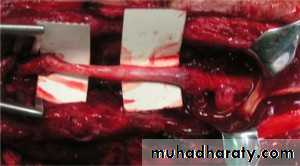
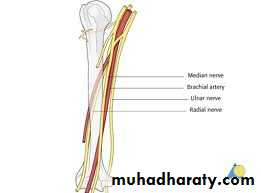
Peripheral nerve lesion
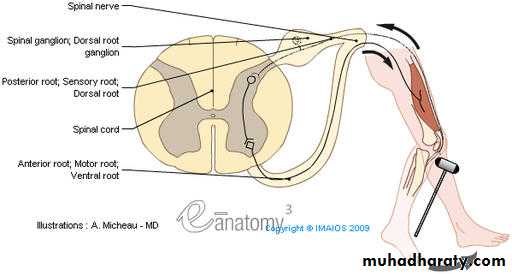
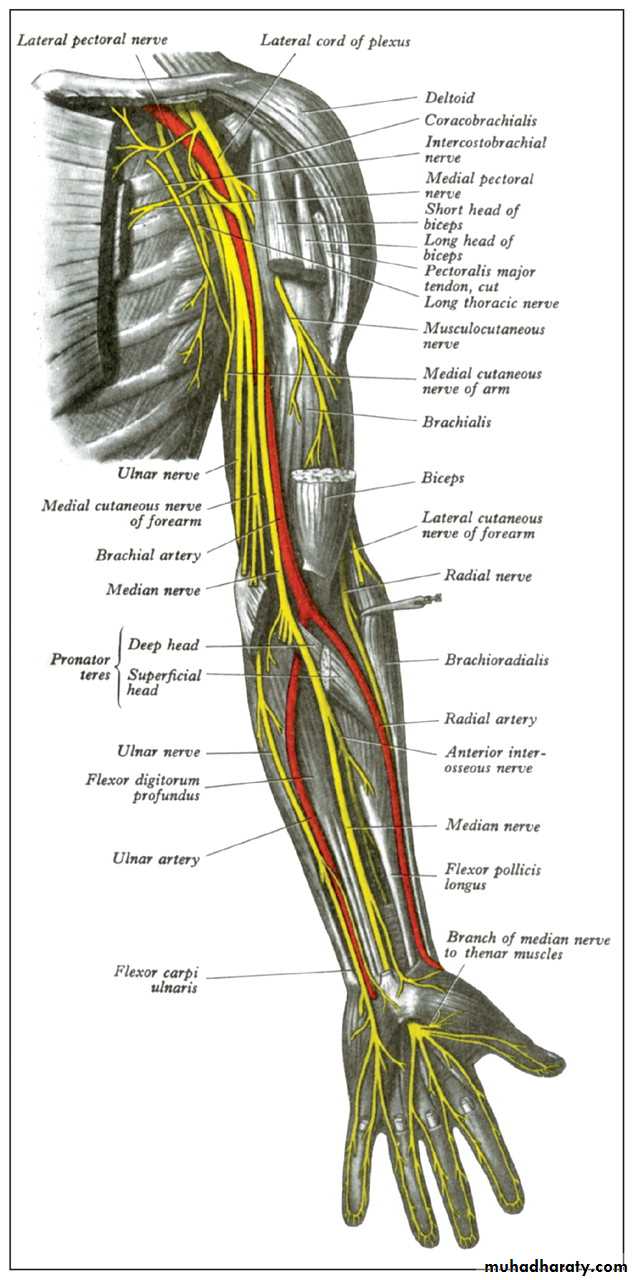
Peripheral nerves are bundles of axons conducting efferent
(motor) impulses from cells in the anteriorhorn of the spinal cord to the muscles, and afferent
(sensory) impulses from peripheral receptors via cells
in the posterior root ganglia to the cord.They also
convey sudomotor and vasomotor fibers from ganglion
cells in the sympathetic chain.
Classifications
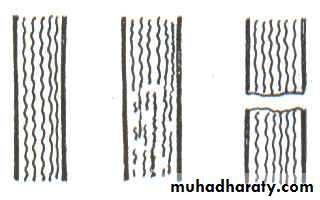
Seddon's classificationNeurapraxia
-- temporary paralysis of a nerve caused by lack of blood flow or by pressure on the affected nerve with no loss of structural continuity
Axonotmesis –
neural tube intact, but axons are disrupted.
nerves are likely to recover.Neurotmesis –
the neural tube is severed.
Injuries are likely permanent without repair.
PATHOLOGY
Nerves can be injured by
1.ischaemia.2.Compression.
3.Traction. 4.Laceration.
5.or burning.
Transient ischaemia
Acute nerve compression causes numbness and tingling within 15 minutes,
loss of pain sensibility after 30 minutes andmuscle weakness after 45 minutes.
Relief of compression is followed by
intense paraesthesiae lasting up to 5 minutes (the familiar ‘pins and needles’ after a limb ‘goes to sleep’); feeling isrestored within 30 seconds and full muscle power after about 10 minutes.
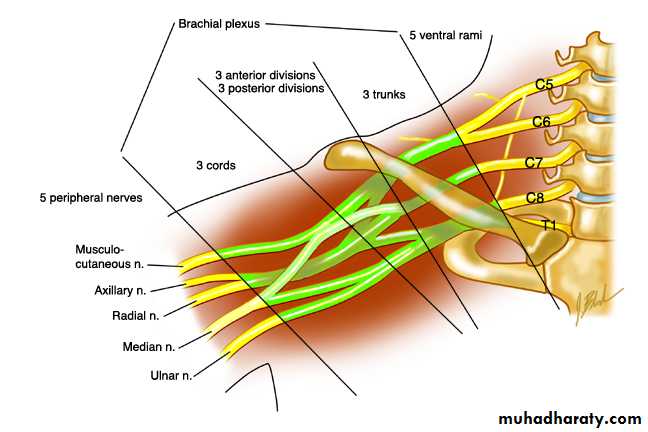
OBSTETRICAL BRACHIAL PLEXUS PALSY
caused by
excessive traction on thebrachial plexus during childbirth, e.g. by pulling the
bay’s head away from the shoulder or
by exerting traction with the baby’s arm in abduction.
Three patterns
are seen: (1) upper root injury (Erb’s palsy), typically in
overweight babies with shoulder dystocia at delivery;
(2) lower root injury (Klumpke’s palsy), usually after
breech delivery of smaller babies; and(3) total plexus injury.
Clinical features
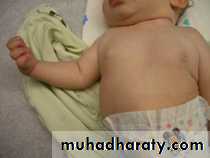
Erb’s palsy is caused by injury of C5, C6 and (sometimes) C7. The abductors and external rotators of the shoulder and the supinators are paralysed.
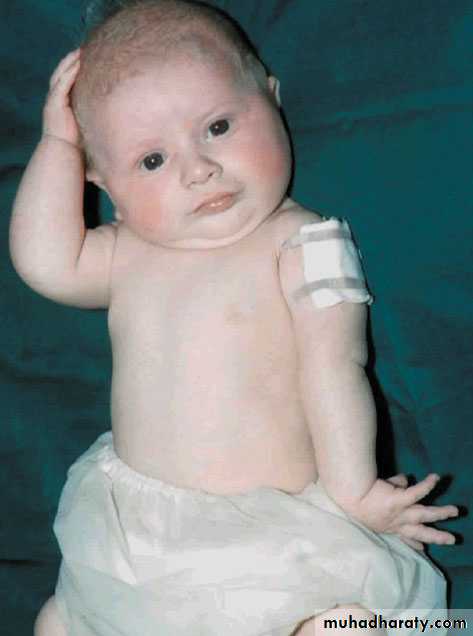
The arm is held to the side,
at birth: after a difficult delivery the baby has a floppy or flail arm.internally rotated and
pronated.There may also be loss of finger extension.
Sensation cannot be tested in a baby.X-rays
should be obtained to exclude fractures of
the shoulder or clavicle (which are not uncommonand which can be mistaken for obstetrical palsy).
Management
Over the next few weeks one of several things may
happen.
Paralysis may recover completely.
Paralysis may be partially resolve.
Paralysis may remain especially in the presence of a Horner’s syndrome
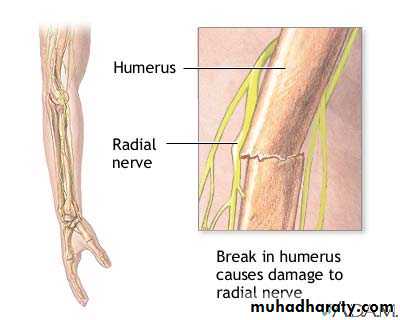
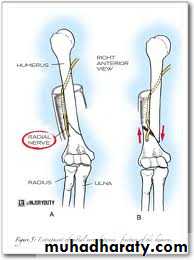
RADIAL NERVE
The radial nerve may be injured at the elbow.
in the upper arm
or in the axilla.
Clinical features
High and Low lesions are usually due to
fractures or dislocationsat mid shaft of humerus or at the elbow,
or to a local wound.
after operations on the proximal end of the radius.
The patient complains of clumsiness and, on testing,
cannot extend the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hand.In the thumb there is also weakness of extension.
Treatment
Open injuries should be explored and the nerve repaired or grafted as soon as possible.
Closed injuriesIn patients with fractures of the humerus it is important to examine for a radial nerve injury on admission,
before
treatment and again after manipulation or internal fixation.If the palsy is present on admission, one can
afford to wait for 12 weeks to see if it starts to recover.
If it does not,
then EMG should be performed;
While recovery is awaited,
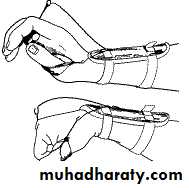
Physiotherapy
The wrist is splinted in extension. ‘
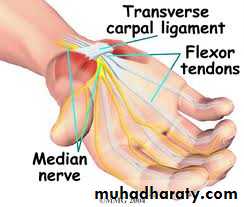
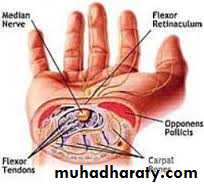
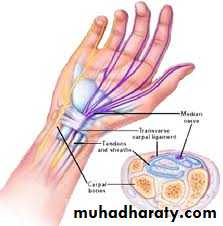
To over come fixed contracturesCARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
In the normal carpal tunnel there is barely room for all the tendons and the median nerve; consequently,
any swelling is likely to result in compression and ischaemia of the nerve.
the syndrome is, however, common
at the menopause.in rheumatoid arthritis.
pregnancy.
and myxoedema.
Clinical features
The history is most helpful in making the diagnosis.
Pain and paraesthesia occur in the distribution of themedian nerve in the hand.
Night after night the
patient is woken with burning pain,tingling and
numbness.Hanging the arm over the side of the bed,
or shaking the arm, may relieve the symptoms.In advanced cases there may be clumsiness and weakness
The condition is far more common in women than in men.
The usual age group is 40–50 years;younger patients it is not uncommon to find related factors such as
pregnancy, rheumatoid disease, chronicrenal failure or gout.
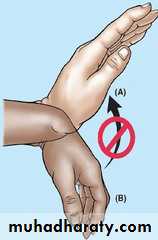
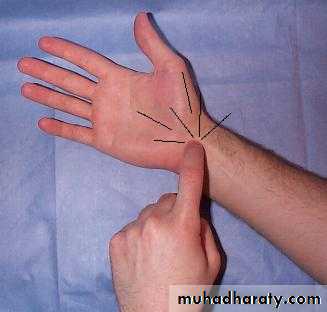
Sensory symptoms can often be reproduced by percussing
over the median nerve(Tinel’s sign) or by
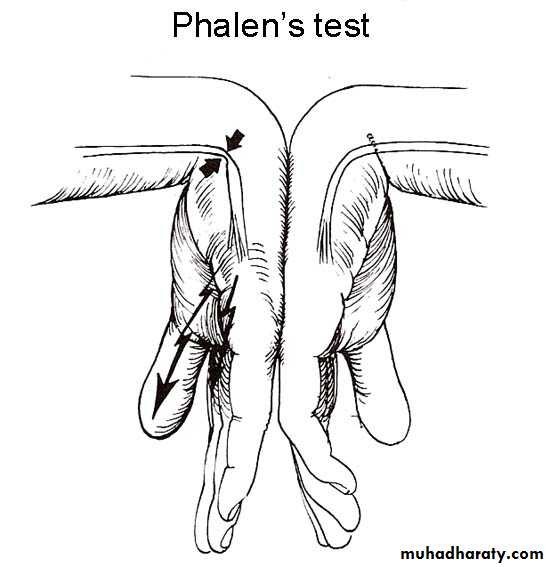
Clinical sign
holding the wrist fully flexed for less than 60 seconds
(Phalen’s test).In late cases
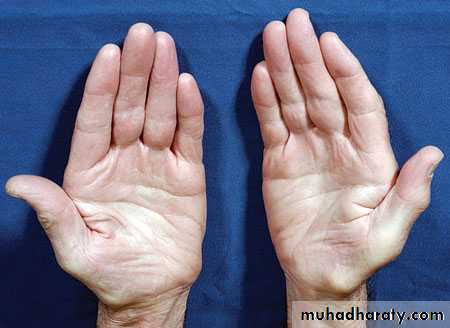
there is wasting of the thenar muscles.
weakness of thumb abduction and
sensory dulling in the median nerve territory.
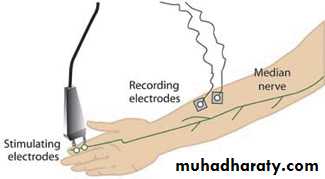
Electrodiagnostic tests,which show slowing of nerve conduction across the wrist
DD:
Radicular symptoms of cervical spondylosis may confuse the diagnosis and
may coincide with carpal tunnel syndrome.Treatment
Light splints that prevent wrist flexion can help those
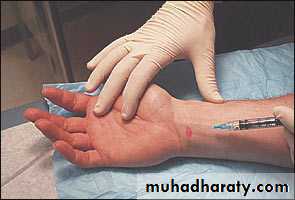
with night pain or with pregnancy-related symptoms.Steroid injection into the carpal canal, likewise, provides temporary relief.
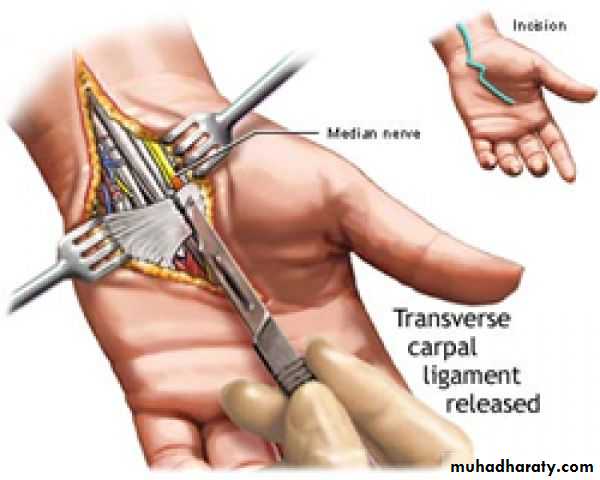
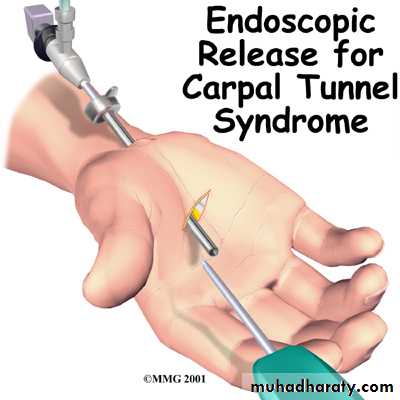
Open surgical division of the transverse carpal ligament usually provides a quick and simple cure.Endoscopic carpal tunnel release.
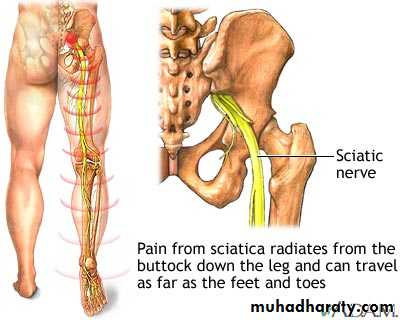
SCIATIC NERVE
Division of the main sciatic nerve is rare except.in
gunshot wounds.
Traction lesions may occur with
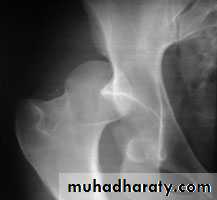
traumatic hip dislocationsand with pelvic fractures.
Intraneural haemorrhage in patients receiving anticoagulantsClinical features
In a complete lesion the hamstrings and all musclesbelow the knee are paralysed;
the ankle jerk is absent.
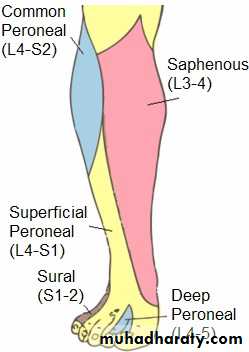
Sensation is lost below the knee, except on the medial
side of the leg which is supplied by the saphenous
branch of the femoral nerve.
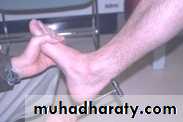
The patient walks with a
drop foot anda high-stepping gait to avoid dragging the insensitive foot on the ground
Treatment
sutureor nerve grafting should be attempted ,more than a year for leg muscles to be re-innervated.
While recovery is awaited,
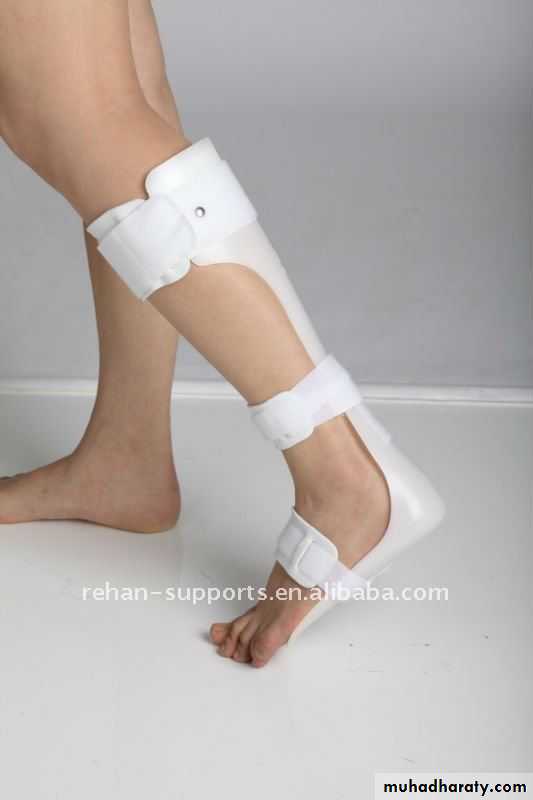
a below-knee drop-foot splint is fitted.Spine injuries
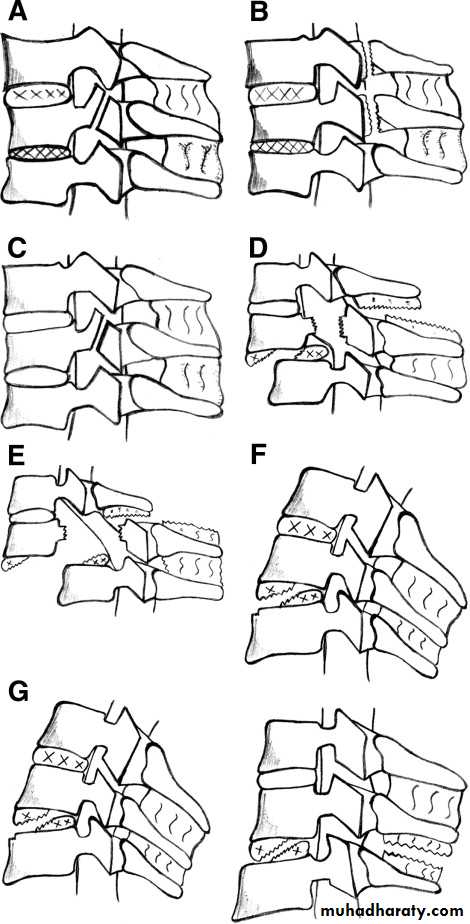
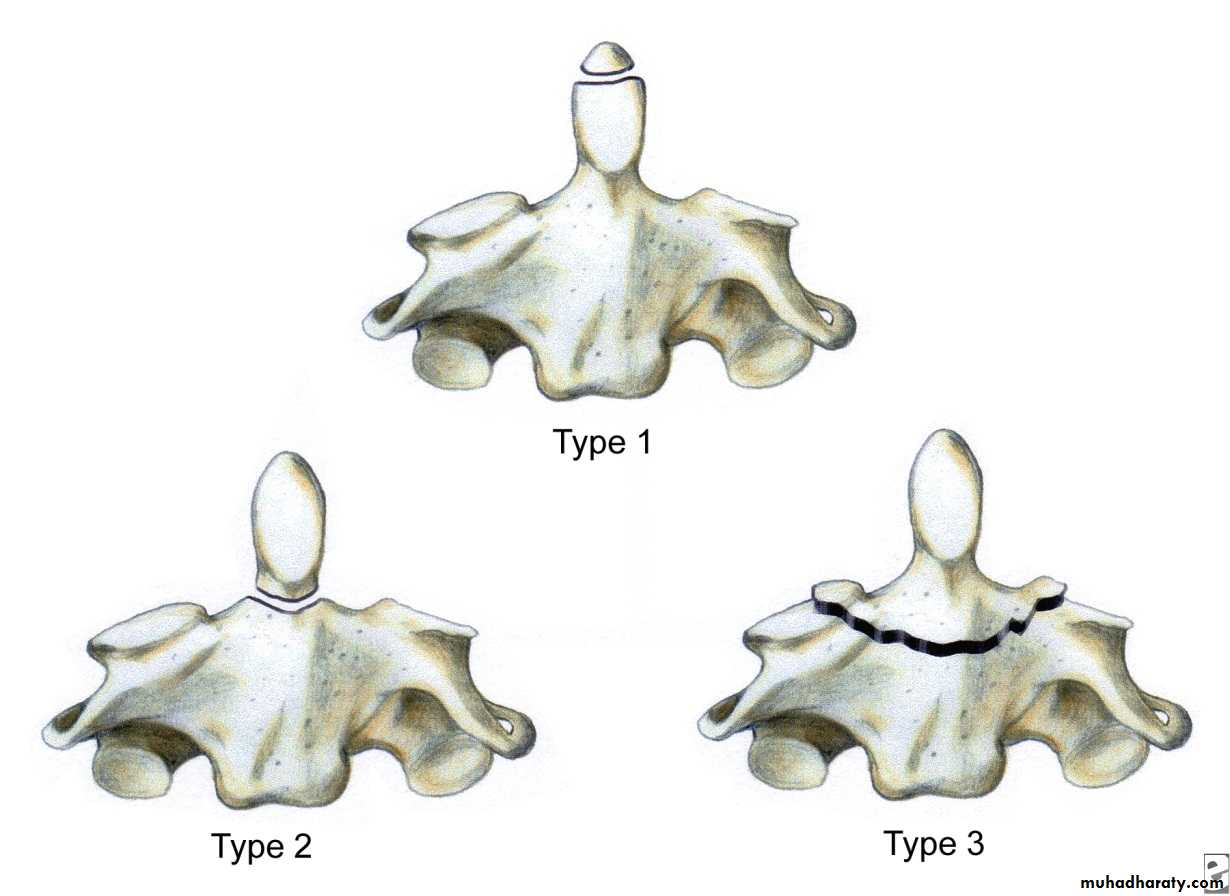
Cervical classificationswedge compression fracture of vertebral body
burst fracture of vertebral body
extension subluxation
flexion subluxation
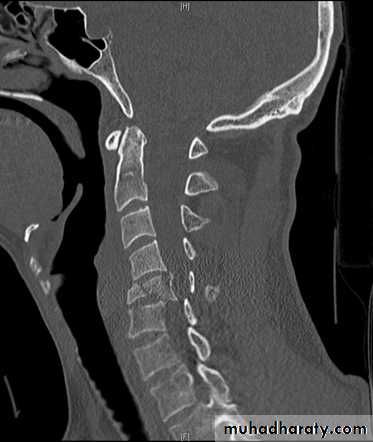
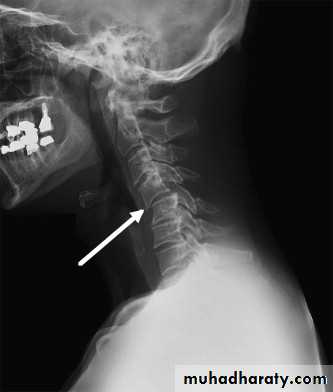
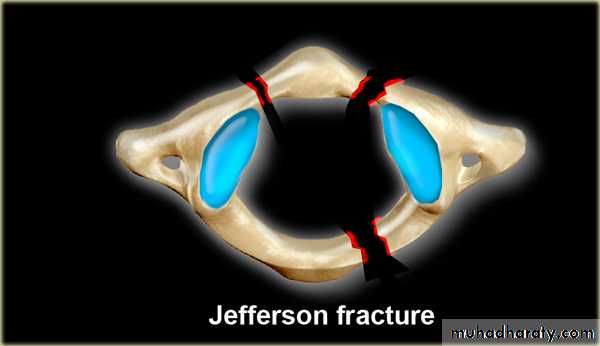
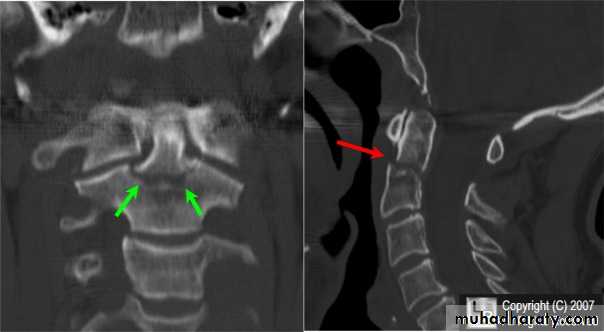
fracture of the atlas
fracture-dislocation of the atlanto-axial joint
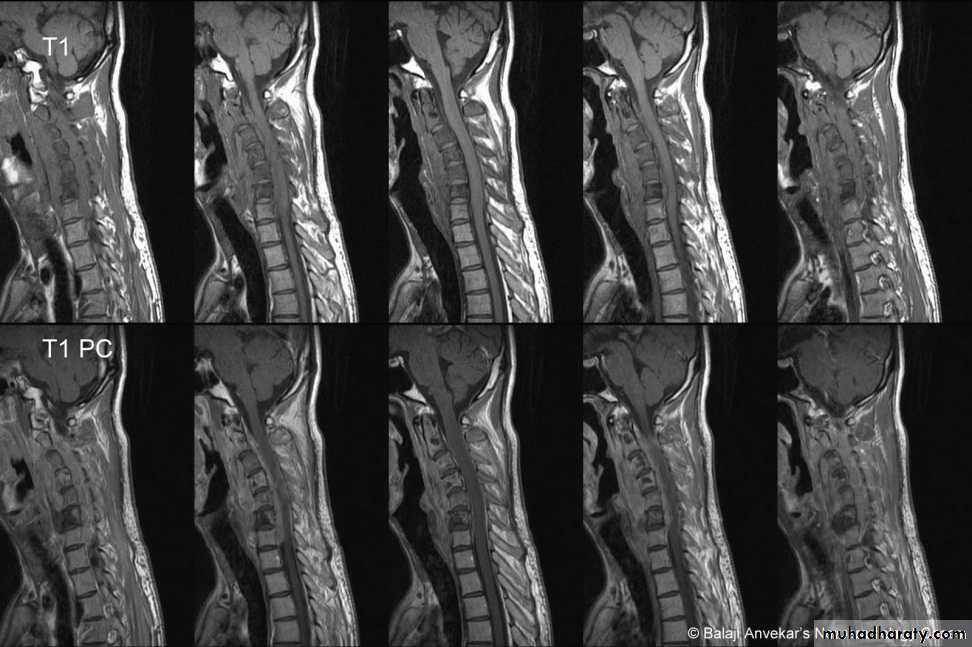
intraspinal displacement of soft tissue
soft-tissue strain
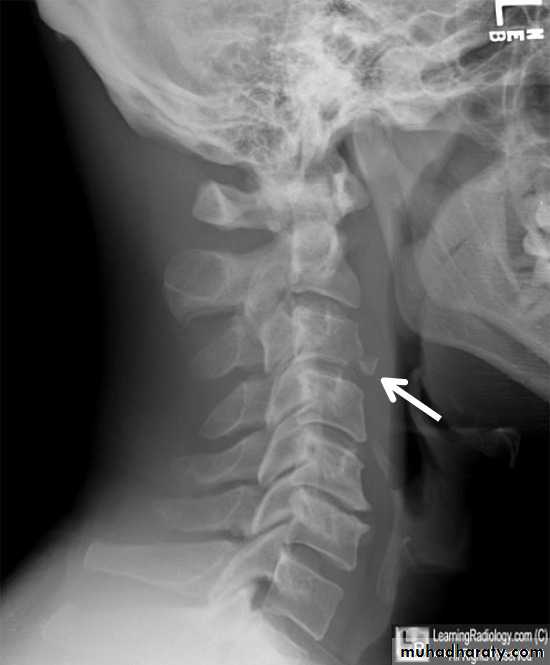
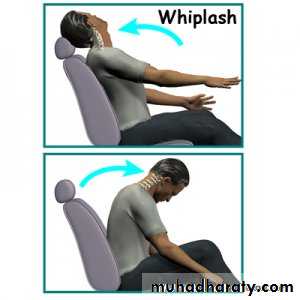
('whiplash injury')MECHANISM OF INJURY
Flexion
Flexion-rotationExtension
Vertical compression.
injuries of the cervical spine are usually caused by indirect violence,
Such as falls on to the head orother violent movements transmitted from the skull. i.e in any direction.
flexion,
tension, lateral flexion or
rotation-
or a vertical compression force acting on
a straight spine.
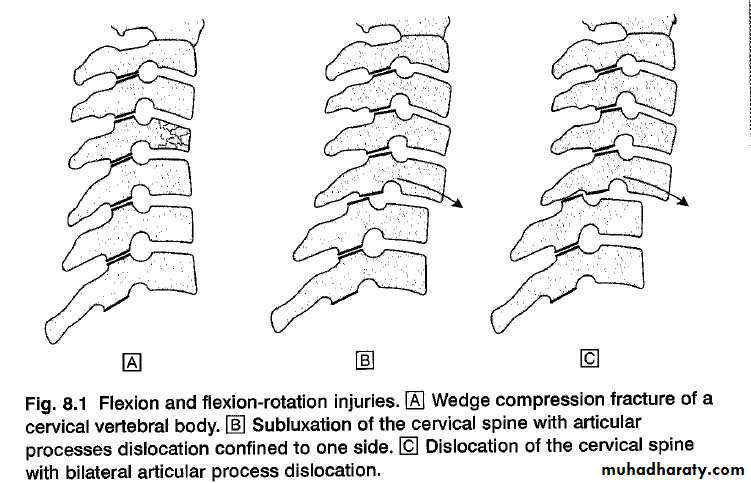
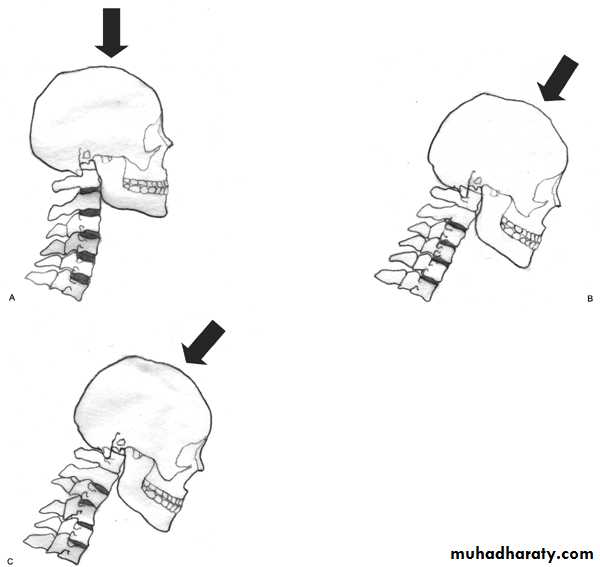
Flexion and flexion-rotation injuries
are common:
flexion alone tends to a wedge compression fracture .whereas combined flexion and rotation cause subluxation ,
dislocation or fracture-disIocation.A flexion or flexion-rotation force may also cause massive displacement of an intervertebral disc, without bone injury
A hyperextension
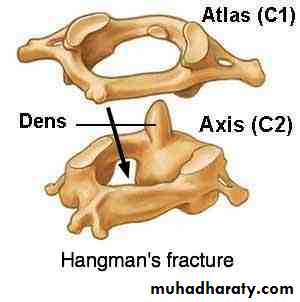
force may fracture the neural arch, especially of the atlas
Or fracture the dens (odontoid process) of the axis.
hyperextension may rupture the anterior longitudinal ligament and the
anulus fibrosus, forcing the vertebral bodies apart anteriorly (extensionsubluxation) .
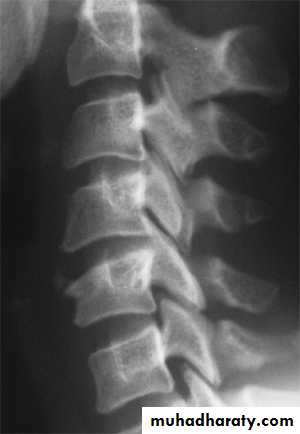
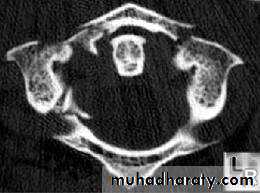
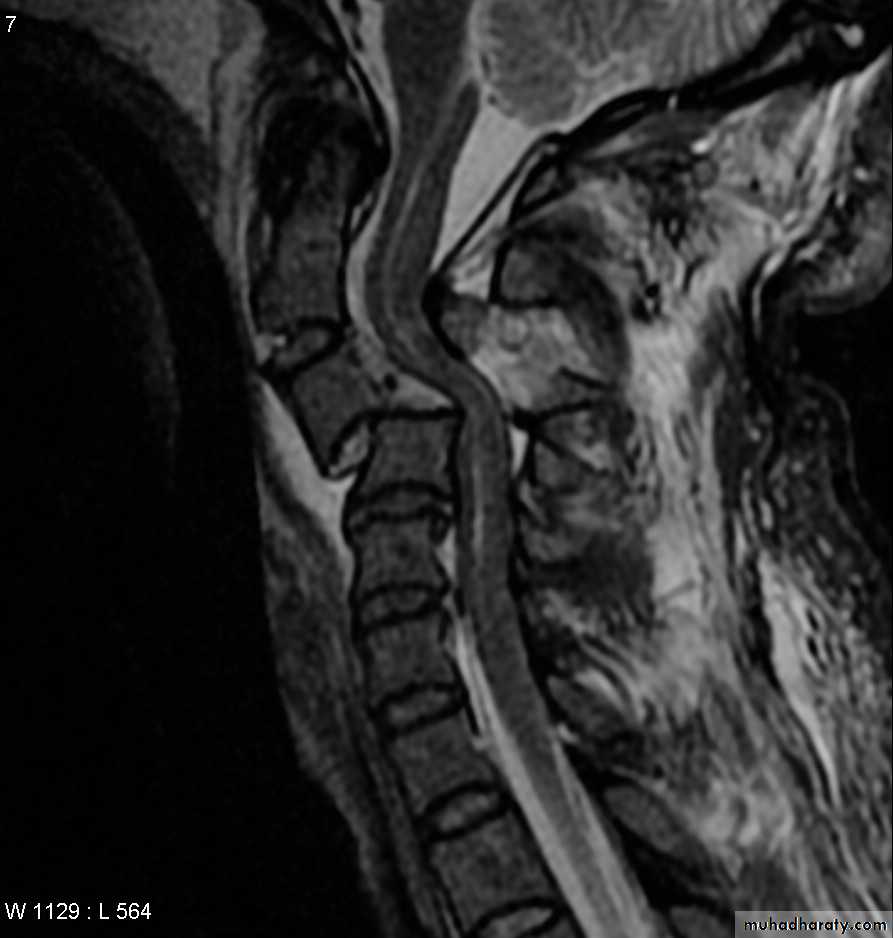
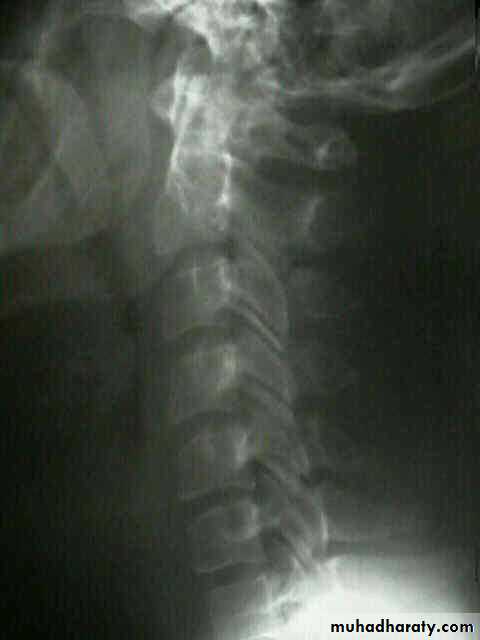
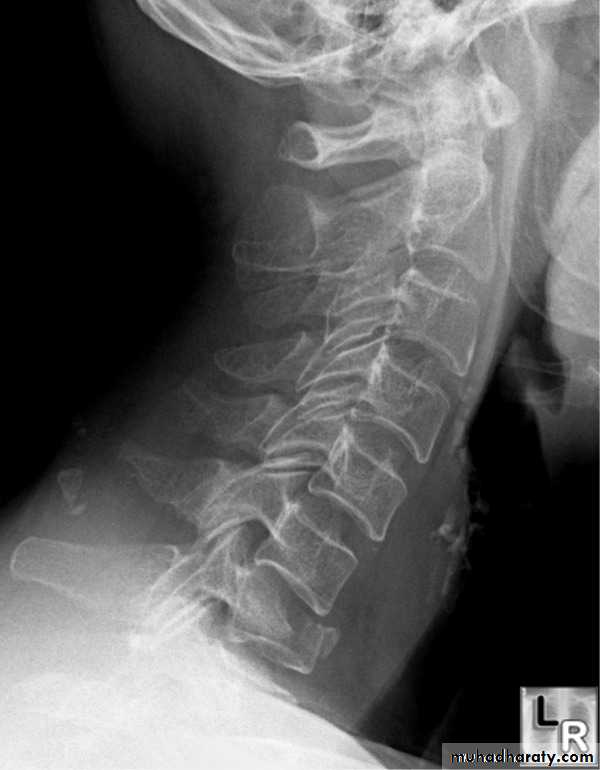
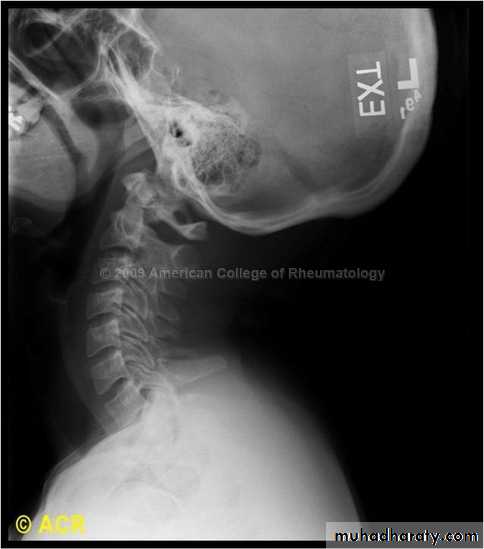
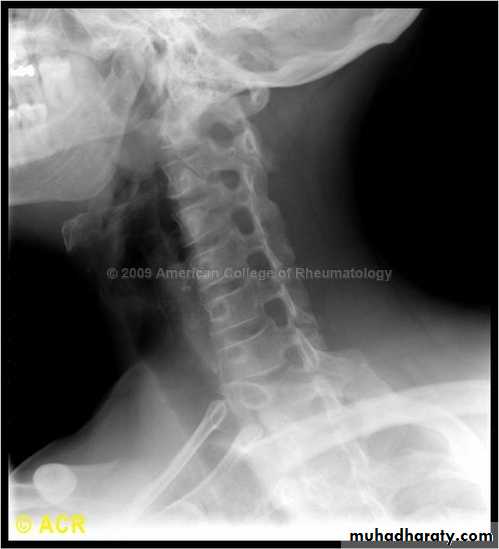
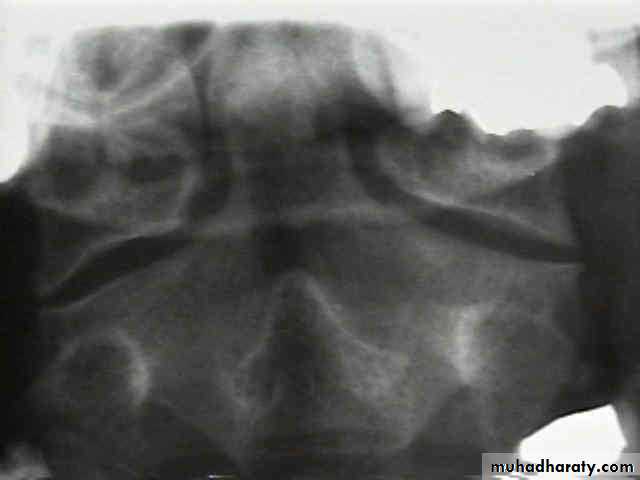
DIAGNOSISX RAY
Anterio posterior X ray radiograph.lateral radiographs with the head in flexion and extension may revealinstability that is not shown in the routine lateral film.
oblique views
at 45° are especially helpfula special projection
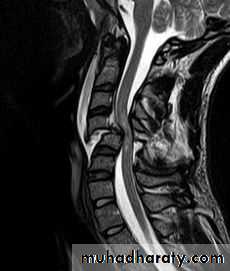
through the open mouth.Computed tomography (CT)
and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Treatment
It is unnecessary to attempt reduction, and all that is required is to support the
neck for 2 months to relieve pain. This may be achieved by a rigid plastic Collar.In addition to N S A I
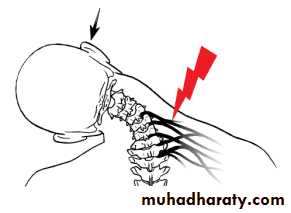
SOFT-TISSUE STRAIN OF THE CERVICAL SPINE
Mechanism of injury and pathology
At the moment of impact, the head is firstsuddenly jolted forwards followed by rebound flexion of the spine.
And a second by extension of the neck.
Clinical features
At impact, the patient may feel jolting or 'wrenching' of the neck or
painful one of the shoulder,neck pain is usually accompanied
by severe headache, whichExamination shows restriction of the range of
movement of the cervical spine, usually in all directions
Treatment
In general, the
principle to provide support and rest for the neck atFirst, in the form of a protective cervical collar.
But after 1or 2 weeks there
should be on the restoration of mobility by exercises within the limitsimposed by pain, preferably under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
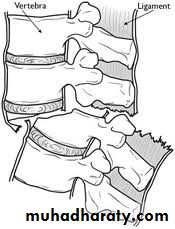
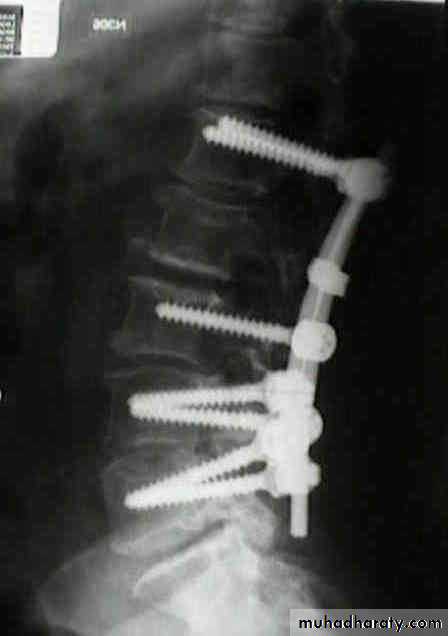
Dorsal and lumbar spine
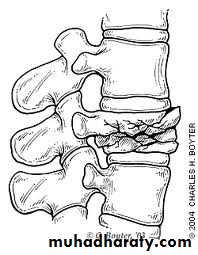
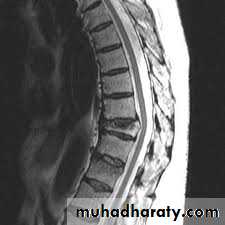
Wedge compression fracture of a vertebral body.
Burst fracture of a vertebral body.
Distraction fracture of a vertebral body.
Dislocation and
fracture-dislocationMinor fractures of the spinal column
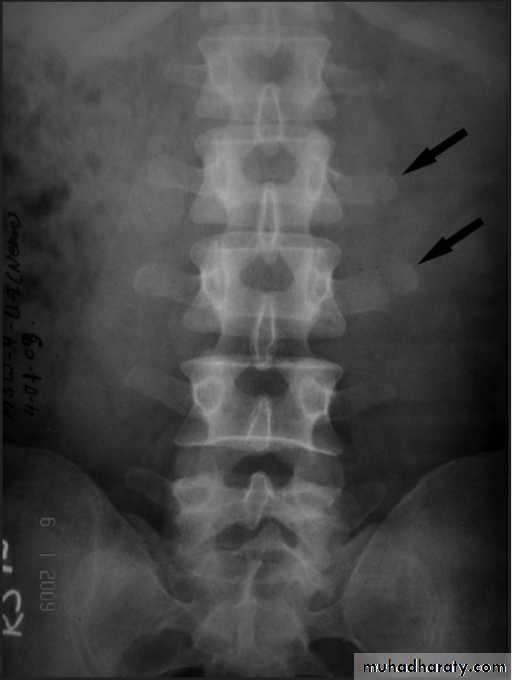
Fractures of transverse processes .
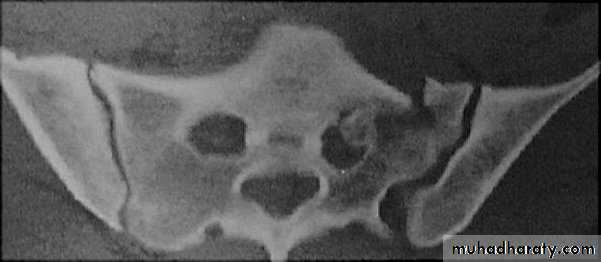
Fracture of the sacrum
Fracture of the coccyx
Fractures of the thoracic cage.
Fractures of the ribsFractures of the sternum
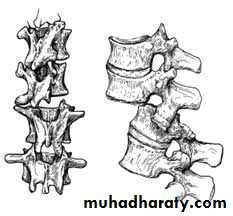
MECHANISM OF INJURY
by vertical force acting through the long axis of the spinal column.
This force.
may act from above, as when a coal miner is buried by a fall of roof.
or from
Below, as by a heavy fall on the feet or buttocks, in high speed motor vehiclecollisions
The thoracolumbar junction
one or more of the vertebral bodies collapses
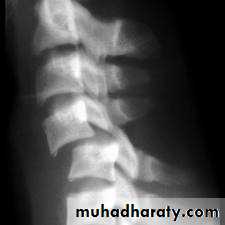
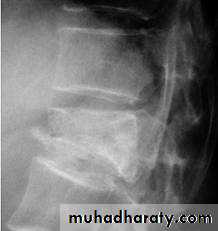
anteriorly and becomes wedge-shaped, giving rise to a localized kyphosis.WEDGE COMPRESSION FRACTURE
Diagnosis .
obvious symptoms and signs pointingIn cases of major fracture there will be only between the T11 and L2
Treatment
It has been shown that persistent wedging of a vertebral body is compatible. With virtually normal function.
so correction of the deformity is not essential.
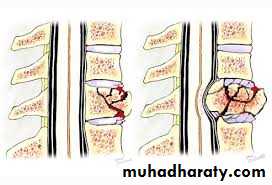
The standard method of treatment may, therefore, be said to be conservative.BURST FRACTURE OF A VERTEBRAL BODY
the compression force thus acts vertically in the line of the vertebral bodies.
The intervertebral disc is forced
In the affected vertebral body, causing a comminuted bursting fracture in which fragments are driven outwards in all directions.