
1
“ Development assessment “
Dr. Ban A Hameed
Department of Pediatrics
Al-Kindy College of medicine
Definition
Development:
Refers to how a child becomes able to do more complex things as they get older.
Factors affecting growth and development
1. Genetic
2. Physical trauma:
any insult in pediatric age group during prenatal, natal, postnatal period any chemical,
immunological, and residual from certain infection may affected the growth.
3. Nutritional:
especially during the first year of life when there is rapid growth and development.
4. Others;
includes social, emotional and cultural factors. I.e. Position of child in the family, the interaction
of the infant or child with other siblings, parents divorce and death of one parent.
Developmental Assessment
Development testing is a routine part of examination of any child especially infants & young
children.
The purpose is to identify development delay early so that, if possible the cause may be corrected
and appropriate help organized for the child and family.
There are standers for the age at which normal children achieve particular skills.
The developmental skills can be divided into four main categories.
1) postural and movement (gross motor )
2) Vision and fine manipulation.
3) Hearing and speech.
4) Social behavior.
2
1) Posture and movement (gross motor)
First 3 months
The term new born infant in supine position lies with his elbow is flexed; knee & hips are partly flexed
The term new born infant in prone position lies on his abdomen, the pelvis is high & knee up under his abdomen.
The prone new born infant can turn his face from side to side.
By 1 month of age the infant can raise the head briefly to the plain of body.
By 2 month the infant can sustain the head in that plane.
By 3 month the infant can raise the head above the plane and his legs can be extended as well.
In supine position; at 4-8 week the head lags when the infant is pulled from supine to sitting position and
there is no head control.
By 12 week there is some head control.
Between the age of 4-12 week tonic neck posture predominates on supine position.
3-6 months
By the age of 3 month an infant on prone position can raise his head and chest with arm extended.
By 4 month the head can be raised to vertical axis and turned easily from side to side.
By 4 month when the infant is pulled from supine to sitting position, the head is held steady without
bobbing this means good head control.
By 3-4 month predominate posture is head maintained in the midline, the arm and legs in symmetric
position and hands together in the middle.
By 6 month infants usually sit for few minutes on firm surface such as the floor with legs abducted and
extended and hand for ward for supporting.
At 5-6 month infant can pulled from sitting to standing position and support their weight on extended legs.
At 5-6 month infant can rolls over at first from prone to supine position then after 1 month from supine to
prone position. And he is able to support his weight on the hands with extended arms.
6-12 months
At 7 month prone infants can pivot in pursuit of an object.
At 7 month they can assume a sitting position with support.
Between 8-9 month they can assume a sitting position un supported with back straight.
From 6 month the child starts to take weight on his legs.
At 9 month a child bounces or stamps when supported and able to stand steadily for a short time as long as
their hands are held.
At 9-10 month start crawling either on his hands and knee this called creeping or crawling on his abdomen
on which the child pull himself forward by his hands.
Some infants crawl by sitting on their buttocks this called bottom shuffling.
At 12 months infant taken 10 steps unsupported.
Second year
At 15 month the infant can walk alone and crawls upstairs.
At 18 month they can run stiffly and can climb up stairs with one hand is held.
At 20 month they can go down stairs with one hand is held.
At 24 month they can run well, walks up and down stairs and they can jump.
Third year
The child can goes up stairs alternating feet.
He can stands momentarily on one foot. He can rides tricycle.
4-5 year
Alternating foot is used to descent stairs by 4 years.
At 48 month he can hop on one foot. Throw ball over head.
At 60 month he can skip.
Middle child hood (6-11 years ):-
At age of 6years the child is -Able to walk on balance beam. - Able to skip using a skipping rope. - Mature
jumping.
3
2) Vision and fine manipulation:-
First 3 months
In the first few days of life infant watch his, her mother, can fixate on objects placed close to or move
through their line of vision 20-30 cm from child face.
At first 4 week the infant fixate his eyes on face or light in the line of vision.
At end of 4 week the infant can watches persons and follows moving object.
At 8 week the infant follows moving object 180 degree.
In fine motor movement the infant within 4 week of life can make contact with stationary objects with in
their reach and elicit reflex grasp.
3-6 months
Infant can follow an object over an arc of 180 following it up ward and down ward.
At 4 month infant can make contact with objects of moderate size, grasping them and bring them to the
midline and to the mouth for visual and oral exploration.
At 6 month can approaches the objects with ulner border of the hand (palmer grasp)
At 6-6.5 month most infant can grasp a large object such as rattle & transfer it from hand to hand.
6-12 months
The infant can follow objects in all directions.
At 9 month infant approaches the objects with radial border and taken it in a scissor grasp between side of
thumb & index finger before transferring it to other hand & putting it in his mouth.
At 12 month he approaches the object with index finger and picks it up precisely between the end of the
thumb and index finger this called unassisted pincer movement of for finger and thumb (pincer grasp).
At 10 months they wave bye-bye.
At 12 month infant enjoy simple games with a toy such as ball and can release object into offered hand.
At 9-10 month they can club hands.
Second year
At 2 year vision is tested by showing small toys hold at three meters away from him and ask him to match
them or if he can name them.
At 15 month the child can place a pellet into a small bottle and can put 3 cubes on top of another.
At 18 month the child can dump the pellet from bottle and can build a tower of 3-4 cubes, he can imitates
scribbling, imitate vertical stroke.
At 24 month the child can build a tower of 6-8 cubes.
At 24 month the infant can do circular scribbling, imitate horizontal stroke, folds paper once imitatively.
Third year
He can build a tower of 9-10 cubes.
He can imitate construction of bridge of 3 cubes.
At 30 month of age the child makes vertical and horizontal strokes but not joint them to make a cross. And
he can imitate circular stroke.
At 36 month the child the child can copies a circle and imitate a cross.
Test near and far vision 3 meter away using five letter matching test or animals.
4-5 year
Test vision at 3 meters with both eyes and with separate eye and use 7 letter matching test. At 4 years he
copies cross and square. At 60 month he draws triangle from copy. Name longer and heavier of two things.
6-11 year
At age of 5-6 years the child can use a 3finger grasp of pencil & use fingers to generate movement.
At age of 6years the child can copy complex shapes like diamond.
At age of 6-7 years the child can form most letters and number correctly.
At age of 6-7 years the child also can write consistently on lines.
4
3) Hearing and speech:
First 3 months
When the infant hear a sound may quite, blink, or startle or cry.
The infant here made no real language but vocalization, he may coos (make noise) at 8 week of life.
Small throaty noise begins at about 4 week, some vowel sounds are produced by 8 week and are usually
uttered with pleasure at social contact by 12 week.
3-6 months
At 6 month hearing is tested by a sound made at 45cm away from the ear but at the level of ear, slightly
behind him using high pitch sound. At 6 month infant start babbling sounds.
6-12 months
At 7 month the infant turn to sound 45 cm lateral to ear.
At 9 month the infant turn promptly to sound 90 cm lateral and diagonally to ear.
At 12 month the infant turn to sound 90 cm vertically above his head.
The optimal age at which to test hearing is 9 month.
At 6-7 month the infant can make repetitive vowel sounds.
At 8 month the infant can make repetitive constant sounds (ba-ba, ma-ma, and da-da).
At 9-10 month the infant can make sounds he say (mama, dada)
At 12month the infant can make single ward like mum, dog.
Second year
At age of 15 months the child follows simple commands and respond to his name.
At 18 month the child can speak 10 words (average). name pictures, identifies one or more parts of body.
At 2 years he can puts 3 wards together (subject, verb, and object)
Follow simple instructions and understand single request example (bring the ball).
Hearing is tested 90 cm out of his sight at a level of the ear
At 2 years he can identify at least 4 parts of his body.
Third year
For test hearing ask the child to obey simple spoken instructions at a distance 3 meter away. Example point
to his head or mouth.
At 30 month the child can refer to himself as I or me.
At 36 month the child knows his age and name and his sex. He counts 3 objects correctly and he can repeat
3 numbers or a sentence of 6 syllables.
At 3 year child can match basic colors.
4-5 year
Hearing is tested at 3 meters away using voices, spoken instructions or toes & watch for his speech.
At 48 month he counts 4 pennies, he tells a story.
At 60 month he names 4 colors, count 10 digits and repeats sentence of 10 syllables.
6-11 year
6-7 years: - can give short oral reports. - Talks about past events in detail.
-Knows the seasons. -Can name the days of a week, and time of day.
7-8 years: -Can use appropriate grammar in their speech and written work.

5
4) Social behavior:
First 3 months
By 2-6 week infants may appear more comfortable with family persons than strangers.
Fragmentary smiles may manifest soon after birth, fully developed social smile occur between 3-5 week.
Primitive reflexes: at birth Moro reflex active, placing& stepping reflex & grasp reflex also active
At 12 week Moro response disappeared.
3-6 months
At 4 month infants start laugh aloud at pleasurable social contact and show displeasure by changes of
expression or crying.
At 6 month infants very excited when see food and protest if a toy taken away from him.
At 6 month infant starts to imitate, for example if you tap on the table he will do the same.
6-12 months
Between 6-8 month infants develop anxiety on separation from regular caretaker.
Between 9-10 month infants usually are less dependant on presence of care takers.
At 9-10 months infant starts to respond to sound of name.
Second year
At 18 month the child cooperates with feeding and drinks from an ordinary cup using 2 hands.
At 2 years he handles the spoon well.
He copy mother to do things about the house (brushing, and cleaning)
At 18 month he is able to tell his mother when he is about to urinate or go to potty.
At 2 years he can identify 2-3 objects (book with figures) ask him to show you where the car is. He also
listens to stories with pictures.
Until the end of 2 years, the play usually solitary.
Third year
The child plays simple games (in parallel with other children)
He helps in Dressing (unbuttons clothing and put on shoes) He washes hands.
He is dry and clean day and night at 3 years, while at 2.5 year he is dry during day only.
4-5 year
At 48 month he plays with other children. He goes to toilet alone.
At 60 month he dresses and UN dresses.
6-11 year
6 years: - can sit at a desk and follow teacher instruction. - Packing the bag of school with assistance.
6-7 years: -Enjoys playing in small group.
7years: - Showering independently. -Packing a bag for school with little assistance.
Reading and Writing:-
At age of 6 years the child can read a few short regularly spelled words.eg:- their names.
At age of 6-7 years the child able to write regular basic words.
At age of 7 years the child can write complete sentence with punctuation
At age of 8 years the child can write at least 2 sentences with appropriate grammar & punctuation.

6
Maturity
Child maturity can be assessed by different ways which includes:-
1) Skeletal maturity. 2) Dental maturity. 3) Sexual maturity. 4) Neurological maturity.
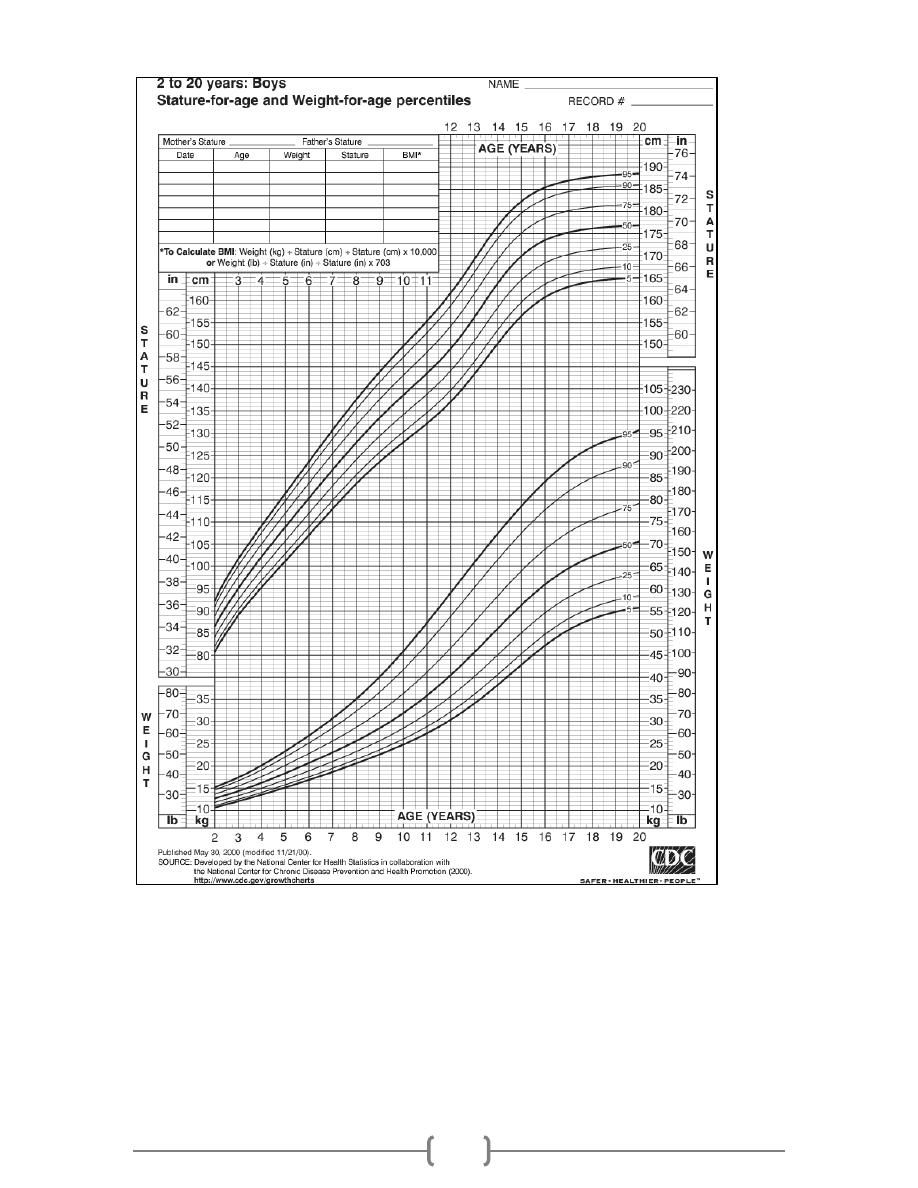
Skeletal maturity
This can be assessed by bone age which is determined by appearance and numbers of bone and
state of fusion of epiphysis, particularly by X- ray of wrist and hand in young children and
infants. And by X- ray of elbow in older children.
Dental maturity
The first tooth appears at 5-9 month it is the lower central incisor then upper central incisor, upper
lateral incisor, lower lateral incisor, first molar, canines (cuspid), second molar. During first year
total number of teeth is 6-8.
During second year total numbers of teeth 12-16, the child completes the deciduous teeth which
are 20 in number at 2.5 years. While the first permanent tooth appears is the first molar at age of 6
years, when the shedding of deciduous teeth begins.
Sexual maturity
o This will starts from the age at which secondary sexual characteristics appears. Between 10 and
20 years of age, children undergo rapid changes in body size, shape, physiologic and
psychological functions.
o Adolescence proceeds across 3 periods.
1. EARLY Adolescence between (10-13 yr).
2. MIDDLE Adolescence between (14-16 yr).
3. LATE Adolescence between (17-20 yr).
o The resulting sequences of somatic and physiological changes give rise to
Sexual maturity rate (S M R) or tanner stages. This is divided into 5 stages of sex maturation.
o In girls, the first visible sign of puberty is the appearance of breast buds between (8-13 yr) there
is also enlargement of ovaries, uterus, thickening of endometrium and vaginal mucosa.
Pubic hair become darker and increase in amount.
Axillary hair appears with axillary perspiration.
Menarche starts during middle adolescence usually between (9-16 yr).
Menses usually begin after appearance of breast bud by 2- 2.5 years.
o In boys testicular enlargement begin at 9.5 years.
Scrotum becomes darker and enlarged.
Pubic hair become darker starts to curl and increase in amount.
Axillary hair appears, axillary perspiration, and then facial hair appears with change in voice.
o For both sexes, growth acceleration begins in early adolescence, but peak growth velocities are
not reached until middle and late adolescence. Boys typically peak 2-3 yr later than girls and
continue their linear growth for approximately 2-3 yr after girls have stopped.
7
