
1
Forth stage
Obstetric
Lec-3
.د
هبة
1/1/6112
Prenatal diagnosis
Prenatal diagnosis:
Prenatal diagnosis is the identification of a disease prior to birth.
The early prenatal diagnosis and detection of congenital abnormality allows both parent
and medical cares to plan the management for the pregnancy as:
Reassurance of the parent
Termination of pregnancy when the anomaly is incompatible with life .
The time ,mode and place of delivery prepared to ensure good prognosis of the
neonate .
Offer in utero treatment.
• Congenital anomaly refer to fetal alformation or disorders conferred by birth (born
with )
• Incidence 2-3 per 100 pregnancies
• The prenatal detection of the congenital abnormality is one of the aims of the routine
antenatal care
Classification of common congenital abnormalities
Structural abnormalities
congenital heart disease
• Neural tube defects
• Cleft lipand palate
• Clubbed foot
Chromosomal abnormalities
• trisomy 21(Downs syndrome) ,trisomy 13 and 18
2
• Monosomy X(Turners syndrone )
Genetic
• Cystic fibrosis
• Sickle cell anaemia
• Thalassemia
Miscellaneous
• viral infection
Test for fetal anomaly
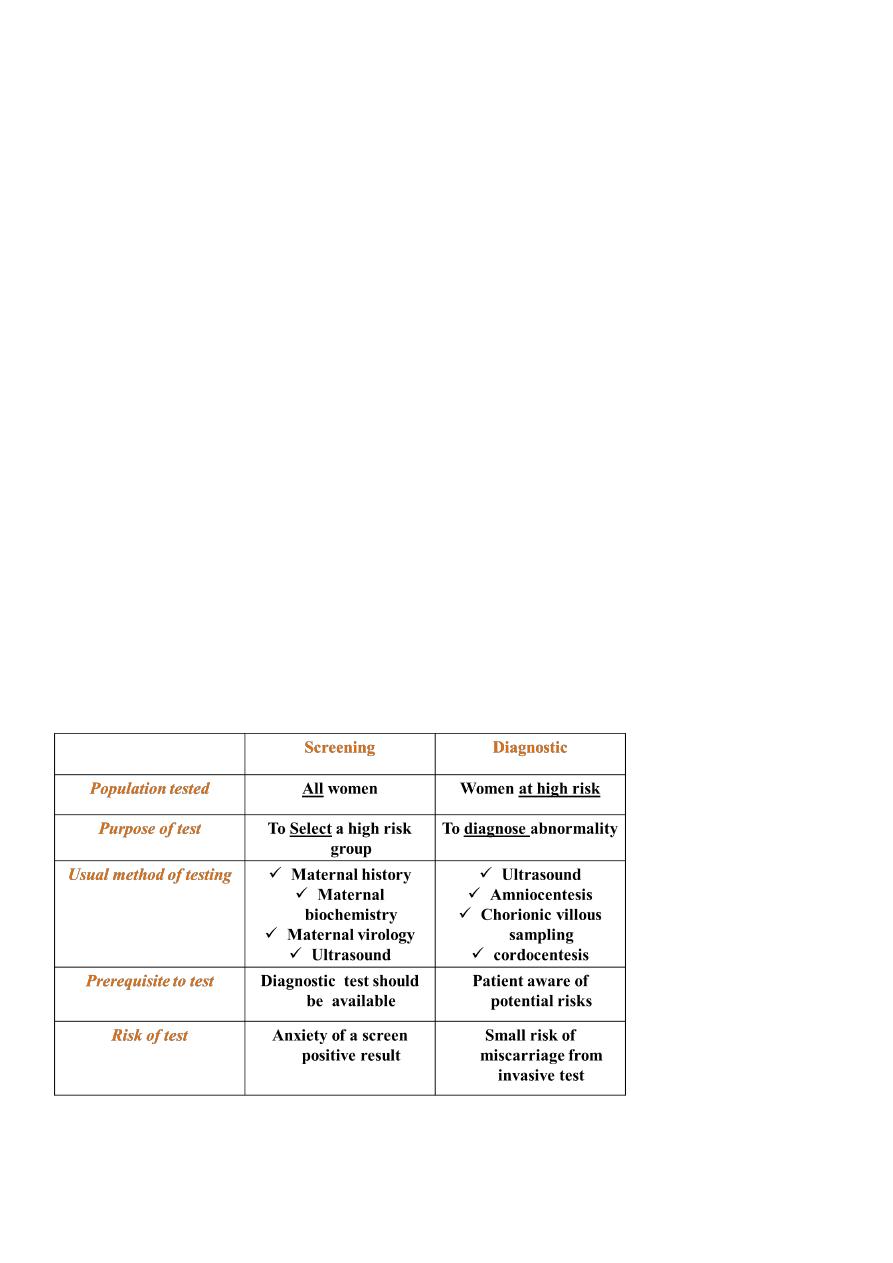
Screening is performed in all women in order to identify women who are at
high risk of a disorder.
They do not confer any risk to the pregnancy and are performed for disorders which there
are accurate prenatal diagnostic tests.
Diagnostic tests are carried out on pregnancies that have been identified as high
risk by a prior screening test. It is usually invasive with risk of miscarriage .
Difference between prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
3
Prenatal diagnostic tests can be divided into:
1-non-invasive tests ultrasound scanning
maternal blood sampling
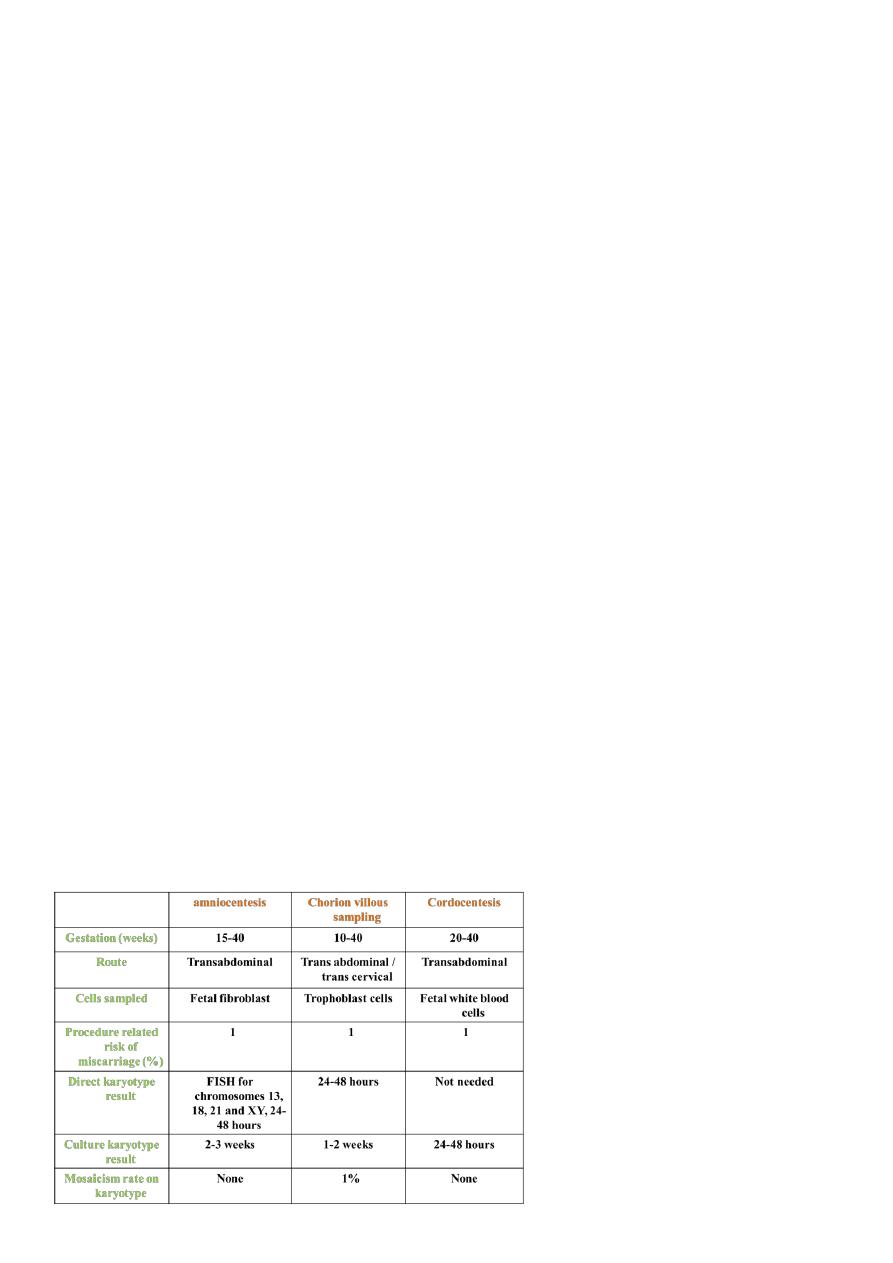
2- invasive tests Amniocentesis
chronic villus sampling
and placental biopsy
Fetal blood sampling
Fetoscopy
1-Non invasive prenatal diagnosis
Ultrasound scan
• At boking (11-14 weeks)
• Anomaly scan at 18-22 weeks
Maternal serum tests
• Free fetal DNA can be extracted from maternal blood to determine fetal
blood group in cases of alloimmunization , or to determine the sex of the fetus in
X- linked disorders.
Other studies
3 dimensional ultrasound scan and fetal MRI this permit the increased resolution required
for certain fetal malformation like cleft lip and palate.
2- Invasive prenatal diagnostic tests

4
Structural anomaly
(Neural tube defects)
Are most common major abnormalities . It occurs due to defect in formation of
neurl tube defects during embryogebrsis.
The aetiology is multi - factorial ( envirumental , genetic , pharmacological and
geographical factors implicated.
Anencephaly ( lethal ) , encephalocele ( prognosis related to size of defects )
Spina bifida usually affect spinal cord at the caudal level. The local effects (paralysis
of legs, urinary and fecal incontinence ) depend on spinal levels and the number of
spinal segments affected in the lesion.
When a parent or previous sibling has had an NTD, the risk of recurrence is 5-10%.
Screening test
• Ultrasound
1- in first trimester can diagnose anencephaly , encephalocele.
2- At 20 weeks anomaly scan for spina bifda and hydrocephalous.
• Mid trimester maternal serum alpha - fetoprotein ( AFP ) levels are increased in
pregnancies affected by open NTDs.
Diagnostic test
• In the past, in case of screen positive women, they referred for amniocentesis to
detect the presence of acetylcholinestrase in the amniotic fluid.
Prevention of neural tube defects:
• Periconceptional folate supplementation to the mother reduce risk
• folic acid should be given for at least 3 months prior to conceptionand for the
first trimester of pregnancy.
• The dosage is 400 mcg for primary prevention and 4 mg for
prevention of NTD in :
1. Women with previously affected baby with NTD
2. with type 1 diabetes mellitus
3. in mother use antiepileptic drugs

5
4. multiple pregnancy
5. mother with hemoglobinopathies .
Structural anomaly
(Congenital heart disease) CHD
• Anomalies of the heart and majors arteries are common heterogeneous
• They range from asymptomatic to the lethal one or that required surgery
• Risk factor:
1) When a previous sibling or father is affected by CHD
2) Offspring of women with type 1 diabetes.
3) Drugs like lithium
4) Viral infection like rubella
5) Chromosomal abnormality
• Can be detected by ultrasound at 20 weeks
Chromosomal abnormalities
(Downs syndrome)
Down's syndrome (trisomy 21 ) it is an abnormal female gametogenesis either due to:
• Non dysjunction in meiosis (90 %)
• Un balanced translocation (6 %)
• Mosaism (4%)
Screening
1. Maternal age and history
Increase risk with advanced maternal age. Age over 35 years old 1:750 , previous history
of Down's 1:100 these should offer prenatal diagnosis.
2. Maternal serum biochemistry
This iclude first trimester test of maternal serum HCG , estriol , inhibin ,PAPP-A , together
with second trimester alpha feto protien (all are reduce except HCG)
3-Ultrasound for nuchal translucency
6
Measurement of subcutaneous collection of fluid in nuchal (behind neck) region of fetus at
10-13 weeks gestation, it increase in affected fetus
Diagnostic test
Women with positive screening test are offered invasive tests
(Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling ) .
Genetics disorders (hemoglobinopathies )
Sickle cell anaemia and thalassaaemia are both autosomal recessive with a risk of 25%
affection of the offsbling
Screening of at high risk populations (african in sickle cell anaemia and Mediterranian
in thalassaemia) is by maternal serum electrophoresis
Prenatal diagnosis by any invasive test (amniocentesis , CVS ,cordocentesis ) to
take fetal cell for DNA study .
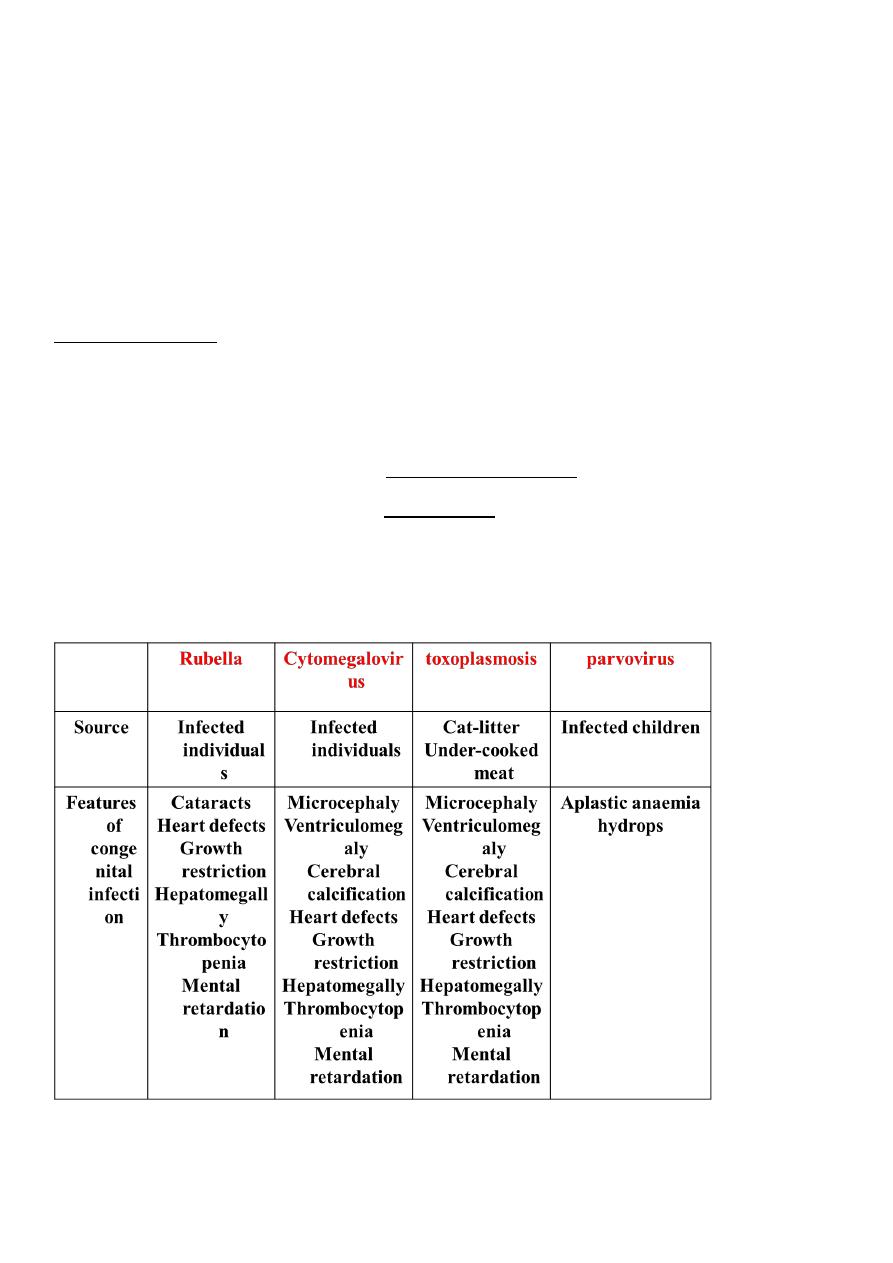
Congenital infections
