
1
Forth stage
Obstetric
Lec-7
.د
ولدان
1/1/2016
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
Diagnosis of Pregnancy:
The diagnosis of pregnancy and its location, based on physical signs and examination alone,
may be quite challenging during the early weeks of amenorrhea. Urine pregnancy tests in
the office are reliable a few days after the first missed period, and office ultrasound is used
increasingly as a routine.
Early symptoms of pregnancy:
The most common symptoms in the early months of pregnancy are amenorrhea, urinary
frequency, breast engorgement, nausea, tiredness and easy fatigability.
1-Amenorrhoea:
If a healthy woman, whose menstrual period were previously regular, has a sudden
cessation of her periods the presumption must always be that she is pregnant unless some
other cause of the amenorrhea can be found.
Amenorrhea does not have the same significance in the case of a woman whose periods
were previously irregular, nor may it have any significance in a woman of menopausal age.
Pregnancy has been known to occur in a young girl before a menstrual period has been
observed, and it can arise during a period of amenorrhea, for example during lactation or
following discontinuation of oral contraception.
2-Breast symptoms:
In the early weeks of pregnancy some tenderness and fullness of the breast may be
noticed.
3-Frequency of micturition:
During the first 12 weeks, when the uterus is still a pelvic organ, there is often some
frequency of micturition, because the enlarging uterus press on the bladder lightly,
particularly when the woman is standing in the day time.

2
4-Abdominal enlargement :
Many women notice some abdominal fullness in early pregnancy at a time when the uterus
is not much enlarged. This can only the result of slight intestinal distension or a progesteronal
effect on the muscle of the anterior abdominal wall.
Later on the uterine enlargement become evident, and sometimes it is this that first brings
the woman to the doctor, especially in a case when the menstrual periods were previously
irregular.
5-Fetal movements :
A primigravida usually first feels fetal movements between the 18th and 20th weeks of
pregnancy, but multiparae may recognize the movements about 2 or 3 weeks earlier .
6-Nausea with or without vomiting:
which can strike at any time of the day or night, is one of the classic symptoms of pregnancy.
7-Fatigue:
High estrogen level, low glucose level, low blood pressure.
8-Faintness and dizziness :
As blood vessels dilate and blood pressure drops, pregnant feel light headache or dizzy. Early
in pregnancy, faintness may also be triggered by low blood sugar.
Signs of pregnancy:
a. Signs due to changes in the uterus:
1-Enlargement of the body of the uterus: It is the earliest alteration which can be detected
on clinical examination. Early uterine enlargement tend to be in the anteroposterior diameter
so that the uterus becomes globular.
2-Softening of the uterus and cervix:
Due to its increased vascularity is a useful sign to the experienced obstetrician.
3-Hegar's sign:
As uterine consistency becomes softer, it may be possible to palpate or to compress the
connection between the cervix and fundus (when the uterine is compressed between
examining fingers, the wall feels tissue paper thin).

3
The physician will use bimanual maneuver simultaneously (abdominal and vaginal) and will
cause the uterus to tilt forward. The Hegar's sign is noted by the sixth to eighth week of
pregnancy.
Although there many other causes for uterine enlargement they do not, as a rule cause
softening. Softening and blue discoloration of the cervix soon follow the softening of the
uterus and are usually complete by the 16th week. When they are marked they are reliable
signs of pregnancy, but in a few cases the cervix remain firm throughout pregnancy.
4-Progressive enlargement of the uterus:
By the 12th week the fundus of the uterus is usually palpable in the abdomen just above the
symphysis pubis and progressive enlargement of the uterus follows. The fundus reaches the
level of the umbilicus at about the 22nd week, and is just below the xiphisternum at the 36
week.
The level of the fundus may be higher than expected from the duration of the pregnancy in
cases of multiple pregnancy, polyhydromnios or fibroids, and at a lower level than expected
with a transverse lie, an abnormal, growth retarded or dead fetus.
If the fundus is at an unexpected level an error in the dates of course to be considered.
5-Painless contractions :
The pregnant uterus varies in consistency on palpation because it has intermittent painless
contractions, Braxton Hicks contractions. It usually begins about the 12th week of pregnancy
and becomes progressively stronger.
B.Signs due to the presence of the fetus:
1-Ballottement:
This is demonstrated during the bimanual exam at the 16th to 20th week. Ballottement is
when the lower uterine segment or the cervix is tapped by the examiner's finger and left
there, the fetus floats upward, then sinks back and a gentle tap is felt on the finger. This is
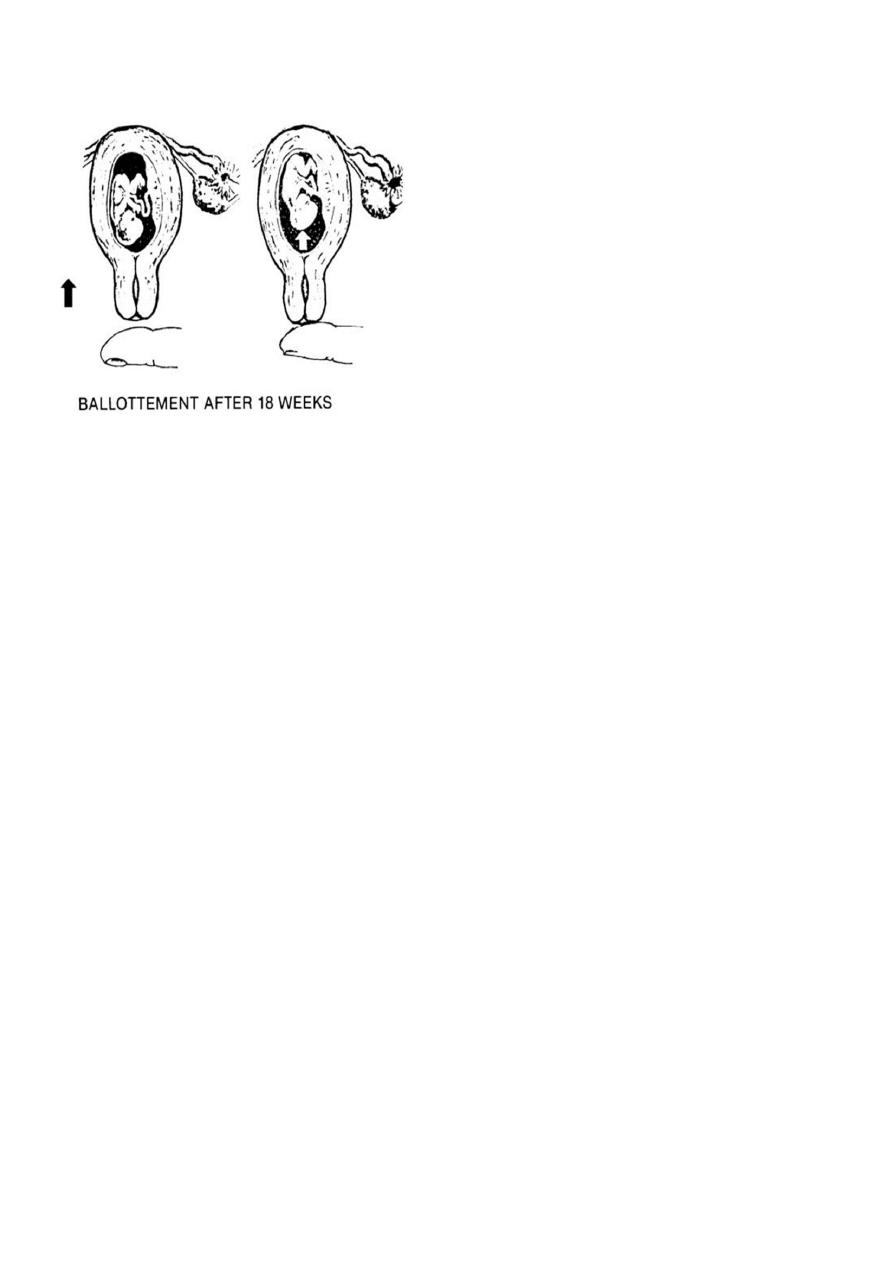
4
not considered diagnostic because it can be elicited in the presence of ascites or ovarian
cysts.
2-Fetal heart sounds :
On auscultation of the abdomen with a Sonicaid the fetal heart sounds may be heard after
the 12th week.
3-Palpation of the fetal parts:
Abdominal palpation of fetal parts is usually possible from the 24th week onwards, and at a
later stage the definite recognition of the head, back and limbs of the fetus is an absolute
sign of pregnancy.
4-Fetal movements :
During palpation fetal movements may be felt, and this is also an absolute sign. These
movements can often be seen as well.
5-Funic soufflé :
The Sonic aid happens to lie directly over the umbilical cord. It is a soft blowing murmur
synchronous with the fetal heart sounds.
C. Signs due to changes in the breasts and the skin:
-Breast changes :
1-Primary areola.
2-Secondary areola.

5
3-Montgomery tubercules.
4-Colostrums.
The primary areola persists after the first pregnancy and this sign is therefore useless in the
diagnosis of any subsequent pregnancy.
-Skin changes :
1-Chloasma.
2-linea nigra.
3-striae gravidarum.
Laboratory tests for pregnancy:
These depend on the detection of hCG levels in maternal plasma and its excretion in urine.
1-Urine pregnancy test: usually positive on day 35 from LMP
2-Serum pregnancy test: usually positive 7-10 days after conception.
Confirming the diagnosis of pregnancy :
1-Identification of a heart beat.
2-Ultrasonographic recognition of the fetus:
After 5 weeks amenorrhoea → transvaginal US gestational sac as small, fluid filled structure
surrounded by echogenic rim of tissue. The embryo appear within it at the 6th week.
3-Fetal heart activity → real time US show fetal heart after 6 weeks of gestation.
Pregnancy dating :
The estimated date of delivery (EDD) is a 9 calendar months and 7 days from the LMP.
Differential diagnosis of pregnancy :
1. Uterine fibroids:
2. Symmetrical enlargement of the uterus.
3. No amenorrhoea.
4. Negative PT.

6
Pregnancy associated with fibroid:
Small tumours can easily be mistaken for fetal parts. A fibroid in the uterine wall is immobile,
unlike a fetal limb which alter its position from time to time. When the uterus contracts fetal
parts become more difficult to feel, whereas a fibroid may become more evident.
Ovarian cyst:
1. Unenlarged uterus felt separately from the ovarian mass.
2. Ovarian neoplasm will not cause amenorrhoea except in the unlikely event of their
being bilateral and totally destroyed both ovaries.
3. Negative pregnancy test.
4. Ultrasound confirm the diagnosis.
Pregnancy associated with ovarian cyst:
Two swelling are usually evident, but in some cases they are in such close juxtaposition that
it is not easy to distinguish them. The combined swelling will then be larger than expected
for the duration of pregnancy. Ultrasound scan will reveal the fetus within the uterus with
the cyst as a separate cavity.
Distended bladder:
Pseudocyesis:
Is a psychological disorder in which the woman has a false but fixed idea that she is pregnant.
It is frequently, but not always, seen near or after the menopause, and not invariably in
woman without children.
There may be amenorrhoea, and the woman may declare that she has morning sickness and
breast enlargement, and that she can feel fetal movements. The abdomen may appear
distended, either by air collected in the stomach by aerophagy, by intestinal distension, by
persistent contraction of the diaphragm or exaggerated lumber lordosis or sometimes just
by fat.
The shape of the swelling is not that of the pregnant uterus, fetal parts cannot be felt and
the fetal heart cannot be heard. A pregnancy test or ultrasound scan will be required but the
difficulty is to convince the woman that she is not pregnant.
