
CASES STUDY/ DATA
INTERPRETATION
HAEMATOLOGY

FULL BLOOD COUNT
• THE ELEMENTS :
1- RBCS
2 - WBCS
3- PLATELETS

RBCS
• ELEMENTS
:
HB.
ERYTHROCYTE COUNT [ RBCS]
HCT
MCV
MCH / MCHC
RDW
RETICULOCYTE
ESR

WBCS
• ELEMENTS
:
NEUTROPHILS
LYMPHOCYTES
MONOCYTES
EOSINOPHILS
BASOPHILS
BLAST

PLATELETS
• ELEMENTS :
INCREASE
DECREASE
NORMAL

GENERAL TOPICS
• THE IMPACT OF
HAEMOGLOBINPATHIES
• PERIMARIATAL SCREENING

ANAEMIA
• DEFINITION:
IT IS A DECREASE IN THE NUMBER OF
CIRCULATING RBCS.
• ETIOLOGY:
1-BLOOD LOSS
2- DECREASE PRODUCTION
[ MARROW FAILURE]
3- INCREASE DESTRUCTION
[ HAEMOLYSIS]
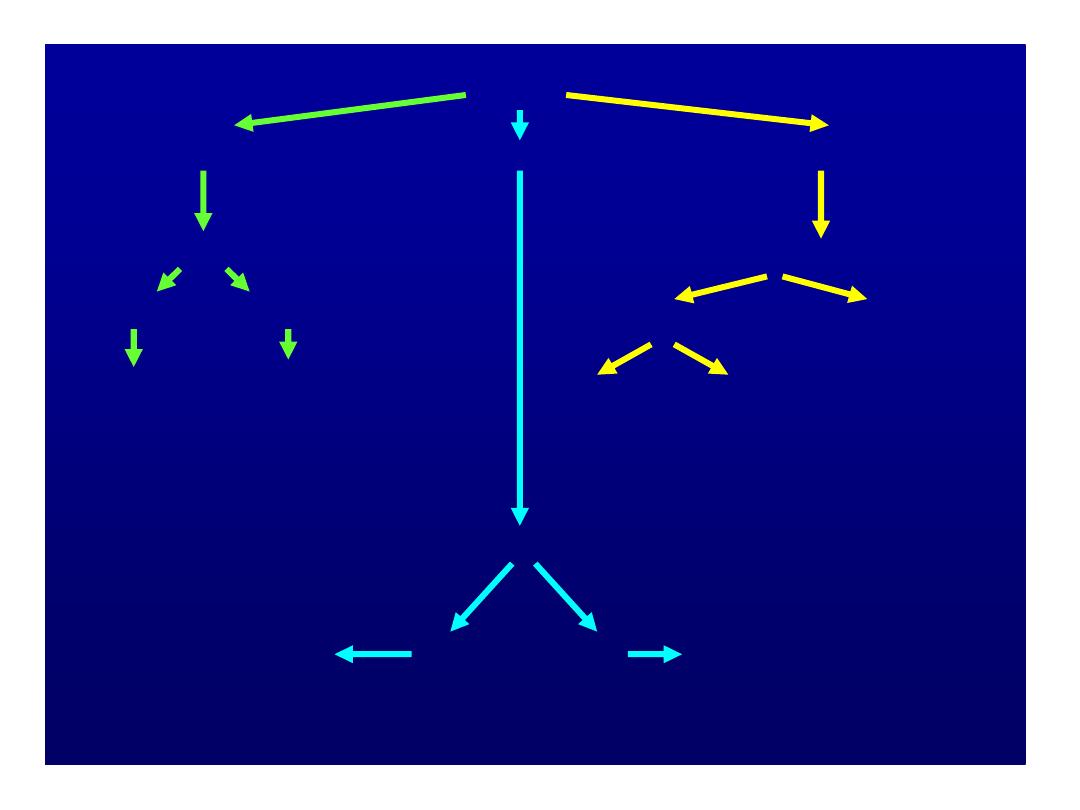
Low Hb=Anemia
MCV
Low=microcytic
Normal=normocytic
High=macrocytic
Ferritin
Fe deficient
Fe normal
Establish
cause
Anemia of
chronic disease
or
hemoglobinopathy
Reticulocyte count
high
low
Anemia of chronic disease
Renal failure
Marrow failure
Hemolysis
or blood
loss
Measure B
12
+ folate
Low -
Establish cause
Normal
Obvious
cause
Cause not obvious
Consider bone marrow

CASE / DISCUSSION
• 19-YEAR OLD FEMALE STUDENT
PRESENT TO THE STUDENTS HEALTH
SERVICE WITH INCREASE FATIGUE&
MALAISE.
NO BLEEDING
MENSTRUAL CYCLE NORMAL.
• P/E NAD
• WHAT IS THE NEXT STEP/S?

CBC
• HB 7
• HCT 22.8
• MCV 72
• RDW 20
• RETIC.COUNT 1.1%
• VIT. B 12 & FOLATE NORMAL
• WBCS 5000
• PLATELETS 285000
• WHAT IS NEXT?

CONT,
• FERRITIN < 4 [ N 12- 200]
• DIAGNOSIS : [ I D A]
• TREATMENT :
A- NON- PHARM.
B- PHARM.

CONT,
IDA CRITERIA
LOW HB
LOW HCT
LOW MCV
LOW MCH
MCHC LOW / N
LOW FERRITIN
LOW FE
HIGH TIBC
HIGH RDW

CASE / DISCUSSION
• AN 18-YEAR OLD MALE DIABETIC
COLLEGE STUDENT, WHO REQUIRES
INSULIN, PRESENT TO THE STUDENTS
HEALTH SERVICE WITH A LOW GRADE
FEVER & COUGH FOR 10 DAYS DURATION.
• P/E: CRACKLES ARE HEARED ON
AUSCULTATION OF BOTH LUNGS AT THE
RIGHT BASE, BUT THERE ARE NO SIGNS
OF CONSOLIDATION.

LAB. RESULTS
CBC:
• HEMOGLOBIN :10.5
ERYTHROCYTE: 3.13 MILLION
HCT :32
MCV :131
MCH :30.6
MCHC :42.5
• WHAT ARE/ IS THE OTHER TESTS
YOU WILL REQUEST?

Cont.
• LEUKOCYTES COUNT : 11500
NEUTROPHILS COUNT: 68%
LYMPHOCYTES COUNT: 24%
MONOCYTES COUNT :7%
EOSINOPHILS COUNT:1%
BASOPHILS COUNT: 0%
• PLATELETS COUNT: NORMAL

CONT,
• VIT. B12 & FOLATE [ B 12 WAS LOW]
• DRUGS & ALCOHOL LEVEL
• SCHILLINGS TEST [ +VE]
• LFT [ GAMMA G –T]
• DD :
• COELIAC DISEASE
• DRUGS
• ALCOHOL INTAKE

CONT,
• THE FINAL DIAGNOSIS [ B12 DEF.]
• TREATMENT:
VIT B12 1000 U IM DAILY X 7 DAYS
THEN WEEKLY X 4 WEEKS
THEN MONTHLY X 4 MONTHS

Haemoglobinopathy Investigation
Usually prompted by clinical findings and/or CBC.
Includes:
• Hb Electrophoresis
• Quantitation of Hb A
2
and Hb F
• Detection of Hb H Inclusions
Other information required : patient age, ethnicity
Additional tests : serum ferritin if microcytic, occasionally molecular
studies and/or family studies
Hb A
Normal
Control
Carbonic
Anhydrase
Hb A2
Abnormal
Control
Anode
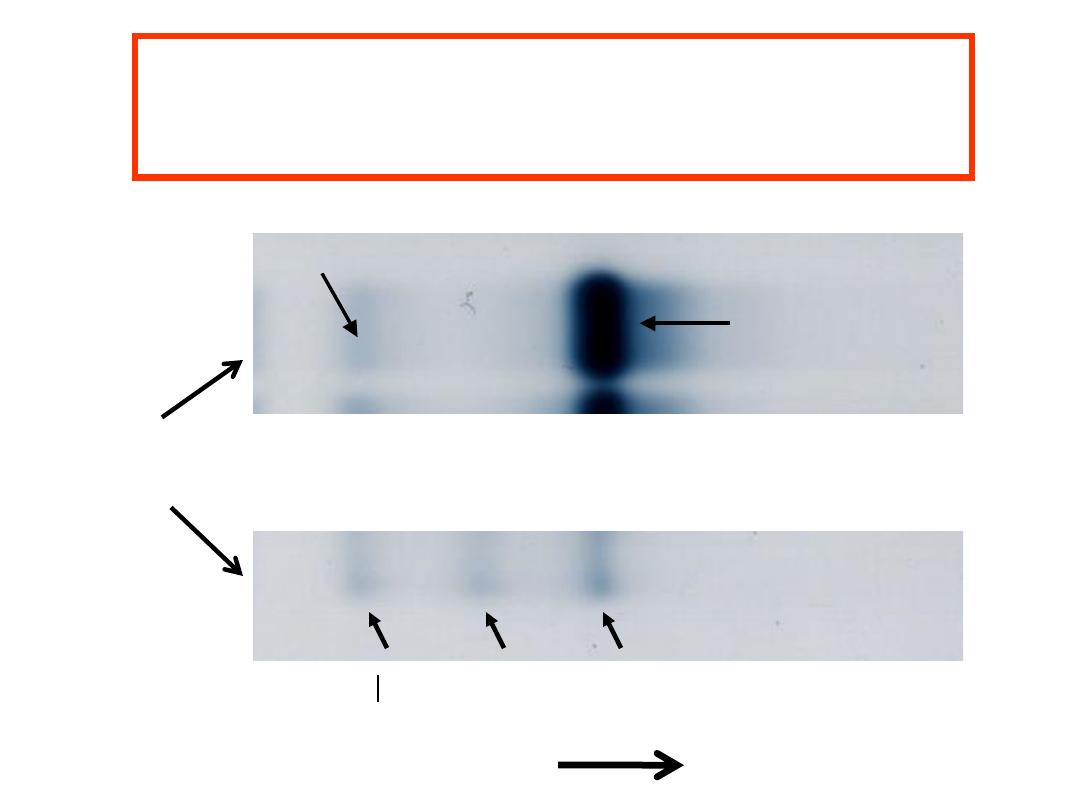
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
at alkaline pH
Case 1
Patient
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis
(alkaline pH )
Hb C
Hb S
Moves in same position as Hb A
2
HbA
Anode
Haemolysate applied
Cathode

Case 1
18 year old young man seen for medical
examination.
Past medical history unremarkable.
Family of middle east descent.
Physical examination normal

Hb
132 g/L (140-180)
MCV 66.1 fL (80-100)
Blood Film: hypochromia,
microcytosis
Case 1
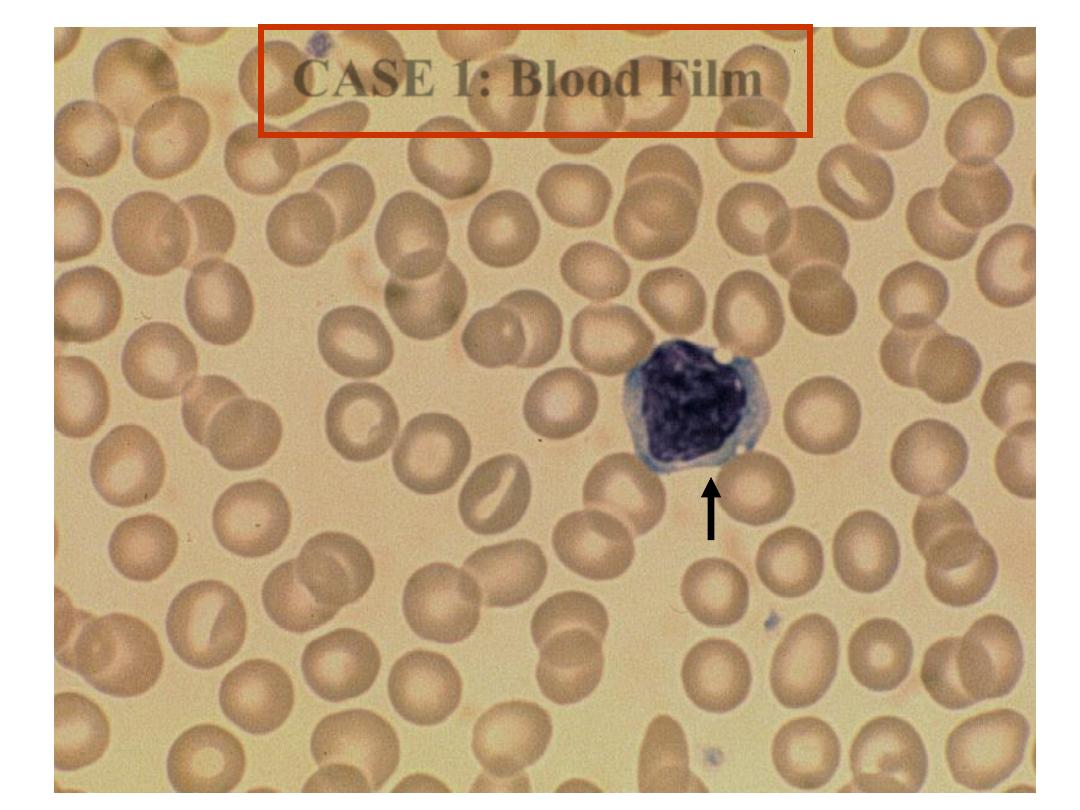
Lymphocyte
CASE 1: Blood Film
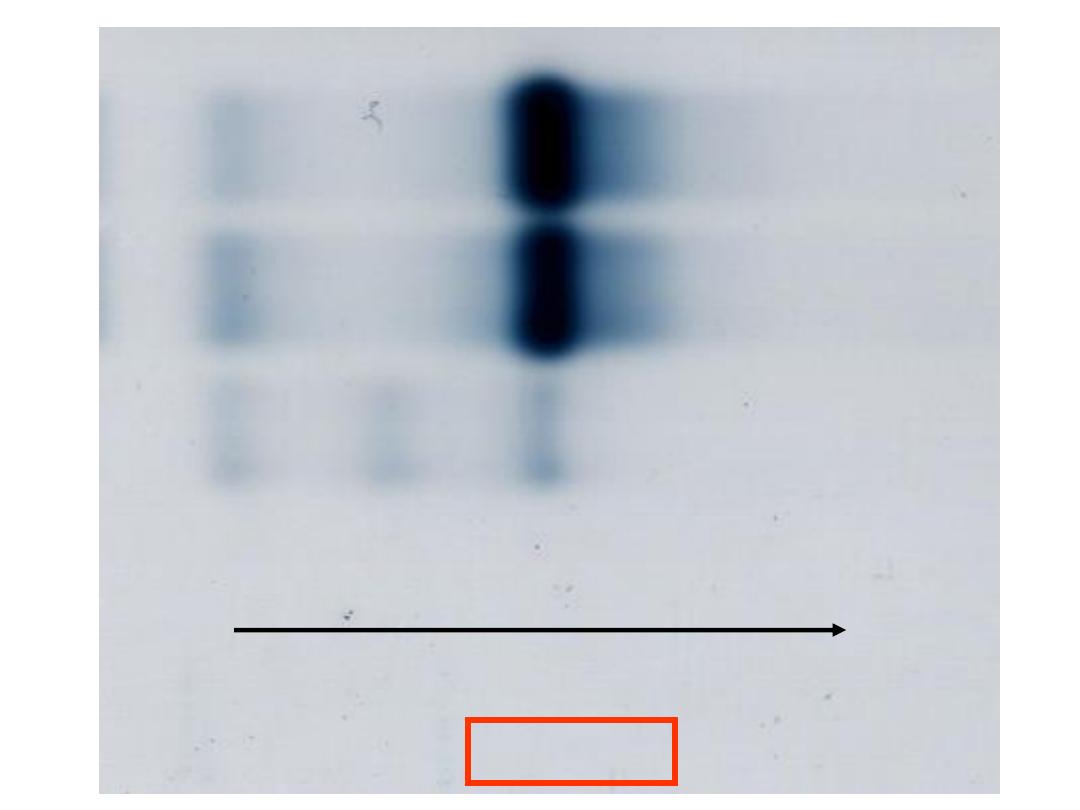
Hb A
Normal
Control
Hb A
2
Abnormal
Control
Anode
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
at alkaline pH
Case 1
Patient
Case 1

Case 1
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis:
Hb A 93.8 %
Hb F 1.0 %
Hb A
2
5.2 %
δ
δ
α
α
β
β
α γ
γ
Hb A
Hb A
2
Hb F
Diagnosis: β Thalassemia trait
Genotype αααα β
β or
β- δδ γγ
Haemoglobins Produced
Laboratory diagnosis of β Thalassemia trait made by CBC, and Hb A
2
>3.5%.
Serum ferritin is normal or increased.

Case Two
• A -12-Year old African boy is tested for Sickle
Cell Disease pre-operatively
• His father is known to have Sickle Cell Triat
• Results:
• HB 10.1g\dl
• RBCS 6.1X10X12\l
• MCV 65fl
• MCH 21.1pg
• MCHC 30g\dl

Cont,
• What is the next step in your investigtions ?

CONT,
• SICKLING TEST
• HB. ELECTROPHORESIS

CONT,
• SICKLING TEST WAS +VE
• IS THAT ENOUGH?

CONT,
• HB. ELECTROPHORESIS RESULT :
HBS 45%
HBA 53%
HBA2 5.2%
HBF 0%
FERRITIN LEVEL NORMAL

Questions
• What Haemoglobinopathy does the boy
have?
• What Haemoglobinopathy would you
expect on testing the mother?

Answer
• [ Sickle- Thal]
• The mother is expected to have Thalassaemia Trait
• NB:
• Presence of Hb A exclude SCD and THAL
.MAJOR
• Presence of HbF ONLY = THAL. MAJOR
• Presence of HbS ONLY = SICKLE CELL DIS.
• Presence of HbS +HbA= Sickle trait
• Presence of HbA+ HbA2 of more than
3.5=THAL.TRAIT
• Presence of HbA + HbA2 + Hbs = Sickle- Thal

Case 3
6 year old girl from Basrah
Admitted to hospital with abdominal pain and fever.
Past history : swelling of hands and feet at age 1
: previous episodes of abdominal pain
Physical examination:
pallor of mucous membranes
mild jaundice
hepatomegaly
no splenomegaly
no evidence of infection
Parents healthy : OK
Case 3
Hb
84 g/L (115-155)
MCV
86.5 fL (77-95)
Blood Film - sickle cells
erythroblasts
Howell-Jolly bodies
polychromasia
target cells
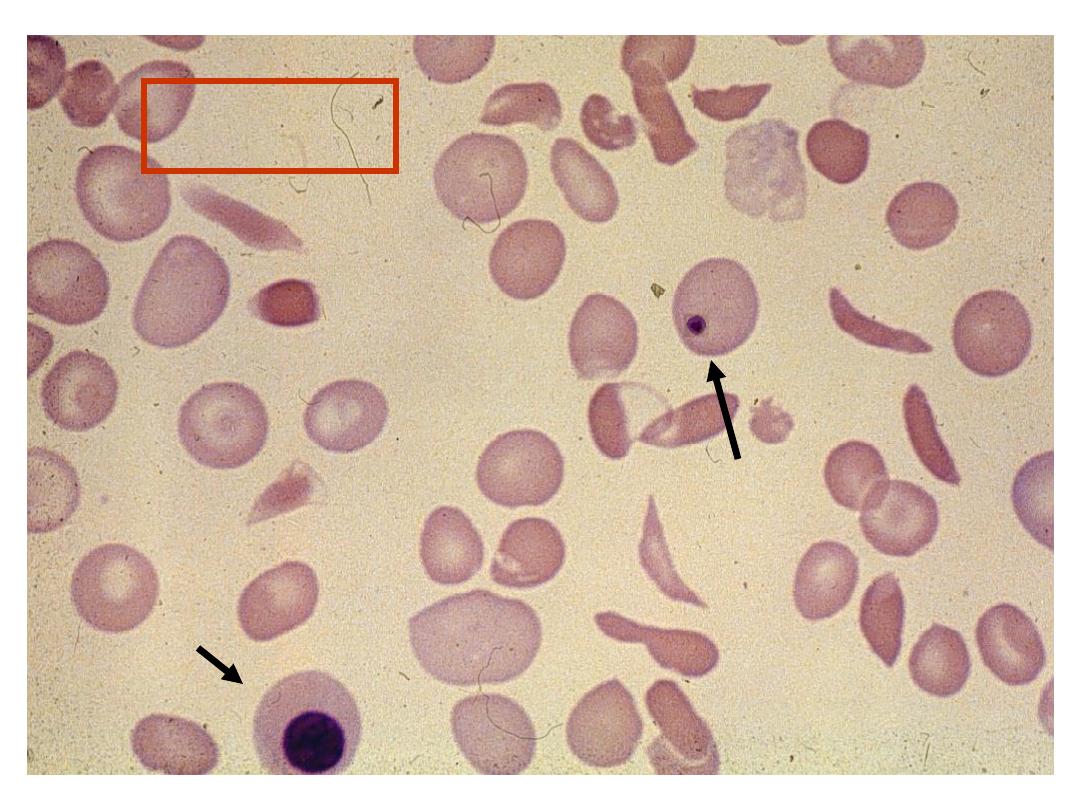
Case 3
Howell Jolly
Body
Erythroblast
Abnormal
Control
Normal
Control
Patient
Case 2
Hb C
Hb S Hb F Hb A
Case 2

Case 3
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis:
Hb A 0 %
Hb S 87.0 %
Hb F 9.7 %
Hb A
2
3.3 %
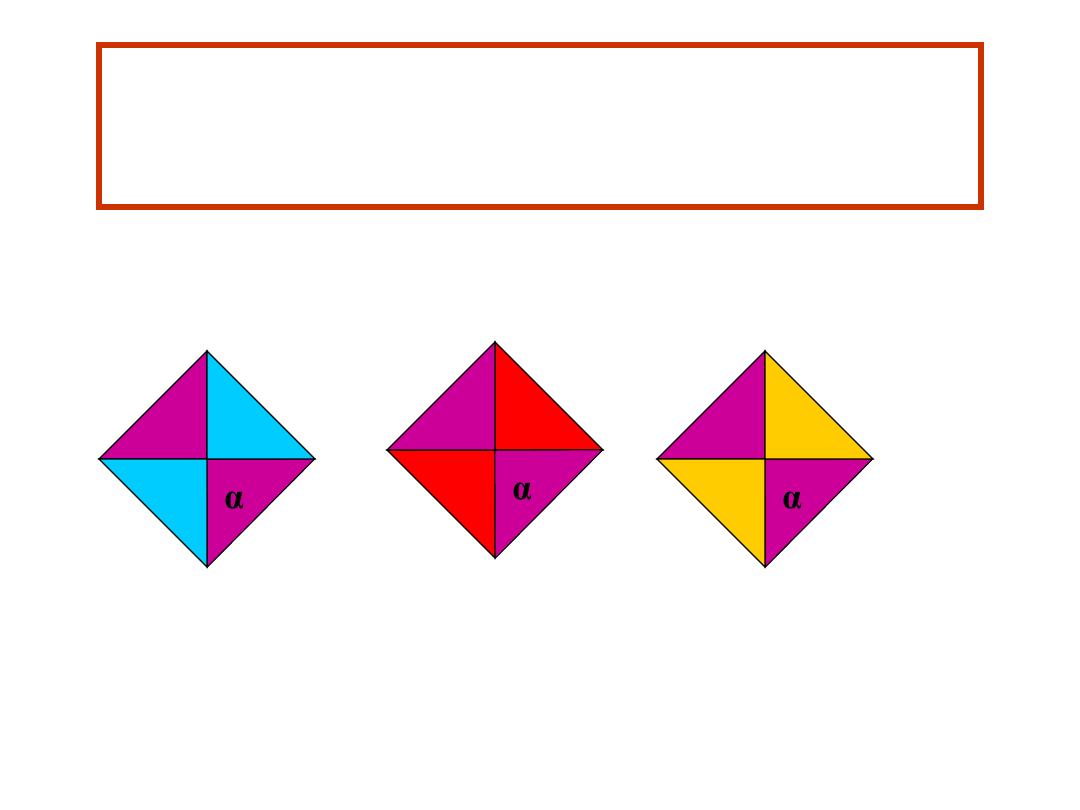
δ
δ
α
α
s
s
α γ
γ
Hb S
Hb A
2
Hb F
Genotype αααα β
s
β
s
δδ γγ
Haemoglobins Produced :
Diagnosis: Hb SS Disease
Laboratory diagnosis of sickle cell anaemia made by presence of only Hb S, Hb A
2
, and Hb
F on Hb electrophoresis with no Hb A, a positive sickling test and presence of sickle cells in
blood film
Case 4
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis:
Hb A 0 %
Hb A
2
3.5 %
Hb F 96.5 %
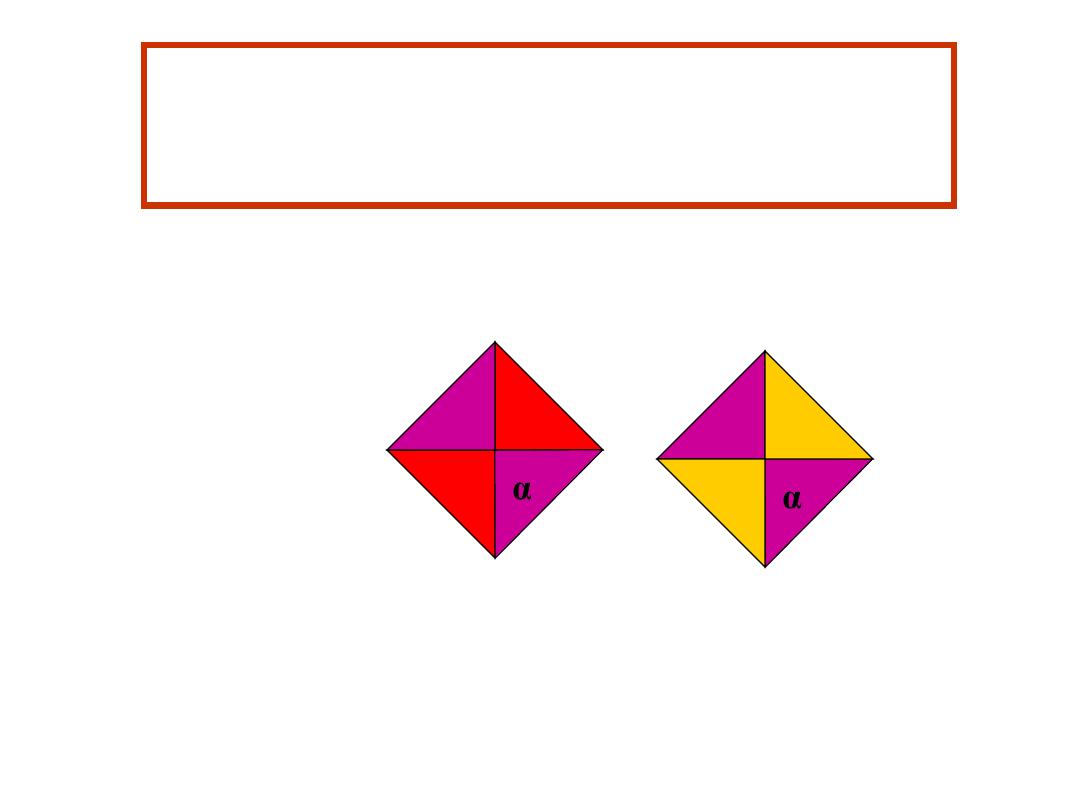
δ
δ
α
α γ
γ
Hb A
2
Hb F
Diagnosis: β Thalassemia major
Genotype αααα - - δδ γγ
Haemoglobins Produced
Laboratory diagnosis of β thalassemia major made by CBC, absence of Hb A, with
increased Hb F. Some patients have small amounts of Hb A if some β globin chain is
produced.

Case 5
28 year old woman
Life long history anaemia and mild jaundice.
Past history : splenectomy.
Family History :
•
Mother: life long history microcytic
hypochromic anaemia, unresponsive to iron
• Father and sister: no known history of a blood
problem.

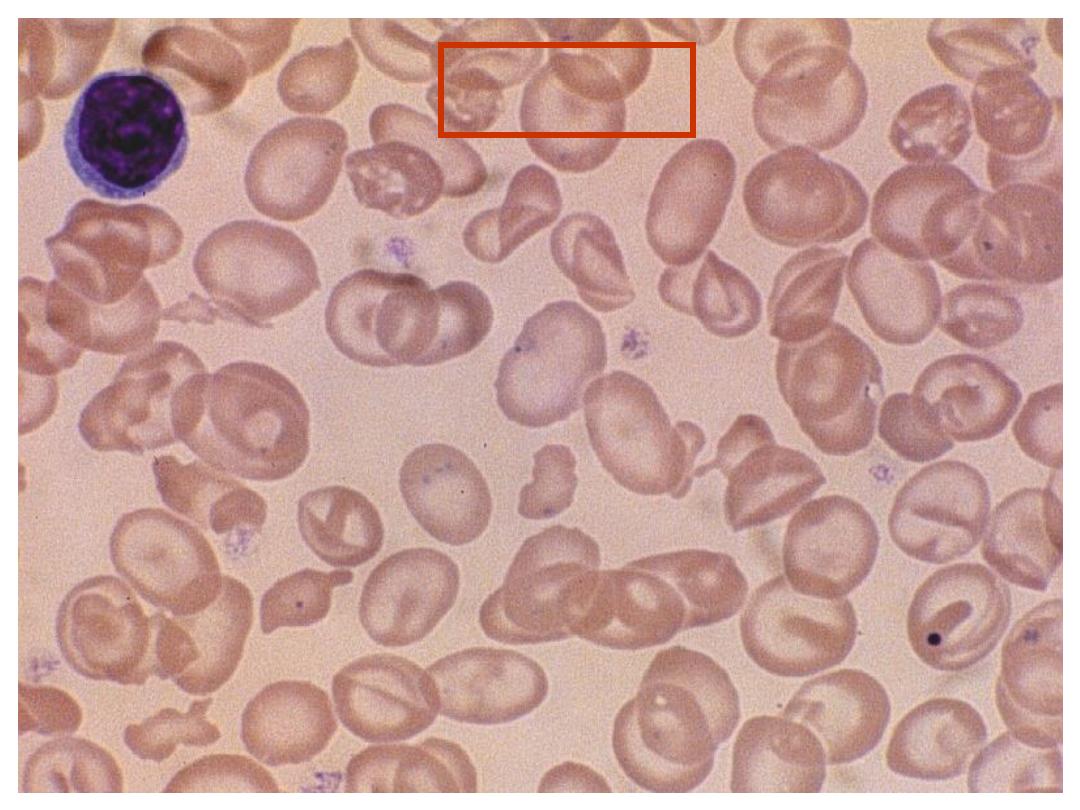
Case 5
Hb
97 g/L (140-180)
MCV
72.1 fL (80-100)
Blood Film: Microcytosis
Hypochromia
Target cells
Fragmented cells
Howell-Jolly bodies
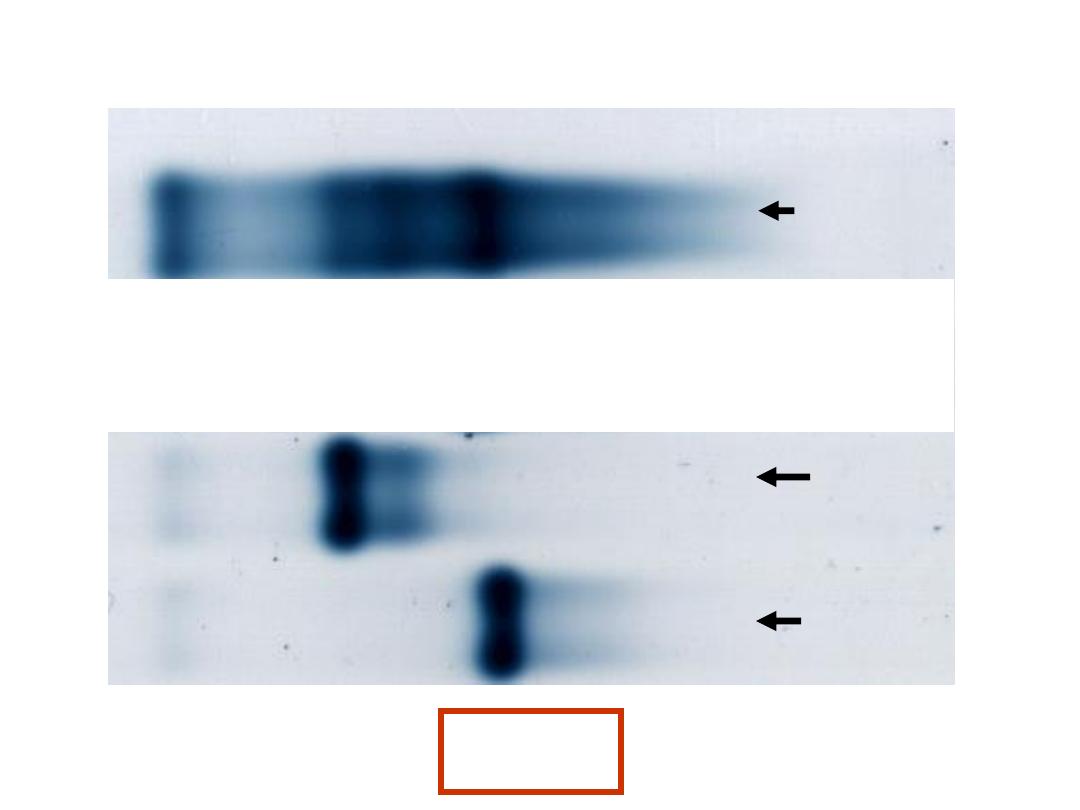
Case 5
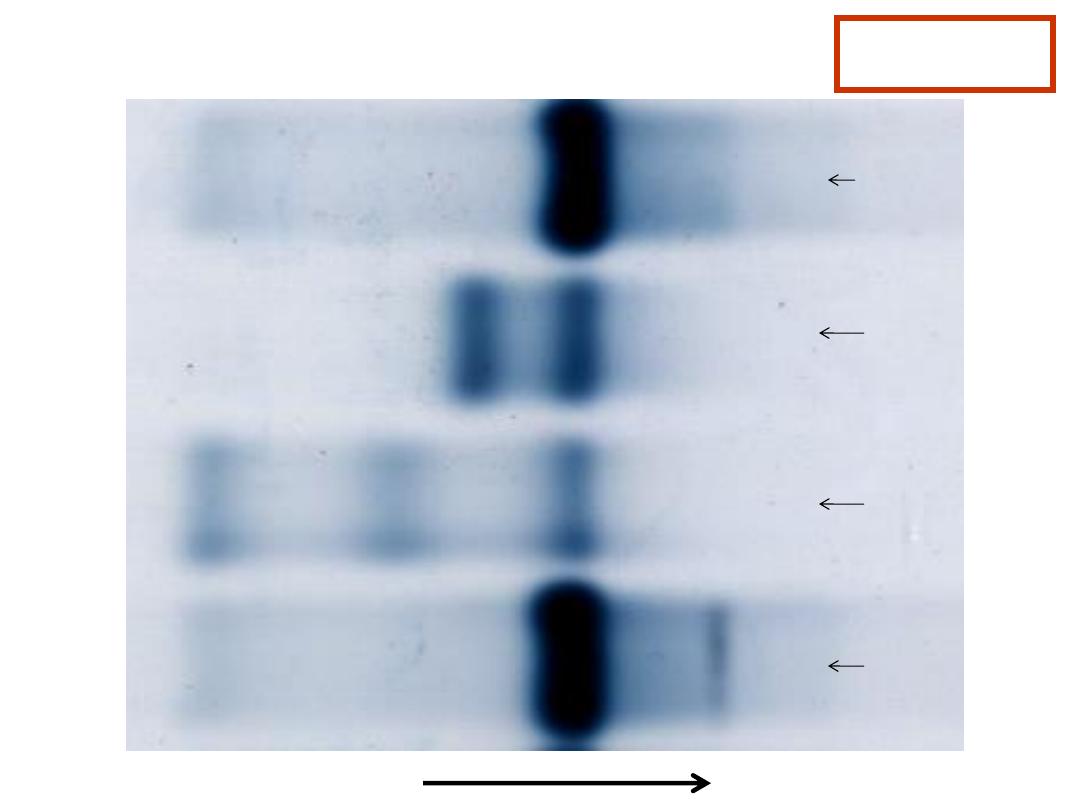
Normal
Control
Abnormal
Control
Abnormal
Control
Patient
Case 5
Case 5
HbA
HbA2
Case 5
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis:
Hb A 91.5 %
Fast moving band 8.5%
Hb A
2
and Hb F decreased
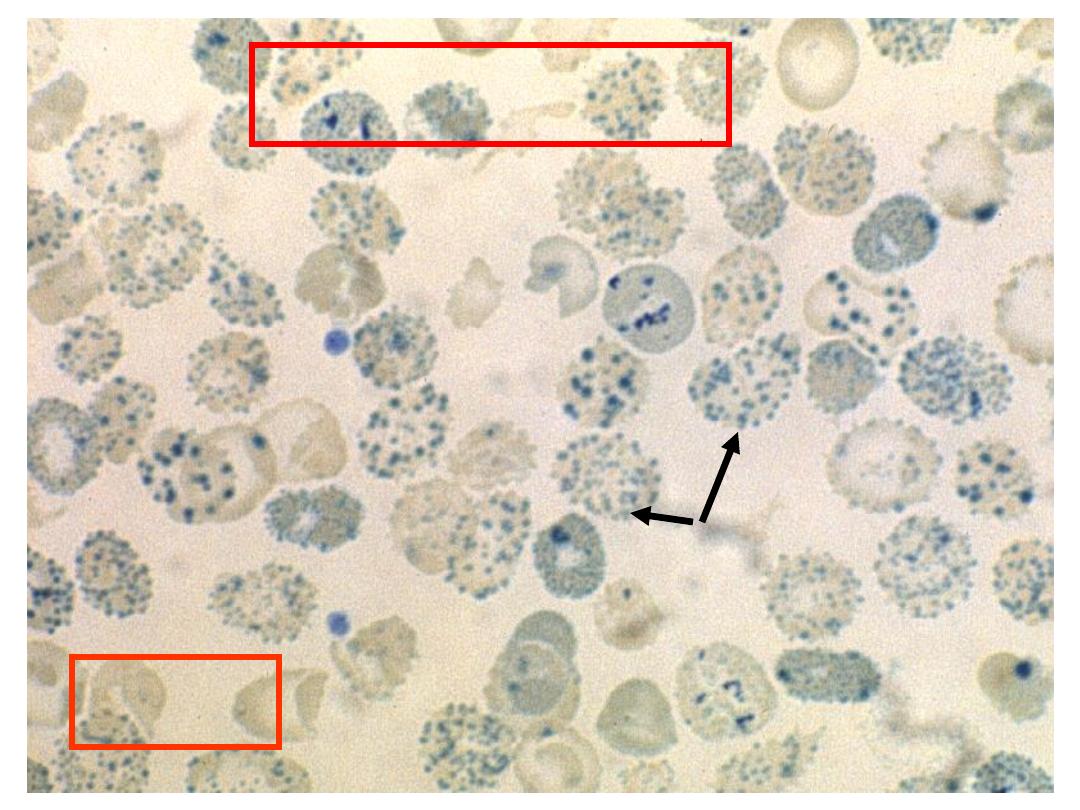
Hb H Preparation
Hb H inclusions
in RBCs
Case 5
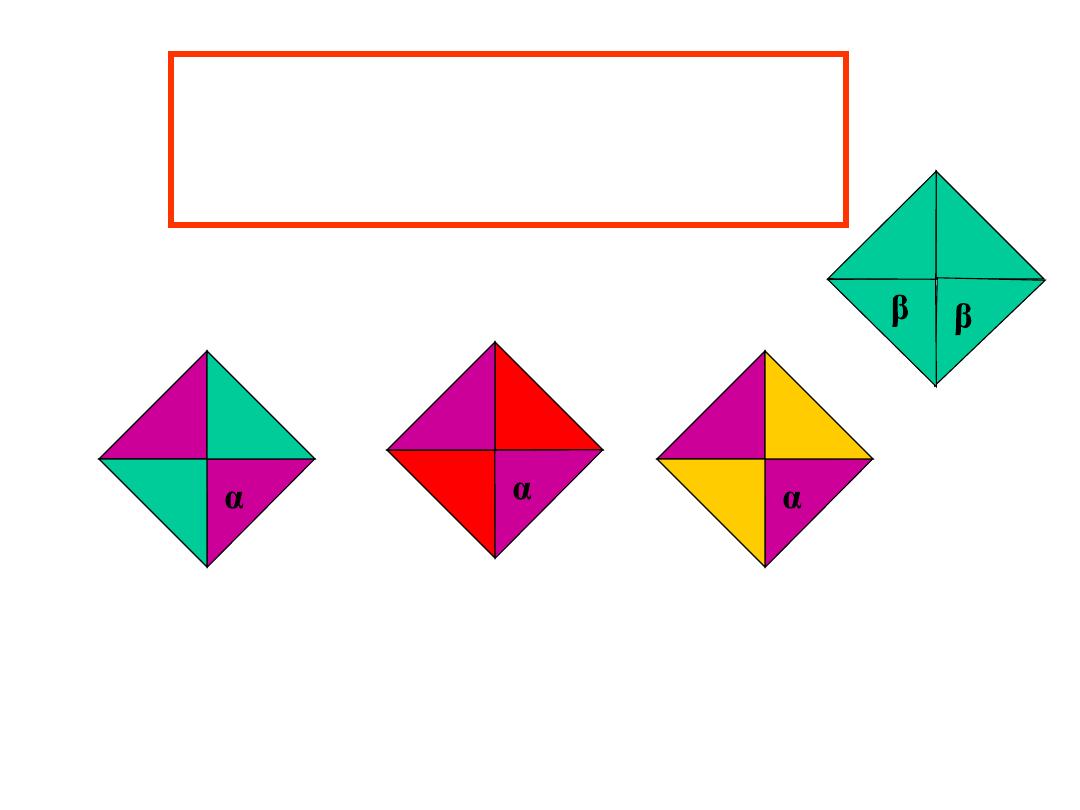
δ
δ
α
α
β
β
α γ
γ
Hb A
Hb A
2
Hb F
Genotype ---α ββ δδ γγ
Haemoglobins Produced :
Hb H Disease
β
β
Hb H
Diagnosis: Hb H Disease
Laboratory diagnosis made by CBC, and presence of Hb H on Hb
electrophoresis and in the Hb H preparation.

Case 5: Family Studies
Father: Hb 139 g/L (140-180)
MCV 79 fl (80-100)
Hb Electrophoresis normal.
Hb H preparation negative
Mother: Hb 100 g/L
MCV 66 fl
Hb Electrophoresis normal.
Hb H preparation : very occasional cell
positive for Hb H inclusions

CASE SCENARIO
• A 65- YEAR OLD MAN PRESENTED
WITH H/O :
• WT. LOSS, NIGHT SWEATS & FEVER
• P/E : LYMPHADENOPATHY
HEPATOSPLENOMEGALY
• HOW CAN YOU APPROACH SUCH A
PATIENT? & WHAT INVESTIGAION/S
ARE YOU GOING TO CARRY OUT?

Blood Count
WBC x
10
9
/L
150.0
[4-11]
Hb g/L
98
[120-16 0]
MCV fl
8 7
[79-98]
Plat elet s x 10
9
/L
48
[150-450]
Neut s x 10
9
/L
1.5
[2-7.5]
Lymphs x 10
9
/L
130.0
[1.5-4]
Monos x 10
9
/L
0 .5
[0.2-0.8]
Eos x 10
9
/L
-
[0-0.7]
Basos x 10
9
/L
-
[0-0.1]
Smudge cells x 10
9
/L
28.0
[0]
Film Comment : appearances suggest CLL

CLL – presenting clinical features
• Chance finding
• Marrow failure
• Symptoms
– weight loss
– night sweats
– fevers
• Lymphadenopathy
• Splenomegaly, hepatomegaly
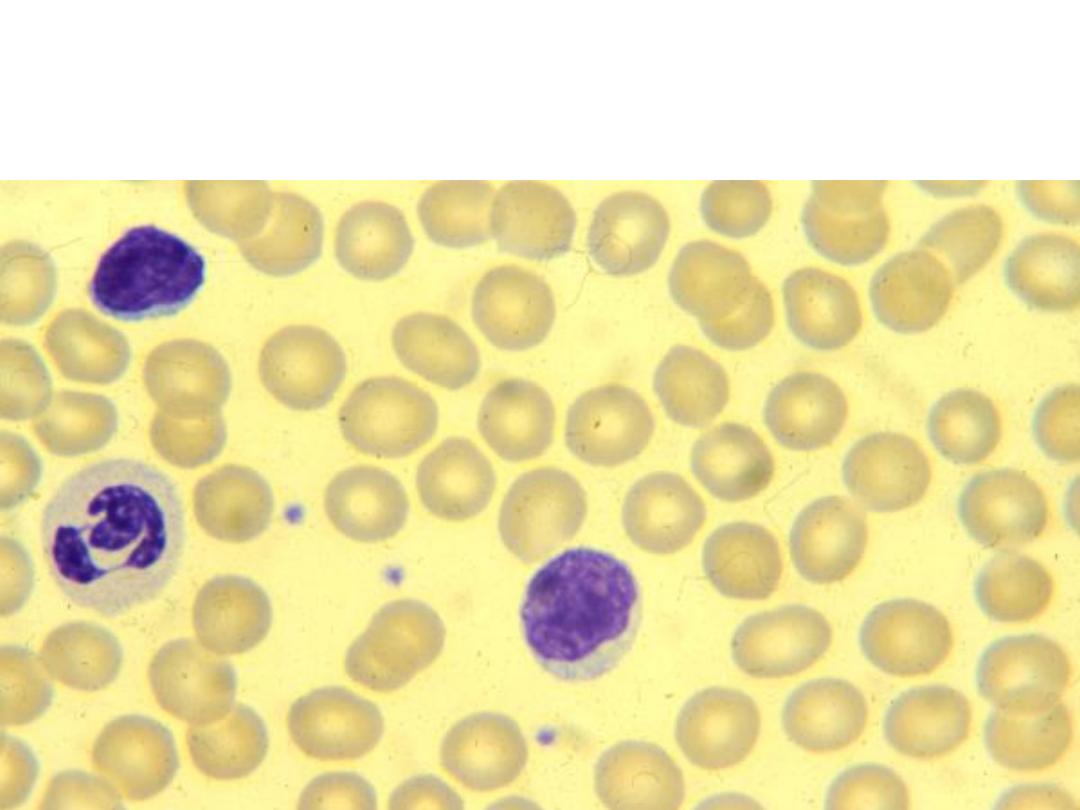
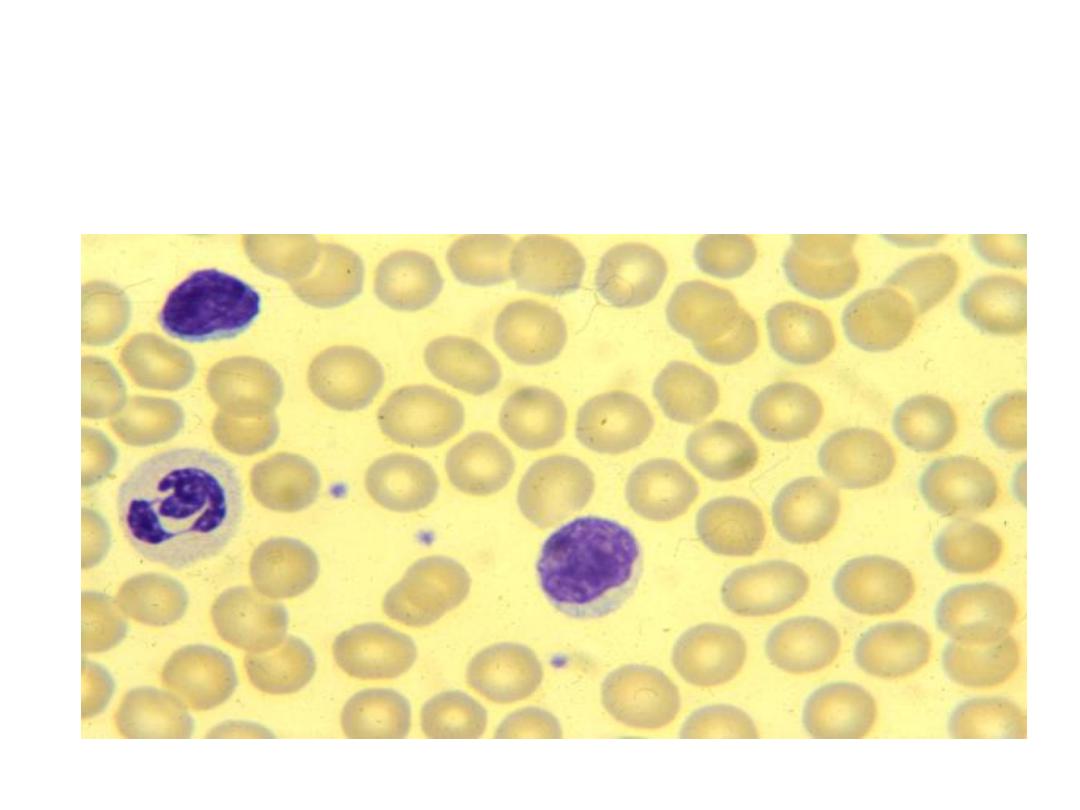
lymphocytes
‘smudge’ cells
lymphocytes

CASE SCENARIO
• A 40-YEAR OLD FEMALE PRESENTED
WITH H/O :
• WT. LOSS, NIGHT SWEATS &
MULTIPLE JOINTS PAIN.
• P/E : PALE LOOKING & BIG SPLEEN
• WHAT SORT OF INVESTIGATION/ S
ARE YOU GOING TO PERFORM ?

Blood Count
W
BC x 10
9
/ L
122.0
[4-11
]
Hb g/ L
9 8 .5
[1
20 -16 0 ]
MCV fl
8 7
[79-9 8 ]
Plat elet s x 1
0
9
/ L
8 43
[1
50 -450 ]
Neut s x 10
9
/ L
8 0 .0
[2-7.5]
Lymphs x 1
0
9
/ L
2.0
[1
.5-4]
Monos x 10
9
/ L
2.0
[0 .2-0 .8 ]
Eos x 1
0
9
/ L
1.0
[0 -0 .7]
Basos x 10
9
/ L
5.0
[0 -0 .1
]
Blast s x 1
0
9
/ L
2.0
[0 ]
Promyelocyt es x 10
9
/ L
4.0
[0 ]
Myelocyt es x 1
0
9
/ L
20 .0
[0 ]
Met amyelocyt es x 10
9
/ L
4.0
[0 ]
Nucleat ed RBC x 1
0
9
/ L
2.0
[0 ]
Film Comment : appearances suggest CML
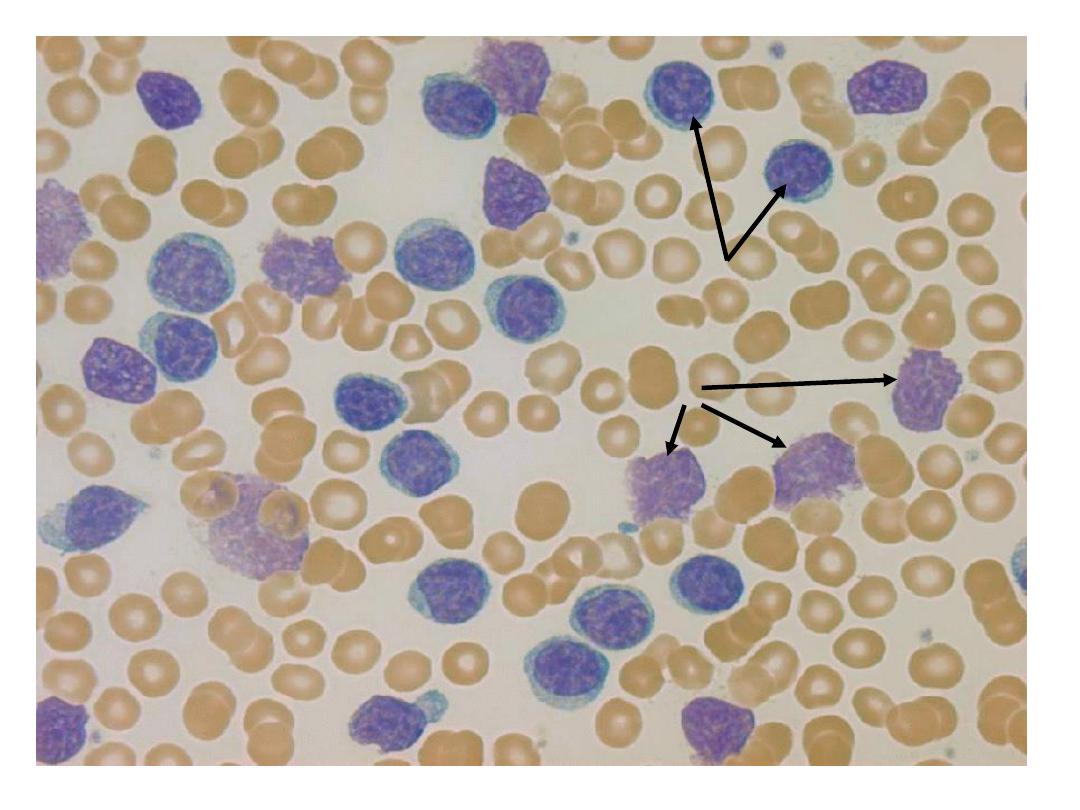
CML - clinical features of chronic
phase
• Peak age 20 to 40 years
• Weight loss, night sweats
• Big spleen
• Gout
• Often found by chance
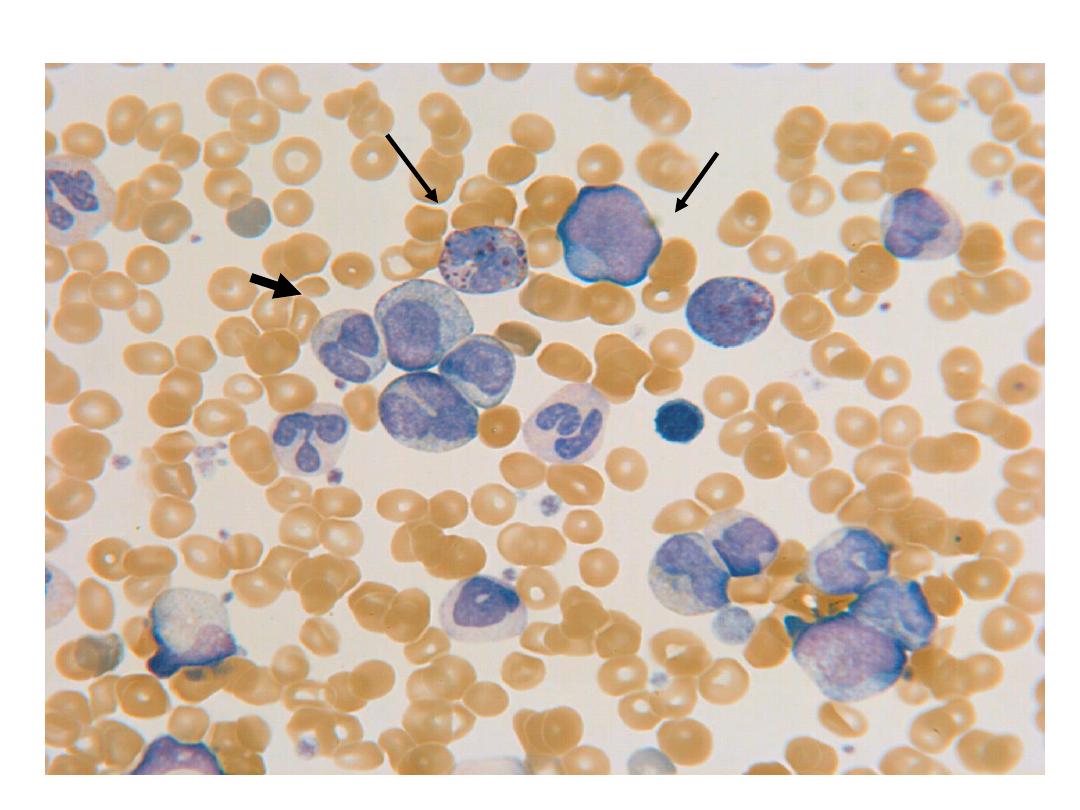
neutrophils
and
precursors
basophil
blast
promyelocyte
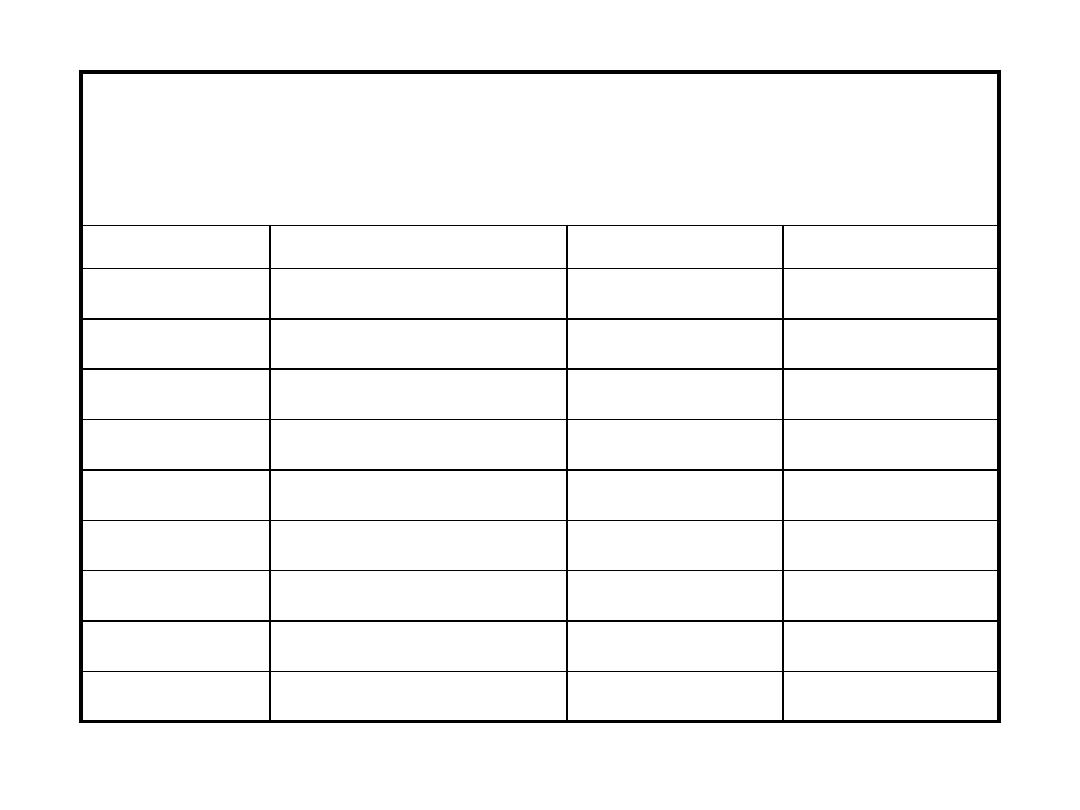
CASE 1
A 73 year old man is to undergo surgery to repair a left inguinal hernia. He is seen for a pre-
operative medical assessment and had the following blood work done the day prior. He has
otherwise been well and is on no medications
.
test
result
normal range
units
leukocytes
5.2
4.0-11.0
x10
9
/L
hemoglobin
14.2
14-18
g/L
MCV
84.5
80-100
fL
platelets
98
140-400
x10
9
/L
neutrophils
3.0
2.0-7.5
x109/L
neutrophils
1.5
1.5-4.0
x109/L
monocytes
0.6
0.2-0.8
x109/L
eosinophils
0.1
0.0-0.7
x109/L
basophils
0.0
0.0-0.1
x109/L
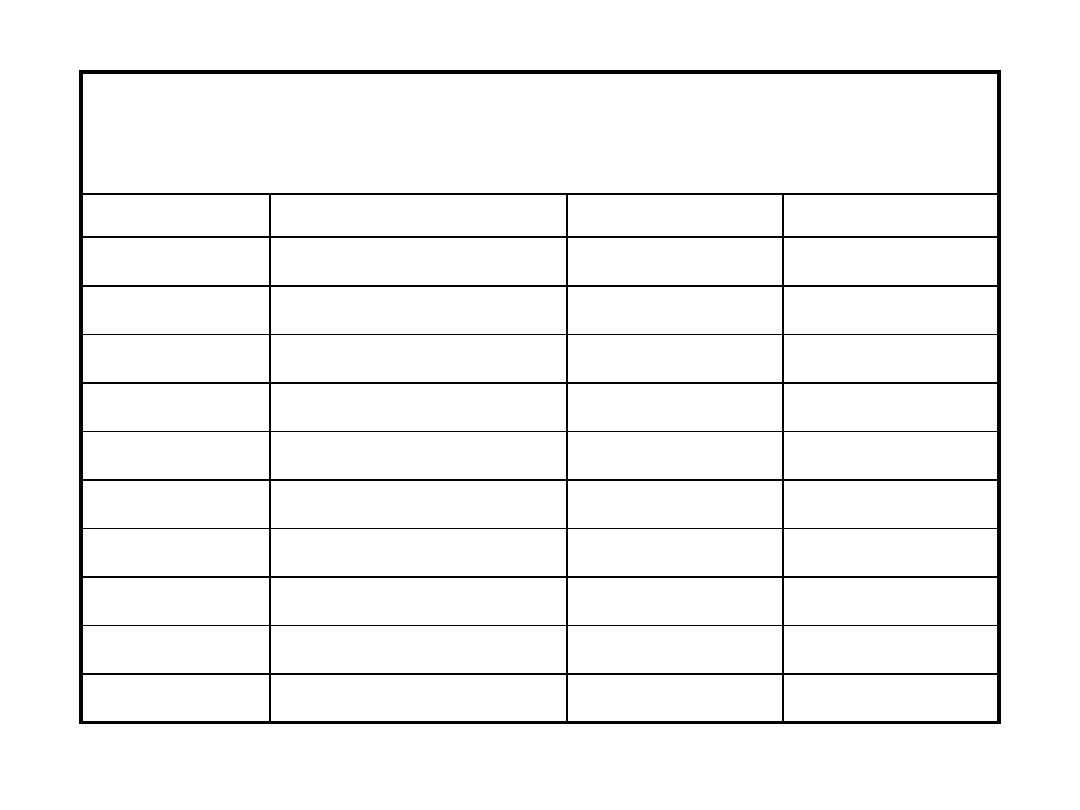
CASE 2
A 23 years old male is seen in the clinic because of a 2 month history of recurrent epistaxis
and increased bruising. The following result were obtained on a CBC
test
result
normal range
units
leukocytes
4 .2
4.0-11.0
x109/L
hemoglobin
14.2
140-180
g/L
MCV
84.5
80-100
fL
RDW
13.1
11.5-14.5
platelets
28
140-400
x109/L
neutrophils
2.2
2.0-7.5
x109/L
neutrophils
1.6
1.5-4.0
x109/L
monocytes
0.4
0.2-0.8
x109L
eosinophils
0.1
0.0-0.7
x109/L
basophils
0.0
0.0-0.1
x109/L
