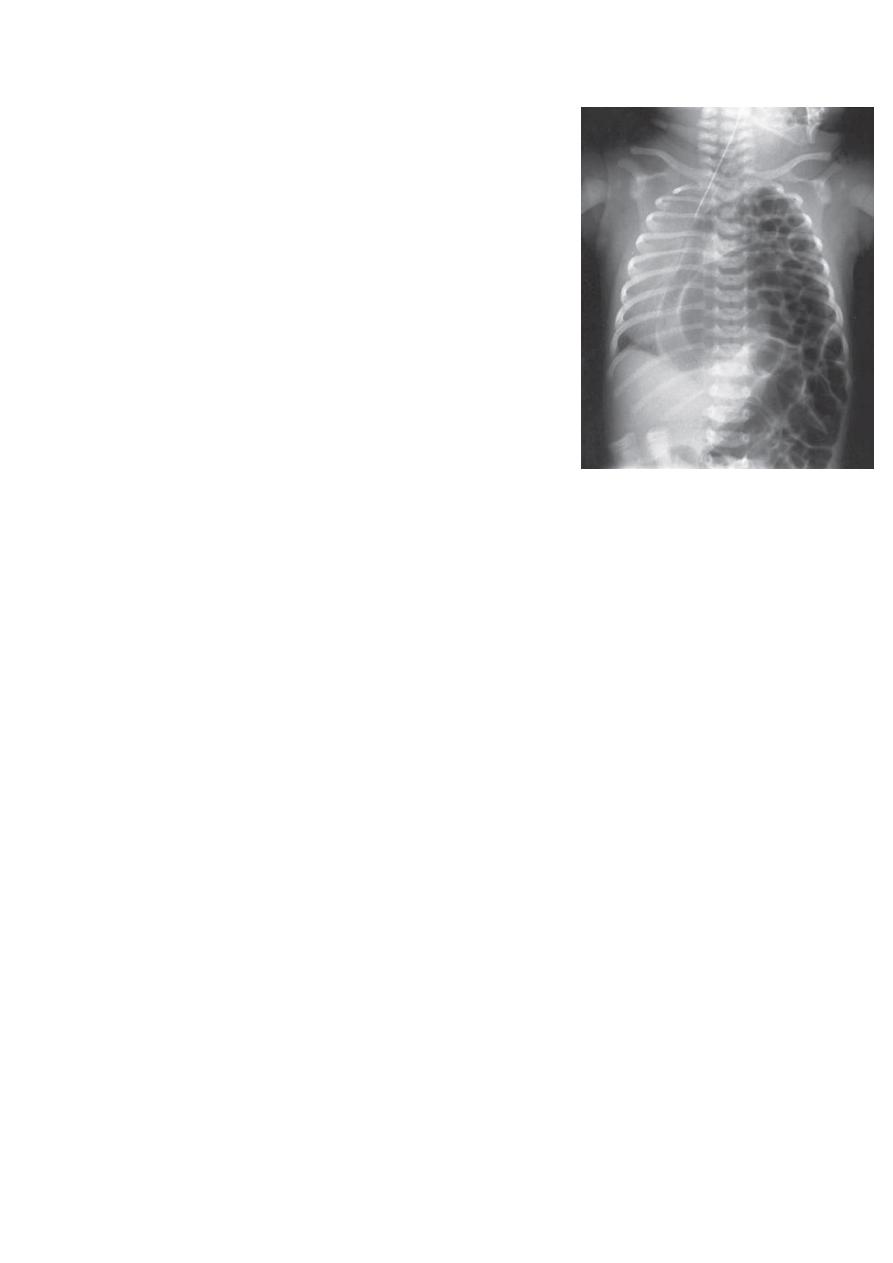
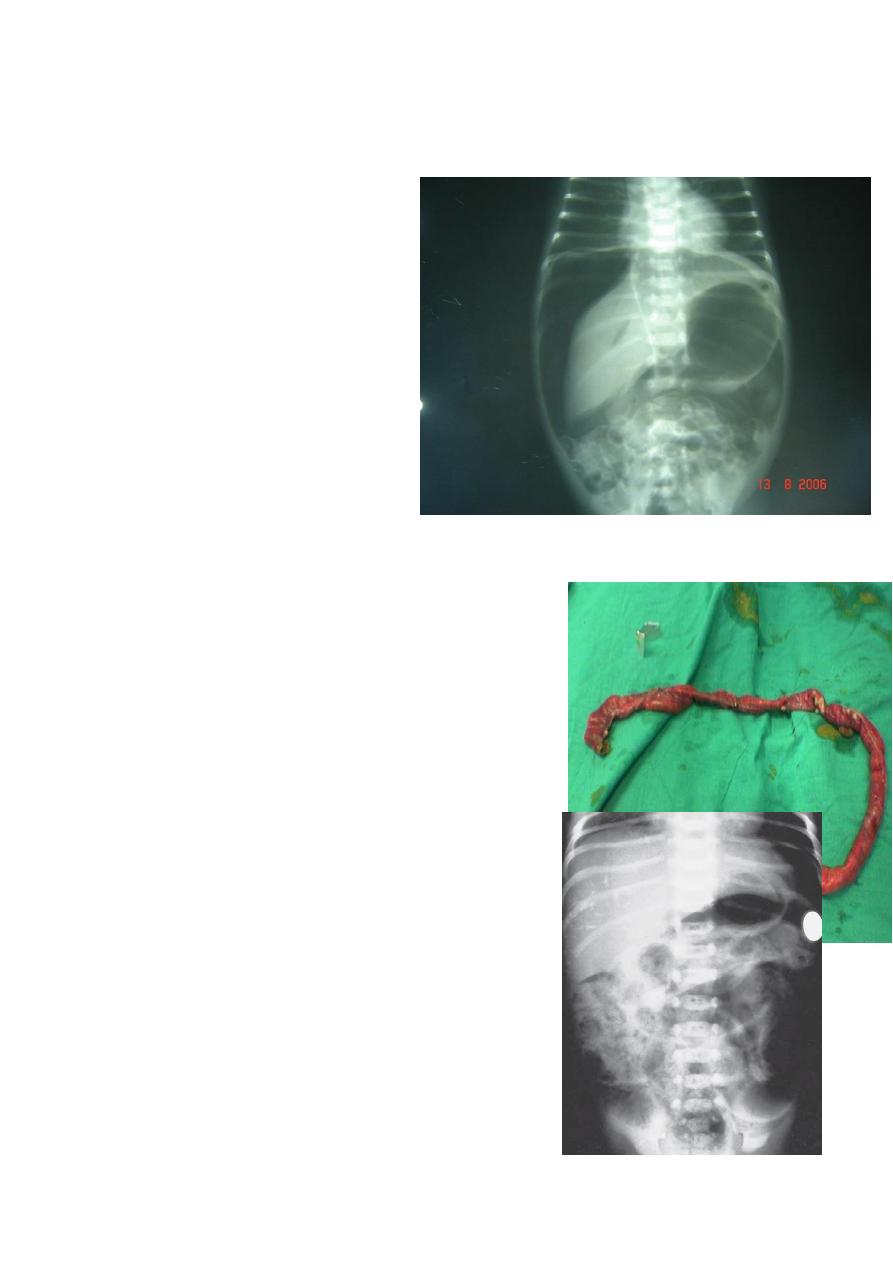
Diagnosis: congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Description: more dextrocardia – diaphragm not present –
there is nasogastric tube
severe distress – very tired - 1 day age baby – more
number of intestinal loops in
the chest - there is no lung tissue in the chest.
Treatment: pull the intestine ad close the hernia (through
abdominal approach).
C/F in lecture
Notes:
1-XR Finding of DH has 4 imp. Points
a-acquired dextrocardia
b-abscent hemidiaphragm
c-Endotracheal tube
d-
2-In ER when U R doing Resuscitation :consider the following
1-ET-tube ----gradual air &avoid what?
Ventilation with a face mask (‘bagging’) should be avoided Vigorous endotracheal
ventilation
should also be avoided because of the risk of causing barotrauma and a tension
pneumothorax
2-position of baby :is on the lateral side on affected side(normal is up)
3-NGT to suction of secretions
2-Scaphoid abdomen
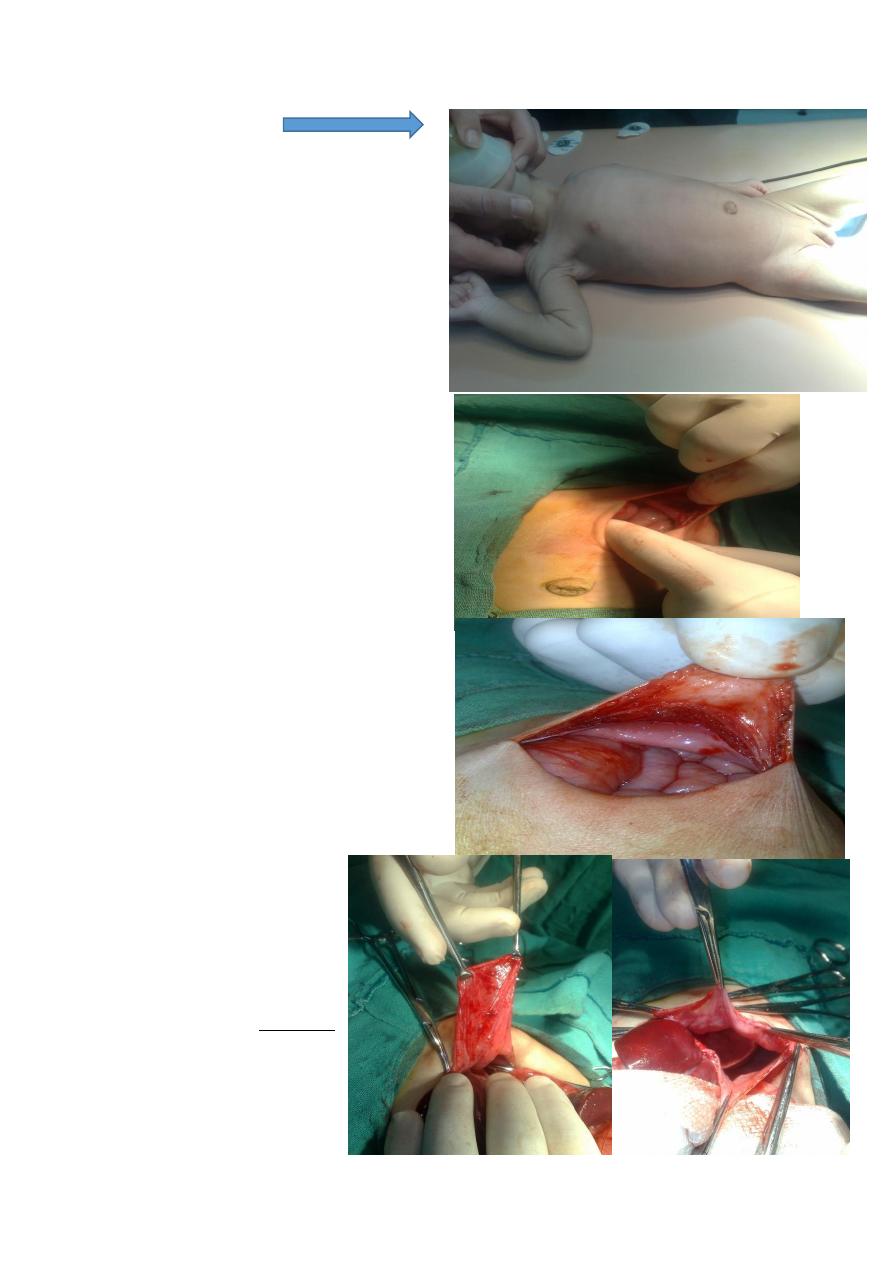
Mx of D.H
1-no special time for op. & do it when
child stabilized(by oximeter >pO2
increased
2-abd. Approach(-ve pressure of thorax )
3-suture it by non-absorbable material
4-chest tube is controversial
Rule in surgery
**never say never in surgery**
Subcostal incision
content
Like other types of hernia
it may contain sac
Sac of D.H
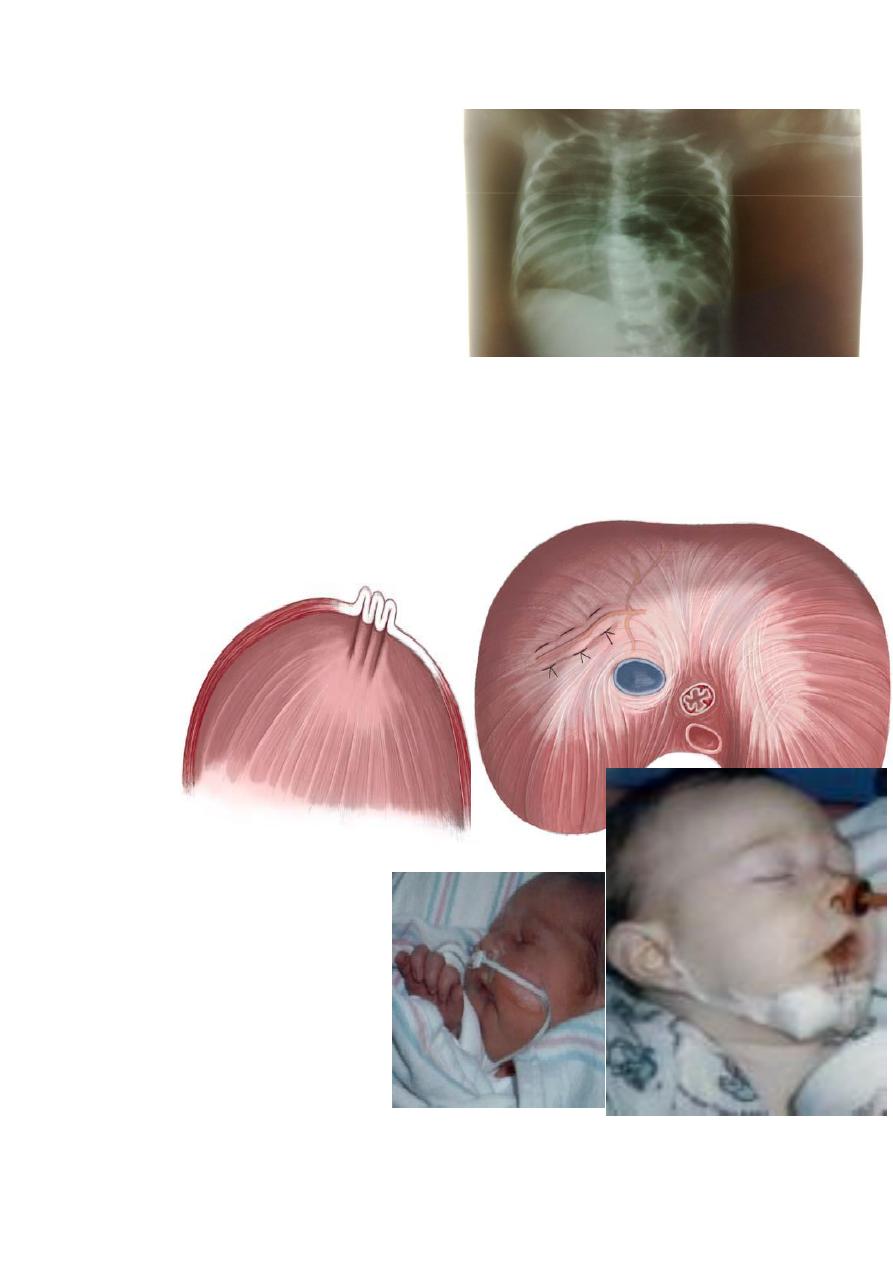
Eventration of diaphragm
Diaphragmatic paralysis of
hemidiaphram .the diaphragm is
elevated to the 3rd or 4th ICS, that’s why
during respiration there is paradoxical
movement of the two hemidiaphragms
C/F:-1-recurrent chest inf.
month and after
rd
presented in 3
-
2
3-
Diagosis by fluoroscopy
Note: no scaphoid abd.
wk
st
Antibiotics in 1
-
Mx:
-Approach is thoracic( it's often in Rt & there is liver. 2-collapsed lung –so large field)
-
Plication (suturing of the hemidiaphram down) through th
e chest incision
-
Plication :also non-absorbable&
يخرطه تخرط
No need for chest tube
pierre Robin syndrome
1-micrognethia
2-macroglosia ( relatively bz
small oral cavity )
3-high arched palate?&cleft
palate). glossoptosis (airway
obstruction caused by backwards
displacement of the tongue
base)
-In ER: suture the tongue on the chin ( bz tracheostomy is so difficult )
Congenital lober emphysema
3 month infant presented w/t
Resp. distress & recurrent chest
infection
-so it's lung problem & defect in
recoiling function & over-
expansion of lung.
-misdiagnosed as pneumothorax
They put chest tube –killing the
child
-differentiate b/t them by
1-
2-
Mx : surgery **lobectomy**
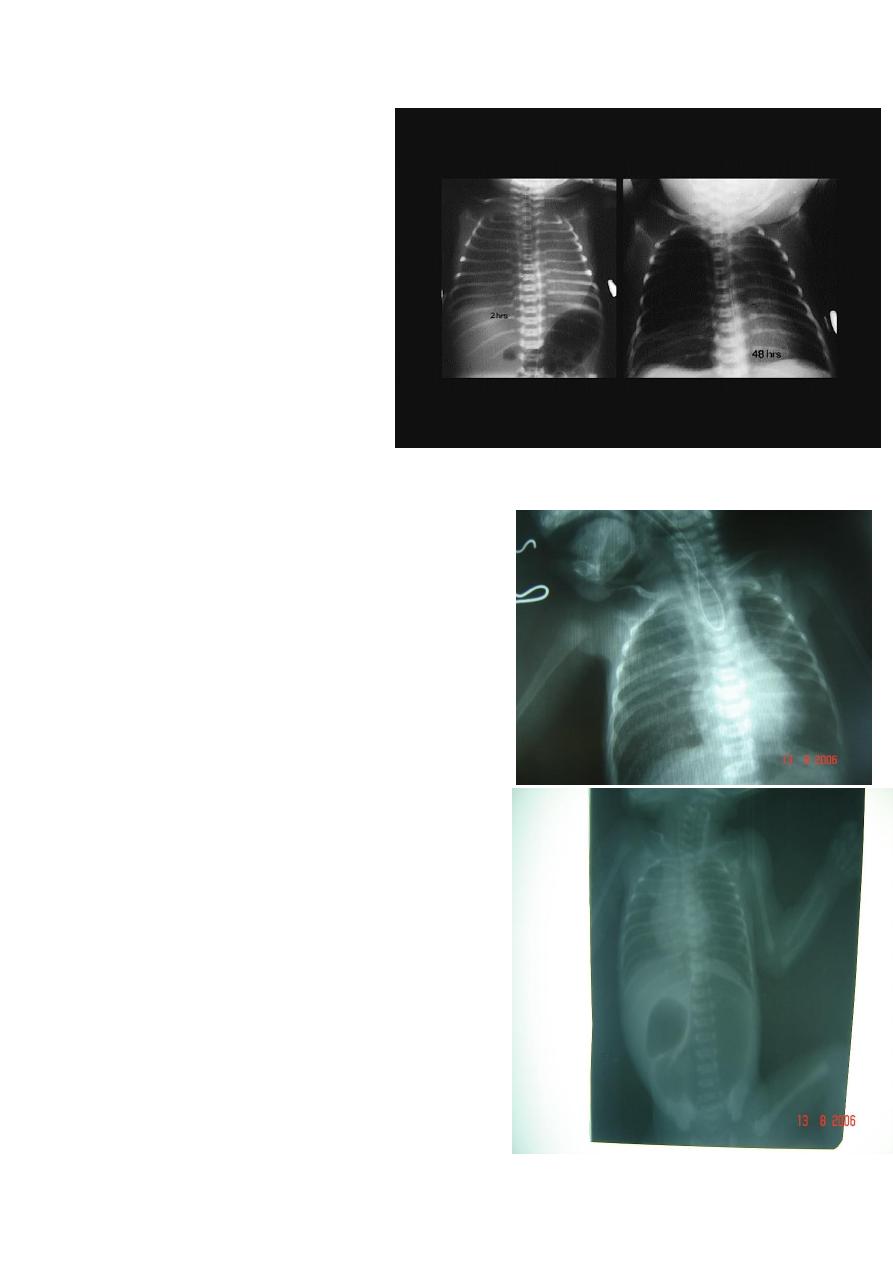
Diagnosis: pure atresia
Description: radiolucent abdomen (no gases) +
failure of nasogastric tube passage.
Diagnosis: TEF (with fistula)
Description: pass of gases to the abdomen +
failure of nasogastric tube passage.
Benefits of X- Ray :
1-Dx and Type of esophageal atresia and fistula
2-Condition of the lung aspiration of saliva and
milk e.g. chemical
pneumonitis
3-look for right aortic arch
4-Other anomalies, vertebral and ribs
5-length of the defect, measure from the end of
pouch to the carina if 2 cm u can do it primarily if
wider it is harder.
Mx:Extra-pleural approach (back to lect.)
Note: NGT is labeled w/t blue line
Benefits of X-ray in TE:
1- to see the failure of nasogastric tube passage.
2- to determine the type of TEF
3- to check the condition of the lung
4- diagnose the associated anomalies (aortic arch – vertebra – ribs)
5- to measure the length of the defect (1-2-3 cm or more)
Bowel Obstruction
Cardinal s & S of I.O
1-bilous vomiting
2-Abd. distension
3-Failure to pass
meconium.
#Causes of Double
bubble signs
1-Doudenal
obstruction
2-Malrotation of
bowel e.g. the cecum
stop at the right
hypochondrium
and there is a band to posterior abdominal wall compressing the
duodenum
3-Annular pancreas
4-Doudenal stenosis
LOWER I.O
Upper I.O
S &S
late
More & earliear
Vomiting
huge
Little (only epigastric
region)
Abd. Distension
Meconium
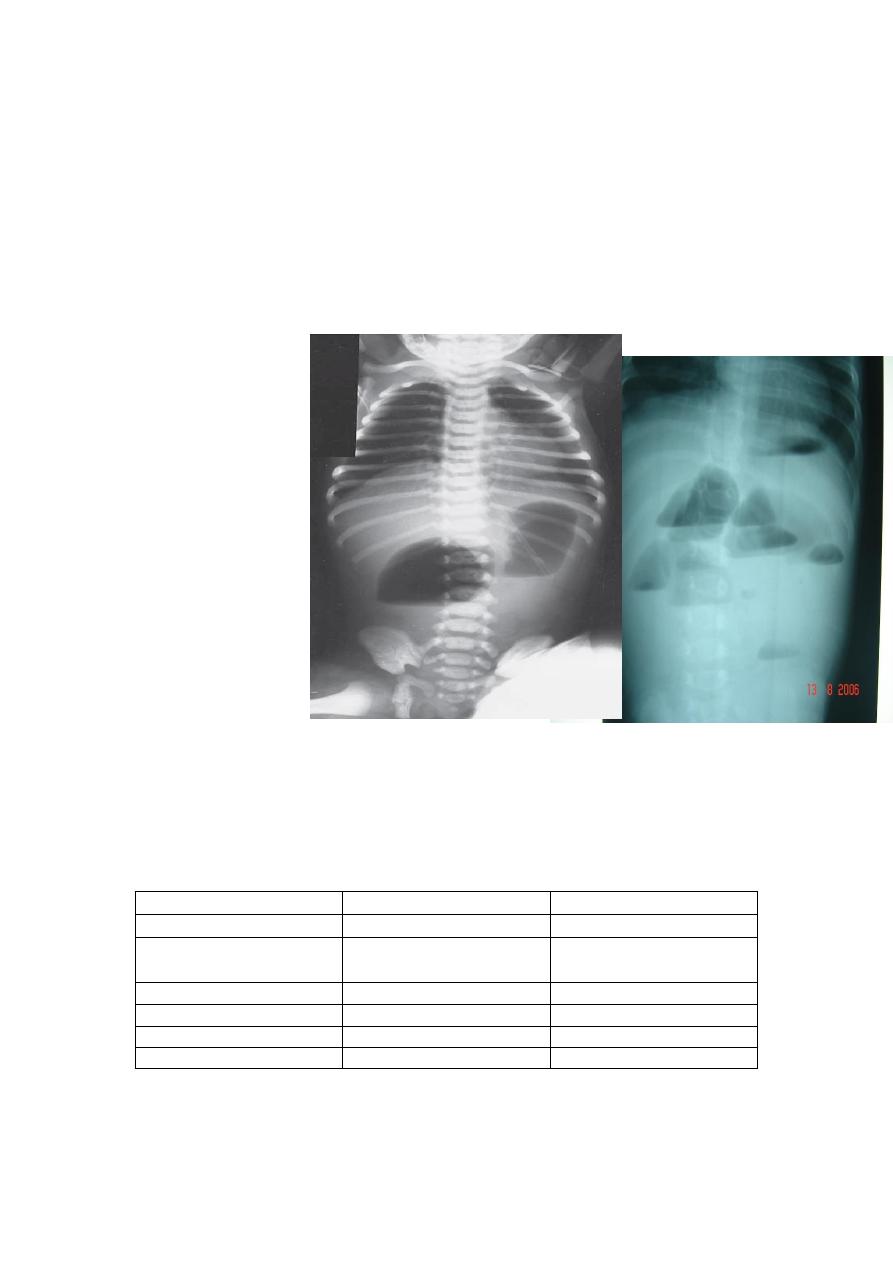
Clinical features of duodenal obstruction:
1-Bileious vomiting
2-Failure to pass meconium
3-Mild epigastria distention which disappear after vomiting
Two gas bubble = proximal obstruction.
#Many bubble = distal obstruction.
# We can't differentiate between large or small bowel obstruction on X –ray in
neonat(bz the size is the same).
Mx; DDD (in lec)
Web
??????
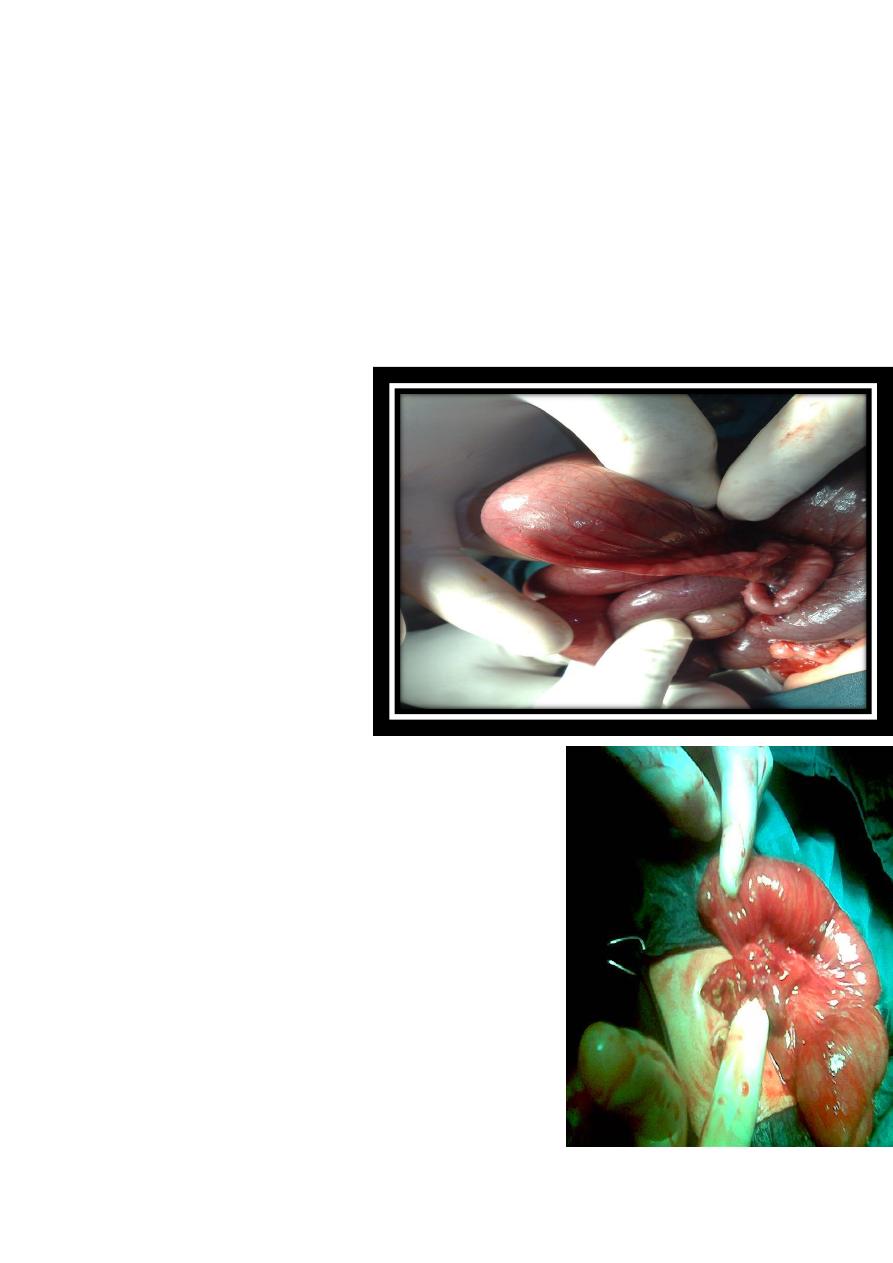
#Meconium ileus
* one of the causes of IO in
neonate
*huge dilatation of small
bowel usually ileum
*Contain thick sticky tenacious secretions, can't be
solubilized by normal saline ,
*Abdominal doughy mass in the right iliac fossa, with
indentation on pressure
* no air fluid level on X ray
*Associated with cystic fibrosis
Note :
Positive sweat test:
— Na > 60 mEq
— Cl > 60 mEq
Terminal ilium
* يضل نهايته مثل نهاية القلم
طعم الجاهل مملح هههههه*
عندمن تبوسه يبين,
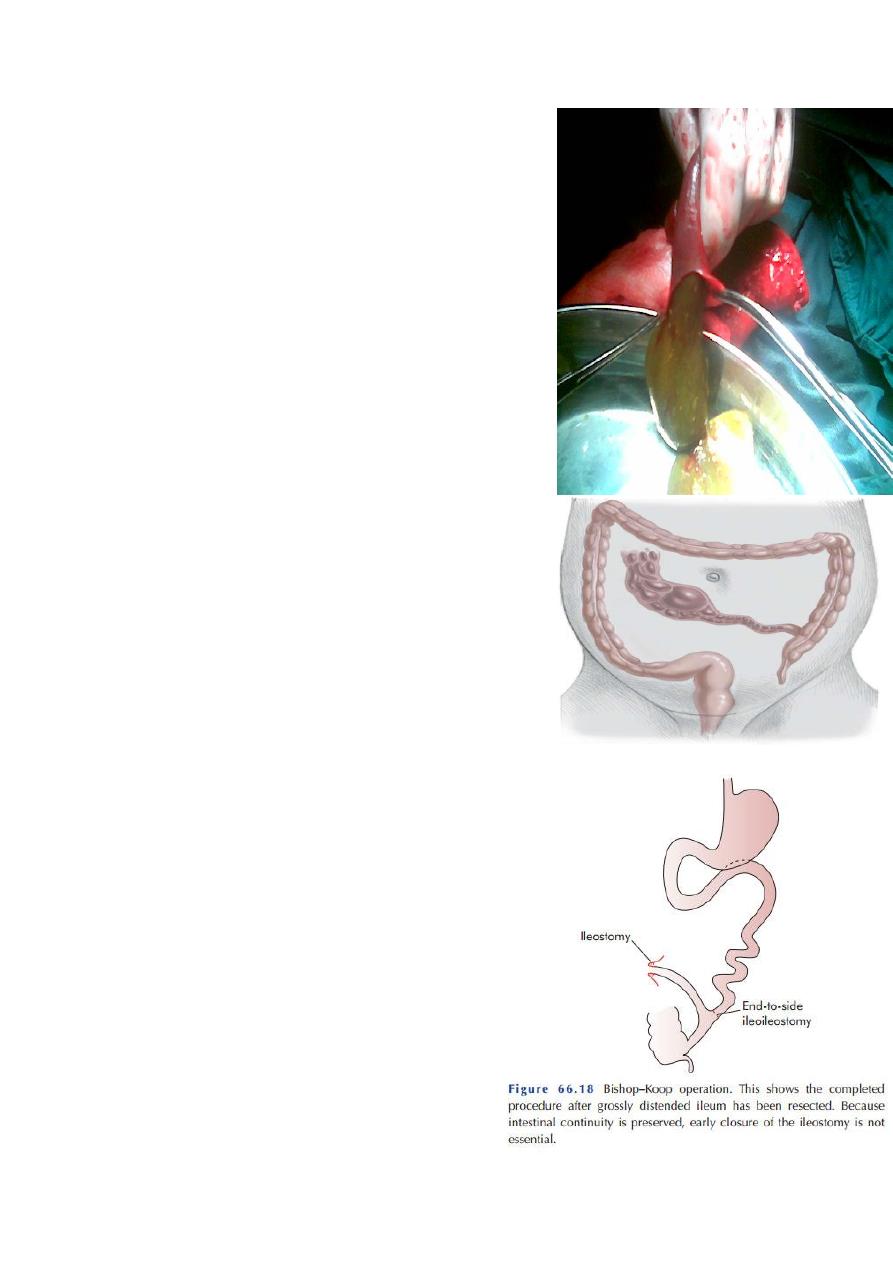
M:1- non-surgical : Dx and Tx ; Gastrograffin enema,
which can liquefy the meconium and make it easy to
pass
out and solve the problem , so it is conservative Tx.
-surgical: Surgical excision of dilated part stoma
formation and re anastomosis(end to side)
Preshoe cap
*
When pass motion ------remove stoma
*
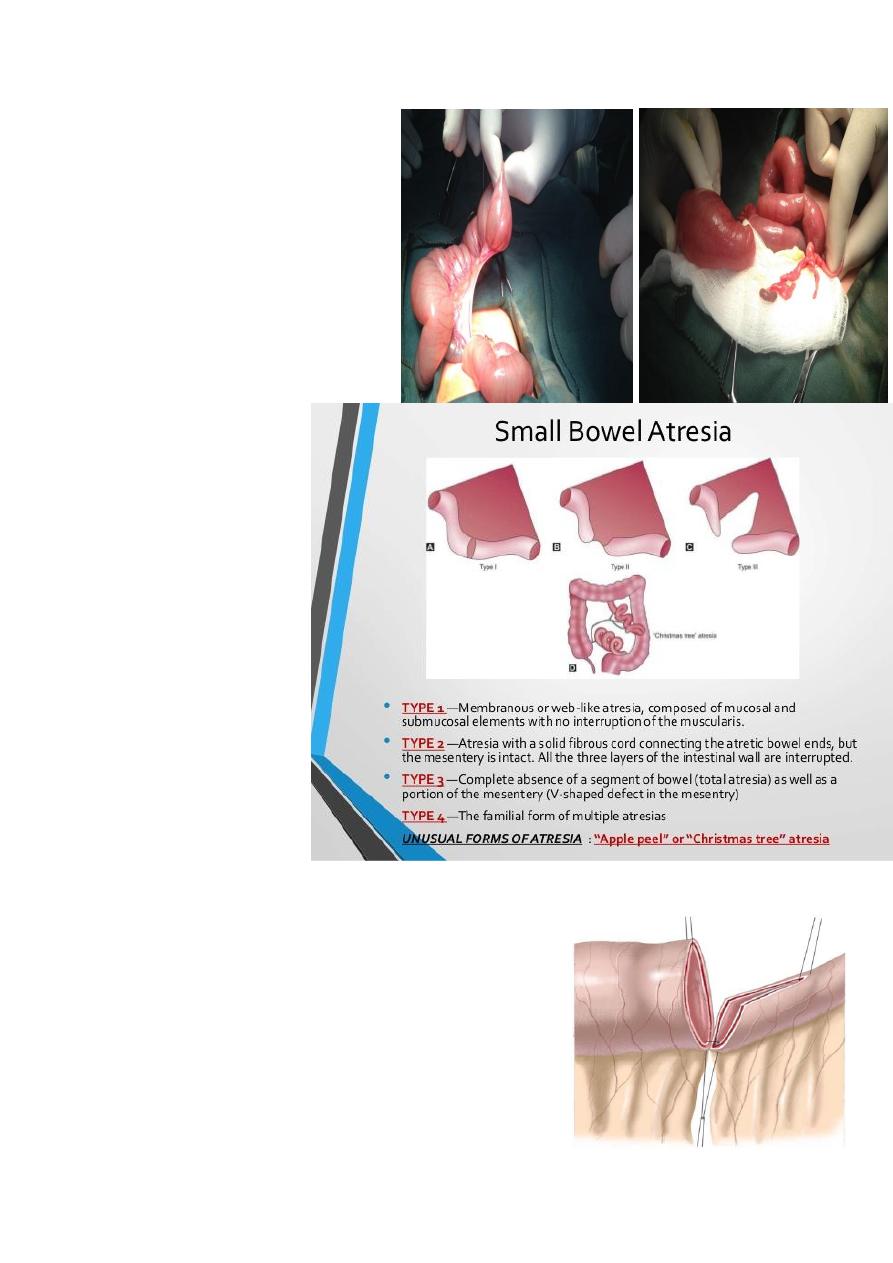
Small bowel atresia
Proximal dilated bowel with distal
thin atretic bowel
Dx: multiple air fluid level
Tx: Surgical resection with end
anastomosis
3 types :-
-type 1 bowel
affected
-type2 normal bowel
-Type3 mesentry non-
affected
-4bowel lost
mesentry affected
األخير صعب تصليحه
Mx :End to back anastomosis(after 6 month)
pneumoperitonium(massive)
w/t saddle sign
cause diaphragm elevation & resp.
distress
causes of it
1-stomach perforation(allways
massive)
Iatrogenic (NGT)
-
Facemask
Drug(indomithecin---PDA)
2-colonic perforation (NEC)
3-Idiopathic
1-Necrotising Enterocollitis (NEC):
It’s common in extreme premature baby.
Incidence increase with the advance nursing care?
Shiny abd. &very tender
Radiological finding:
o Pneumatosis intestinalis---gas b/t bowel well
o Portal v.gas.---Diagnostic
o Pneumoperitonium
Factors Predispose to NEC
. congenital anomalies
. jaundice & lung not well formed &sepsis
Treatment:
o Adequate ventillatory care.
o Resting for GIT(stop milk-giving)
o Antibiotics.(vancomycin)
o Surgery if full bowel necrosis or no response to
supportive treatment.
Notes:-the commonest M.O IS C.difficile.then E.coli
Indx of Surgery:
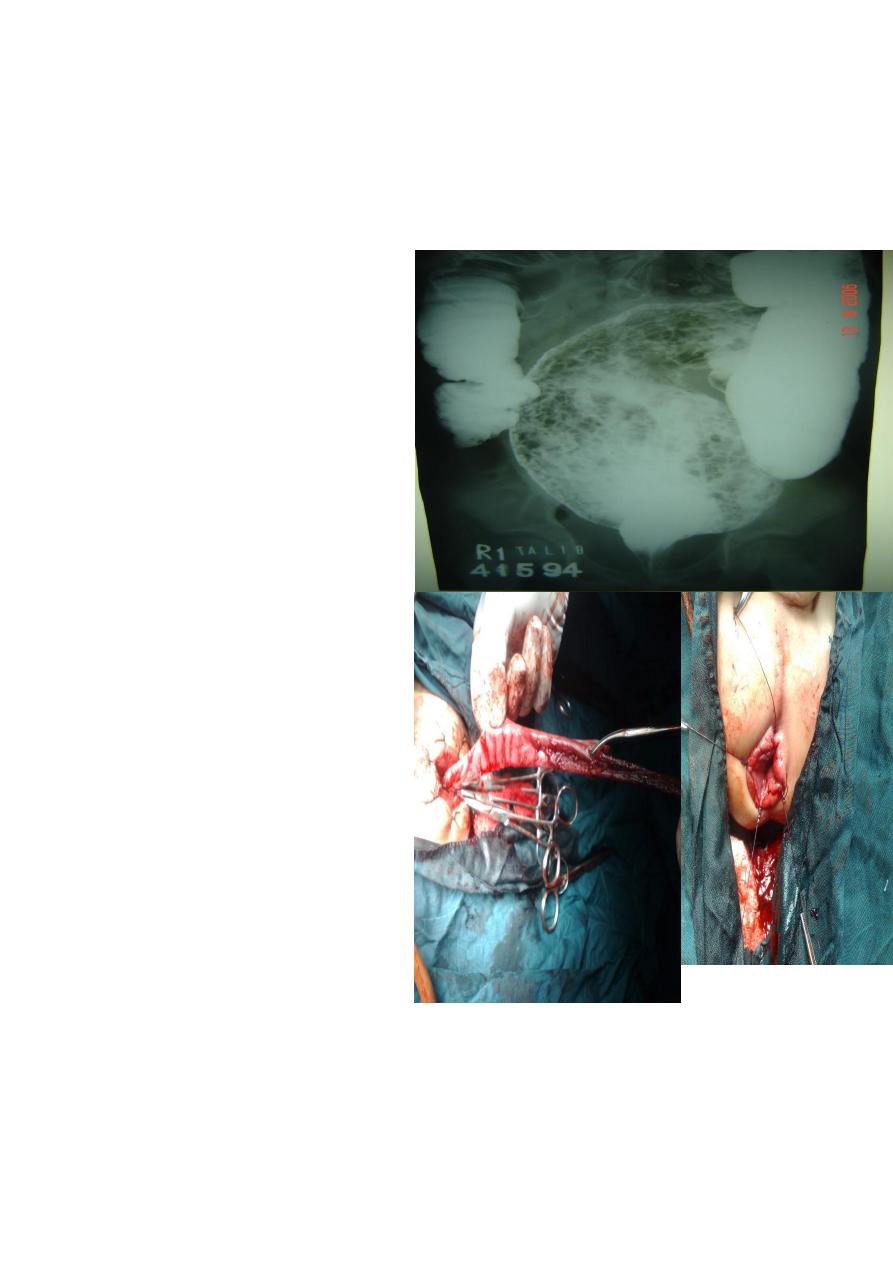
Hirchsbrung Dz
Description:
Barium enema study, showing huge
dilatation of the sigmoid up to the
descending colon, and narrowing at
rectosgimoid junction
filled with
material.
The cause is problem in the ganglia
-
Presentation:
•
Neonate delay to pass
meconium – intestinal obstruction
•
Old child chronic constipation
more than 2 months &FTT
&offensive odor stool
•
– complications like enterocolitis
(diarrhea)
and perforation
Dx:-1-enama
2-Rectal biopsy(
ماتاخذ من
dentate line
الن أصال ما بيه
فوكاها ب
2
سم
Note:transitional zone*hypogaglion
site
عالمود
colostomy
3-anorectall manometry
Treatment:
Surgery 1-colostomy-pull-through-closure the colostomy
2-laproscopic assisted pullthrough 3-transanal pullthrough
Abdominal Wall Defects
-note:reduce gradual to avoid H.F due to I.V.C obstr. Or lymph. Obstr.
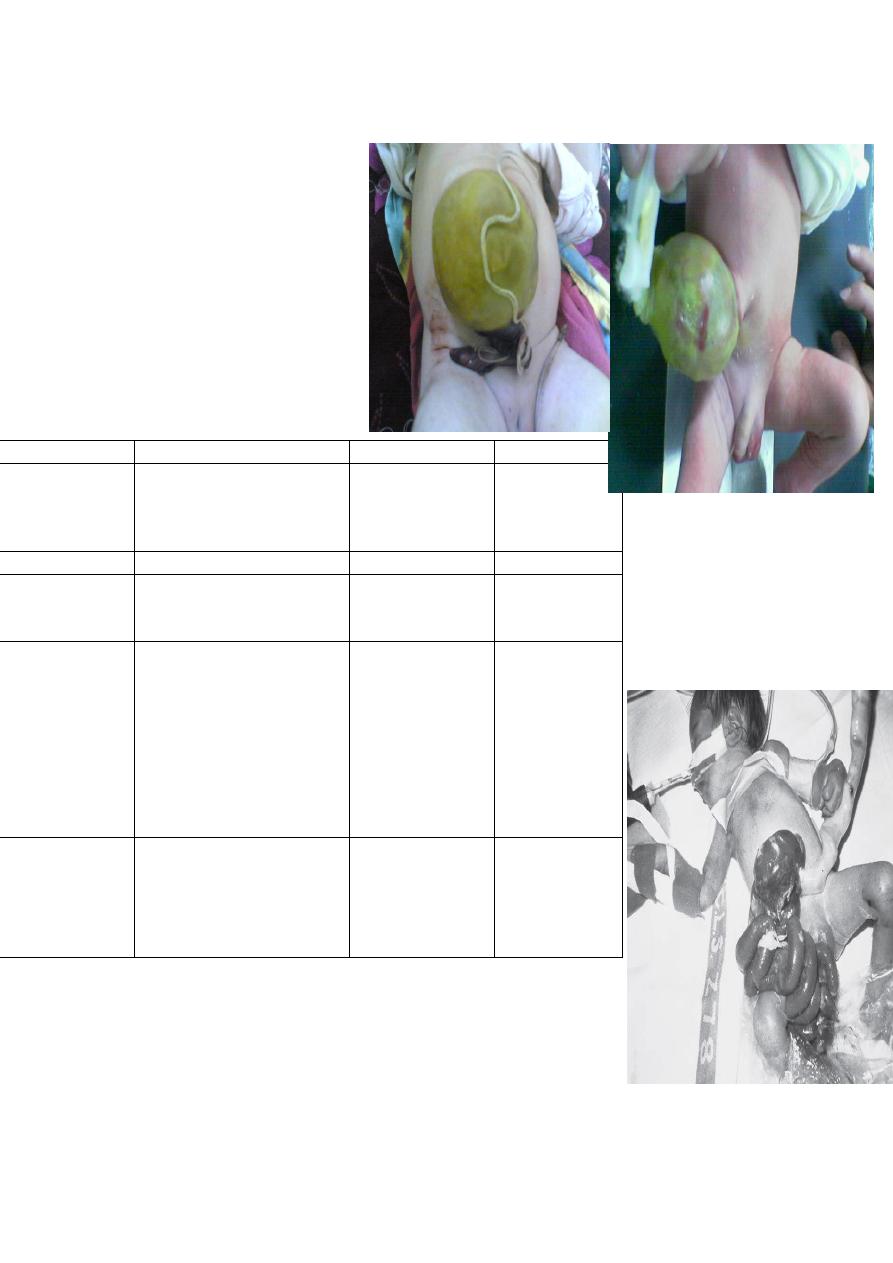
gastochiasis
omphalocele
Item
no covering sac
bowel exposed
completely there
is
With covering
Covering
Emergency
Not emergency
Urgency to op.
with less
congenital
anomalie
more
Cong.
Anomalies
associated
; reduce and
close the defect,
sometimes we
also may use silo
bag to reduce
the bowel
gradual
Non-surgical treatment of
omphalocele(conservative)
“paint” membrane with
betadine-iodine-(induce
fibrosis).
-surgical:silo bag
Mx
to right side of
umbilicus
umbilical
site
Ectopia vesica
-Abscent of Ant. Wall
Complication : incontinence
Associated with epispadias
* Treatment; 1_ approximation
2_ Pelvic osteotomy
gallows traction
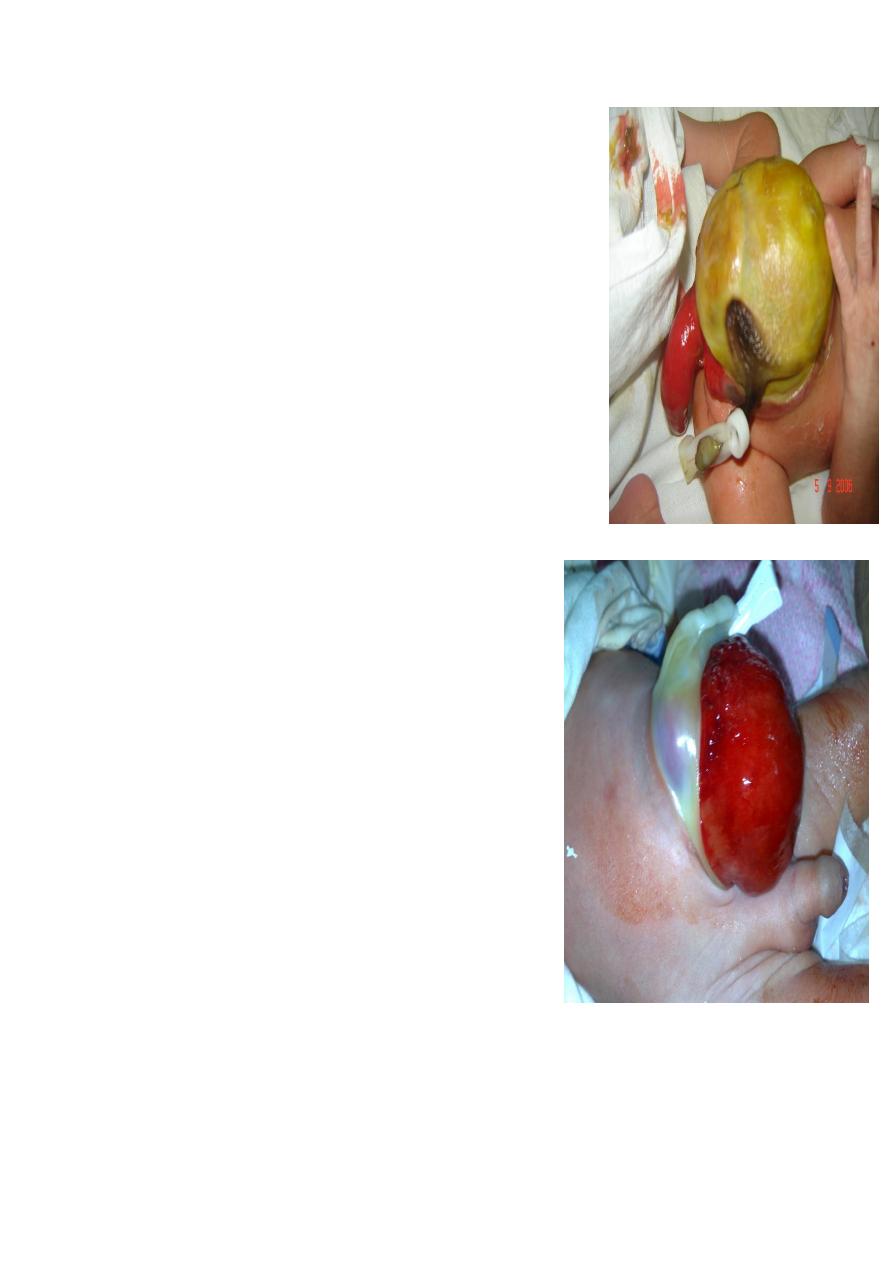
Cloacal exotrophy(omphalocele + imporforate anus)
. bladder exstrophy
. no genitalia
. omphalocele
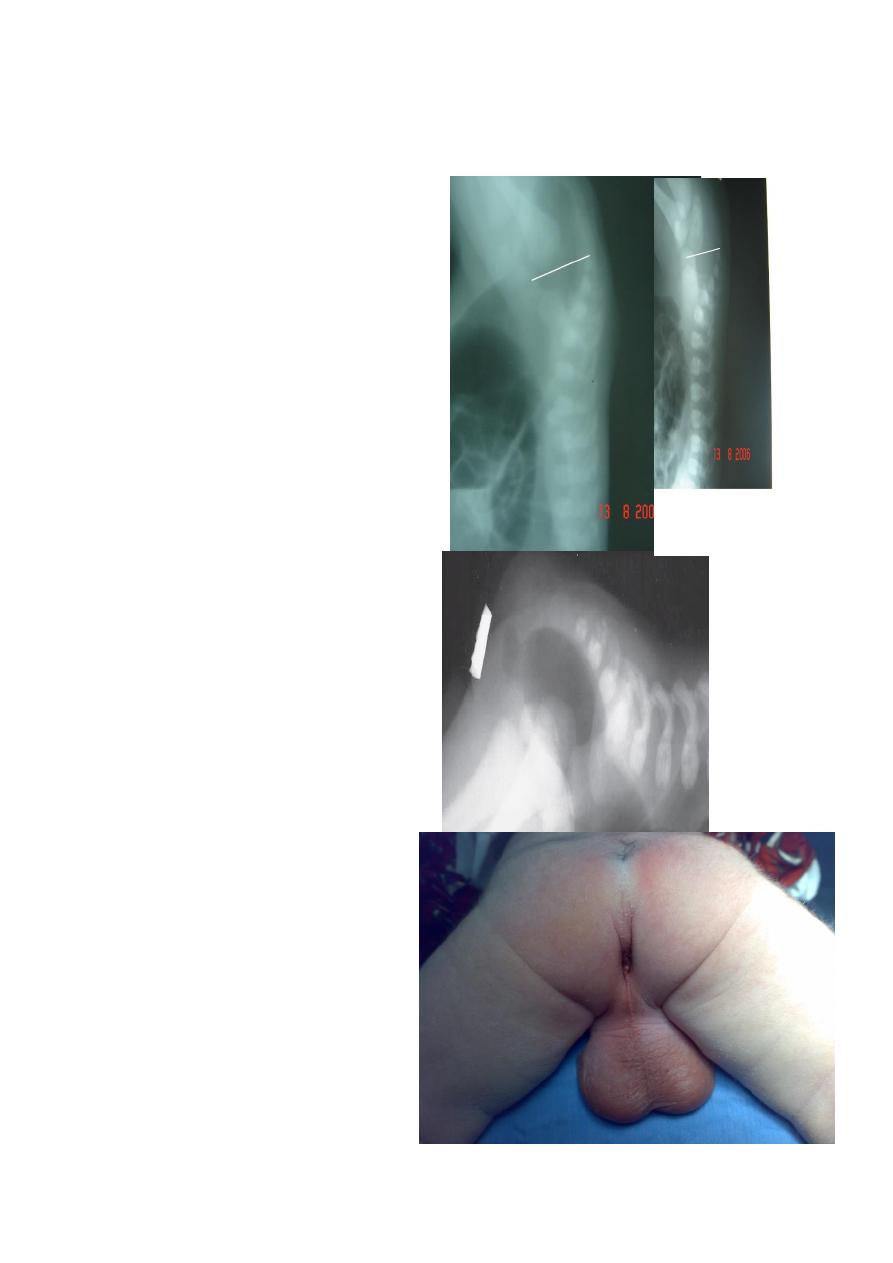
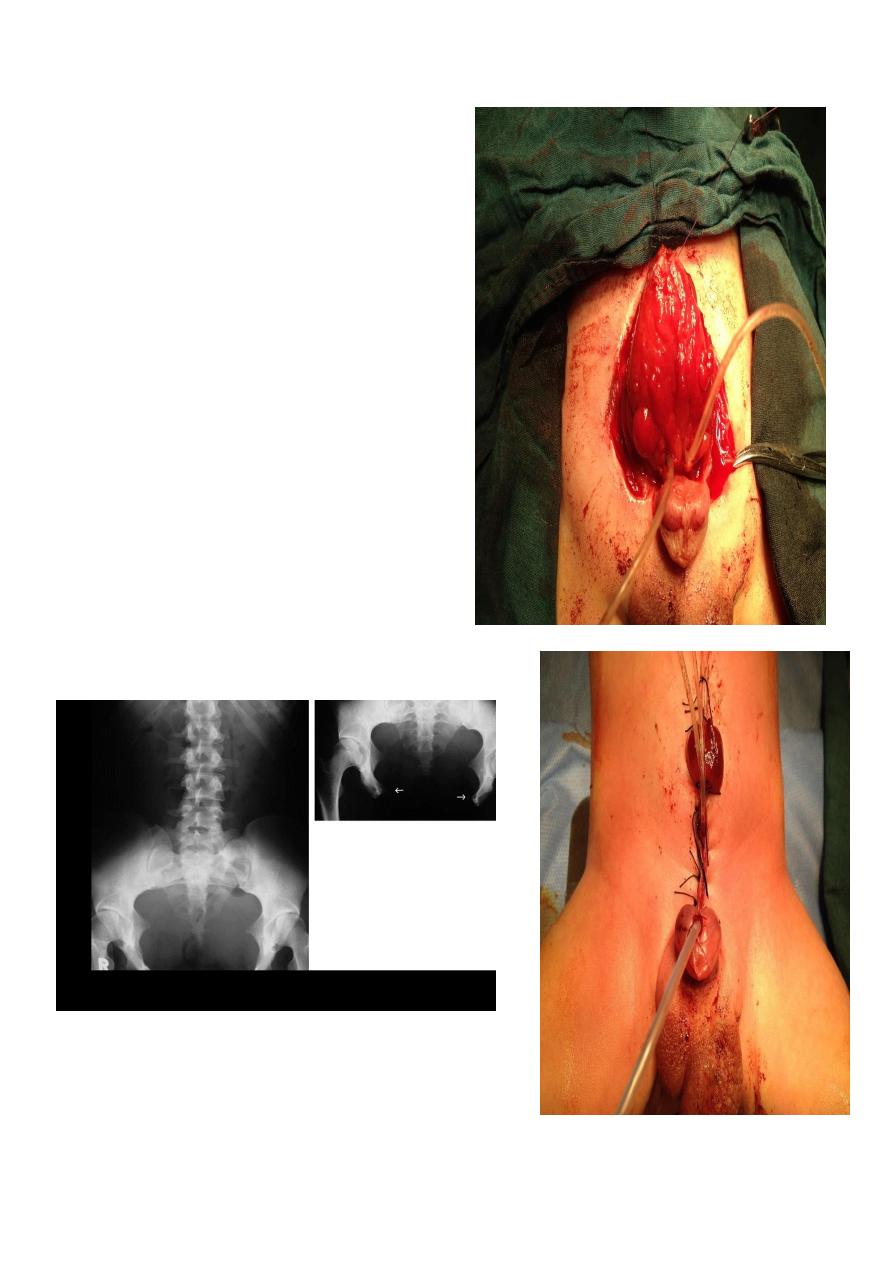
Anorectal anomaly
Lateral invertogram
=pubococcegeal line (below or above gas
bubble ) means lower or upper
type of anorectal atresia respectively.
= mark gas distance
=well formed anal dumble associated
with low type,
## Cloaca treated as high type IA
##Vestibular fistula = Low type IA
Lateral decubitus x-ray
Low type
Anal dimple
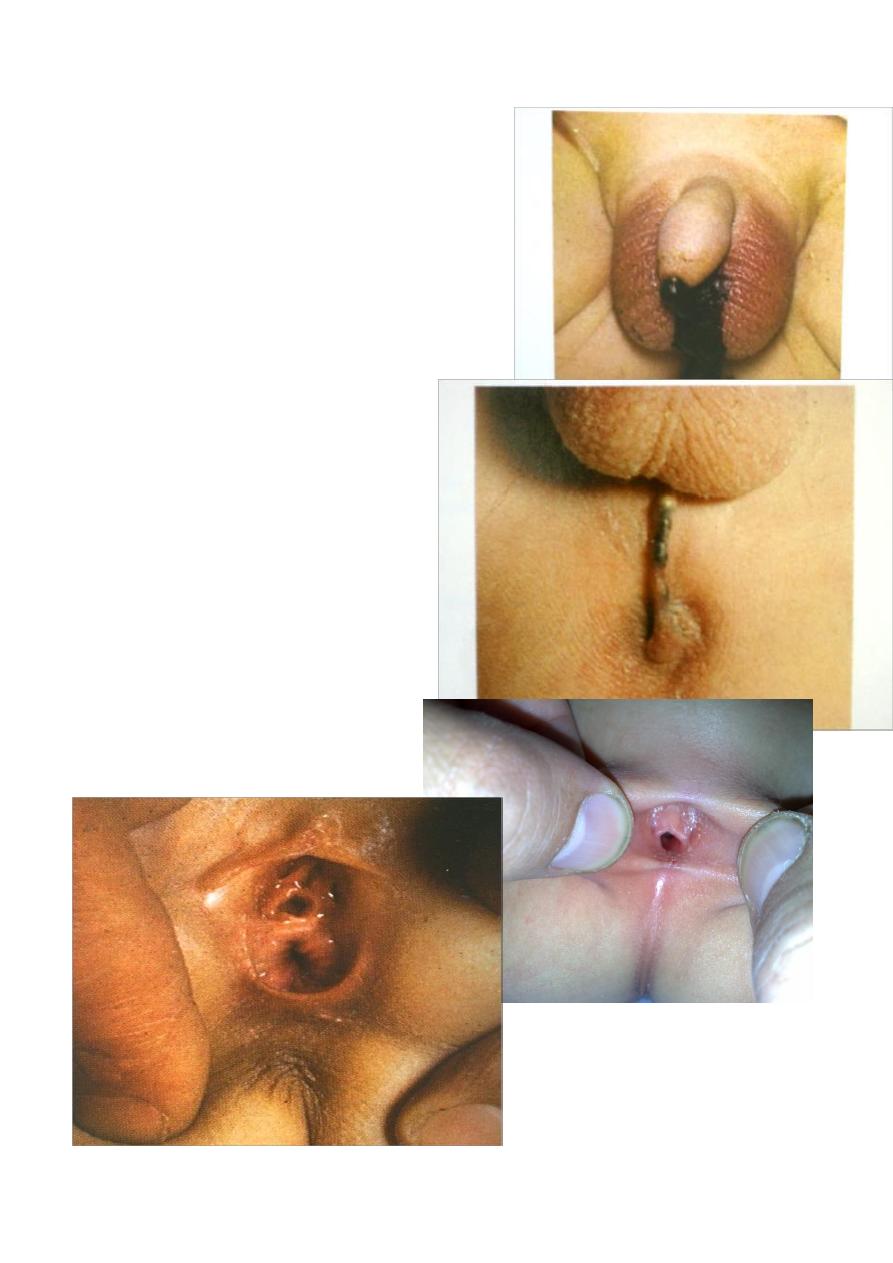
meconium in urethra
Subcutaneous meconium – cutaneous
fistula – low type
Cloaca
High type
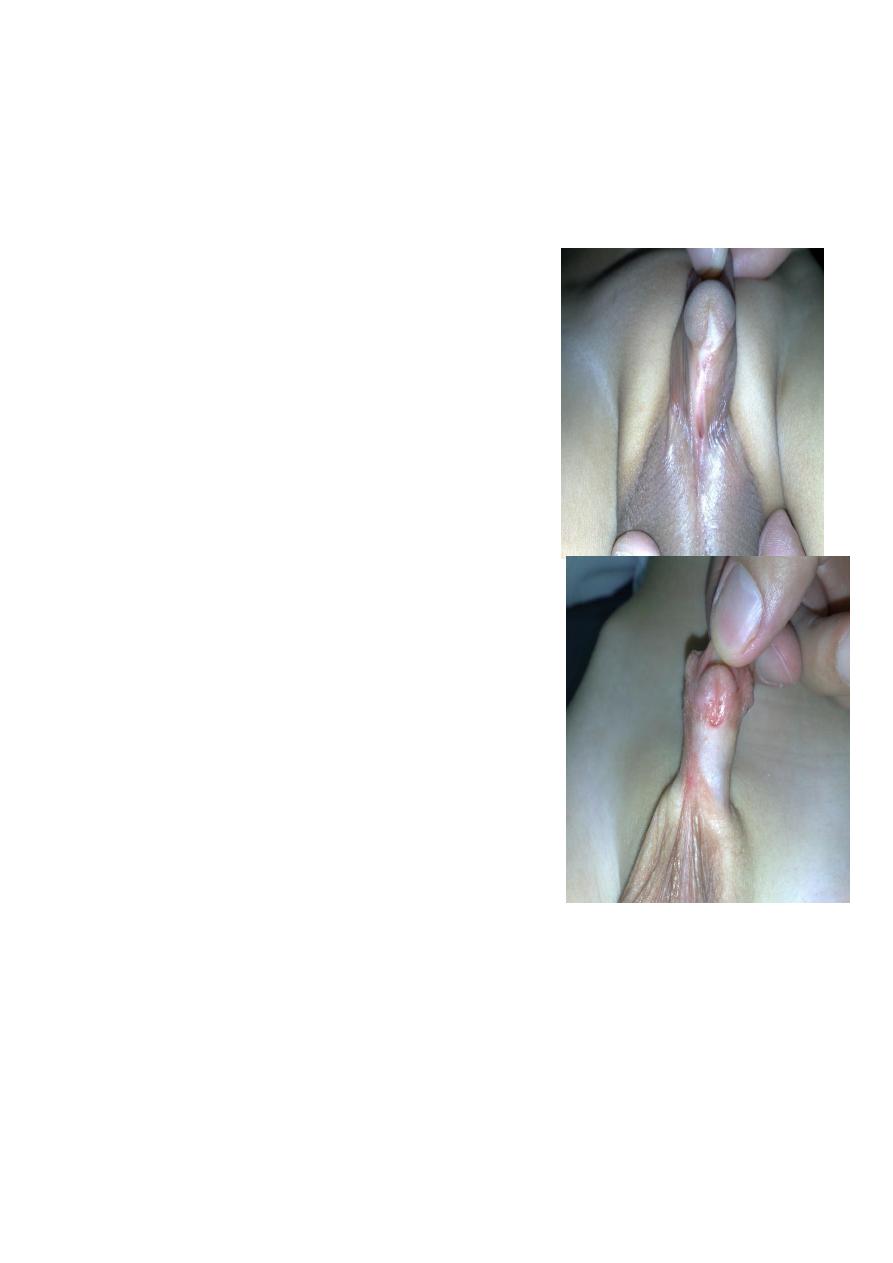
Disorders of Sexual Development
hypospadias 2 types
Proximal ( righ picture) is more severe
** complication. Infertility ,infection, psychological
problem and ventral chordee.
** Time of surgery: at 1 year age
** hypospadias is contraindication for
circumcision...
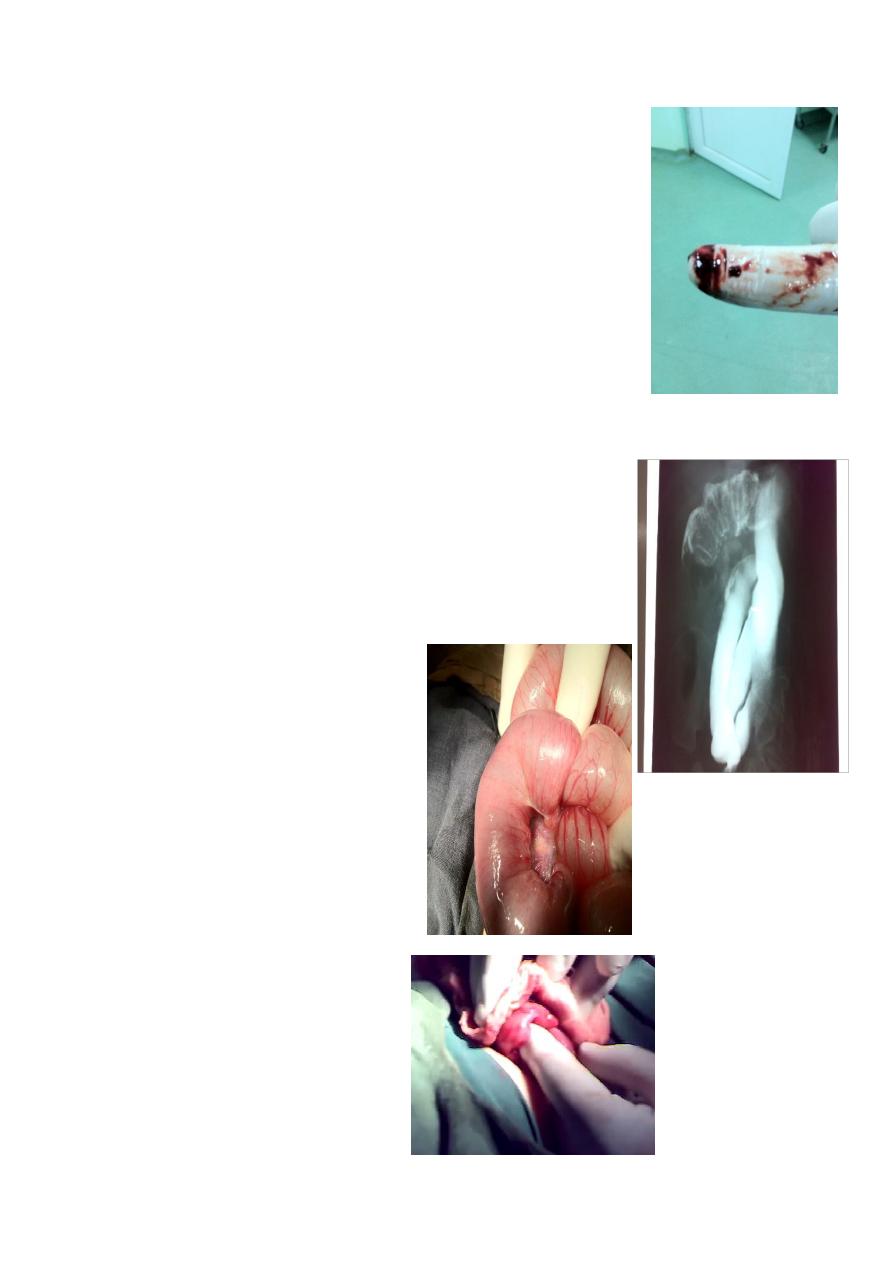
intussusception
Primary (congenital)
screaming, put his feet on his
abdomen, bleeding per-rectum (red current jelly stool),
sausage mass (big mass to the right of the umbilicus).
Secondary (in older children)
due to tumor, mass,
bleeding, polyp.
Leading point may be normal structure like appendix or
abnormal structure
Ex. PR exam
Do Ultrasound( target sign) and barium enema (spring coil sign-kidney sign).
month year old presented with severe acute screaming
and pulling his legs toward his abdomen, with sausage like mass
to right of umbilicus with red currant jelly stool = Intucessuption
Barium enema can lead to hydrostatic reduction (Dx and
Therapeutic), or also pneumatic enema also used to reduce it, or
if failed do laparotomy and reduce it by pushing from distal to
proximal
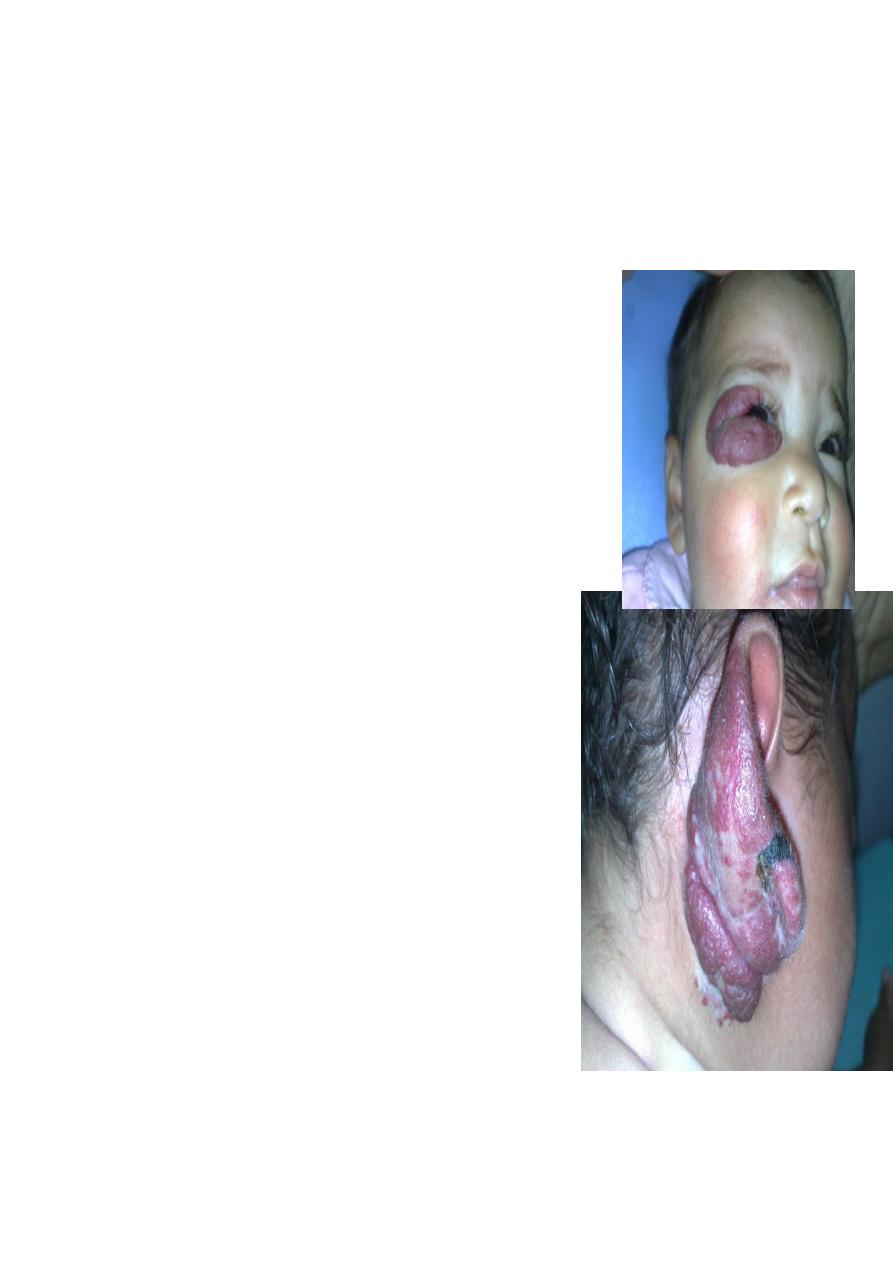
Cavernous Hemangioma.
Complication:
1-bleeding
2-Ulcer
3-Infection
4-Pressure effect according to site e.g. eye affect vision, ear may
cause deafness
5-consumptive coagulopathy due to hemolysis inside the
hemangioma =
activation of clot mechanism = consumption = DIC = Casabach
syndrome.
On exam:
compressibility, can be compressed and refill after removal of
pressure.
Treatment;
Small red spot increases in size rapidly within 2-3 month Up to 1
or 2 increase in size then
become stable( Platue phase) till the 5 year start to
decrease and within 7 years it involute
mostly by itself according to the type and site.;
