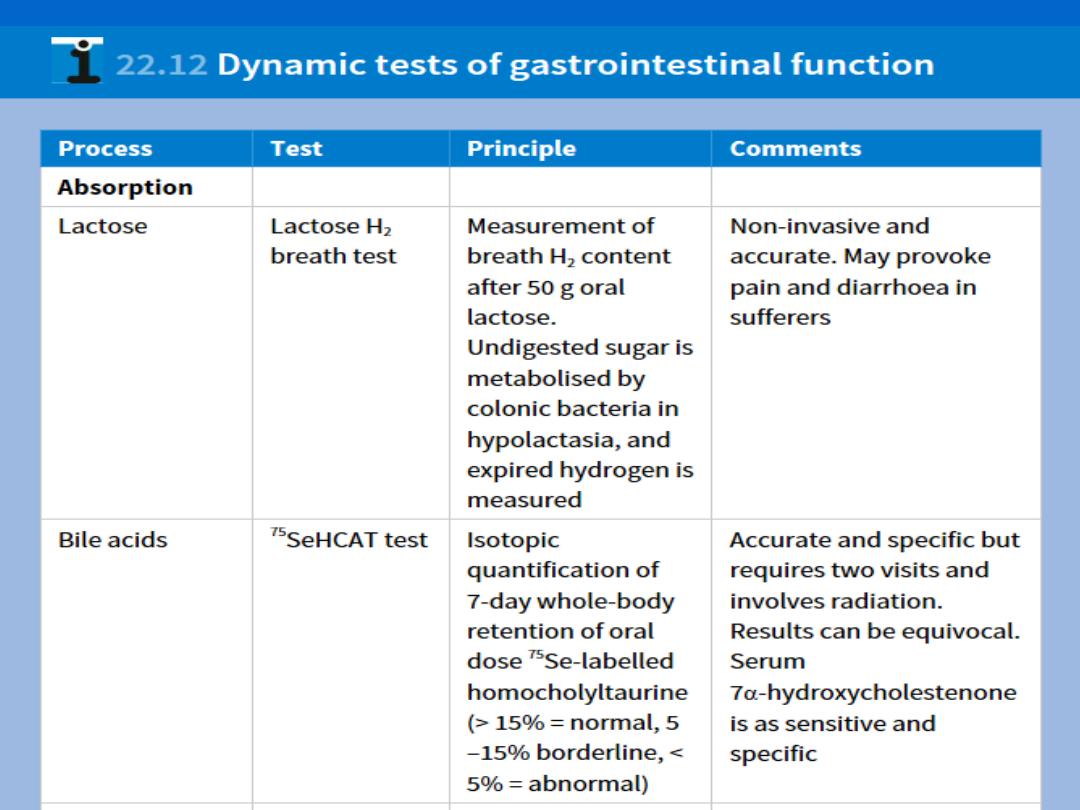
Gastrointestinal motility
Oesophageal motility:
Gastric emptying:
Small intestinal transit:
Colonic & anorectal motility:
A.F.A.
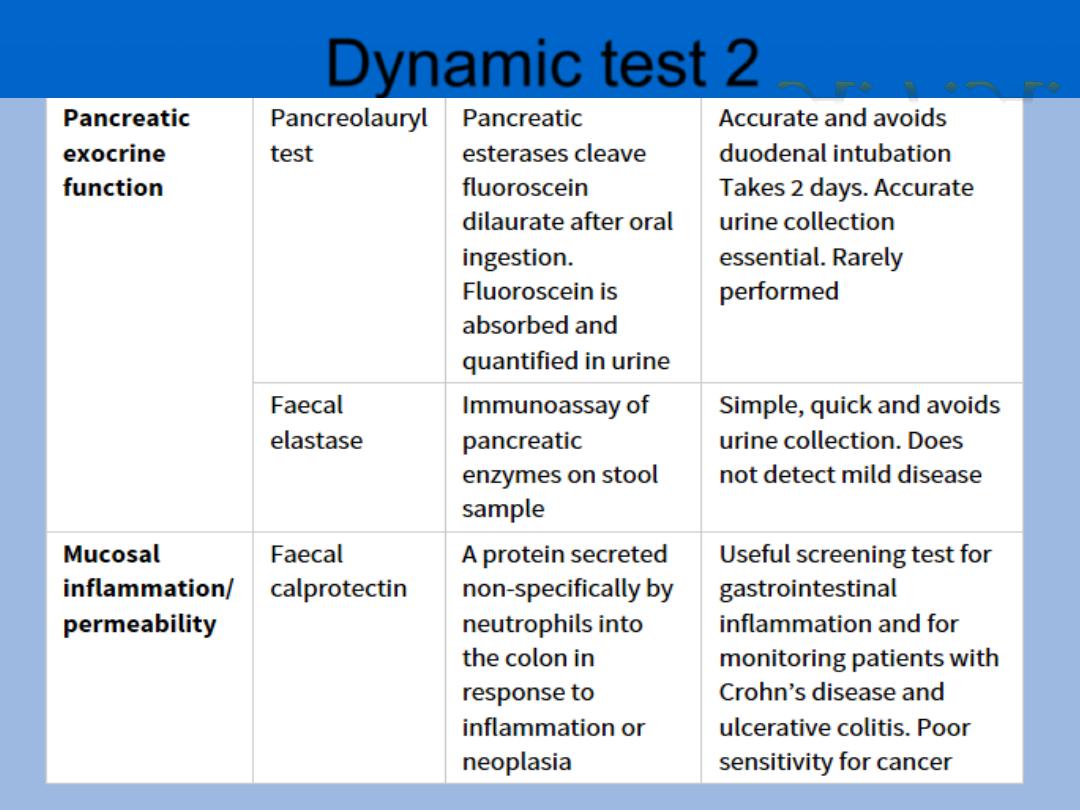
Dynamic test 2
A.F.A.

Radioisotope tests
Gastric emptying study.
Urea breath test.
Meckles scan..
Somatostatin receptor scan.
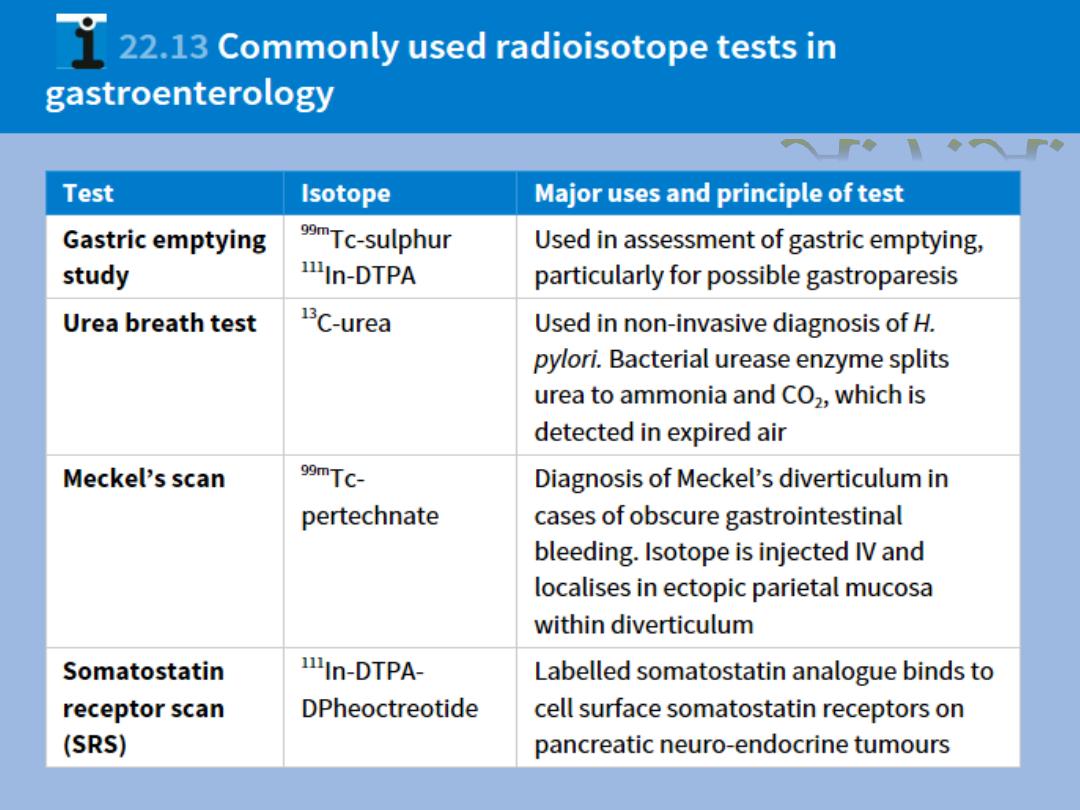
A.F.A.
