Operating System
Operating system.Functions and components of OS.
Types of OS.
Process and a program.
Real time operating system (RTOS).
AGENDA
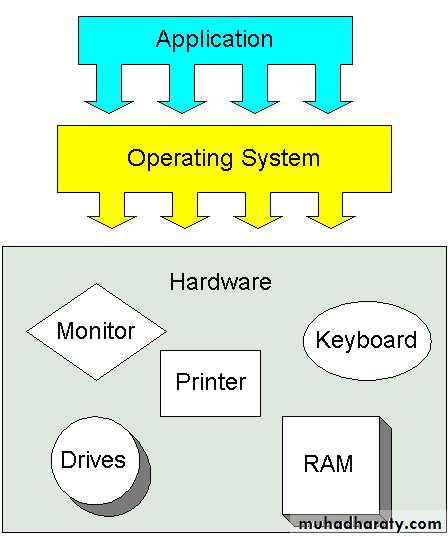
An operating system (OS) is a collection of software that manages computer hardware resources and provides common services for computer programs. The operating system is a vital component of the system software in a computer system. Application programs usually require an operating system to function.
What is an Operating System (OS)
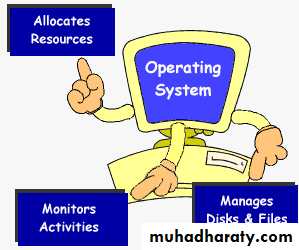
Functions of OS
Managing resourcesProviding a user interface
Running applications
Support for built in utility programs.
Control to the computer hardware
Components of OS
Process ManagementMemory management
I/O Device management
File system
Protection
Network management
Network services
User Interface
Real time operating systems.
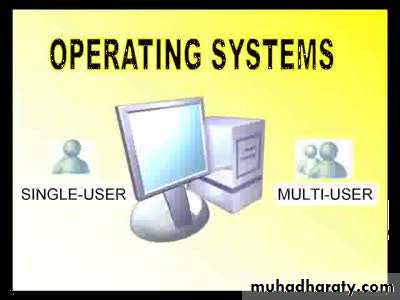
Single user, Single TaskSingle user, Multi-tasking
Multi user, Multi-tasking.
Types of OS
Reliable.
Operational at all times.Should coordinate and have good control of input and output operations and the devices on which they are performed.
Enhance time sharing.
Features of Operating System
Computers
Mobile phones
3d televisions
Video game
ATM
Ticket Wending Machine
Programmable logic controller (PLC)
Examples of computing devices which use OS
Easy to useUser friendly
Intermediate between all hardware's and software's of the system
No need to know any technical languages
Its the platform of all programs
Advantages of OS
If any problems affected in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored already
Unwanted user can use your own system
Disadvantages
A process invokes or initiates a program. It is an instance of a program that can be multiple and running the same application.
Example:- Notepad is one program and can be opened twice.
Process and Program:
An operating system (OS) intended to serve real-time application requestsAn RTOS has an advanced algorithm for scheduling.
Real Time Operating System
Cooperative schedulingPreemptive scheduling
Rate-monotonic scheduling
Round-robin scheduling
Fixed priority pre-emptive scheduling, an implementation of preemptive time slicing
Fixed-Priority Scheduling with Deferred Preemption
Fixed-Priority Non-preemptive Scheduling
Critical section preemptive scheduling
Static time scheduling
Earliest Deadline First approach
Stochastic digraphs with multi-threaded graph traversal
Algorithms Used in RTOS
Running (executing on the CPU);
Ready (ready to be executed);Blocked (waiting for an event, I/O for example).
Scheduling in RTOS
World without Operating system is like human without heart..Conclusion