Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy LGMD
-Autosomal dominant (type 1) or autosomal recessive ( type 2) inheritance.-The onset ranging from late of the first decade to the fourth decade.
-Progressive weakness of pelvic and shoulder girdle musculature , Gower's sign positive.
- Respiratory insufficiency from weakness of the diaphragm, and cardiomyopathy may occurs also.
- Serum CK level less elevated than in the Duchenne's muscle dystrophy
- EMG shows myopathic pattern.Facioscapulohumeral (FSH ) Muscular Dystrophy
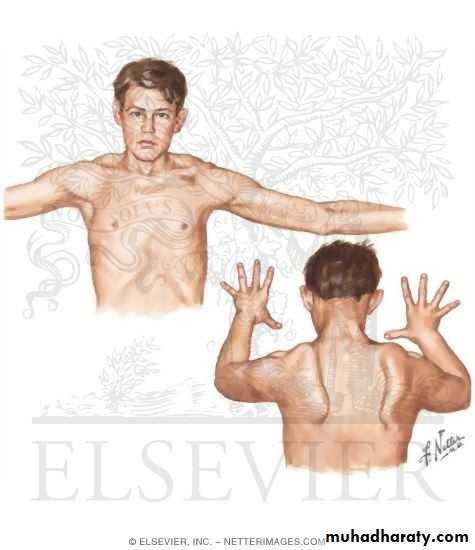
-Autosomal dominant-The onset in the childhood or young adulthood.
-Facial weakness appear as an inability to smile, whistle or fully close the eyes.
-Weakness of shoulder girdles which is usually brings the patient to medical attention.
• loss of scapular stabilizer muscles make arm
elevation difficult and scapular winging
become apparent with attempts to abduction
and forward movement of the arms.
• Biceps and triceps muscles severely affected
with relative sparing of the deltoid muscle .
- 20 % of patient the weakness progresses to involve the pelvic girdle muscles
-Serum CK level may be normal or mildly elevated- EMG indicates myopathic pattern
•TreatmentNo specific treatment is available
Ocular Dystrophy
-Typically autosomal dominant, Autosomal recessive and sporadic cases also occur- Onset before the age of 30years
- Ptosis is the earliest manifestation
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia
- Facial muscle weakness also common
- Subclinical involvement of limb muscle may occur
Oculopharyngeal Dystrophy
- Autosomal dominant .
- The onset in the third to fifth decade .
- Ptosis, total external ophthalmoplegia.
- Dysphagia , facial weakness and often proximal muscle weakness .
- Serum CK is mildly elevated .
- Dysphagia may require nasogastric tube or by gastrostomy for feeding .
Distal Myopathy
- Autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or sporadic .- Onset after age of 40years .
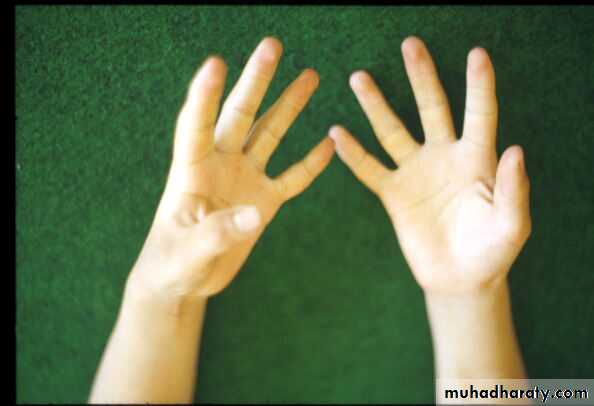
- Small muscles of hand and feet , wrist extensor and dorsiflexor of feet are affected .
Emery – Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy
-X- linked recessive , mutation in emerin gene .- Onset from childhood to late adolescence or adulthood.
-Weakness affect first the upper arm and pectoral girdle muscles later pelvic girdle and distal muscles in lower extremities.
-The distinguishing feature is the early appearance of contractures in the flexors of elbow ,extensor of the neck ,and calf muscles . Facial muscles are affected occasionally
- Severe cardiomyopathy with variable sinoaterial and aterioventricular conduction defects .
Myotonia
Abnormality of muscle fiber membrane leading to marked delay of relaxation after contraction causing apparent muscle stiffness .
▪On examination
-Difficulty in relaxing the hand after sustained grip .
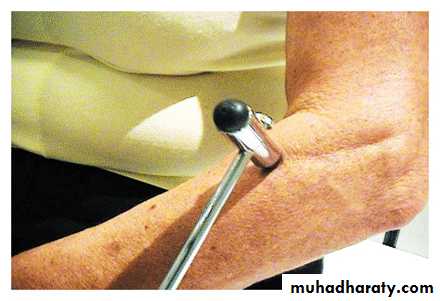
- Persistent contraction after percussion of the belly of the muscle .
- EMG show characteristic high-frequency discharge of potential that wax and wane in amplitude and frequency .Myotonic Dystrophy
-Autosomal dominant .-The onset in the third or fourth decade and may appear in early childhood .
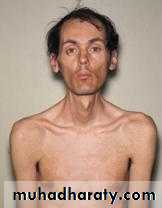
-Hatchet-face appearance due to facial muscle atrophy and weakness .
-Frontal baldness .
-sternocliedomastoids and distal limb muscle are involved early .
- Weakness of wrist extensors .
- Finger extensor and intrinsic hand muscle impair function .
-Ankle dorsiflexor weakness may cause foot
drop
- Palatal, pharyngeal and tongue involvement produce dysartheric speech and swallowing problems .
- Cataract, Diabetes mellitus, testicular atrophy, cardiac and intellectual defect .
Treatment
Is treatment of myotonia by Quinine sulphate 300mg-400mg tds or procainamide 0.5-1g/qd or phenytoin 100mg tdsMyotonia congenita
1-Autosomal dominant ((thomsen's disease)) mutation in chromosome 7 .-Generalized myotonia , the symptoms may not appear until early childhood
-Muscle stiffness enhanced by cold and inactivity, relieved by exercise .
-Muscle hypertrophy sometime pronounced
2-Autosomal recessive form
Later onset, slight weakness, and atrophy of distal muscle .Treatment
Is treatment of myotonia .
Metabolic Myopathy
Osteomalacia: characterized by proximal muscle weakness with bone pain and tenderness mild decrease in serum ca++ and increased ALK phosphatase .Treatment with vit D
Acute or chronic hypo or hyperkalemia leading to proximal muscle weakness reversed by correcting the metabolic disturbances .
Periodic Paralysis Syndromes
May be familial, autosomal dominant .-Episodes of flaccid weakness or paralysis .
-The power is normal between the attacks .
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis
- Occurs at adolescence
- Men are affected more than women because of decrease penetrance in women
-It may associated with thyrotoxicosis
-The attacks provoked by meals high in carbohydrate or sodium or after prolong exercise
-Weakness usually affect proximal limbs muscles more than distal muscles
-Ocular and bulbar muscles are less likely to be affected
-Respiratory muscles are usually spared but when involved may be fatal
-Life threatening cardiac arrhythmias related to hypokalemia may occur during the attack .
-The weakness may take as long as 24 hours to resolve.Diagnosis of Hypo KPP
-A low serum potassium level during an attack with excluding secondary causes establish the diagnosis .
-Interattacks muscle biopsies show the presence of single or multiple centrally placed vacuoles or tubular aggregates .
-EMG shows electrical silence in severely weak muscle .
Treatment of Hypo KPP
-The acute paralysis improve by oral KCL (0.2-0.4mmol/kg) should be given every 30min .
-Only rarely is IV therapy necessary (e.g. swallowing problem or vomiting) .
And mannitol is preferred vehical for administration of IV potassium .
Prophylaxis-low carbohydrate, low-sodium diet and avoid intense exercise .
-Acetazolamide (125-1000mg/day) in divided doses by beneficial effect of metabolic acidosis.
-If weakness persist oral KCL should be added .
-Spironolactone (25-100mg/day) may be used.
-Thyrotoxicosis if present should be treated also.
Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis (Hyper KPP)
-The attacks of weakness are precipitated by potassium administration is the best definition of the disease ((the patients are often normokalemic during attacks )) .-The onset is in the first decade .
-The attacks brief and mild lasting 30min to 4 hours .
-Some times associated with myotonia without weakness but the muscle stiff, painful aggravated by cold .
Diagnosis of Hyper KPP
-Serum potassium may be slightly elevated but may be normal during the attack.
-Muscle biopsy shows vacuole that are smaller, less numerous and more peripheral than in the Hypo KPP .
Treatment of Hyper KPP
Treatment of acute attack by calcium Gluconat IV, diuretics ((furosemide 20-40mg)) or Glucose IV fluid .Prevention
Acetazolamide or chlorothiazide.
mexiletine may be helpful in patient with significant myotonia .
Normokalemic Periodic Paralysis
Affected patients are sensitive to K ingestion and have episodes of mild weakness that occur without any change in serum K .Treatment of normo KPP
Treatment with large dose of Na alleviate the weakness .
Inflammatory myopathy
Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis
Characterized by distruction of muscle fibers and inflammatory cells infiltration of the muscles .
- occur at any age .
- low grade fever, muscle pain, tenderness and wasting affect proximal limb and girdle muscles .
- Arthralgia , malaise , weight loss , dysphagia, respiratory difficulties .
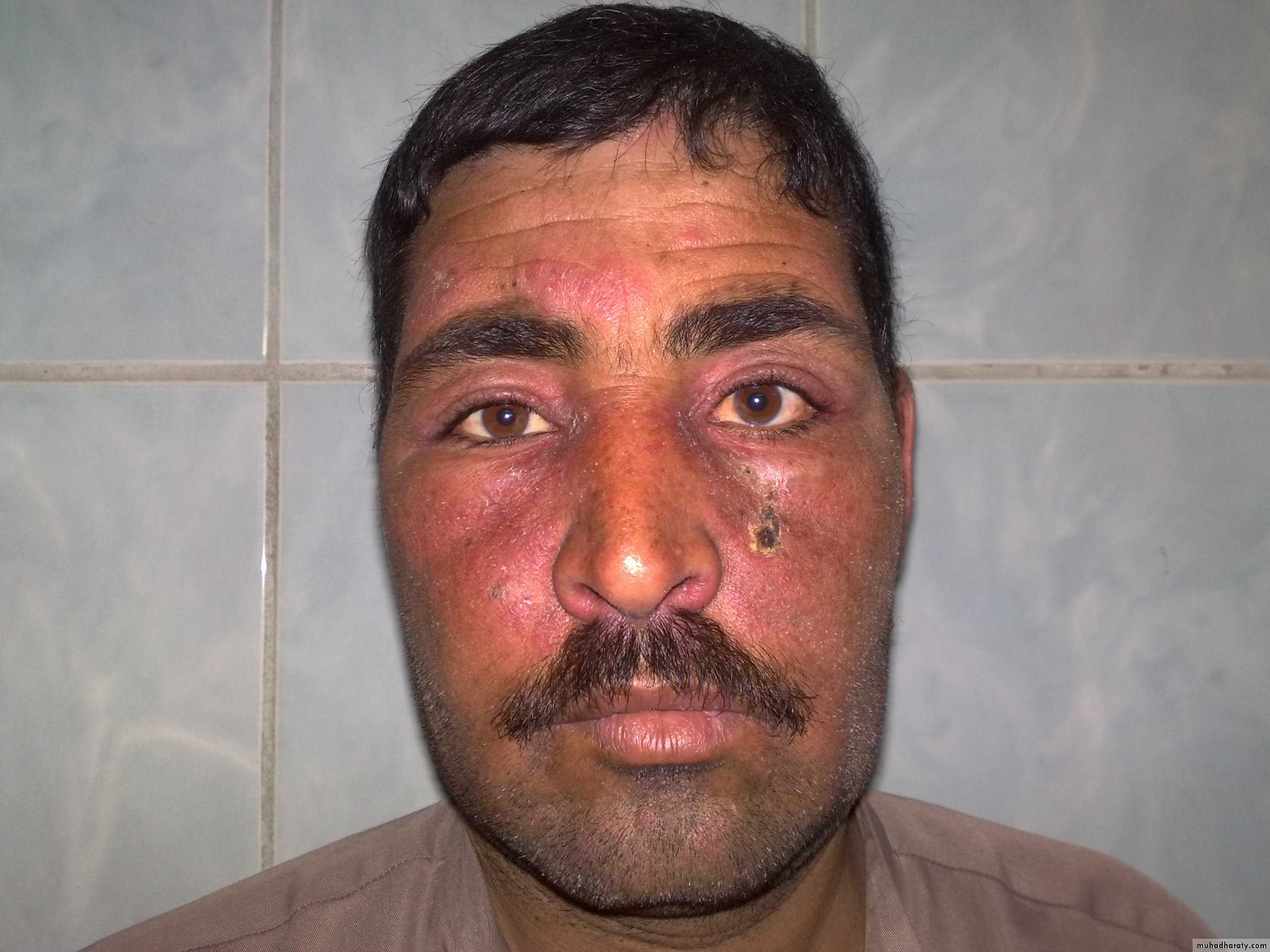
- Raynaud phenomena may occur .- In dermatomyositis there is erythematous rash around the eyes and eyelids ((heliotrop rash))
-May be associated with autoimmune diseases e.g. scleroderma, SLE and Rh artheritis .
- In adult it may associated with cancer .
-Serum CK level elevated, if normal dont exclude the diagnosis .
-EMG shows myopathic pattern .
Treatment
With steroid prednisolone 60-80mg/day and when improvement occur and CK decreased the dose of prednisolone decrease to 10-20mg/day for 2-3years; azathioprine or methotrexate used in steroid resistant patient.Polymyalgia Rhumatica
-More in women above 50years .
-Muscles pain and stiffness about the neck and girdle muscles .
-Headache, Anorexia, weight loss and low grade fever .
-Serious complication may occur such as Giant cell arteritis .
-Raised ESR .
-Enzyme, EMG and muscle biopsy are normal .
Treatment
Prednisolone 10-15mg/d for one year .Endocrine myopathy
- hyper or hypothyroidism .
- Hyper or hypoparathyroidism .
- Hyper or hypoadrenalism .
- Hypopituitarism .
- Acromegaly .
Drug induced myopathy
- Steroid- Chloroquine
- Clofibrate
- B-Blockers
- Colchicine
- Zidovudine