1
1
The Basic Neurologic
Examination
Sally De Castro Tilsen, P.A.-C, MSCS
Hoag Neuroscience Center and
MS Center of Southern California
Newport Beach, California
OBJECTIVES:
Understanding the importance of the basic
neurologic history and examination
• To Teach How to Conduct a Basic Neurologic
Examination
• Review the Use of Instruments Needed for a Complete
NE
• Review Specific Clinical Testing and Techniques
• Discuss Abnormal Findings
• Learn How to Conduct Specific Tests for the Following
Disorders:
Dementia
Multiple Sclerosis
Parkinson’s Disease
A mechanic does not need to use every tool on every project
2
2
Tools of the Trade
•
Steel measuring tape
•
Stethoscope
•
Flashlight
•
Ophthalmoscope
•
Tongue blades
•
Vials of coffee, salt, sugar
•
Cotton wisp
•
Two stopped tubes
•
Disposable straight pins
•
Reflex hammer
•
Penny, nickel, dime, key
•
Blood pressure cuff
•
Forms for various tests
http://www.cbu.edu/~mcondren/IRM/Stop-Look-Listen-sign-IRM-7-7-07.jpg
Take a Good HISTORY
• Much of the NE comes from the History
• Assess the Pts. word articulation, content of speech,
and overall mental status.
• Inspect facial features.
• Inspect eye movements, facial movements and any
asymmetry.
• Observe how a Pt. swallows saliva and breathes.
• Inspect the posture, look for tremors
• The history and observation can help you focus on
specific systems: motor, sensory, cranial nerves or
cerebral functions.
Neurologic Examination
• Mental Status Exam
• Cranial Nerve Examination
• Motor Examination
• Reflexes
• Sensory
• Coordination
• Gait
3
3
MENTAL STATUS
Outline of Mental Status
Examination
• General behavior and appearance
• Stream of talk
• Mood and affective responses
• Content of thought
• Intellectual capacity
• Sensorium
Level of Consciousness
• Awake and alert
• Agitated
• Lethargic
– Arousable with
• Voice
• Gentle stimulation
• Painful/vigorous stimulation
• Comatose
ORIENTATION
• PERSON
– NOT WHO THEY ARE BUT WHO YOU ARE
• PLACE
• TIME
4
4
LANGUAGE
• FLUENCY
• NAMING
• REPETITION
• READING
• WRITING
• COMPREHENSION
Aphasia vs. dysarthria
Mental Status Exam
• Family story of memory loss
• Orientation
• General Information
• Spelling &/or numbers
• Recognition of objects
Mental Status Exam
• When there is a history of cognitive decline
• What tests?
– Mini-mental State Examination
– Halstead-Reitan Performance Test
– Full Cognitive and Neuropsychological testing
5
5
CRANIAL NERVES
CRANIAL NERVE EXAM
• I - OLFACTORY
– DON’T USE A NOXIOUS STIMULUS
– COFFEE, LEMON EXTRACT
• II - OPTIC
– VISUAL ACUITY
– VISUAL FIELDS
– FUNDOSCOPIC EXAM
C.N. 1 (olfactory)
• Each nostril separately
– non-irritating substances : ideally coffee/aromatic oils;
practically soap/toothpaste
• Anosmia
(olfactory)
vs. Ageusia
(taste)
• First consider nasal disorders
C.N. II (optic)
• Ophthalmoscopy:
– Optic atrophy, papilledema
• Visual acuity
– Snellen chart or
– Hand-held card
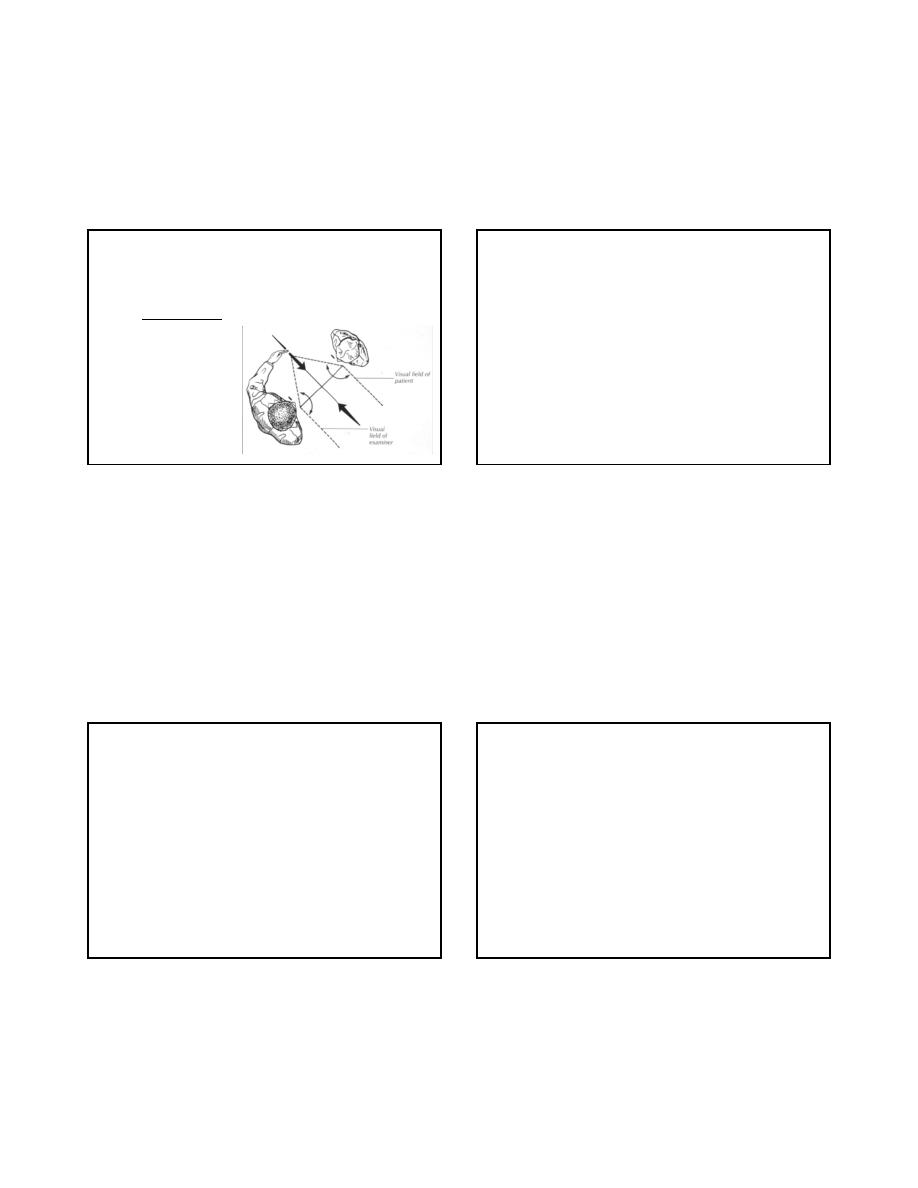
Color Vision
6
6
C.N. II (optic)
• Visual fields
– Outline perimetry : misses relative defect or inattention
– Other confrontation
techniques(Beck):
Pupillary reflexes (CN 2 & 3)
• Eyes looking in the distance, bright light
• “ Swinging flashlight test “
– e.g. is there a relative afferent pup. defect?
– a sensitive test for optic neuropathy
• Horner syndrome (oculo-sympathetic)
– miosis, ptosis, anhydrosis
CRANIAL NERVE EXAM
• III/IV/VI OCULMOTOR, TROCHLEAR,
ABDUCENS
– PUPILLARY RESPONSE
– EYE MOVEMENTS
• 9 CARDINAL POSITIONS
– OBSERVE LIDS FOR PTOSIS
• V - TRIGEMINAL
– MOTOR - JAW STRENGTH
– SENS - ALL 3 DIVISIONS
CN 3, 4 , 6
• Parasympathetic (pupillo-constrictor) in CN 3
• CN 3,4,6 are under “central” control; Ex:
– Medial longitudinal fasciculus
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia: ipsilateral eye fails to adduct,
contra lateral eye shows nystagmus
– Frontal eye fields
Tend to direct gaze contra laterally : with a frontal lesion,
eyes are deviated ipsilaterally (“towards the lesion”)
7
7
Extraocular movements
C.N. 5 (trigeminal)
• Test light touch and/or pinprick in 3 divisions
• Corneal reflex
– cotton / kleenex on cornea (not conjunctiva)
– Avoid visual threat
• Palpate contracting masseter & temporalis m
• Jaw jerk
C .N. VII
Special visceral
efferent
frontalis, corrugator,
orbicul oris & ocul.
Buccin., platysma
stapedius
inspect facial muscles
> 8 maneuvers
e.g. raise eyebrows
smile, frown, etc.
General visceral
efferent
lacrimal gland
submandigular gland
inspect eye
Schirmer test
Special visceral
afferent
taste buds
anterior 2/3 tongue
test taste
salt, sugar, acetic a.
& quinine solutions
General somatic
afferent
external ear
test light touch
in post ext. ear canal
8
8
CRANIAL NERVES
• VII - FACIAL
– OBSERVE FOR FACIAL ASYMMETRY
– FOREHEAD WRINKLING, EYELID CLOSURE,
WHISTLE/PUCKER
• VIII - VESTIBULAR
– ACUITY
– RINNE, WEBER
Rinne test
CRANIAL NERVES
• IX/X - GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL, VAGUS
– GAG
• XI - SPINAL ACCESSORY
– STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID M.
– TRAPEZIUS MUSCLE
• XII - HYPOGLOSSAL
– TONGUE STRENGTH
– RIGHT XII THRUSTS TONGUE TO LEFT
C.N. 9 & 10
• Is there dysphonia?
• Assess palatal movement with phonation
• IF
there is dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia:
– Test gag reflex
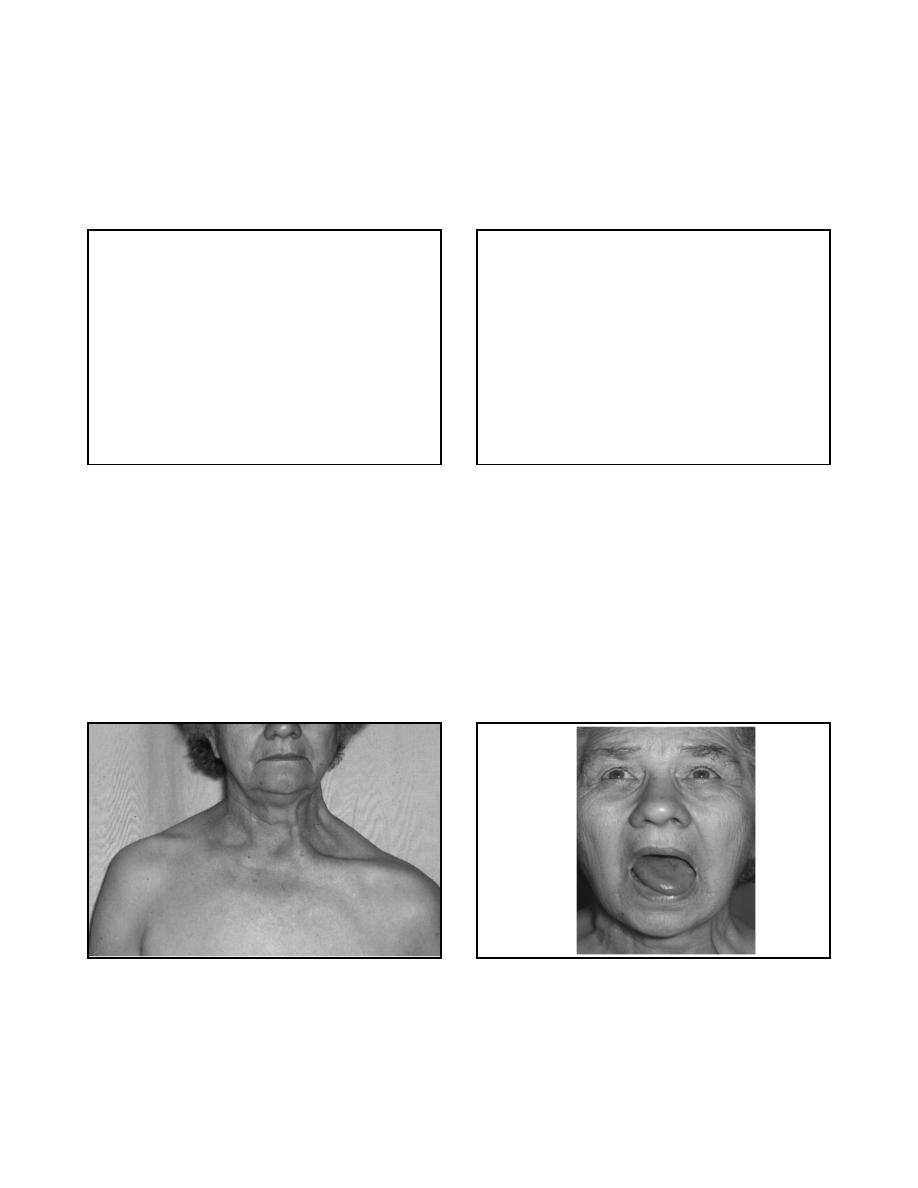
9
9
C.N. 11 (spinal accessory)
• Two muscles:
– trapezius: shoulder shrug ; abduction of arm beyond
90 degrees
– sternocleidomastoid: turn chin to opp shoulder
C.N. 12 (hypoglossal)
• Inspect tongue at rest
– atrophy, fasciculations
• Tongue protrusion
– deviation towards paretic side
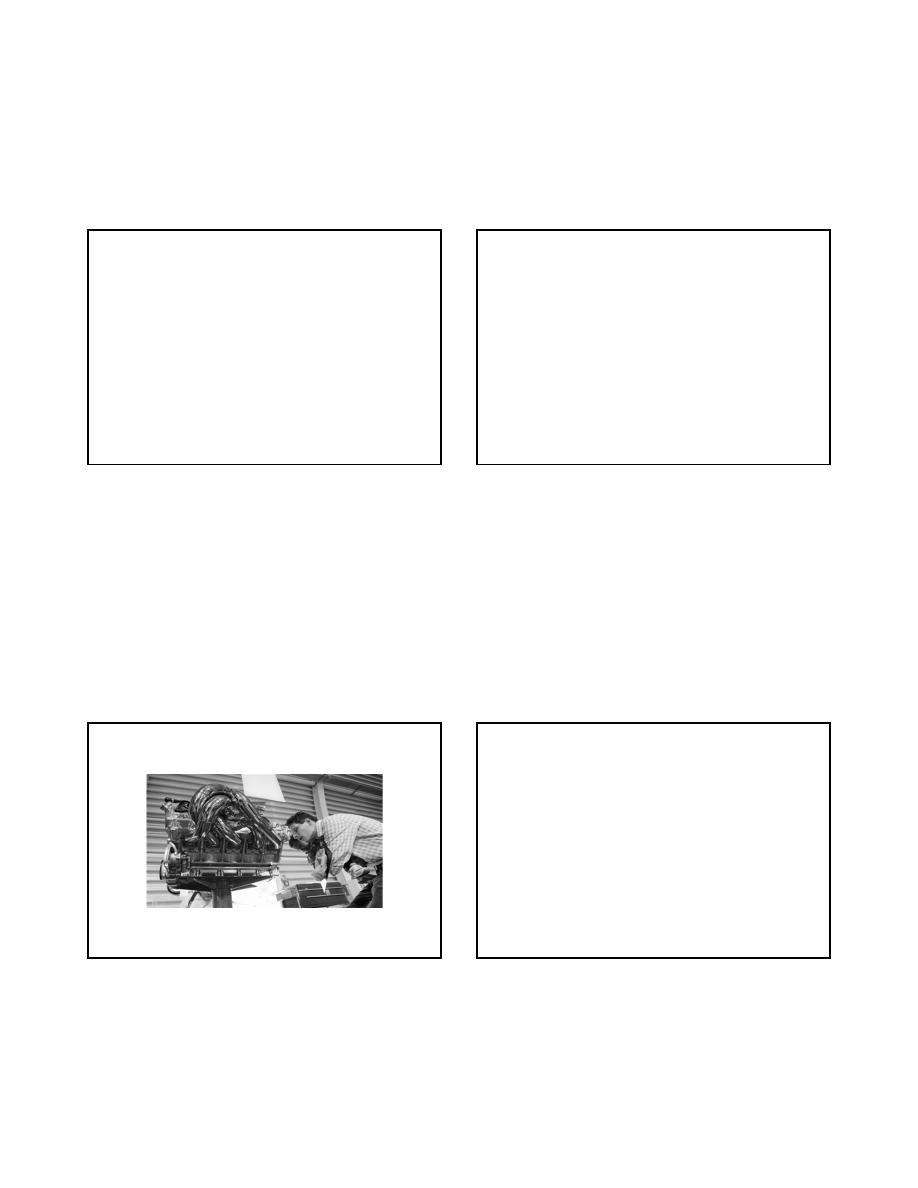
10
10
MOTOR EXAMINATION
Motor Examination
STRENGTH
• STRENGTH
– GRADED 0 - 5
– 0 - NO MOVEMENT
– 1 - FLICKER
– 2 - MOVEMENT WITH GRAVITY REMOVED
– 3 - MOVEMENT AGAINST GRAVITY
– 4 - MOVEMENT AGAINST RESISTANCE
– 5 - NORMAL STRENGTH
STRENGTH EXAM
• UPPER AND LOWER EXTREMITIES
• DISTAL AND PROXIMAL MUSCLES
• GRIP STRENGTH IS A POOR SCREENING
TOOL FOR STRENGTH
• SUBTLE WEAKNESS
– TOE WALK, HEEL WALK
– OUT OF CHAIR
– DEEP KNEE BEND
11
11
MUSCLE OBSERVATION
• ATROPHY
• FASCIULATIONS
TONE
• INCREASED, DECREASED, NORMAL
• COGWHEELING
• CLASP KNIFE
ABNORMAL MOVEMENTS
• TREMOR
– REST
– WITH ARMS OUTSTRETCHED
– INTENTION
• CHOREA
• ATHETOSIS
• ABNORMAL POSTURES
CEREBELLAR FUNCTION
• RAPID ALTERNATING MOVEMENTS
• FINGER TO FINGER TO NOSE TESTING
• HEEL TO SHIN
• GAIT
– TANDEM
12
12
Romberg Sign
• Stand with feet together - assure patient
stable - have them close eyes
• Romberg is positive if they do worse with
eyes closed
• Measures
– Cerebellar function
– Frequently poor balance with eyes open and
closed
– Proprioception
– Frequently do worse with eyes closed
– Vestibular system
Gait:
• Normal Walking
• Toe Walking
• Heel Walking
• Inversion Walking
• Eversion Walking
• Tandem Walking
• Romberg
Gait Evaluation
• Include walking and turning
• Examples of abnormal gait
– High steppage
– Waddling
– Hemiparetic
– Shuffling
– Turns en bloc
REFLEXES
13
13
MUSCLE STRETCH REFLEXES
(DEEP TENDON REFLEXES)
• GRADED 0 - 5
– 0 - ABSENT
– 1 - PRESENT WITH REINFORCEMENT
– 2 - NORMAL
– 3 - ENHANCED
– 4 - UNSUSTAINED CLONUS
– 5 - SUSTAINED CLONUS
MSR / DTR
• BICEPS
• BRACHIORADIALIS
• TRICEPS
• KNEE
• ANKLE
OTHER REFLEXES
• Upper motor neuron dysfunction
– BABINSKI
• present or absent
• toes downgoing/ flexor plantar response
– HOFMAN’S
– JAW JERK
• Frontal release signs
– GRASP
– SNOUT
– SUCK
– PALMOMENTAL
SENSORY EXAM
14
14
SENSORY EXAM
• VIBRATION
– 128 hz tuning fork
• JOINT POSITION SENSE
• PIN PRICK
• TEMPERATURE
Start distally and move proximally
HIGHER CORTICAL SENSATIONS
• GRAPHESTHESIA
• STEREOGNOSIS
• DOUBLE SIMULTANEOUS STIMULATION
• BAROSTHESIA
• TEXTURES
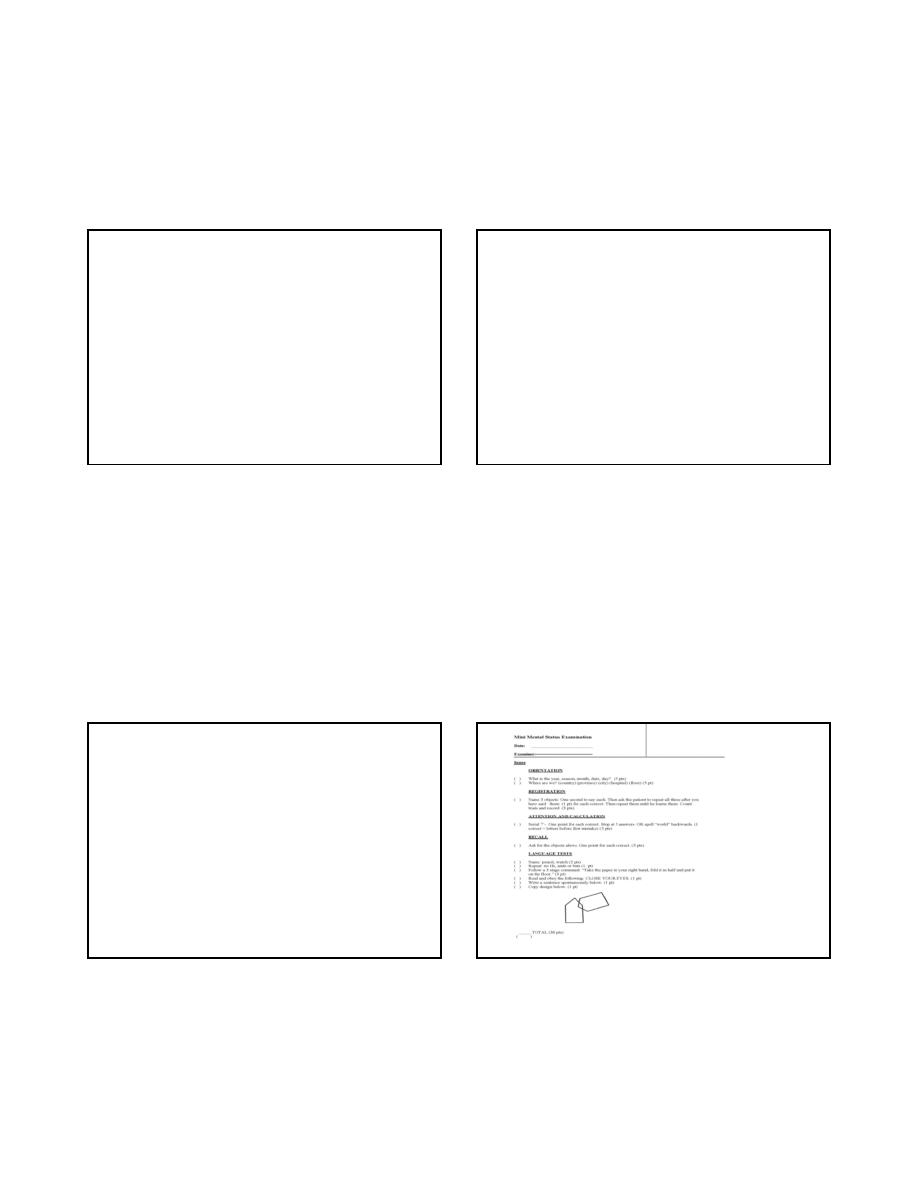
Mini-Mental State Examination
Halstead-Reitan Battery Test
Cognitive Impairment
15
15
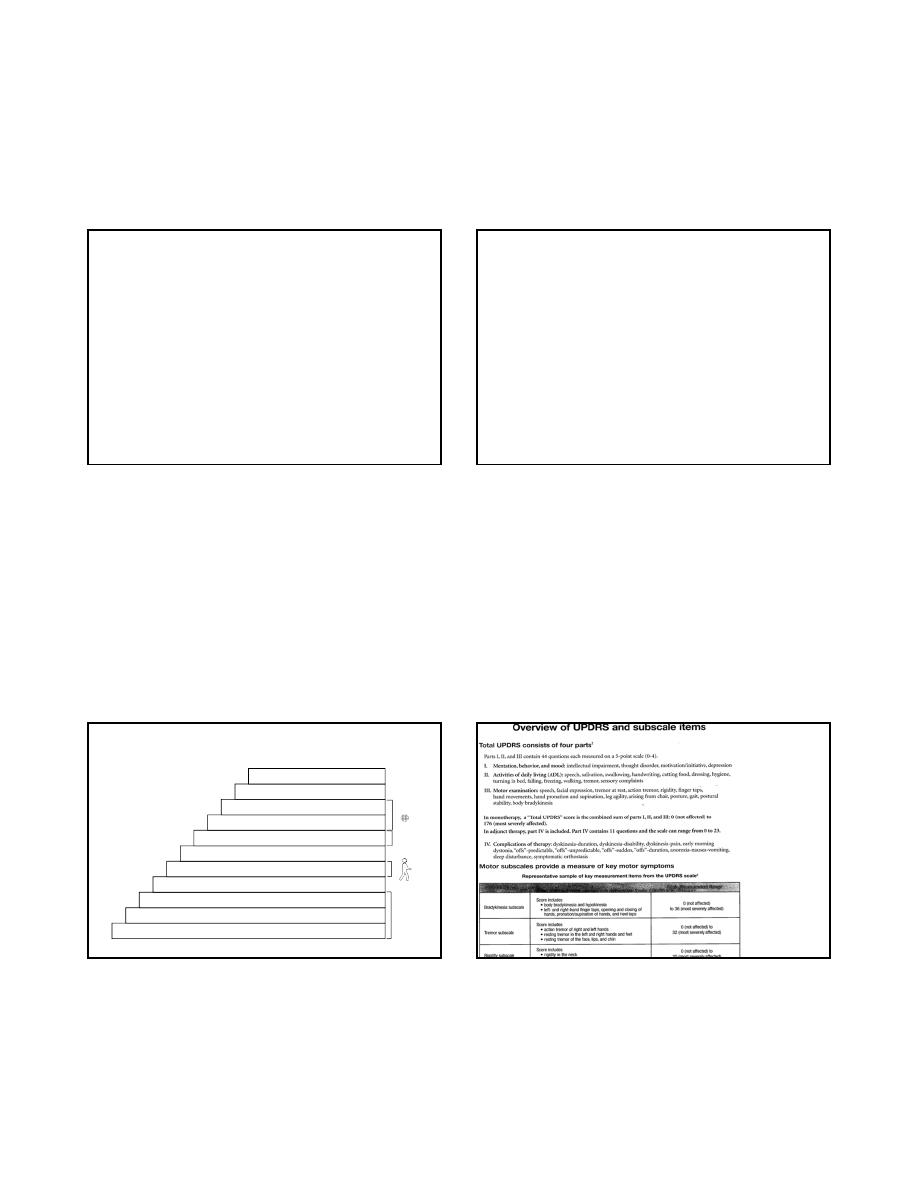
Expanded Disability
Status Scale
Neurostatus scoring
For Multiple Sclerosis
EDSS:
Scoring to Quantify Impairment
Associated with Multiple Sclerosis
7. Kurtzke JF. Neurology. 1983;33:1444-1452.
0 = Normal neurologic exam
1.0-1.5 = No impairment
2.0-2.5 = Impairment is minimal
3.0-3.5 = Impairment is mild to moderate
4.0-4.5 = Impairment is relatively severe
5.0-5.5 = Increasing limitation in ability to walk
6.0-6.5 = Walking assistance is needed
7.0-7.5 = Confined to wheelchair
8.0-8.5 = Confined to bed/chair; self-care with help
9.0-9.5 = Completely dependent
10.0 = Death due to MS
Unified Parkinson’s
Disease Rating Scale
Comprehensive
Parkinson’s Disease Tool
16
16
References
• The Technique of the Neurologic Examination
by W. DeMyer, 2004, McGraw Hill, 5
th
edition
• Basic Clinical Neuroscience by P. Young, P.H.
Young, D. Tolber, 2008, Lippincott, Williams and
Wilkins
• Neurology for Dummies, 2008
• Neuroanatomy Through Clinical Cases, Hal
Blumenfeld, 2010
