1
Fourth stage
Obstetrics
Lec-
Dr.Ahmed Jasim
25/11/2015
Gestational trophoblastic disease
(GTD)
Is term applied for a group of pregnancy-related disorders arising from abnormal placental
trophoblast cells.
The main categories of GTD are:
A. The pre-malignant conditions:
Hydatidiform mole (benign):
Complete hydatidiform mole
Partial hydatidiform mole.
B.Malignant gestational trophoblastic neoplasias (Gestational trophoblastic tumour
(GTT))(malignant disorders):
invasive mole
choriocarcinoma
placental site trophoblastic tumour. very rare
2
all forms of GTD produce β -human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hCG ).The amount of β-hCG
correlates with disease volume and so monitoring this hormone is an accurate biomarker
for screening, diagnosis, therapeutic response and follow up of women with GTD.
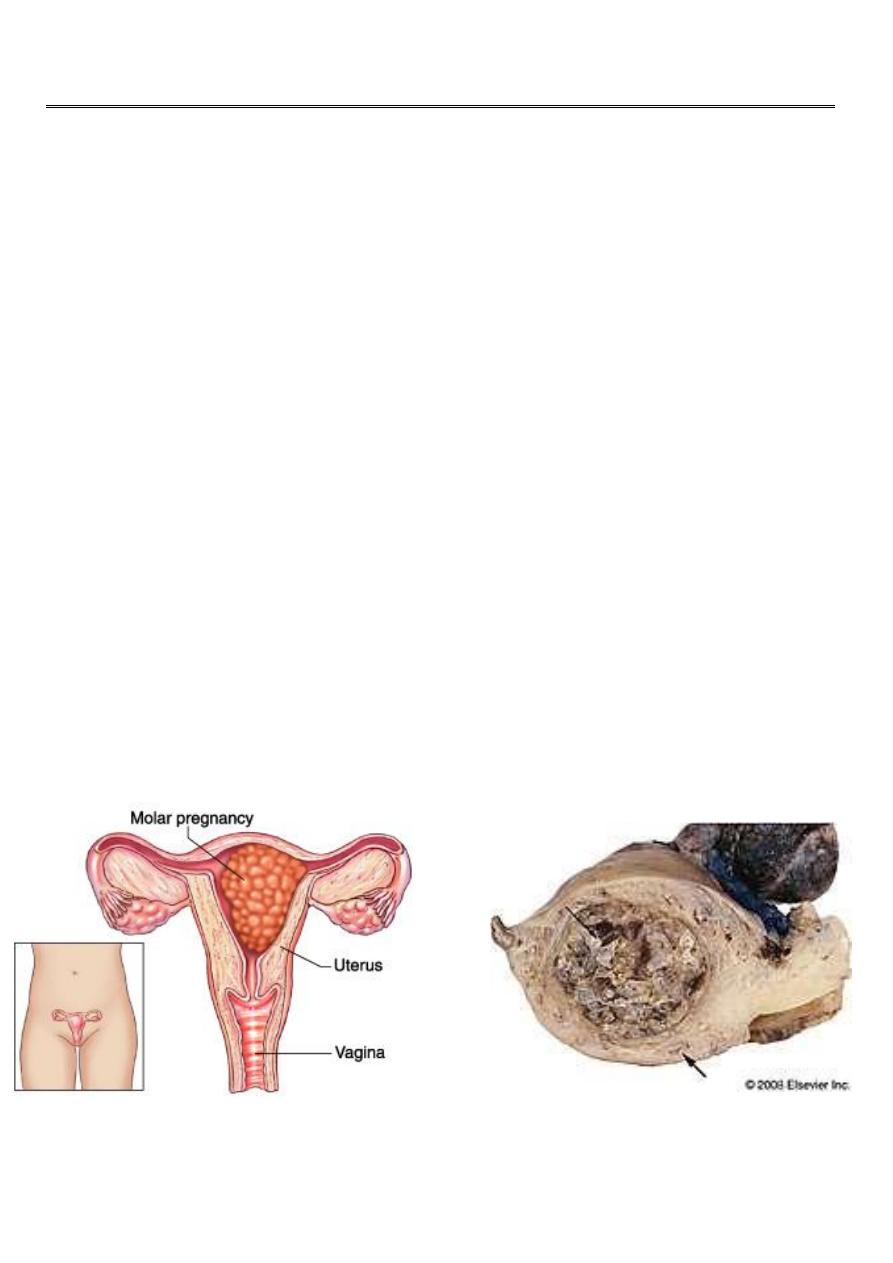
Hydatidiform mole
The name Hydatiform stems from the Greek word hydatis, meaning droplet of water.
Are abnormal conception events, which produce rapidly growing, highly vascular,
placenta-like structures. It is a Benign tumour of trophoblast and the commonest form
of GTD.
Rarely, a molar pregnancy may develop as a twin to a normal embryo.
16% of complete hydatidiform mole and 0.5% of partial hydatidiform mole undergo
malignant transformation
Incidence:
Complete mole 1 / 1000 pregnancy.
Partial mole 3 / 1000 pregnancy.
Risk factors:
1. maternal age (≤15 and ≥40 years old).
2. previous history of molar pregnancies (0.5-2% risk of recurrence)
3. ethinic variation and increased rates in Asian women.
4. familial syndrome of recurrent complete hydatidiform mole (inherited in autosomal
recessive pattern) but it is extremely rare.
3
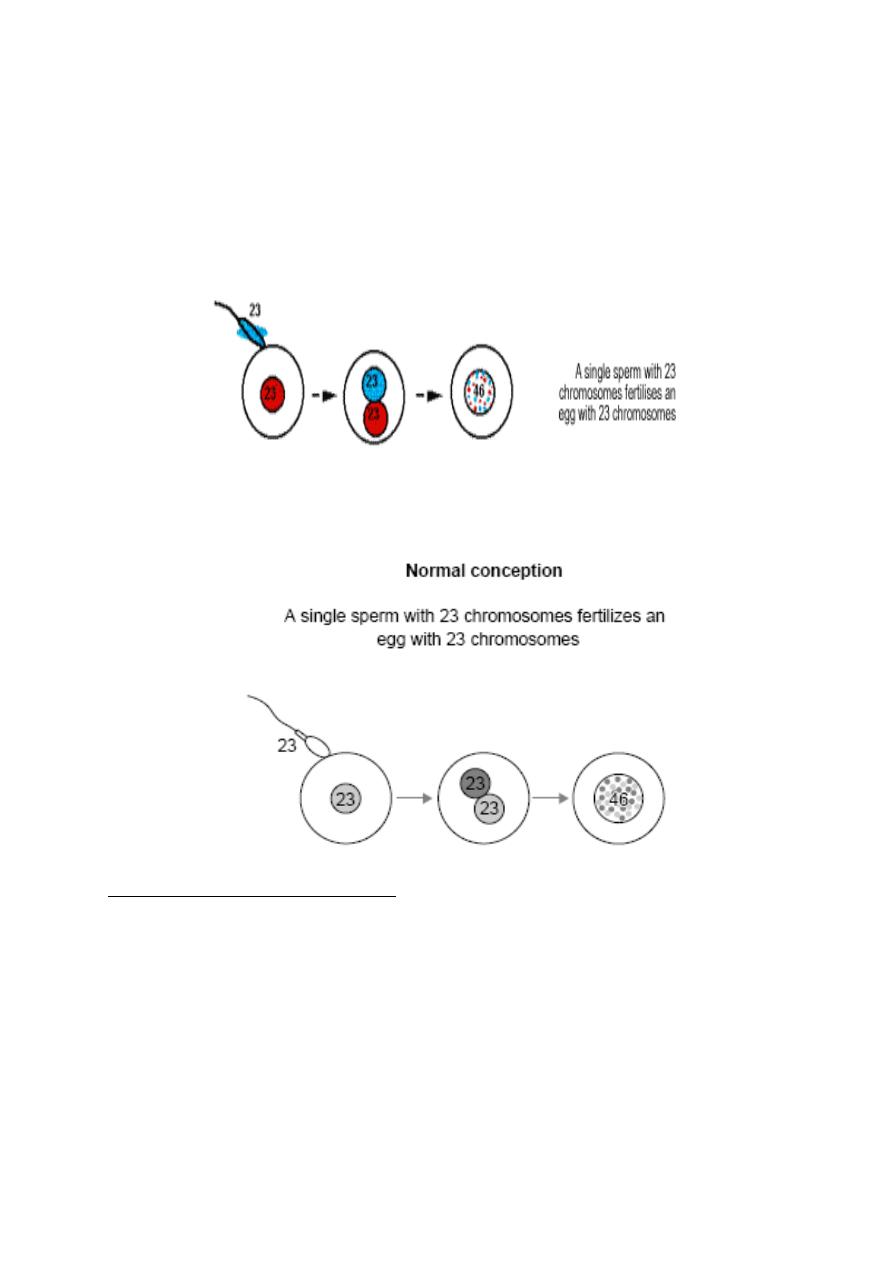
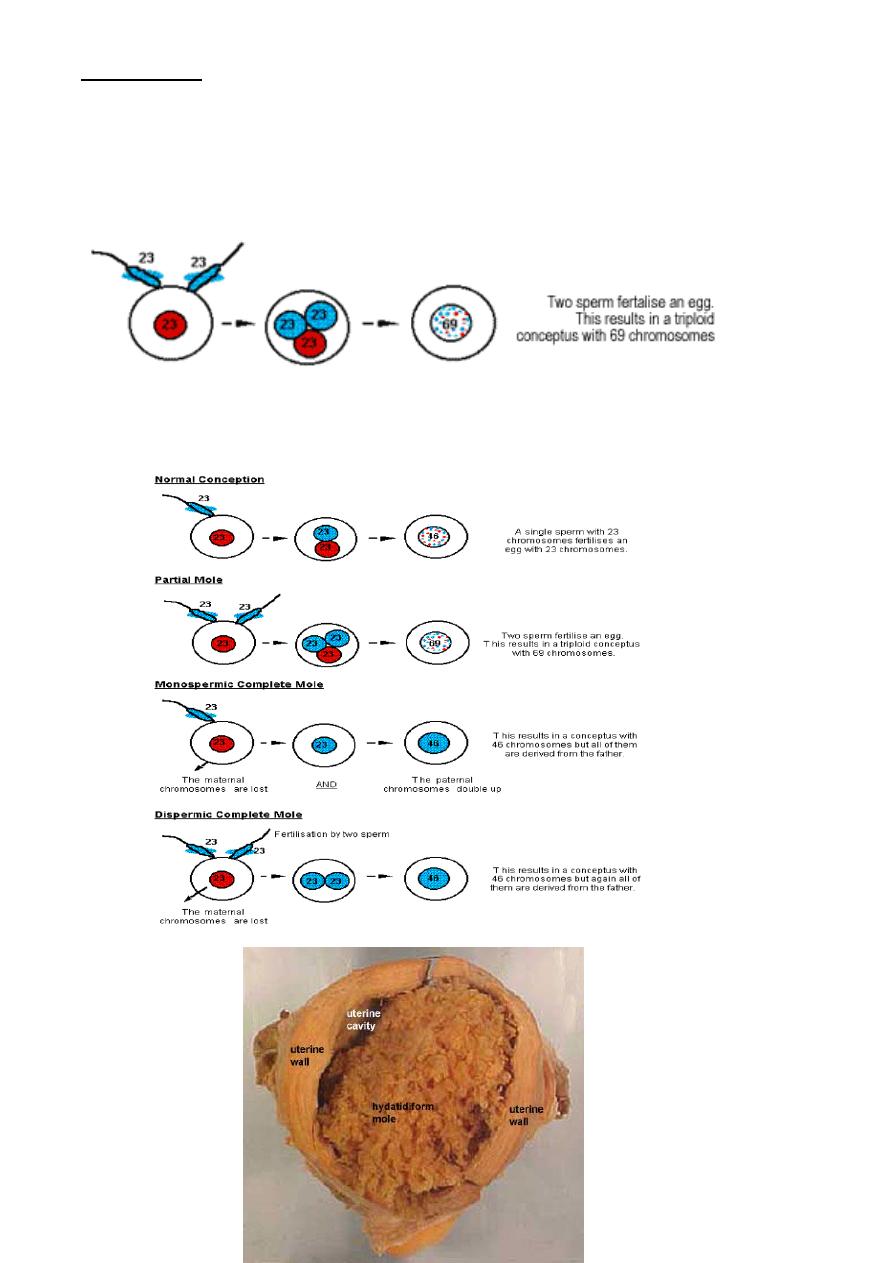
Pathophysiology (cytogenitics)
In normal fertilization single sperm with 23 chromosome fertilize an ovum with 23
chromosome.
Hydatidiform mole occurs because of an abnormal fertilization process.
Normal fertilization
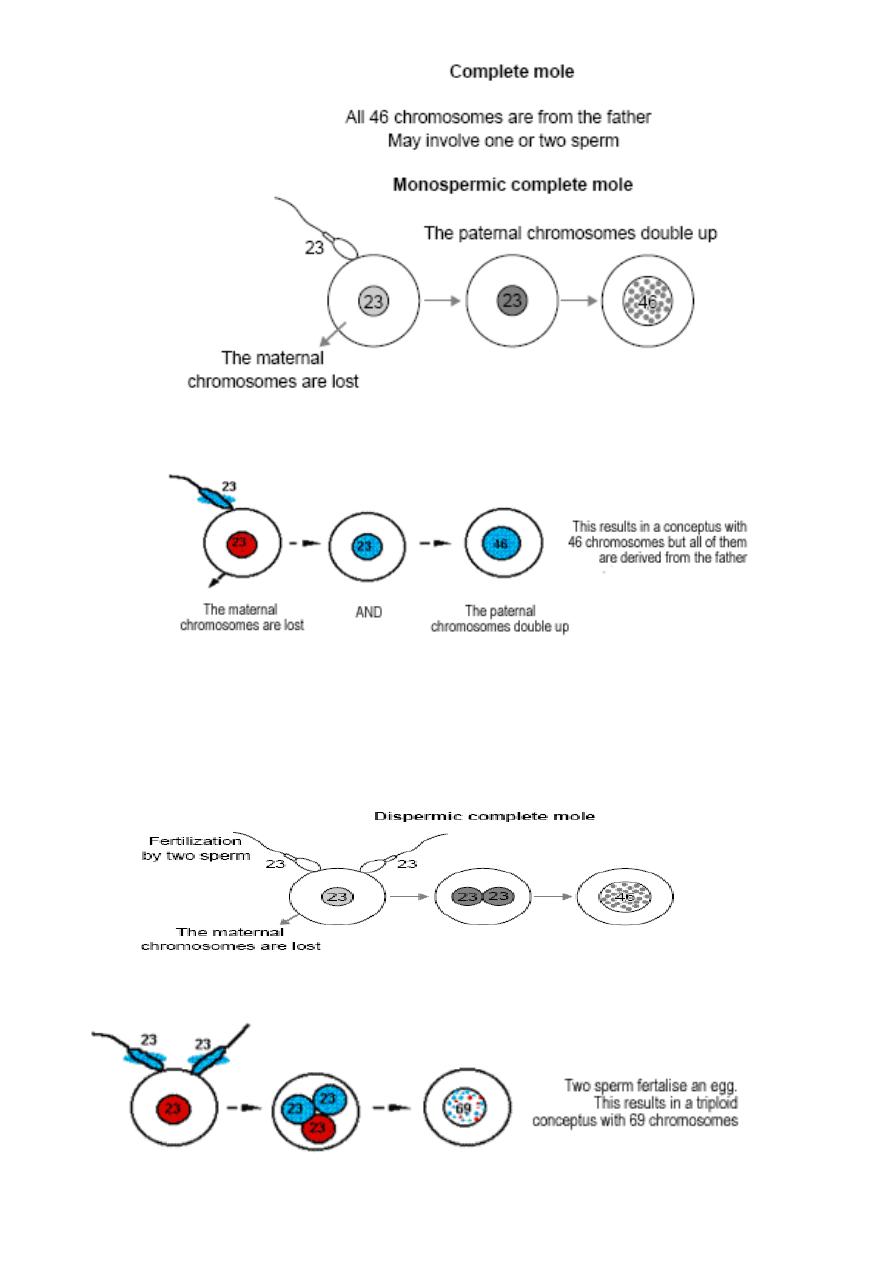
Complete hydatidiform mole
Are androgenic in origin and have diploid chromosomal constitution totally derived from
paternal (male) genome results from the fertilization of an ‘empty’ oocyte it is usually
resulting from:
the single haploid sperm duplicating it's own chromosome after meiosis leading to
homozygous 46XX karyotype. In majority of cases.
4
less frequently , two haploid sperm fertilize an empty ovum leading to heterozygous
46XX OR 46XY.
5
Partial mole
Are genetically biparental ,Usually with a triploid karyotype and arise due to two sperm
fertilize an ovum or reduplication of paternal sperm haploid set and having 2 set of
chromosome from paternal origin and one from maternal origin 69XXX, 69XXY, 69XYY.
6
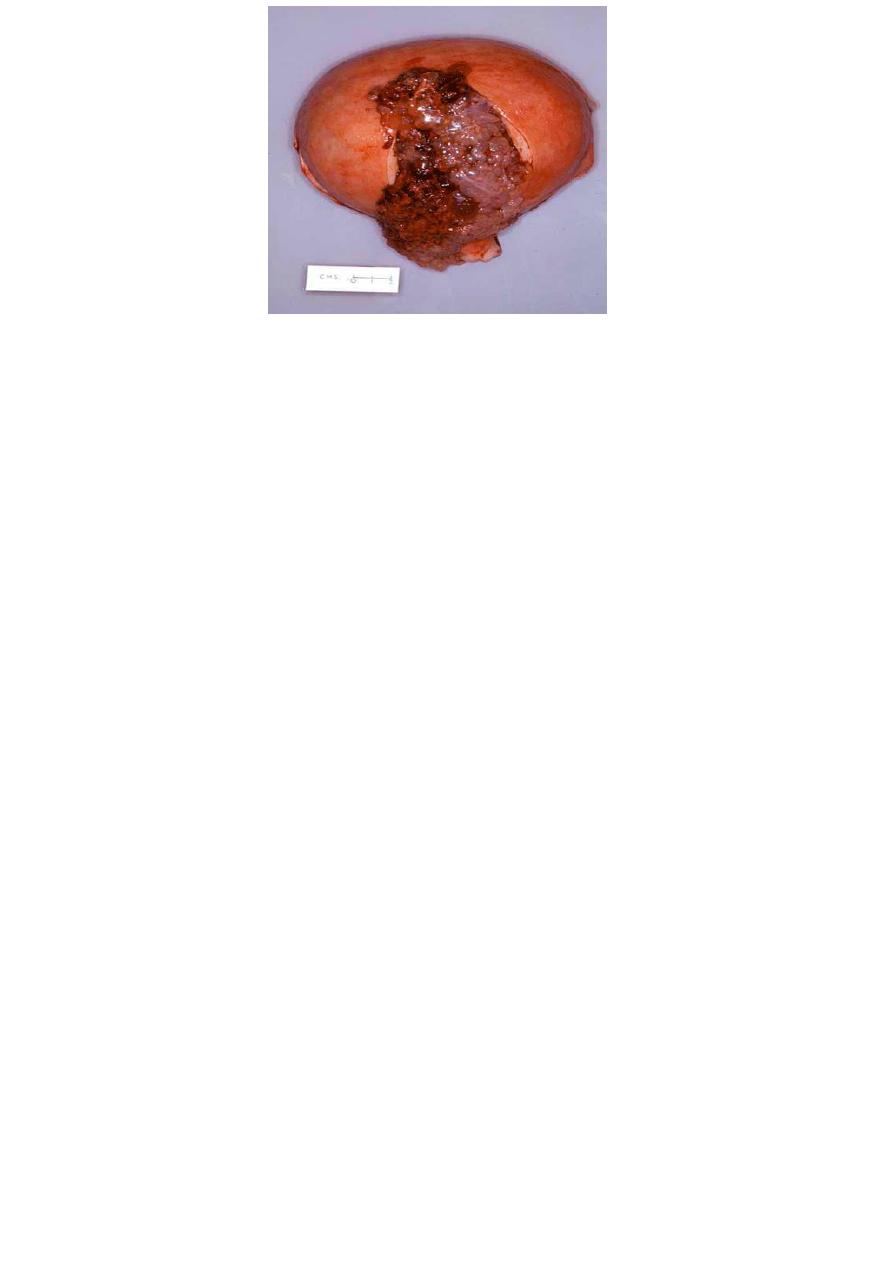
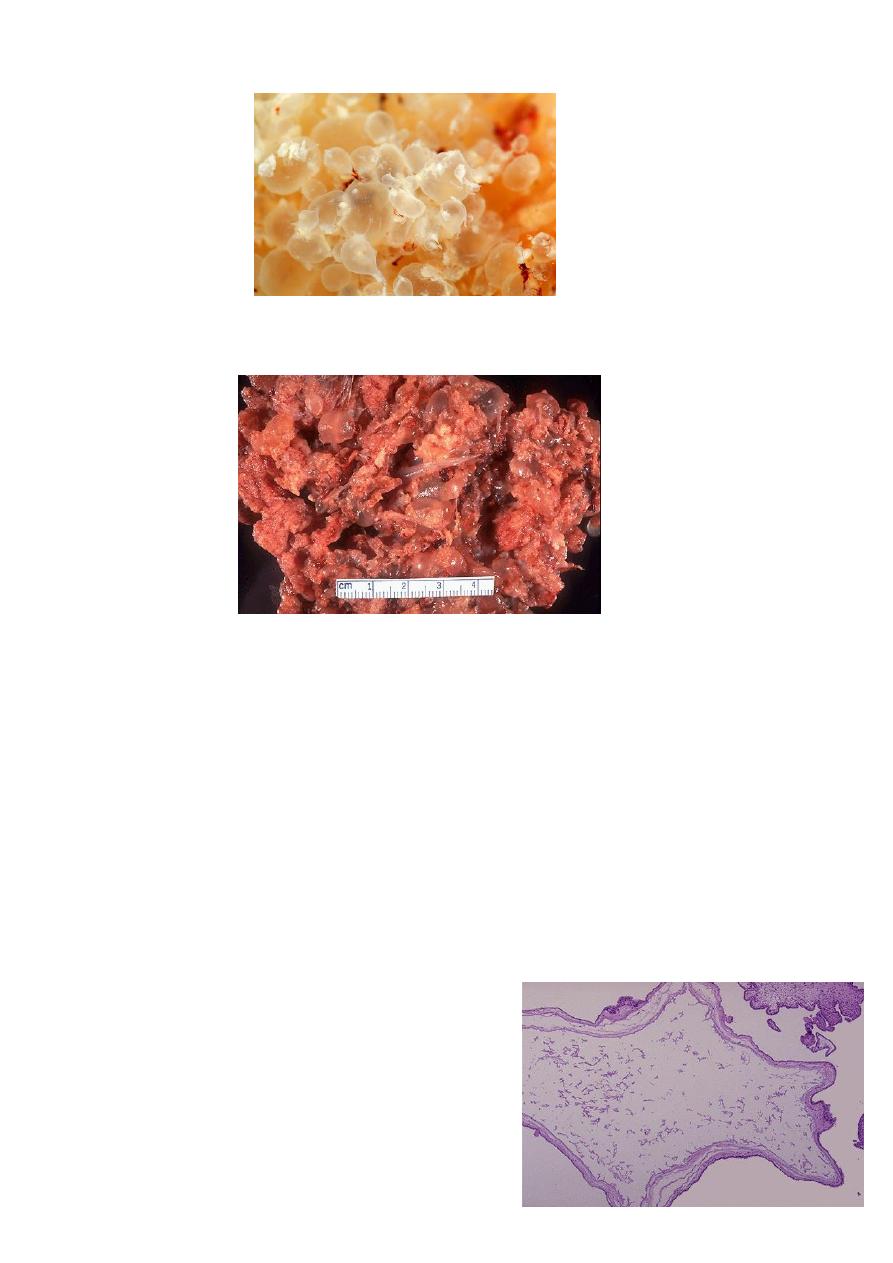
Hydatidiutiform mole appears as multiple vesicles as bunch of grapes in complete mole
In partial mole less clear cut clear picture, vesicles and fetus and placenta.
Microscopical:
complete mole
1. Generalized swelling of villous tissue
2. Diffuse trophoblastic hyperplasia
3. No embryonic or fetal tissue
4. Absence of fetal blood vessel
The avascular villi of molar pregnancy are quite large
however these most be distinguished form simple
hydropic degeneration seen in placenta of fetus
undergoing intrauterine demise
7
Partial mole
1. Focal swelling of villous tissue
2. focal trophoblastic hyperplasia
3. there is embryonic or fetal tissue
4. Fetal vessels seen
In partial moles, some villi (as seen here at the
lower left) appear normal, whereas others are
swollen. There is minimal trophoblastic
proliferation.
Clinical features
1.Typical clinical feature in complete mole:
amenorrhoea.
Vaginal bleeding is most common sign of variable amount mostly in early pregnancy
around 12-14 weeks.
Usually painless but sometimes associated with pain due to uterine contractions.
Symptome of pregnancy in exaggerated form.
2. symptoms of complications of hydatidiform mole:
pre-eclampsia early onset before 20th weeks
hyperemesis gravidarum.
Anaemia.
hyperthyroidism.
complication of theca lutein cyst of ovary (rupture, torsion).molar pregnancy
produces excessive hCG , which stimulates excessive growth of ovaries.
pelvic infection.
perforated uterus.

8
disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC).
embolization and respiratory symptoms.
3. spontaneous expulsion of vesicles from vagina around 16 weeks.(if undiagnosed before).
4. discovered accidentally by ultrasound at booking which make the gestational age at
evacuation of hydatidiform mole is about 9-10 weeks.
Examinations:
General condition and vital sign can be : Normal or reflect preeclampsia or
hyperthyroidism or bleeding or anaemia and pallor
Chest examination: finding if respiratory embolization.
Abdominal examination:
Uterus is often large for date and feel very soft and doughy in consistency.
No fetal part or fetal heart can be detected.
Ovarian enlargement occurs in 1/3 of cases and difficult to palpated until uterus
evacuated
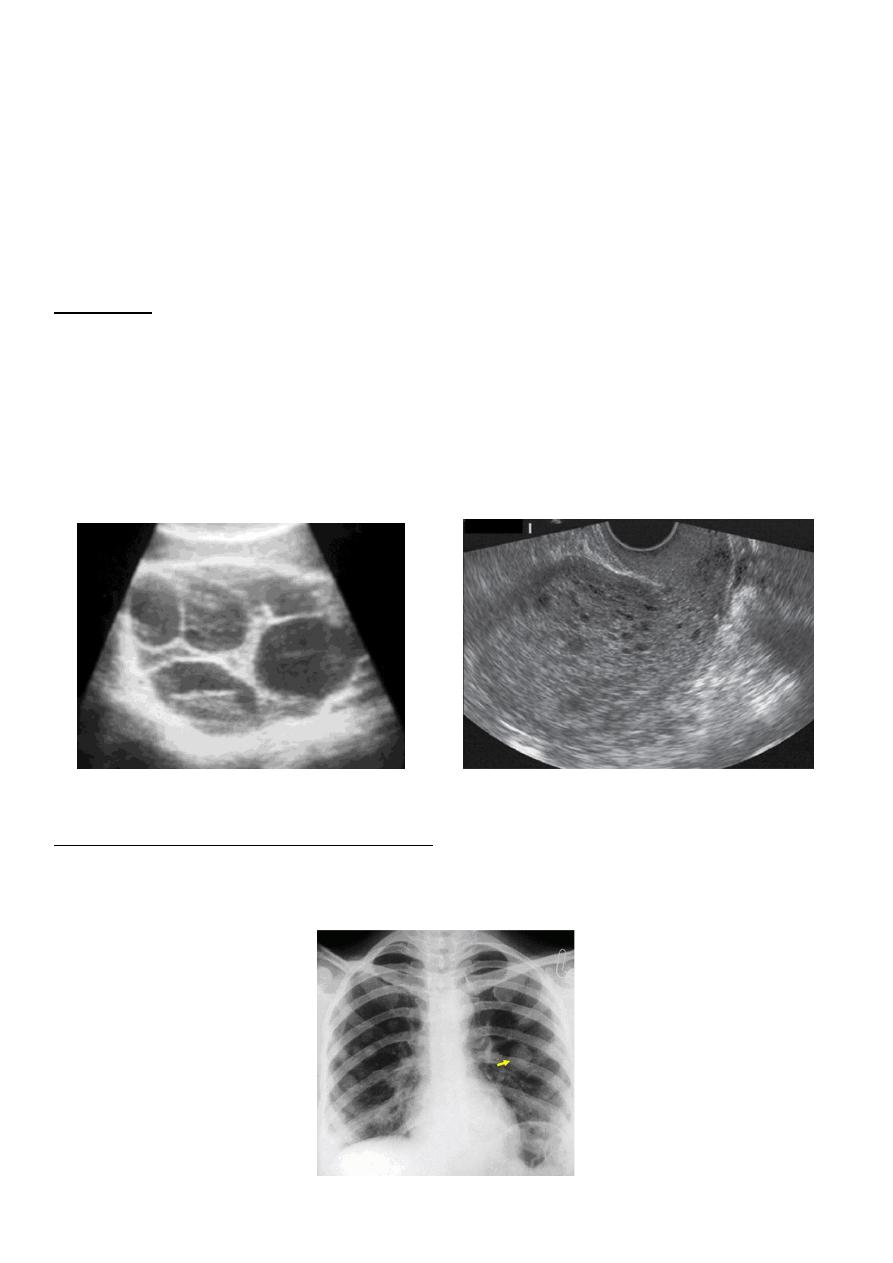
This is only a second trimester pregnancy, but note how large for dates the uterus is
because of a molar pregnancy. An ultrasound in this case revealed no fetus, only a
"snowstorm" effect .
9
Pelvic examination
Sometimes grape like vesicles of mole may be detected which is confirmation to
diagnosis if spontaneous expulsion occurs only.
Investigations:
Clinical finding of amenorrhoea and vaginal bleeding with larger than expected size uterus
arouse suspicion for molar pregnancy
ultrasound:
which confirm diagnosis of mole as show snowstorm appearance (uterine cavity
filled with multiple sonolucent area of varying size and shape).
absence of fetus.
Theca Lutein cyst of ovary.
β-human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hCG ) :
It is high but does not give useful distinction between mole and normal pregnancy. it
is pivotal in diagnosis and follow up of GTD.

10
others:
Full blood count, coagulation screen, liver function test, renal function test, blood type
and cross match
partial mole
In partial mole many of the feature which seen in complete hydatidiform mole may be
absent and clinical feature may be less obvious and patients with partial mole present
with signs and symptoms of an incomplete or missed abortion, and have bleeding, a
small uterus, and low hCG levels.
Treatment:
All molar pregnancy has the potential to develop into potentially fatal carcinoma.
Treatment consist of two phases:
A. Immediate evacuation of mole
B. Subsequent follow up for detection of persistent trophoblastic proliferation or malignant
changes.
termination of molar pregnancy:
Termination of mole more common than spontaneous abortion of mole so adequate
evaluation of women should be done and combatable blood should be available
If preeclampsia , thyrotoxicosis is present ,may require treatment.
Evacuation by suction curettage is performed regardless uterine size under general
anesthesia (other form of surgical intervention or use of oxytocic drug to induce
uterine contraction increase the likelihood of needing chemotherapy and the risk of
trophoblastic embolism).

11
There is no clinical indication for the routine use of a second uterine evacuation in the
management of molar pregnancies. Uterine evacuation may be recommended, in
selected cases.
Hysterectomy is indicated for:
Older women or those of high parity
Severe uncontrolled haemorhhage.
Theca lutein cyst regress in size as the hCG level falls to normal and need no special
treatment unless complicated (rupture , torsion).
If patient present with Spontaneous abortion of mole:
May required gentle curettage and oxytocics drug .
Send for histopathological examination.(must be)
Anti D should be given to non sensitized Rh negative mother.
Prophylactic chemotherapy: It is not advised for all patient as 80% has spontaneous
remission and risk of drug toxicity.
Women should be advised to avoid pregnancy until hCG levels have been normal for six
months following evacuation of a molar pregnancy and for one year following
chemotherapy for gestational trophoblastic tumour.
Advice patient to use barrier method as contraceptive method at beginning and then
combined oral contraceptive pill (if no other contraindications) which can be used safely
after the hCG levels have returned to normal (if taken while hCG levels are raised, may
increase the need for treatment)
Postmolar Surveillance (Follow up):
Aim is to prompt detection of any change suggestive of malignancy.
16% of complete hydatidiform mole and 0.5% of partial hydatidiform mole undergo
malignant transformation.
β-human chorionic gonadotrophin
postmolar surveillance with serial quantitative serum -hCG levels should be the
standard. Titers should be monitored following uterine evacuation at least every 1 to
2 weeks until they become undetectable.
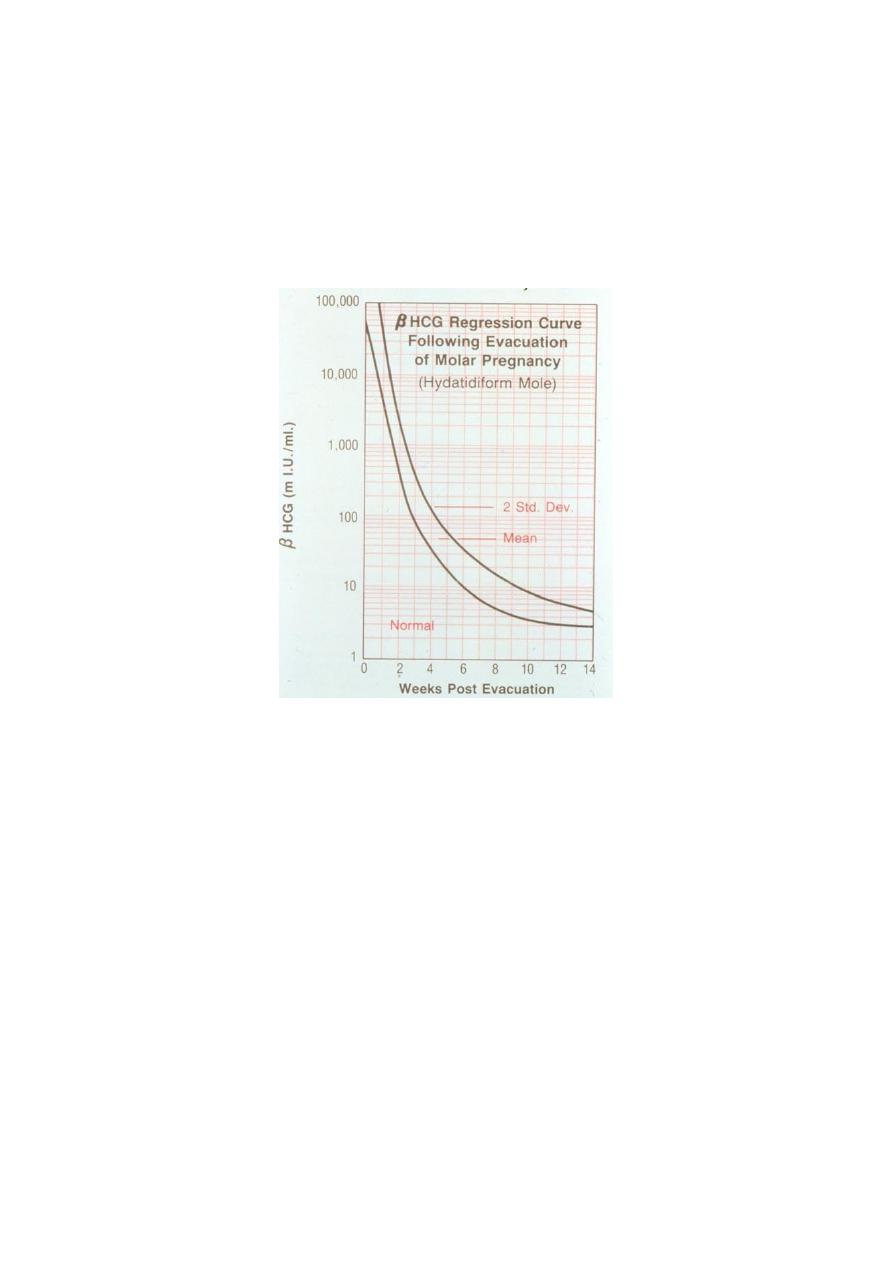
12
6 months of surveillance after achieving an undetectable -hCG levels (hCG become
negative) was recommended for all patients with molar gestation.
hCG should be progressively fall to undetectable levels ,if not decrease main trophoblast
persist and trophoblast proliferation which main either:
malignant changes
or b. pregnancy.
Physical examination:
Including pelvic examination at regular interval for first year until involuation of pelvic
organ.
Chest x ray: If hCG titer plateau or rises.
Chemotherapy is indicated if
1. -hCG titer rises or plataue during follow up.
2. Evidence of choriocarcinoma.
3. Persistant uterine bleeding and positive hCG .
4. hCG levels >20000IU/Lit serum at 4-6 weeks post evacuation.

13
In subsequent pregnancy
An early ultrasound should be performed in all subsequent pregnancies
because of the 1–2% risk of a second molar pregnancy.
b. In subsequent pregnancy in any patient had prior trophoblastic tumour of any type
should have hCG assay at 6 and 10 weeks post-delivery.
Risk of hydatidiform mole:
Before evacuation:
pre-eclampsia early onset before 20th weeks
hyperemesis gravidarum.
Anaemia.
hyperthyroidism.
complication of theca lutein cyst of ovary (rupture, torsion).molar pregnancy
produces excessive hCG , which stimulates excessive growth of ovaries.
pelvic infection.
perforated uterus.
disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC).
embolization and respiratory symptoms.
During evacuation
Bleeding can be profuse.
Sepsis.
Perforation of uterus.
Air embolism.
Incomplete evacuation of uterus.
After evacuation:
Choriocarcinoma.
Increase risk of recurrence of mole.
14
Causes of vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy:
1.miscarriage (spontaneous abortion).
2.ectopic pregnancy.
3.Hydatidiform mole.
4. Incidental cause
A. Cervical cause
Infection
Carcinoma
Polyp
Ectropion
Trauma
b. Vaginal cause
Infection
Trauma
Varicosities
5. Blood dyscarasia
