
Acute Respiratory
Tract Infections

Introduction
ARI responsible for 20% of childhood (< 5 years)
deaths
–
90% from pneumonia
ARI mortality highest in children
–
HIV-infected
–
Under 2 year of age
–
Malnourished
–
Weaned early
–
Poorly educated parents
–
Difficult access to healthcare
Out- patient visits
–
20-60%
Admissions
–
12-45%

Introduction
In South Africa
–
Same picture as elsewhere
• 20% deaths under 5 years
• Acute pneumonia 90%
Western Cape
–
Pulmonary TB incidence among highest in world
• 576/100 000 children per year
ARI and TB influenced by HIV

Introduction
Upper and lower respiratory tract separated
at base of epiglottis
Six to eight respiratory tract infections per
year (2-3years)
Lower respiratory tract involved in 20-30%
of these

Factors influencing the
incidence of respiratory tract
infections
Poor nutritional status
Poor socio-economic status
Parental smoking
Parasitic infection
Structural abnormalities
Breastfeeding and early weaning
Immunization
HIV incidence
Rainy and cold weather

Danger Signs (IMCI)
High risk of death from respiratory illness
–
Younger than 2 months
–
Decreased level of consciousness
–
Stridor when calm
–
Severe malnutrition
–
Associated symptomatic HIV/AIDS

Pneumonia
Developed world
–
Viral infections
–
Low morbidity and mortality
Developing world
–
Common cause of death
–
Bacteria and PCP in 65%
ARI case management WHO
–
84% reduction in mortality
–
Respiratory rate, recession, ability to drink
–
Cheap, oral and effective antibiotics
• Co-trimoxazole, amoxycillin
–
Maternal education
–
Referral
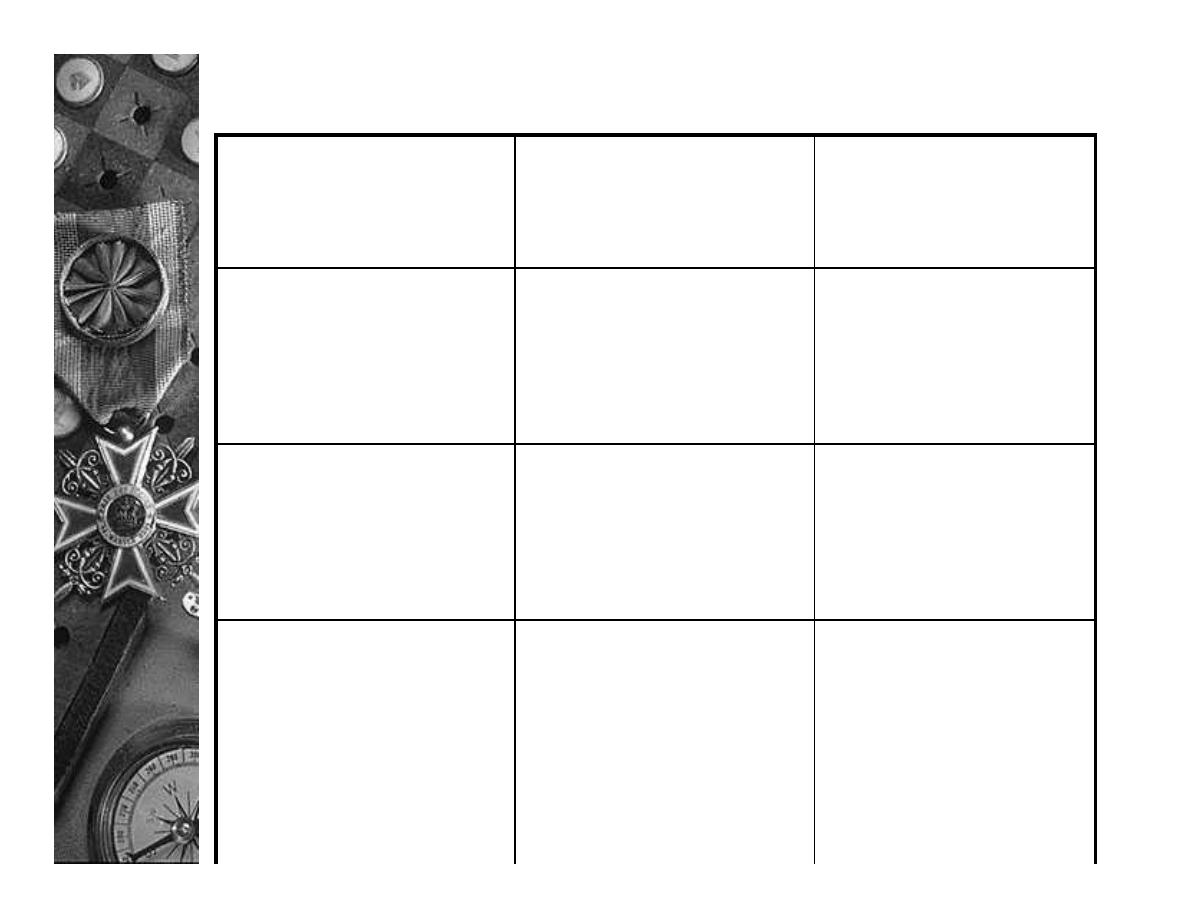

ARI: Classification and management
Supportive measures
Oxygen
Antibiotics
Immediate referral to
level 2 or 3 hospital
Cough
Tachypnoea
Chest wall retraction
Unable to drink
Cyanosis
4. Very severe
pneumonia
Supportive measures
Antibiotics
Refer to hospital
Cough
Tachypnoea
Rib and sternal
retraction
3. Severe pneumonia
Supportive measures
Antipyretic
Antibiotics
Cough
Tachypnoea
No rib or sternal
retraction
2. Pneumonia
Supportive measures
Antipyretic
No antibiotics
Cough
Not tachypnoea
1. No pneumonia

Tachypnoea
Less than 3 months
> 60 breaths per minute
3 months - 12 months > 50 breaths per minute
1year –4 years
> 40 breaths per minute

Measures before transferring to
hospital
Antipyretics
Oxygen
–
40% by mask or prongs
Suctioning of secretions
Stomach tube
–
For decompression,
–
Give fluids
Severely distressed, IV fluids
Intravenous penicillin

Etiology
Vary according to
–
Age, immune status, where contracted
Community acquired (CAP)
–
Developing countries
• S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, S aureus
• Viruses 40%
• Other: Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Moraxella
–
Developed countries
• Viruses: RSV, Adenovirus, Parainfluenza, Influenza
• Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae
• Bacteria: 5-10%
Etiology in special groups
Aminoglycoside +
Vancomycin +
Cephalosporin (3
rd
generation)
Gram negative
Methicillin resistant S.
aureus
Hospital
acquired
pneumonia
Ampicillin +
Aminoglycoside
Gram negative
Group B streptococcus
S.aureus
Less than 3
months
Ampicillin +
Cloxacillin +
Aminoglycoside
Gram negative
S. aureus
Opportunistic
Pneumocystis jiroveci
M. tuberculosis
Immune
compromised
Antibiotic
Organisms
Group

Clinical picture
Neonates may have non-specific signs
–
Lethargy, failure to feed, temperature instability,
apnoea or tachypnoea
Older children
–
Runny nose , sore throat followed by cough, fever and
tachypnoea
More serious pneumonia
–
Tachypnoea, chest indrawing, feeding difficulty
Respiratory failure
–
Severe tachypnoea, chest indrawing, restlessness,
grunting, tachycardia and central cyanosis

Examination
Altered breath sounds and crackles
Signs of lobar pneumonia in minority
–
dullness to percussion, bronchial breathing
Mild pneumonia only tachypnoea
Measure severity of hypoxia with transcutaneous
saturation monitor
Sudden deterioration suggestive of complication
–
Pneumothorax, pyopneumothorax
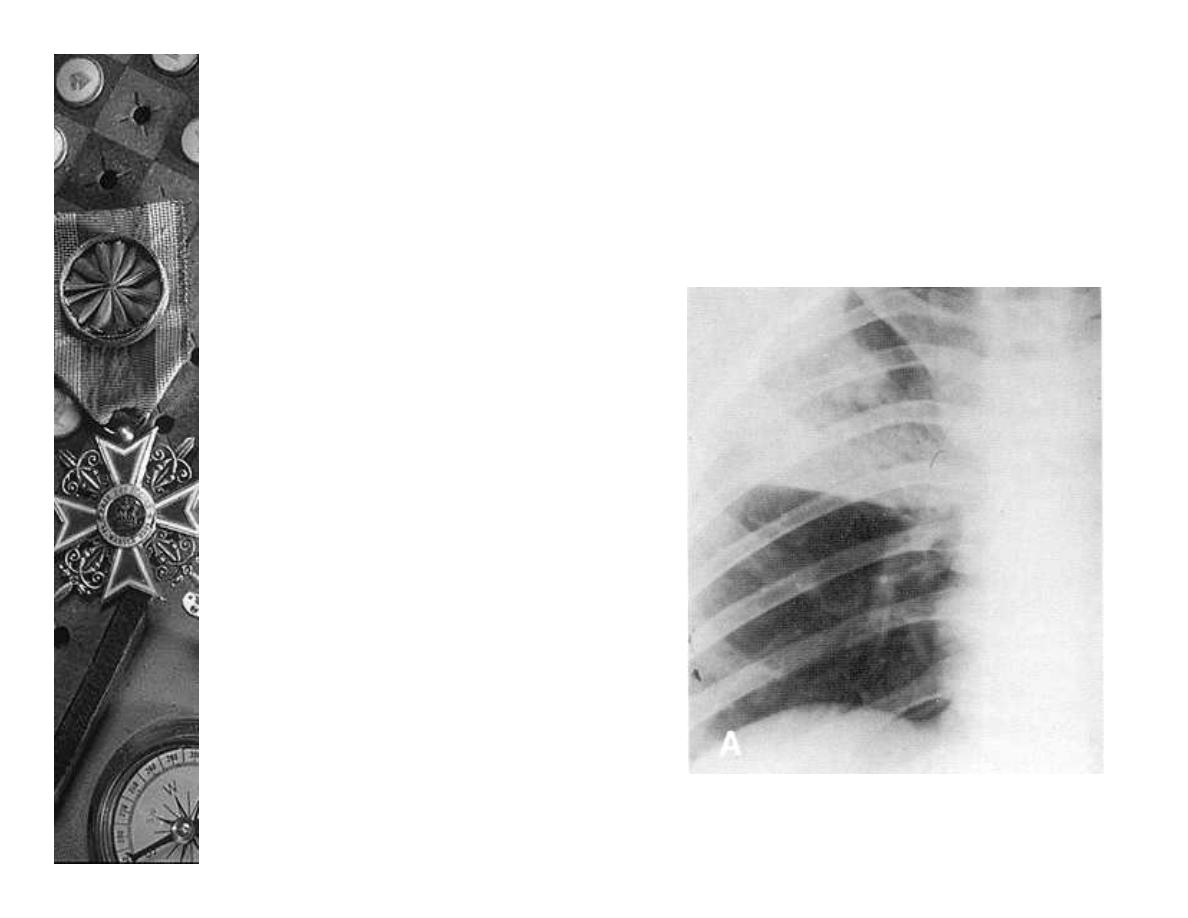
Radiology
Bacterial
–
Poorly demarcated
alveolar opacities
with air
bronchograms
–
Lobar or segmental
opacification
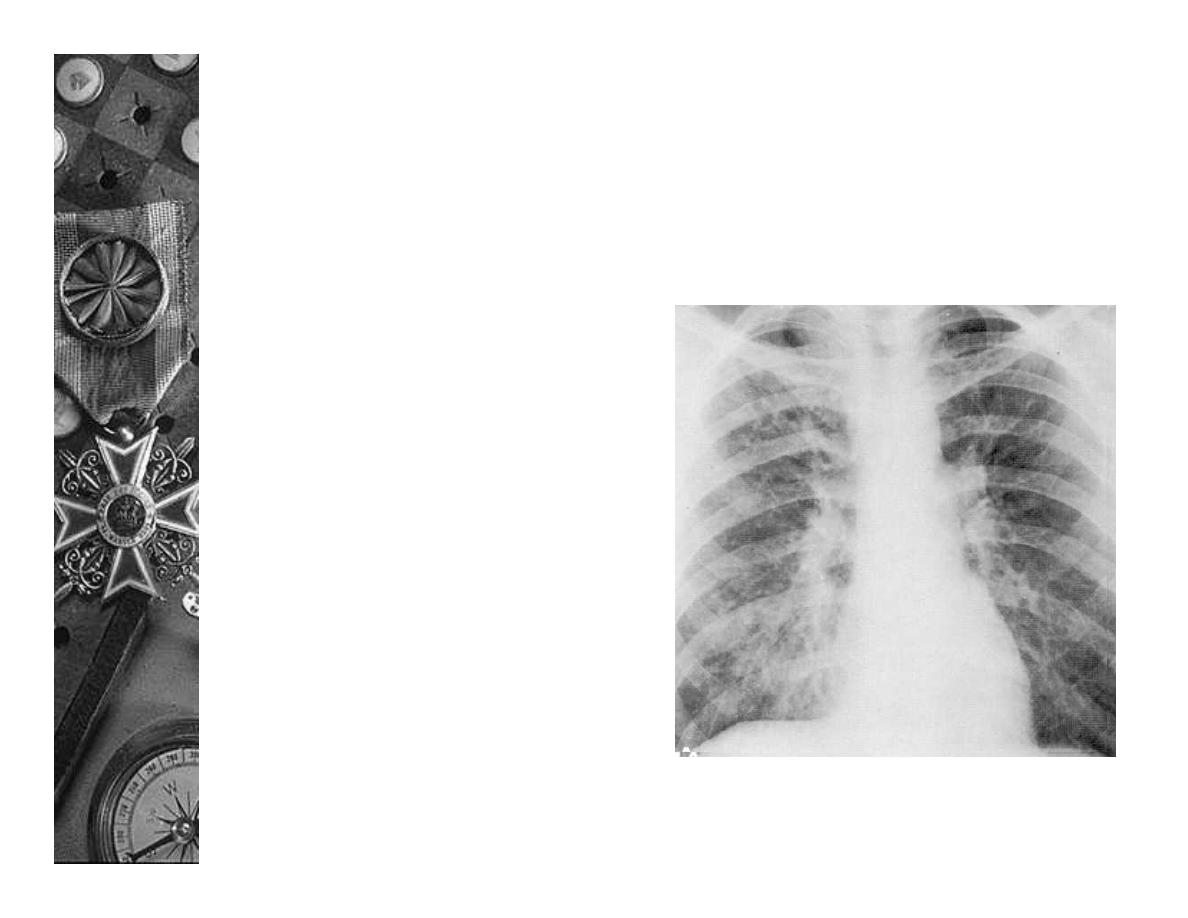
Radiology
Viral
–
Perihilar streaking,
interstitial changes,
air trapping
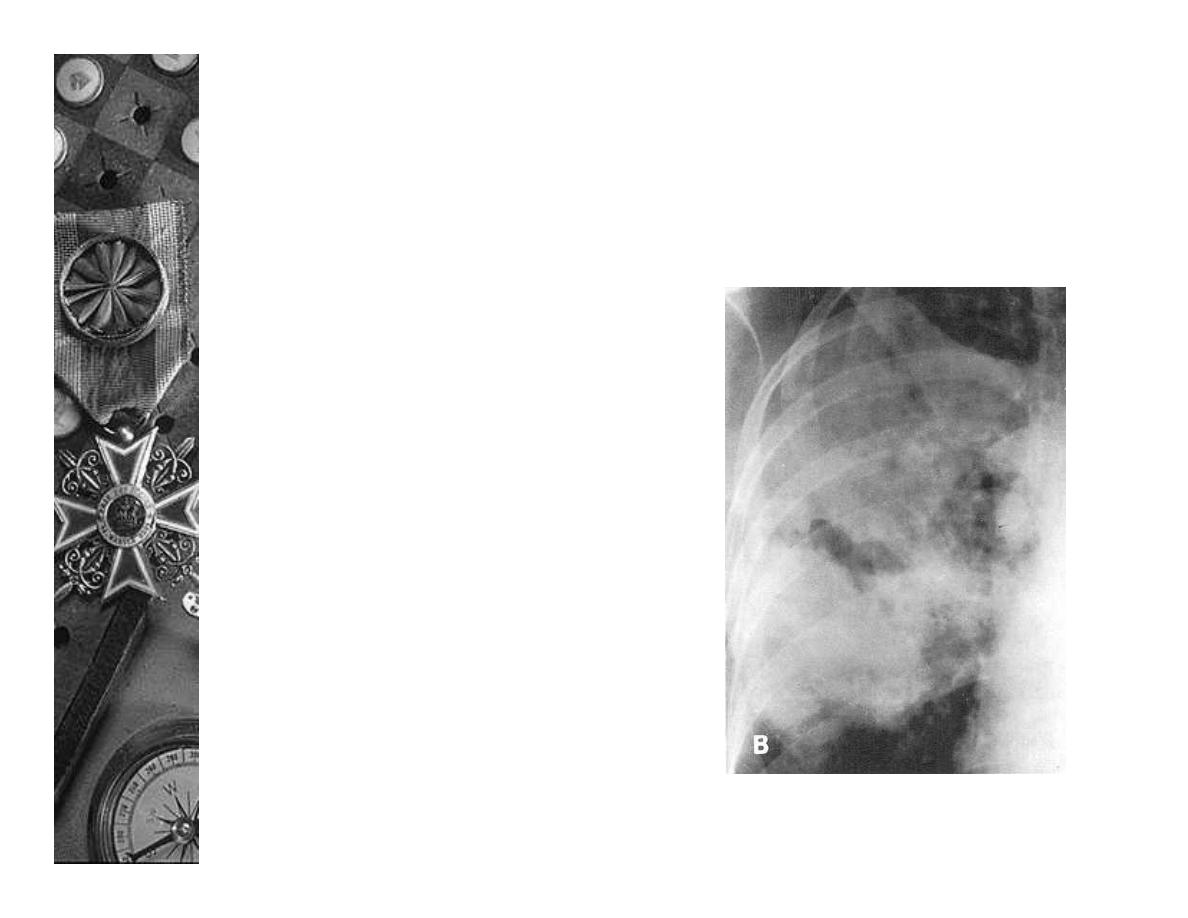
Radiology
Clues to other specific
organisms
–
Staphylococcus – areas of
break-down
–
Klebsiella, anaerobes, H.
influenza or TB –
cavitating or expansile
pneumonia
–
TB, S. aureus, H. influenza
– pleural effusion and
empyema

Diagnosis
White cell count and CRP
Blood cultures
–
25% positive
Sputum specimen
–
Induced sputum
• PCP
• TB
Lung aspirates
Tuberculin skin test
Viruses
–
culture
–
antigen

Treatment
Antibiotics
–
Primary care level
• Amoxycillin, co- trimoxazole
–
Regional hospital
• Amoxycillin, cloxacillin, penicillin, erythromycin
–
Special categories – see table
Oxygen
–
When?
–
Methods of delivery
Blood transfusion
Hydration
–
50 – 80ml/kg/day
Temperature control
Airway obstruction
Other e.g. Vit A

Treatments with NO proven benefit
in acute pneumonia in children
Mucolytics
Chest physiotherapy
Postural drainage
Nebulization

Failure to respond
Incorrect or inadequate dose of antibiotic
Resistant or not suspected organism
Empyema or other complication
TB
Suppressed immunity
Underlying cause
–
e.g. foreign body or bronchiectasis
Left heart failure and not pneumonia
Refer if no improvement after 3 – 5 days

Prognosis
Most children recover without residual
damage
Incorrect treatment leads to tissue
destruction and bronchiectasis
Half of children with pneumonia secondary
to measles or adenovirus have persistent
airway obstruction
